Last Updated on November 17, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir

At LivHospital, we know how worried you can get if your leg hurts or swells without reason. A blood clot in the leg, or deep vein thrombosis (DVT), can cause pain, swelling, warmth, tenderness, and redness. It’s important to know the signs of DVT because a clot can move to the lungs and be deadly.
We’ll help you understand the feelings you might have with DVT. We’ll tell you what to look out for and if you can feel a clot moving. Our team will give you all the details on the symptoms and feelings of a blood clot in the leg.
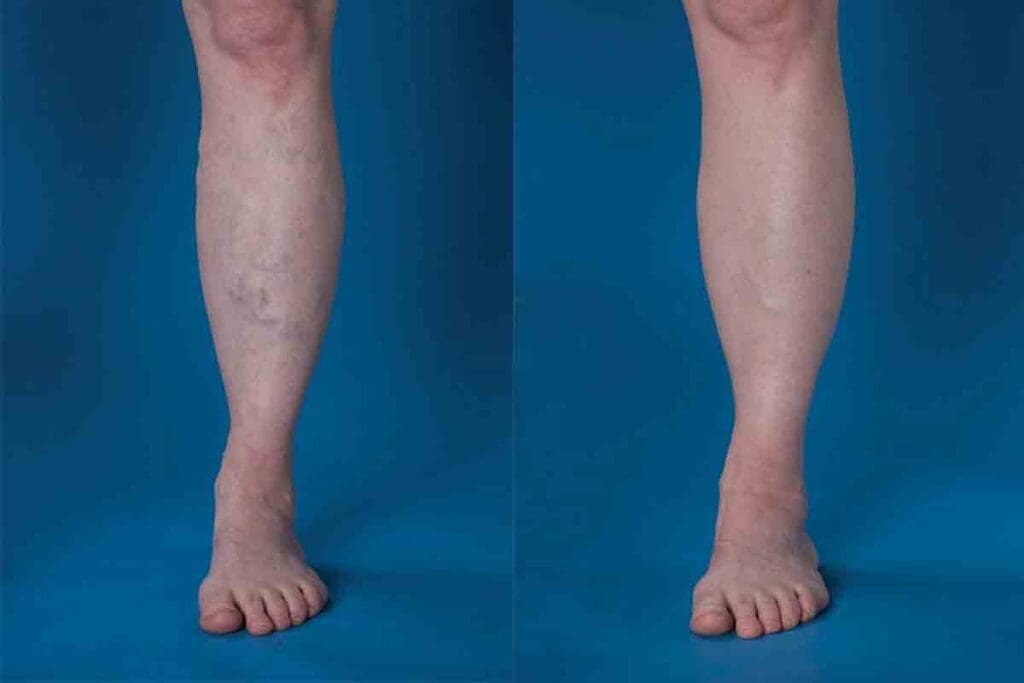
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition. It happens when a blood clot forms in the deep veins, often in the legs. If not treated quickly, it can cause serious health problems.
A blood clot in the leg is when blood thickens and clumps. This forms a solid mass in the veins. It can block blood flow, causing swelling, pain, and serious health risks. Deep Vein Thrombosis is when clots form in the deep veins, inside the leg muscles.
Blood clots from DVT usually happen in the lower legs. They often occur in:
These spots are more likely to clot because of factors like staying in one place for too long, genetics, and some health conditions.
| Location | Characteristics | Potential Complications |
| Calf Veins | Clots here can cause pain and swelling in the lower leg. | If the clot breaks loose, it can travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. |
| Thigh Veins | Clots in the thigh can lead to more significant obstruction of blood flow. | Higher risk of pulmonary embolism if the clot dislodges. |
| Popliteal Vein | Located behind the knee, clots here can be very problematic. | Increased risk of clot migration and subsequent pulmonary embolism. |
Knowing where DVT happens and how it shows up helps people spot the signs early. This way, they can get medical help fast.
