Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik

Achilles tendonitis is a common issue for athletes and those who are active. Achilles tendon pain is a clear sign that something is wrong.
Did you know Achilles tendonitis is a big cause of sports injuries? It happens when the tendon gets inflamed, often from too much use or strain. Knowing the signs of Achilles tendonitis is key for quick diagnosis and treatment.
Achilles tendonitis can really hurt your ability to do everyday things and sports. Spotting the symptoms early can greatly help in getting better.
The Achilles tendon is key to our movement and sports performance. It links the calf muscles to the heel bone. This connection helps us run, jump, and climb stairs.
The Achilles tendon is a thick, fibrous cord in our musculoskeletal system. It’s made of tendon fibers from the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. This makes it strong enough to handle the stress of physical activities.
Its thickness and strength are vital for its job. They allow it to pass forces from the calf muscles to the heel. This enables ankle movement. Knowing the Achilles tendon anatomy helps us understand its role in movement.
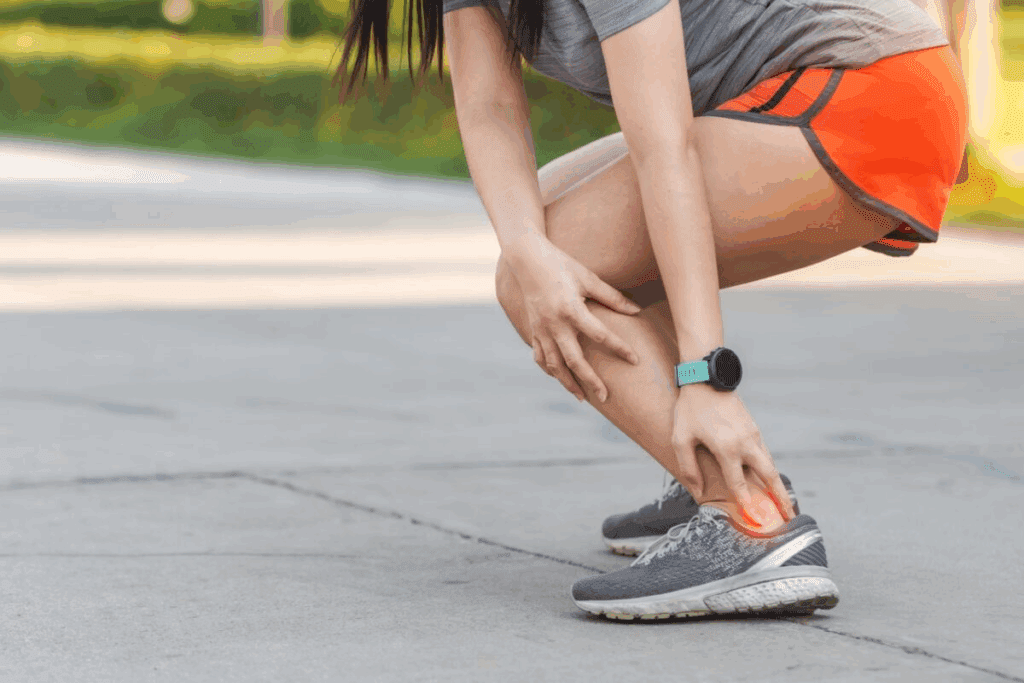

The Achilles tendon is essential for athletic performance. It’s important in sports that need running, jumping, or quick turns. It helps store and release energy, making movements more efficient.
Athletes like Jermaine Johnson and Deshaun Watson have faced Achilles tendon injuries. This shows how critical the tendon is for sports. Pain during activity can signal tendon problems, affecting performance and needing quick action.
Achilles tendonitis is when the Achilles tendon gets inflamed. This tendon connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. It causes pain, swelling, and stiffness.
The Achilles tendon is key for walking, running, and jumping. When it’s inflamed, it hurts a lot and makes moving hard.
Achilles tendonitis has two types: non-insertional and insertional. Non-insertional happens when the tendon gets inflamed but not at the heel. Insertional affects the tendon’s spot on the heel.
