Last Updated on November 17, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir

Blood in lungs is a serious and life-threatening condition known medically as pulmonary hemorrhage. It happens when bleeding occurs inside the lung tissue or airways, making it hard for oxygen to reach the bloodstream.
At Liv Hospital, we treat cases of blood in lungs with urgency and advanced care. This condition can happen suddenly or build up over time. It may result from autoimmune diseases, clotting disorders, infections, or exposure to harmful substances.
Recognizing the early symptoms of blood in lungs—like coughing up blood, shortness of breath, or chest pain—is crucial. Quick diagnosis and treatment can prevent severe complications.
Doctors at Liv Hospital stress that untreated blood in lungs can lead to respiratory failure. That’s why immediate medical help is vital.
Learning about the blood in lungs causes and symptoms helps patients understand how serious this condition can be. By acting fast, treatment outcomes improve significantly.
If you suspect blood in lungs, seek medical attention right away. Early detection saves lives and protects lung health.
It’s key to understand pulmonary hemorrhage to treat it well. This condition is when bleeding into the lungs happens, either suddenly or slowly.
Pulmonary hemorrhage is a serious issue. It can come from many causes like autoimmune diseases, infections, or injuries. Knowing if it’s acute or chronic is vital for the right care.
Bleeding into the lung tissue and airways happens in pulmonary hemorrhage. This can cause respiratory distress, anemia, and more. The symptoms’ severity depends on how much bleeding there is.
Doctors say, “Pulmonary hemorrhage symptoms can be mild or very serious. It needs quick evaluation and treatment.”
This condition shows why knowing how it works is key to managing it well.
Acute pulmonary hemorrhage starts suddenly and can be very dangerous. Chronic pulmonary hemorrhage means bleeding keeps happening, causing long-term health problems.
Newborns, and those who are premature or have low birth weight, face big risks. Intrauterine growth restriction is one of them.
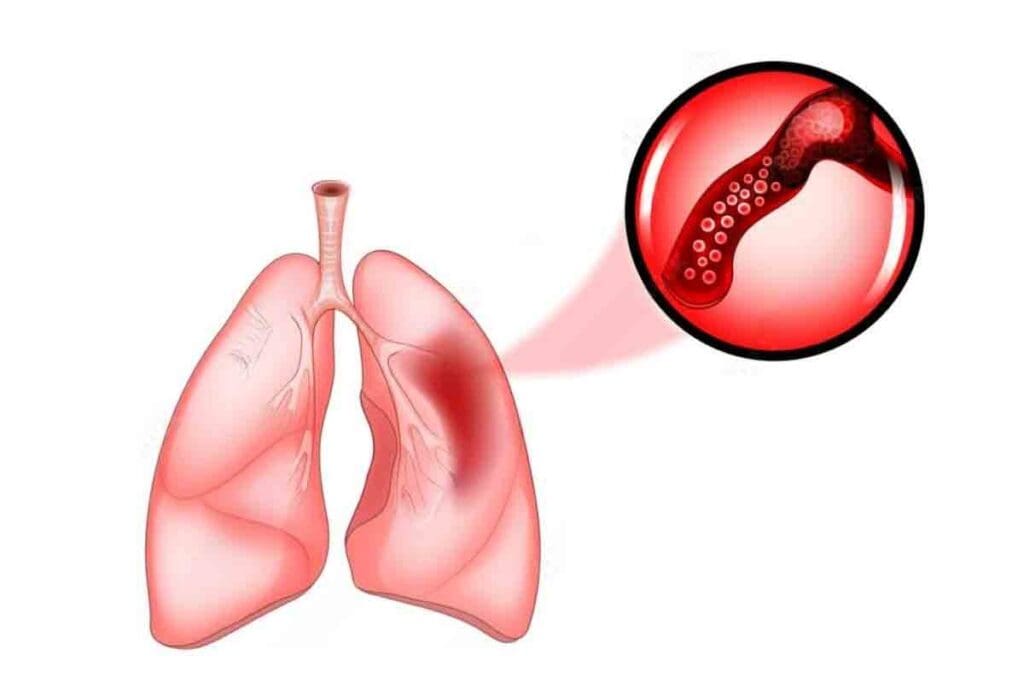
Pulmonary hemorrhage can be a silent condition. It often presents without the expected visible symptoms. This makes it hard to diagnose, as patients may not show typical signs of bleeding into the lungs.
In some cases, pulmonary hemorrhage may not show hemoptysis (coughing up blood). This is a common symptom many think of when they hear about bleeding in the lungs. Instead, patients might feel anemia, fatigue, or just not feel well. These signs can be hard to spot, as they can mean many things, not just bleeding in the lungs.
Key Indicators of Hidden Pulmonary Hemorrhage:
| Symptom | Description | Possible Indication |
| Anemia | Low red blood cell count | Chronic blood loss |
| Fatigue | Persistent feeling of tiredness | Internal bleeding |
| Respiratory Distress | Difficulty breathing | Bleeding into lungs |
Pediatric patients need special care because pulmonary hemorrhage can affect their growth and development. Children might not show obvious symptoms. So, pediatricians must watch for signs like unexplained anemia or failure to thrive.