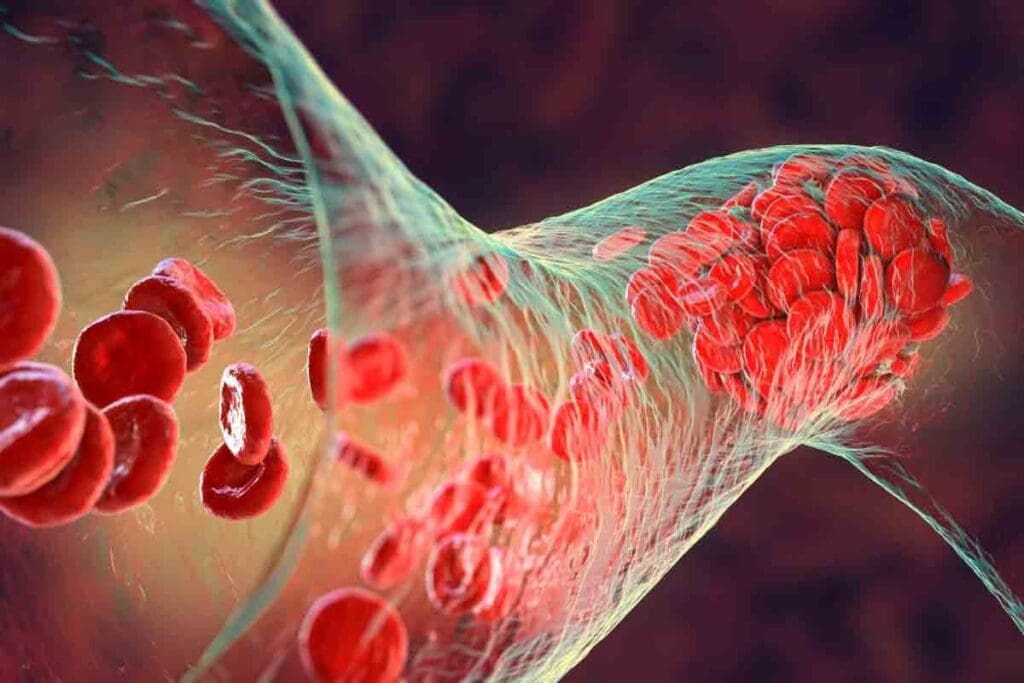
Having a blood clot in the leg can feel different for everyone. Yet, there are common signs to watch for. A blood clot in the deep veins of the leg can cause various sensations. These sensations are often misunderstood or thought to be from other issues.
Those with Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) often feel pain or discomfort in their leg. This pain might feel like a charley horse or muscle cramp. It can get worse when you walk or stand. Other symptoms include:
DVT pain is different from other leg pains. Unlike muscle strain or cramp, which is usually more focused, DVT pain spreads out. It doesn’t get better with rest or stretching and can get worse if not treated.
Also, DVT pain comes with swelling, warmth, and redness. These signs are not common with simple muscle cramps or strains. Knowing these differences helps spot when leg pain might be a sign of DVT.
Some visual signs in the leg can mean a blood clot is present. It’s important to spot these signs early to get medical help fast.
Redness or discoloration in the leg can be a blood clot sign. The skin might look:
This redness or discoloration shows the body is reacting to a clot. Watching for any skin color changes is key, as they show how serious the issue is.
Swelling is another sign of a possible blood clot in the leg. Swelling from DVT can cause:
It’s important to tell swelling from DVT apart from other causes. If swelling is big and you see redness or discoloration, get medical help.
Many people wonder if they can feel a blood clot in their leg move. This is a big concern because blood clots in the leg can be serious. We’ll look into whether you can feel a clot move and what you might experience.
Most of the time, you can’t feel a blood clot moving in your leg. Blood clots usually stay in one place once they form. The feeling of a clot moving is often due to other things, like changes in blood flow or inflammation.
Doctors say that the body’s reaction to a clot can cause different feelings. But, these feelings are not usually because the clot is moving. Instead, you might feel pain, swelling, or warmth in your leg.
When people think they feel a clot moving, they’re often feeling symptoms of DVT. These symptoms include:
It’s important to know that these symptoms don’t always mean the clot is moving. They show how your body is reacting to the clot and might mean there’s inflammation or blocked blood flow.
