Last Updated on November 17, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
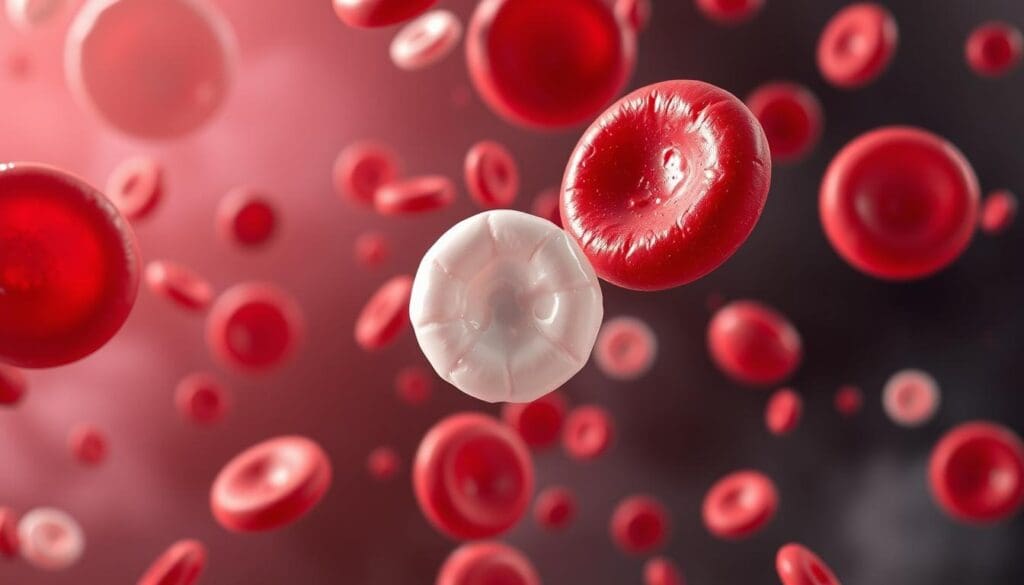
It’s important to know about the three main types of blood cells. Our body has red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Each one has a special job to keep us healthy.
Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, make up about 40% to 45% of our blood. They carry oxygen from our lungs to our body’s tissues. White blood cells are our immune system’s first line of defense, fighting off infections. Platelets help our blood clotting, stopping too much bleeding when we get hurt.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on these cells and how they’re made in the bone marrow. Our team offers top-notch healthcare and support for international patients.
Blood is a complex fluid that keeps our bodies alive. It has many parts, each with its own job. These jobs help keep us healthy.
Blood is key to delivering oxygen and fighting off germs. It flows through our body, bringing nutrients and oxygen to our cells. It also takes away carbon dioxide.
Blood helps fight infections by carrying white blood cells. It stops bleeding by clotting, thanks to platelets. A study on the National Center for Biotechnology Information shows how vital blood is for our health.
Blood is made of four main parts: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma is the liquid part, making up 55% of blood. It has water, proteins, nutrients, hormones, and waste.
Red blood cells carry oxygen. White blood cells fight infections. Platelets help stop bleeding by clotting.
Knowing about blood’s parts and what they do is key. They all work together to keep our bodies healthy. This includes delivering oxygen and fighting off germs.