In conclusion, knowing that blood in the lungs can be hidden is key for early diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare providers and patients must be aware of these hidden signs, even more so in children.
Autoimmune diseases are a big reason for bleeding in the lungs. These diseases happen when the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues. This leads to inflammation and damage in places like the lungs.
Many autoimmune disorders can cause lung bleeding. Knowing about these conditions helps doctors diagnose and treat lung hemorrhage better.
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis, also known as Wegener’s, is a rare disease. It causes inflammation in blood vessels. This mainly affects the lungs, kidneys, and upper airways.
The inflammation from this disease can damage lung blood vessels. This can lead to lung bleeding.
Key Features of Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis:
Goodpasture syndrome is another disease that can cause lung bleeding. It’s caused by antibodies attacking the lungs and kidneys. This leads to inflammation, bleeding in the lungs, and kidney damage.
Goodpasture syndrome is a rare condition that needs quick diagnosis and treatment to avoid serious problems.
| Autoimmune Disorder | Primary Organs Affected | Key Features |
| Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener’s) | Lungs, kidneys, upper respiratory tract | Vasculitis, granulomas, multi-organ involvement |
| Goodpasture Syndrome | Lungs, kidneys | Anti-GBM antibodies, basement membrane damage |
Other autoimmune diseases can also cause lung bleeding. These include systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, and other systemic vasculitides.
It’s important to know the different autoimmune causes of lung bleeding. This helps doctors create better treatment plans. By understanding the cause, they can tailor care for each patient.
Many things can cause blood to appear in the lungs, not just autoimmune diseases. It’s important to know about these other causes. This helps doctors understand and treat the problem better.
Blood clotting problems can also cause bleeding in the lungs. These issues can be genetic or caused by certain medicines. They make it hard for blood to clot properly.
For example, people taking blood thinners are at a higher risk. Liver disease can also cause clotting problems because the liver makes clotting factors.
Infections can also lead to bleeding in the lungs. Bacteria, viruses, or fungi can harm lung tissue. This damage can cause bleeding.
Heart problems can also cause bleeding in the lungs. For instance, mitral stenosis can raise pressure in the lungs. This can lead to bleeding.
Other heart issues like heart failure or pulmonary embolism can also cause bleeding. Knowing about these causes is key to treating pulmonary hemorrhage effectively.
Environmental exposures and physical trauma can cause pulmonary hemorrhage. It’s important to know these factors for diagnosing and treating this serious condition.
Trauma to the chest can lead to pulmonary hemorrhage. This happens when the lungs get injured. Such injuries can come from car accidents, falls, or other incidents that hurt the chest.
Key factors in trauma-related pulmonary bleeding include:
| Trauma Type | Mechanism of Injury | Risk of Pulmonary Hemorrhage |
| Blunt Trauma | Forceful impact without penetration | High |
| Penetrating Trauma | Object penetrates chest cavity | Very High |
Being exposed to certain toxins can raise the risk of pulmonary hemorrhage. Breathing in chemicals, drugs, or vaping-related lung injury are known risks.
“Exposure to environmental toxins can lead to pulmonary hemorrhage by damaging lung tissue and disrupting normal lung function.”
In some cases, pulmonary hemorrhage happens without a clear cause. This is called idiopathic pulmonary hemorrhage. It shows how complex this condition is and why we need detailed diagnostic methods.
Factors that may contribute to idiopathic pulmonary hemorrhage include:
Pulmonary hemorrhage shows a wide range of symptoms. This makes it hard to diagnose because it can look different in each person.
People with pulmonary hemorrhage often have symptoms related to breathing. Hemoptysis, or coughing up blood, is a key sign. The amount of blood can vary. Respiratory distress, or trouble breathing, is another important symptom that needs quick medical help.
Hemoptysis and respiratory distress together suggest a serious case of pulmonary hemorrhage. Knowing these symptoms is key for doctors to start the right treatment fast.
Patients with pulmonary hemorrhage may also have secondary symptoms. Anemia can happen from bleeding in the lungs, causing fewer red blood cells. Fatigue is common, often because of anemia or being sick. Chest pain might happen due to inflammation or other lung problems.
| Symptom | Description | Clinical Significance |
| Hemoptysis | Coughing up blood | Indicates bleeding in the lungs |
| Respiratory Distress | Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing | Signifies compromised respiratory function |
| Anemia | Decrease in red blood cells | May result from chronic bleeding |
| Fatigue | Feeling tired or weak | Can be related to anemia or illness |
| Chest Pain | Pain in the chest area | May indicate inflammation or other pathology |
It’s important to know both primary and secondary symptoms of pulmonary hemorrhage. This helps doctors create a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs.
Healthcare experts use several methods to diagnose pulmonary hemorrhage. They often combine imaging studies with invasive procedures like bronchoscopy.
Imaging studies are key in diagnosing pulmonary hemorrhage. Chest X-ray and CT scans are vital for spotting lung issues. They show where and how much bleeding is happening in the lungs.