A doctor explained, “Patients often think they feel the clot moving, but it’s usually because of how their body is reacting to the clot, not the clot itself moving.”
“The sensation of a blood clot moving is more often related to the progression of the clot or the body’s inflammatory response, not the actual movement of the clot.”
Medical Expert
It’s key to know the difference between a clot moving and how your body reacts to DVT. If you’re worried about your symptoms, you should see a doctor.
Deep vein thrombosis can happen without symptoms, affecting nearly half of those with it. This silent condition, known as asymptomatic DVT, is dangerous because it can lead to serious problems without being noticed.
There are several reasons why some DVTs don’t show symptoms. One key factor is the location of the clot. Clots in smaller veins are less likely to cause pain or swelling. The body might also find ways to work around the clot, hiding symptoms.
Another important factor is the size of the clot. Small clots might not block blood flow enough to cause pain or swelling. How much pain someone can feel and other health conditions also play a role in noticing symptoms.
Some people are more likely to get asymptomatic DVT. This includes those who are limited in their mobility, like those who are bedridden or paralyzed. Others at risk are those having major surgery, people with cancer and its treatments, and those with a family history of clotting disorders.
Knowing who is at risk is key to catching and preventing asymptomatic DVT early. Doctors use special tools to find out who needs extra care, like blood thinners or other preventive steps.
As a blood clot forms in the leg, symptoms can grow stronger and more serious. Knowing how symptoms change is key for catching Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) early and treating it well.
The first signs of DVT are often mild, like a bit of cramping or warmth in the leg. These early signs might seem like muscle strain or other minor issues. But it’s important to notice them, as they could signal a blood clot is forming.
Mild cramping or aching in the leg is a common first sign. This pain can be off and on or constant, feeling like a dull ache or sharp pain. Some people also feel a warmth or heaviness in the affected leg.
As DVT gets worse, symptoms can get more severe. Pain might get stronger, and swelling could become more obvious. The skin might turn red or change color due to inflammation. It’s important to watch for these signs and get medical help if they get worse.
How symptoms change can differ from person to person. But common signs include:
Spotting these changes and knowing when to get help is critical for DVT treatment. If you notice any of these symptoms, seeing a doctor right away is essential.
The risk of getting blood clots in the leg comes from medical conditions, lifestyle choices, and temporary situations. Knowing these risks is key to preventing and catching them early.
Some medical conditions raise the risk of blood clots in the leg. These include:
Lifestyle choices and temporary situations can also increase clot risk. These include:
Smoking and hormonal therapies, like birth control or hormone replacement, can also affect blood clotting.
Understanding these risks helps people take steps to lower their chance of getting blood clots in the leg.
Leg discomfort can come from many sources. It’s key to tell DVT apart from other leg problems. DVT is serious and needs quick medical help. But, other issues might look similar but need different treatments.
Knowing the differences helps find the right medical care. We’ll look at how to tell DVT from muscle cramps and other similar symptoms.
Muscle cramps are common and can hurt a lot. But, they’re different from blood clots. Muscle cramps are:
DVT pain is a dull ache that gets worse. While muscle cramps are uncomfortable, they’re not as serious as DVT.
Many conditions can look like DVT, making it hard to diagnose without a doctor. These include:
| Condition | Similarities to DVT | Differences |
| Varicose Veins | Swelling, leg pain | Visible, twisted veins; pain often relieved by elevation |
| Superficial Thrombophlebitis | Pain, redness, swelling | Affects superficial veins; often associated with warmth and tenderness along the vein |
| Baker’s Cyst | Swelling, pain behind the knee | Typically involves fluid-filled cyst behind the knee; may cause knee pain |
As the table shows, these conditions share some DVT symptoms but are different. Getting a correct diagnosis from a doctor is vital for the right treatment.
If you think you have a blood clot in your leg, it’s important to know when to get help. This can prevent serious problems. We’ll show you the signs that mean you need to see a doctor right away. We’ll also tell you what to tell your doctor.