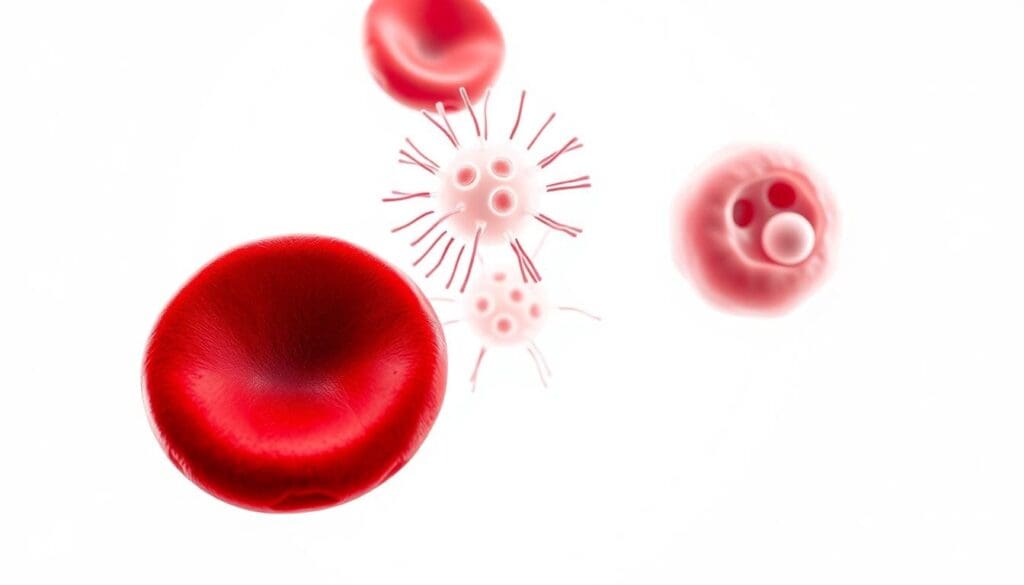
It’s important to know about the three types of blood cells. They are made in the bone marrow and flow through our blood. These cells are called red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Blood cells are special because of their shape and what they do. Red blood cells (erythrocytes) carry oxygen all over our bodies. White blood cells (leukocytes) help fight off infections. Platelets (thrombocytes) help stop bleeding when we get hurt.
These cells start from special stem cells in the bone marrow. They turn into different types based on what they need to do.
Each type of blood cell is unique. Red blood cells are shaped like disks and carry oxygen. White blood cells are bigger and have a nucleus. They come in many shapes and sizes. Platelets are small and don’t have a regular shape.
Here’s a table to show how they differ:
| Type of Blood Cell | Main Function | Key Characteristics |
| Red Blood Cells | Oxygen Transport | Disk-shaped, contains hemoglobin |
| White Blood Cells | Immune Response | Larger, have a nucleus, variable shape |
| Platelets | Blood Clotting | Small, irregularly shaped cell fragments |
Each blood cell plays a key role in keeping us healthy. Knowing about these differences helps doctors diagnose and treat blood disorders.
Erythrocytes, or red blood cells, are key to keeping oxygen and carbon dioxide levels balanced in our bodies. They carry oxygen from the lungs to our body’s tissues. They also remove carbon dioxide, a byproduct of our metabolism.
Red blood cells are shaped like disks and are very flexible. They contain hemoglobin, a protein that grabs onto oxygen. This shape and flexibility help them move through narrow blood vessels, making sure oxygen reaches every part of our body.
The bone marrow in our bones makes red blood cells. It produces millions every day to replace old or damaged ones.
Red blood cells’ main job is to carry oxygen from the lungs to our body’s tissues. Hemoglobin in these cells binds to oxygen, forming oxyhemoglobin. This is then sent to various tissues.
At the same time, red blood cells pick up carbon dioxide, a waste product. They carry it back to the lungs, where we breathe it out. This is vital for our body’s tissues, as oxygen is needed for metabolism, and removing carbon dioxide prevents acidosis, which can harm tissues.
Red blood cells live for about 120 days. After that, they are removed and recycled. The spleen helps by filtering out old or damaged red blood cells from the blood.
The parts of old red blood cells are broken down, and the iron from hemoglobin is reused to make new red blood cells. This recycling is important for keeping our iron levels balanced and ensuring we have healthy red blood cells.
White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are key to our immune system. They fight off infections and invaders. These cells are vital for our health and help us fight diseases.
There are several types of white blood cells, each with its own role. The main types are lymphocytes, granulocytes, and monocytes. Lymphocytes include B cells and T cells, important for specific immune responses. Granulocytes, like neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils, respond first to infections. Monocytes turn into macrophages, which clean up debris and pathogens.
White blood cells protect us from infections and diseases. They find and destroy pathogens, like bacteria and viruses. They also help repair damaged tissues.
Neutrophils, a type of granulocyte, fight bacterial infections first. Lymphocytes are key to viral infections and building immunity.