Knowing the type helps find the best treatment.
Achilles tendonitis is common, mainly in athletes. It’s seen in 11% of runners. Middle-aged men get it more often.
It affects many, from casual athletes to pros. Age, how hard you train, and how you move can increase your risk.
It gets more common with age, over 30. Past tendon injuries, bad shoes, and wrong training can also cause it.
Knowing the early signs of Achilles tendonitis is key for athletes and those who stay active. This condition shows two main signs that can affect how well you move and perform.
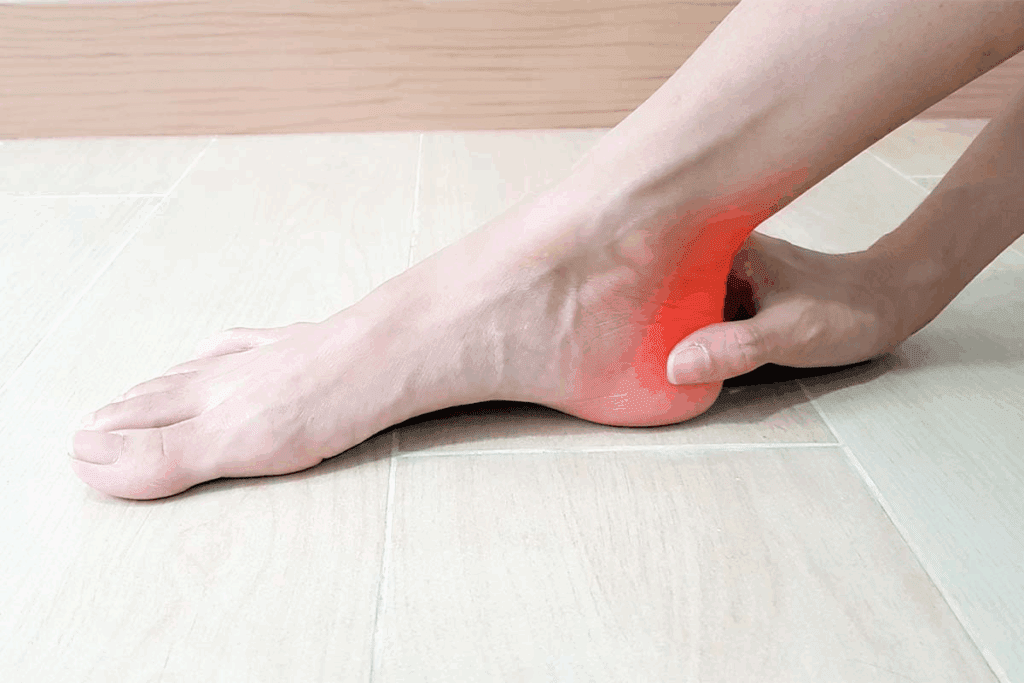
Pain and tenderness above the heel are common signs of Achilles tendonitis. This pain is usually felt along the tendon, just above the heel. It gets worse with activity. At first, the pain might be mild but can get worse if not treated.
The pain is often more noticeable in the morning or after resting. Also, the area above the heel may feel tender when pressed or touched. This shows inflammation or irritation of the tendon.
Swelling around the Achilles tendon is another important sign. This swelling happens because of inflammation in the tendon and nearby tissues. It may also cause redness and warmth in the area.
Swelling is more obvious after exercising and goes down with rest. But, if it keeps coming back, it means the tendon is under too much stress and needs care.
In summary, knowing these two main signs—pain and tenderness above the heel, and swelling around the Achilles tendon—helps spot Achilles tendonitis early. This way, you can get the right treatment sooner.
It’s important to know the pain patterns of Achilles tendonitis for early treatment. This condition shows up in different ways, affecting daily life and sports performance.
Pain during activity is a key sign of Achilles tendonitis. It often happens in the morning or after rest. Runners and jumpers usually feel this pain.
“The pain can be sharp or dull and is usually localized to the area just above the heel.”