Some symptoms are very serious and need quick attention. If you notice any of these, get medical help fast:
These signs might mean you have a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or something worse. Getting medical help quickly is key to avoid serious problems.
When you see a doctor, tell them everything about your symptoms and health history. This includes:
| Information to Provide | Details to Include |
| Symptom Description | When the symptoms started, their severity, and any factors that relieve or exacerbate them |
| Medical History | Any previous history of blood clots, recent surgeries, or periods of immobility |
| Current Medications | List of current medications, including anticoagulants and any recent changes |
Sharing this info helps your doctor make the right diagnosis and treatment plan for you.
Diagnosing a blood clot in the leg involves several steps. These include an initial assessment and specific diagnostic tests. Accurate diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is key for effective treatment.
Several tests are used to confirm a blood clot in the leg. The most common include:
During DVT evaluation, patients undergo a thorough medical history review and physical exam. Healthcare providers look for signs like swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected leg.
The diagnostic process may include one or more of these tests. It’s essential for patients to follow their healthcare provider’s instructions and report any symptoms or concerns.
After diagnosis, treatment options will be discussed. These aim to prevent the clot from growing and reduce complications.
Dealing with blood clots in the leg needs a mix of medicine, lifestyle changes, and sometimes, medical devices. It’s key to manage Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) well. This helps avoid serious problems and improves health outcomes.
For DVT, doctors often use anticoagulant medicines. These stop the clot from getting bigger and prevent new ones. Anticoagulants are usually taken by mouth or injected. Sometimes, thrombolytic therapy is used to break up the clot. But, this is rare because it can lead to bleeding.
“The use of anticoagulation therapy has revolutionized the treatment of DVT, significantly reducing the risk of pulmonary embolism and other complications.”
Vascular Specialist
Doctors might also give other medicines to ease symptoms and prevent long-term pain and swelling.
Changing your lifestyle can lower the chance of DVT coming back. Here are some tips:
Lifestyle changes are key in managing DVT long-term and lowering risks.
Wearing compression stockings can help with swelling and blood flow. Compression therapy is great for preventing long-term problems. Walking and other exercises are also good. They help blood flow better and lower clot risk.
By using medicine, making lifestyle changes, and wearing compression stockings, you can manage DVT well. This helps avoid future problems.
It’s important to know the signs and risks of blood clots in the leg. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) can show as pain, swelling, and color changes. Spotting these signs early and getting medical help fast can really help.
We’ve looked at the signs and risks of DVT. It’s key to know the difference between DVT and other leg issues. Also, knowing DVT can sometimes not show symptoms is important. Being informed helps people take care of their health.
To wrap it up, being aware and acting quickly is key to dealing with leg blood clots. If you think you or someone else might have DVT symptoms, see a doctor right away. There are treatments and ways to prevent DVT, and knowing about them can greatly improve health outcomes.
A blood clot in the calf feels like a cramp that won’t go away. It might also cause swelling, redness, or warmth.
It’s rare to feel a blood clot move in your leg. Some people might feel something moving, but it’s usually due to inflammation, not the clot itself.
Leg blood clots, or Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), can cause pain, swelling, warmth, or redness. The pain can be dull or sharp and may stay constant or change.
A blood clot in the leg can cause pain, swelling, or warmth. The pain can be mild or severe and may be accompanied by redness or discoloration. Sometimes, there are no symptoms at all.
Yes, blood clots in the leg can hurt. The pain can be mild or severe and may be constant or change.
The pain from a blood clot in the leg varies. Some people feel mild discomfort, while others have severe pain. The pain can stay the same or change.
A leg clot can cause pain, swelling, warmth, or redness. The pain can be dull or sharp and may stay constant or change.
Blood clots in the legs can cause pain, swelling, warmth, or redness. The pain can be mild or severe and may be accompanied by redness or discoloration.
Yes, some people can feel a blood clot in their leg. Others may not feel anything. The sensations can include pain, swelling, warmth, or redness.
A leg blood clot can cause pain, swelling, or warmth. The pain can be mild or severe and may be accompanied by redness or discoloration.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!