The lifespan of white blood cells varies. For example, neutrophils live only a few days. But lymphocytes can live months or years. They move through the bloodstream and lymphatic system to reach different parts of the body.
Knowing about white blood cells helps us understand how our immune system works. It shows how it fights infections and diseases.
Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are key in our body’s clotting process. They help stop bleeding and are made in the bone marrow. These tiny cells are vital for starting the blood clotting process.
Platelets are small, irregularly shaped cells. They come from the breakdown of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. This process is complex, needing many growth factors and cytokines.
Once in the blood, platelets live for about 8 to 12 days. They are then removed by the spleen. Platelets have a special membrane for their job. This membrane has receptors for various agonists that start their activation.
When activated, platelets change to help form a platelet plug. This plug is key in stopping bleeding at injury sites.
Platelets are mainly involved in blood clotting. When a blood vessel is injured, platelets stick to the injury site. They then release signals that attract more platelets.
These platelets form a plug. The plug is then strengthened by a fibrin clot. This clot is vital in stopping too much bleeding.
Platelets also help in wound healing. They release growth factors. These factors help cells grow and new tissue form.
Platelets have roles beyond clotting. They are part of the inflammatory process and can release chemicals that cause inflammation. They are also linked to diseases like atherosclerosis and tumor metastasis.
Understanding platelets’ many roles shows their importance in health and disease. Problems with platelets can cause conditions like thrombocytopenia or thrombocytosis. This highlights the need for more research into platelet biology.
Hematopoiesis is key to our health. It’s how our bodies make blood cells. These cells come from stem cells and have different jobs.
The bone marrow is where most blood cells are made. Stem cells turn into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets here. This process keeps our blood cell balance right.
It all starts with hematopoietic stem cells. These cells can grow and change into any blood cell type. They go through many stages before becoming the blood cells we need.
The stages are:
Producing blood cells is a precise process. Growth factors and cytokines play a big role. They make sure we have the right number of blood cells.
| Regulatory Factor | Function |
| Erythropoietin | Stimulates red blood cell production |
| Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) | Promotes the production of granulocytes (a type of white blood cell) |
| Thrombopoietin | Regulates platelet production |
Knowing about hematopoiesis helps us understand how our bodies keep blood cell counts healthy. It shows how we adapt to changes in our body’s needs.
Bone marrow is called the “factory” of blood cells because it’s key in making blood cells. It’s a spongy tissue inside bones like the hips and thighbones. It’s where blood cells are made, thanks to a network of blood vessels and special cells.
The bone marrow’s design helps it make blood cells. It has lots of blood vessels for nutrients and oxygen. Special cells, like stem cells, work together to help blood cells grow and mature.
There are two kinds of bone marrow: red and yellow. Red bone marrow is where blood cells are made. It’s found in bones like the vertebrae, pelvis, and sternum. Yellow bone marrow is mostly fat and doesn’t make as many blood cells. But it can turn into red bone marrow if the body needs it, like after a big blood loss.
The difference between red and yellow bone marrow shows how bone marrow changes to meet our needs. Knowing about both types helps us understand how blood cells are made.
Our body can make blood cells thanks to the hematopoietic system. It’s a network of organs and tissues that kkeepsour blood cell count right. This system is key to our health, making blood cells for oxygen transport, fighting off infections, and clotting blood.
The bone marrow, spleen, and lymph nodes are the main players in making blood cells. The bone marrow, found in bones like the hips and thighbones, is where blood cells are made. The spleen filters blood and stores red blood cells. Lymph nodes help fight off infections.
Hematopoiesis is the process of making blood cells from stem cells. It’s carefully controlled to ensure we have the right blood cells.
The skeletal system is vital for blood cell production. It houses the bone marrow where blood cells are made. The bone marrow has the stem cells and support cells needed for blood cell development.
Let’s look at how the skeletal system and hematopoiesis are connected:
| Skeletal Component | Role in Hematopoiesis |
| Bone Marrow | Produces blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets |
| Bone Structure | Provides a protective environment for bone marrow |
| Stem Cells | Found in bone marrow, these cells differentiate into various blood cell types. |
The skeletal system’s role in hematopoiesis is complex. It’s not just the bone marrow but also the structure it provides.