Besides imaging, bronchoscopy and other invasive methods are also important. Bronchoscopy lets doctors see the airways directly. It helps find where the bleeding is coming from.
Using these methods together gives a full picture of pulmonary hemorrhage. This helps doctors create a good treatment plan.
It’s key to understand the severity of pulmonary hemorrhage for good patient care. This condition can range from mild to severe, needing different treatments. Mild cases might need just watching and support, while severe ones require quick and strong action.
For mild to moderate cases, symptoms are often manageable. Patients might cough up blood or have trouble breathing. Doctors treat these cases by fixing the cause and supporting the patient.
Severe cases are very dangerous and need fast help. They cause a lot of bleeding in the lungs, leading to serious breathing problems and anemia. Treatment includes emergency care like breathing machines and blood transfusions.
What makes a case severe includes the cause, how fast and much it bleeds, and the patient’s health. Knowing these helps doctors choose the best treatment and improve results.
Understanding the severity of pulmonary hemorrhage is vital. It helps doctors tailor treatments for each case. This way, they can better care for patients and improve their chances of recovery.
Managing pulmonary hemorrhage requires a mix of emergency steps, treating the root cause, and supportive care. This approach helps stabilize the patient. The condition’s complexity means a treatment plan must fit the patient’s specific needs.
Severe cases of pulmonary hemorrhage need quick action to avoid more harm. These steps include:
It’s key to find and treat the cause of pulmonary hemorrhage. This might mean:
Treatment Approaches for Common Underlying Causes:
| Underlying Cause | Treatment Approach |
| Autoimmune Disorders | Immunosuppressive therapy |
| Infections | Antibiotics |
| Coagulopathies | Clotting factor replacement |
Supportive care is vital in managing pulmonary hemorrhage. It focuses on easing symptoms and improving outcomes. Key steps include:
Combining emergency steps, treating the cause, and supportive care is essential. This approach helps manage pulmonary hemorrhage effectively. Healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes and lower complication risks by using a detailed treatment plan.
Understanding the causes of pulmonary hemorrhage is key to long-term management. A good plan must meet the patient’s immediate needs and prevent future problems. It also helps manage any complications that might come up.
Follow-up care is vital for patients with pulmonary hemorrhage. It helps keep an eye on the condition and handle any new issues. This includes:
Monitoring for Complications is a key part of follow-up care. Patients should watch for signs like increased shortness of breath, chest pain, or coughing up blood. If these symptoms show up, they should get medical help right away.
The outlook for patients with pulmonary hemorrhage can vary a lot. It depends on several things. These include:
Understanding these factors is key for doctors to create the right treatment plan. It also helps patients know what to expect. Medical experts say, “The prognosis is generally better for patients whose underlying cause is identified and effectively managed.”
In summary, managing pulmonary hemorrhage long-term requires a detailed plan. This includes regular check-ups and knowing what affects the patient’s outlook. By tackling the root causes and managing complications well, patients can live better lives.
Spotting and treating pulmonary hemorrhage early is key to saving lives and preventing long-term health issues. Knowing the causes, signs, and how to diagnose it helps doctors act fast and effectively.
Research shows that catching and treating pulmonary hemorrhage early is vital. Quick action can lower the chance of serious and deadly cases. This leads to better health outcomes for patients.
To manage pulmonary hemorrhage well, a complete plan is needed. This includes emergency steps, treating the root cause, and supportive care. With this approach, doctors can help patients recover better and reduce death rates from pulmonary hemorrhage.
Pulmonary hemorrhage is a serious lung condition. It happens when blood builds up in the lung tissue and airways. This can cause severe health problems if not treated.
Many things can cause pulmonary hemorrhage. This includes autoimmune diseases, blood clotting issues, infections, and physical injuries. Environmental toxins and unknown causes can also play a role.
Symptoms of pulmonary hemorrhage vary. They include coughing up blood and trouble breathing. Other signs are anemia, feeling very tired, and chest pain.
Yes, it’s possible for pulmonary hemorrhage to happen without obvious signs. Some people might not cough up blood, even though they have it.
Doctors use different methods to find pulmonary hemorrhage. They might take chest X-rays or CT scans. They also use bronchoscopy and other detailed tests.
Treating pulmonary hemorrhage is urgent. It includes using ventilators and giving blood products. Doctors also work on treating the underlying cause, like autoimmune diseases or infections.
The outcome of pulmonary hemorrhage varies. It depends on how severe it is, the cause, and how well treatment works.
Managing pulmonary hemorrhage long-term means ongoing care. This includes watching for complications and managing any underlying conditions.
Yes, autoimmune diseases like granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s) and Goodpasture syndrome can lead to pulmonary hemorrhage.
Non-autoimmune causes include blood clotting disorders, infections, and heart conditions. These can also cause pulmonary hemorrhage.
Yes, things like trauma, environmental toxins, and certain exposures can trigger pulmonary hemorrhage.
Acute pulmonary hemorrhage happens suddenly. It’s when blood quickly fills the lung tissue and airways. Chronic pulmonary hemorrhage is ongoing or keeps happening over time.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!