Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik
A person with a physically demanding job has been dealing with a herniated disc.This shows how important it is to get a correct diagnosis and treatment. A herniated disc can really hurt your daily life, causing a lot of pain and discomfort. Learn how Herniated disc diagnosis is done using MRI, X-rays, and physical examinations.
To diagnose a herniated disc, doctors look for symptoms like back pain, numbness, and tingling. We’ll dive into how doctors figure this out and why getting treatment quickly is key.
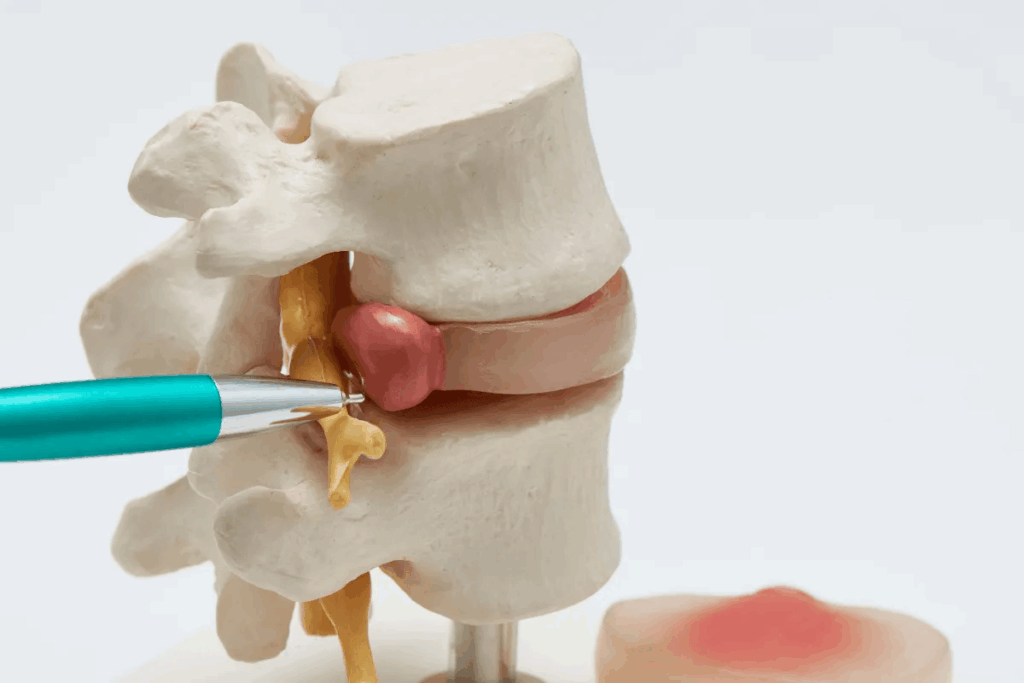
It’s important to understand what a herniated disc is to diagnose and treat it. A herniated disc happens when the soft center of the disc leaks out. This can cause a lot of pain and affect how well you live.
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, is when the soft center bulges out. This can hurt nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the back or legs.
Common Causes of Disc Herniation
Disc herniation can come from aging, wear and tear, or injury. As we get older, our discs lose water and can herniate more easily. Lifting heavy things wrong or getting hurt suddenly can also cause it. Knowing these causes helps in preventing and treating it.
Exploring herniated discs shows that early diagnosis and treatment are key. They help manage symptoms and prevent more problems. Healthcare experts can then give better care by understanding the causes and effects of disc herniation.
A herniated disc can cause many symptoms that affect your daily life. It’s important to know these signs to get the right medical help.
The pain from a herniated disc can be different in intensity and where it is felt. It usually happens when nerves nearby get compressed or irritated.
The pain often goes to the limbs, following the nerve path. For example, a disc problem in the lower back can cause sciatica. This is a sharp pain that goes down the leg.
Neurological symptoms can also happen, like numbness, tingling, or weakness in a limb. Experts say, “Nerve compression can cause many neurological problems.” Getting an early diagnosis is important to avoid lasting damage.
A herniated disc can make simple tasks hard. For instance,
Knowing these signs and symptoms is key to managing and treating the issue. If you notice any of these, seeing a healthcare professional for a detailed check-up is a must.