In conclusion, the hematopoietic system, supported by the skeletal system, is essential for blood cell production. Understanding how these systems work together helps us appreciate the complexity of our body’s ability to maintain healthy blood cells.
Many disorders can affect the blood corpuscles in our body. These are important for our health. We will look at common problems with red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Red blood cell disorders impact how our body gets oxygen. Anemia happens when there are not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. This leads to tiredness, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Polycythemia is when there are too many red blood cells. This can make blood thicker and increase the risk of blood clots.
Anemia can be caused by many things, like iron or vitamin deficiencies. Treatment depends on the cause and might include diet changes, supplements, or blood transfusions. Polycythemia vera, a type of polycythemia, needs careful management to avoid serious problems like blood clots and stroke.
White blood cell disorders affect our immune system. Leukemia is a cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It causes abnormal white blood cells to grow too much. Treatment includes chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or bone marrow transplantation.
Immunodeficiencies make it hard for our bodies to fight off infections. This can be due to genetics, infections like HIV/AIDS, or drugs that weaken the immune system. People with these conditions are more likely to get sick and may need antibiotics, immunoglobulin, or other treatments.
Platelet disorders affect how our blood clots. Thrombocytopenia means we have too few platelets, making us more likely to bleed. Causes include bone marrow problems, autoimmune diseases, and some medicines. Treatment might include platelet transfusions or medicines to help make more platelets.
Thrombocytosis means we have too many platelets, which can lead to blood clots. It can be caused by a myeloproliferative disorder or by other conditions like infections. Treatment focuses on the cause and might include medicines to prevent blood clots.
Knowing about these disorders helps us give better care. By understanding symptoms and causes, we can offer treatments that improve health outcomes.
Discoveries in testing and treatments have changed how we care for blood and bone marrow. We aim to give top-notch healthcare by using the latest methods in blood and bone marrow care.
New medical tech has made diagnosing blood and bone marrow issues better. Tools like flow cytometry and genetic testing help doctors find the right treatment for each patient. For example, a study on the National Center for Biotechnology Information shows how accurate diagnosis is key in blood diseases.
Some main ways to diagnose include:
New treatments have also made care better. These include targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and bone marrow transplants. Liv Hospital leads in these new methods, giving full care to those with blood and bone marrow issues.
Liv Hospital is dedicated to top healthcare by using the latest in blood and bone marrow care. Our team works together to give care that fits each patient’s needs.
Our main points include:
We use the newest tests and treatments to make sure our patients get the best care for their blood and bone marrow health.
It’s important to know about the three types of blood corpuscles and their roles. They help us understand blood and bone marrow health better. The bone marrow makes blood cells, which are key to health.
Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells fight off infections, and platelets help blood to clot. These cells work together to keep us healthy.
Keeping blood corpuscles healthy is key to avoiding diseases like anemia and leukemia. Knowing about blood and bone marrow health helps us stay healthy.
Liv Hospital offers advanced tests and treatments for blood and bone marrow issues. They combine medical skills with care to help people with blood health problems.
The three types are red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Each has a special role in keeping us healthy.
Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to our body’s tissues. They also remove carbon dioxide.
White blood cells are key to our immune system. They fight infections and protect us from harm.
Platelets are vital for blood clotting and healing wounds. They help stop bleeding when a blood vessel is injured.
Blood cells are made in the bone marrow. This is a spongy tissue inside some bones.
Hematopoiesis is how blood cells are made. It’s the process of stem cells turning into mature blood cells.
Red bone marrow makes blood cells. Yellow bone marrow is mostly fat and stores energy.
Disorders include anemia and polycythemia (red blood cell issues), leukemia and immunodeficiencies (white blood cell problems), and thrombocytopenia and thrombocytosis (platelet issues).
Tests like blood counts and bone marrow biopsies are used for diagnosis. Treatment depends on the disorder and may include medicines, transfusions, and other therapies.
The skeletal system supports bone marrow in making blood cells. It’s essential for hematopoiesis.
PubMed Central. Hematopoiesis: Regulation and Cell Differentiation.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!