People with Achilles tendonitis also feel pain after exercise. This pain shows the tendon is inflamed. Watching how long and how bad the pain is can tell how serious it is.
Morning pain and stiffness are common in Achilles tendonitis. The tendon gets stiff, causing pain when you first step in the morning. This pain usually gets better as you move around.
Stretching can also cause pain with stretching in Achilles tendonitis. This is a big issue for athletes who do calf raises or toe walks.
Spotting these pain patterns early can help treat Achilles tendonitis quickly. This can stop more damage to the tendon.
Beyond pain, several other signs can indicate Achillesendonitis. Recognizing these symptoms is key for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
One common symptom is stiffness in the Achilles tendon. This stiffness is often more pronounced in the morning or after rest. The tendon may feel tight, making it hard to stretch or move the ankle.
Achilles tendonitis can cause limited ankle mobility. As the tendon becomes inflamed, it restricts the ankle’s normal movement. This makes daily activities or sports challenging.
In some cases, the affected area may feel warm to the touch. This warmth at the tendonitis site is a sign of inflammation. It’s an important indicator of the condition.
Another symptom is creaking or crackling sounds when moving the ankle. This sensation, known as crepitus, occurs due to inflammation and tendon degeneration.
The presence of these signs and symptoms can help diagnose Achilles tendonitis. If you’re experiencing any of these, it’s vital to see a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
Understanding these symptoms can aid in early detection and prevention of further injury.
It’s important to know the difference between acute and chronic Achilles tendonitis. This knowledge helps in managing and treating the condition. Achilles tendonitis can really affect someone’s life, more so for athletes and those who are active.
The signs of Achilles tendonitis can differ between acute and chronic cases. Acute Achilles tendonitis shows sudden pain, usually above the heel. It also comes with swelling and warmth around the tendon.
Early detection is vital to stop it from becoming chronic. Spotting these signs early helps in starting treatment right away.
As Achilles tendonitis moves from acute to chronic, symptoms change. Chronic cases have ongoing pain and stiffness, often in the morning or after rest.
| Symptom | Acute Achilles Tendonitis | Chronic Achilles Tendonitis |
| Pain Location | Above the heel, sudden onset | Above the heel, persistent |
| Swelling | Common, with warmth | Less pronounced, may be minimal |
| Morning Stiffness | May be present | Typically more pronounced |
Chronic Achilles tendonitis causes the tendon to degenerate. This includes thickening and possible partial tears. These changes harm the tendon’s function and the person’s mobility.
Knowing these differences is key to a good treatment plan. Whether it’s acute or chronic, a mix of rest, physical therapy, and orthotics can help. This approach can ease symptoms and improve results.
Understanding what causes Achilles tendonitis is key to preventing and treating it. This condition comes from a mix of overuse, biomechanical issues, aging, and some medical conditions.
Overuse or repetitive strain on the tendon is a main cause of Achilles tendonitis. This happens when athletes suddenly up their training without enough rest. Training errors like bad warm-ups, wrong shoes, or uneven surfaces also play a part.
Biomechanical factors are also big players in Achilles tendonitis. Problems like overpronation or supination can put uneven stress on the tendon, causing pain. Leg length differences or poor foot mechanics can also lead to the condition.
As we age, our tendons repair more slowly, making them more prone to injury. This is why Achilles tendonitis is more common in middle-aged and older folks.
Certain health issues can raise the risk of Achilles tendonitis. These include rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, and hypertension. Some medicines, like fluoroquinolone antibiotics, can also up the risk.
Knowing the risk factors for Achilles tendonitis is key to preventing and treating it early. Many things can make someone more likely to get this condition.
People who play sports that involve running, jumping, and quick changes are at higher risk. Sports like basketball, soccer, and tennis are risky because they stress the Achilles tendon a lot.
Also, sudden changes in training can lead to Achilles tendonitis. Athletes should slowly increase their training to help their tendons adjust.
The shoes you wear during sports can affect your risk of Achilles tendonitis. Worn-out or unsupportive shoes can stress the Achilles tendon too much.
Shoes that change how your foot moves, like high heels or those without good arch support, also increase the risk.
Some people are more likely to get Achilles tendonitis because of their body shape. For example, those with flat feet or high arches may have different foot movements that stress the Achilles tendon.
| Anatomical Factor | Description | Impact on Achilles Tendon |
| Flat Feet | Condition where the arch of the foot is flattened | Increased stress due to overpronation |
| High Arches | Condition where the arch of the foot is higher than normal | Increased stress due to underpronation |
| Leg Length Discrepancy | Difference in the length of the legs | Altered gait mechanics, increasing tendon stress |
People who have had tendon injuries before are more likely to get Achilles tendonitis. Past injuries can weaken the tendon, making it more likely to get hurt again.
It’s important for those with tendon injury history to do strengthening exercises and follow proper warm-up and cool-down routines during sports.
Doctors use a mix of physical checks and imaging tests to spot Achilles tendonitis. This method helps them figure out the best way to treat it.
A detailed physical check is key in finding Achilles tendonitis. Doctors look at the tendon in several ways, like:
Doctors say a careful check is vital to spot Achilles tendonitis and rule out other heel pain causes. This shows how important a detailed check is.
Imaging tests are also very important in diagnosing Achilles tendonitis. They include:
MRI is very helpful because it shows the tendon in great detail. It helps doctors see how bad the inflammation or damage is.
“Imaging studies, like MRI, have changed how we diagnose Achilles tendonitis. They give us clear views of tendon problems.”
Differential diagnosis is a big part of finding the right diagnosis. It’s about ruling out other conditions that might look like Achilles tendonitis. Doctors look at things like:
Doing a good differential diagnosis makes sure patients get the right treatment for their real problem.
Achilles tendonitis can often be managed without surgery. Several effective methods can reduce pain, promote healing, and restore function to the affected tendon.
The first step in treating Achilles tendonitis is to give the tendon a break. Rest and activity modification are key in the initial stages. Avoid activities that make the condition worse, like running or jumping.
By reducing stress on the tendon, the body can start to heal the damaged area.
Physical therapy is vital in treating Achilles tendonitis. A physical therapist can create a personalized exercise program. This program strengthens the calf muscles, improves ankle mobility, and enhances overall lower limb function.
Managing pain is a critical aspect of treating Achilles tendonitis. Various pain management options are available. These include over-the-counter pain relievers, anti-inflammatory medications, and sometimes corticosteroid injections.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best pain management strategy.
Orthotic devices and supports can provide additional relief. They reduce stress on the Achilles tendon. Custom orthotics, heel lifts, and supportive footwear can help alleviate pain and promote healing.
By combining these non-surgical treatment approaches, individuals with Achilles tendonitis can see significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
Recovering from Achilles tendonitis takes time, care, and a good plan. It involves knowing the healing phases, recovery times, and how to get back to activities safely. It also means watching for any signs of the injury coming back.
The healing of Achilles tendonitis goes through several stages:
Doctors say, “A slow and planned approach is key to healing well.”
‘Recovery from Achilles tendonitis is not just about healing the tendon; it’s about restoring function and preventing future injuries.’ An Orthopedic Specialist
The time it takes to recover can differ a lot. Mild cases might heal in 2-4 weeks, but more serious ones could take months. It’s important to be patient and not rush things.
Going back to activities too soon can cause more harm. Here are some safe steps to follow:
Even after you’re back to full activity, keep an eye out for any signs of tendonitis coming back. Regular stretching and strengthening can help prevent this.
By knowing the recovery process and sticking to a good rehabilitation plan, you can manage Achilles tendonitis well. This way, you can get back to your usual activities.
In severe cases of Achilles tendonitis, surgery might be needed to fix the tendon. While treatments like physical therapy and bracing work for many, some need more serious help.
Doctors consider surgery for those who don’t get better with usual treatments. This includes:
Surgical intervention aims to repair or remove the damaged tendon. This helps the tendon heal and function better.
Several surgeries can treat Achilles tendonitis. These include:
| Procedure | Description | Benefits |
| Tendon Debridement | Removal of damaged tendon tissue | Promotes healing, reduces pain |
| Tendon Repair | Repair of torn or ruptured tendon | Restores tendon function, alleviates pain |
| Tendon Transfer | Transfer of a healthy tendon to support the Achilles tendon | Enhances ankle stability, reduces pain |
Choosing the right surgical procedure depends on the extent of tendon damage and the patient’s overall health.
After surgery, a detailed rehabilitation program is key for recovery. This includes:
Rehabilitation after surgery can take months. During this time, patients are closely watched for progress and any complications.
To avoid Achilles tendonitis, athletes need to take steps like warm-ups, choosing the right shoes, and adjusting their training. These actions can greatly lower the chance of getting this painful condition.
Starting with a good warm-up and stretching is key to preventing Achilles tendonitis. Dynamic stretching is very helpful. It involves moving your joints and keeping your muscles active. Leg swings, calf raises, and toe walks are good examples.
Wearing the right shoes is also critical. Shoes that support and cushion well can lessen the stress on your Achilles tendon. Look for shoes with a sufficient heel-to-toe drop and ones that fit your foot type and activity level.
Changing your training can also help prevent Achilles tendonitis. It’s important to slowly increase the intensity and duration of your workouts to avoid sudden changes. Rest days and cross-training can also help lower the risk.
Strengthening the muscles around your Achilles tendon, like your calf muscles, is also important. Doing calf raises and eccentric heel drops can make these muscles stronger. This can help prevent tendonitis.
Knowing when to see a doctor for Achilles tendon pain is key. It helps treat the issue and avoid more harm. Achilles tendonitis can be mild or severe. It’s important to know when to get medical help.
Some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include:
If you notice any of these, get medical help fast.
Some symptoms need quick medical check-up to avoid injury or complications. These include:
Seeing a doctor quickly can stop the problem from getting worse.
When talking to a doctor about Achilles tendon pain, be ready with questions. Ask:
Being informed and asking the right questions helps you understand your condition and treatment options.
Achilles tendonitis is a common issue. It affects the tendon that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Knowing the signs and symptoms is key to treating it early and preventing more damage.
The main signs include pain and tenderness above the heel, along with swelling around the tendon. Spotting these symptoms early can help avoid long-term tendon damage.
Treatment for Achilles tendonitis varies. It can range from rest and physical therapy to surgery in severe cases. Preventive measures like proper warm-up, stretching, and choosing the right shoes can also help.
Understanding Achilles tendonitis can help protect your tendon. It ensures your foot health stays in top shape.
The main signs are pain and tenderness above the heel. You might also see swelling around the Achilles tendon.
It can happen from overusing your tendon or making training mistakes. It’s also caused by how your body is built, aging, and some health issues.
Doctors use physical checks, imaging tests, and rule out other conditions to diagnose it.
Treatments include resting and changing how you move. You can also try physical therapy, manage pain, and use supports.
Yes, you can prevent it. Warm up well, stretch, wear the right shoes, and do strengthening exercises.
See a doctor if you notice serious injury signs, need immediate help, or are unsure about your symptoms.
Recovery goes through healing phases. It has expected times and guidelines for getting back to activities. Watch for signs it might come back.
Yes, if not treated right, it can become chronic. This leads to long-term tendon changes and ongoing symptoms.
Risks include certain sports, bad shoes, body shape, and past tendon injuries.
Manage pain with rest, ice, compression, elevation, and pain meds.
No, surgery isn’t always needed. It’s for severe cases that don’t get better with other treatments.
Surgery is for severe tendon tears, chronic tendonitis, and big tendon damage.
Recovery times vary. It depends on how bad the condition is and how well treatment works. It can take weeks to months.
It’s best to stop or change activities that make it worse until it heals to avoid more injury.
Physical therapy improves ankle movement, strengthens the tendon, and helps it heal. It uses exercises and techniques.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!