Knowing when to get medical help for a herniated disc is key. It can make a big difference in how well someone recovers. We need to watch for signs that mean we should act fast.
Some symptoms are red flags that mean serious trouble. These include sudden, severe pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs. Red flag symptoms are signs that something is very wrong and should not be ignored.
Cauda equina syndrome is a serious issue. It happens when nerves in the spinal canal get compressed. This can cause permanent damage if not treated quickly. Symptoms include severe lower back pain, numbness around the genitals, and loss of bladder or bowel control.
For cauda equina syndrome, emergency signs and symptoms are critical. These include sudden loss of leg function or severe numbness in the legs and groin area. Getting medical help right away is vital to avoid permanent damage.
| Symptom | Description | Action Required |
| Severe Lower Back Pain | Pain that is intense and unrelenting | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Numbness Around Genitals | Numbness or tingling in the genital area | Emergency medical evaluation |
| Loss of Bladder/Bowel Control | Inability to control urination or bowel movements | Immediate medical intervention |
Diagnosing a herniated disc starts with a detailed medical history. Knowing a patient’s medical background is key to finding the root of their symptoms. A complete medical history helps doctors narrow down possible causes and decide on further tests.
Your doctor will ask many questions during a medical history assessment. They want to know about your symptoms and medical history. Some important questions might be:
By answering these questions, you help your doctor understand your situation. They can then create a treatment plan that works for you.
Keeping a record of your pain is very important. We suggest using a pain journal to track when and how bad your pain is. Also, note any things that make it better or worse. This information helps your doctor spot patterns and possible causes of your pain.
For example, if your pain gets worse after certain activities or at certain times, it’s helpful to note that. It gives your doctor important clues about your condition.
Physical exams are key in checking for herniated discs. We use different methods to see how the condition affects patients.
The Straight Leg Raise Test is a basic tool. It lifts the patient’s leg while they lie down to check for sciatic pain. A positive test shows pain below the knee when the leg is lifted between 30 and 70 degrees. This test helps find lumbar disc herniation, mainly at the L4-L5 or L5-S1 levels.
The Crossed Straight Leg Raise Sign is another important test. It’s positive if lifting the unaffected leg causes pain in the affected leg. This sign is very specific for disc herniation and shows severe nerve root irritation.
We also use other tests, like the femoral nerve stretch test for upper lumbar disc herniation. These tests help check nerve root irritation and confirm the diagnosis.
“A thorough physical exam, including various tests, is vital for accurately diagnosing herniated discs and planning treatment.”
By using these physical exam techniques and a detailed medical history, we can make a precise diagnosis. Then, we can create a treatment plan that meets the patient’s needs.
A thorough neurological examination is key to diagnosing herniated discs and understanding nerve damage. It helps us check how well the nervous system works, focusing on the spine.
Muscle strength testing is a big part of the exam. We check the strength of different muscles to find any weakness. For example, a herniated disc in the lower back might make the legs weak.
Sensory function testing is also very important. We check how well the patient feels pain, temperature, and vibrations. This helps us see if nerves are being squeezed or damaged.
Reflex testing is another key part. We look at the patient’s reflexes to find any signs of nerve problems. For instance, a herniated disc in the neck might make reflexes in the arm weak.
| Test | Purpose | Significance |
| Muscle Strength Testing | Assess muscle strength | Identify weakness or deficits |
| Sensory Function Testing | Evaluate sensation | Detect abnormalities |
| Reflex Testing | Assess reflexes | Identify nerve compression or damage |
By looking at muscle strength, sensation, and reflexes, we get a full picture of the patient’s nerves. This helps us accurately diagnose a herniated disc.
Imaging technologies are key in diagnosing herniated discs. These tools give detailed images of the spine. They help doctors confirm a herniated disc and plan treatment.
MRI is the top choice for finding herniated discs. It shows clear images of soft tissues like discs, nerves, and the spinal cord.
Key advantages of MRI:
CT scans are great for seeing bony structures and calcified herniated discs. They’re not as good as MRI for soft tissues but show the spine’s anatomy well.
| Imaging Modality | Strengths | Limitations |
| MRI | Excellent soft tissue visualization | Contraindicated in some metal implants |
| CT Scan | Bony structure detail, quick | Radiation exposure, less sensitive for soft tissues |
X-rays are first used to check for fractures or deformities. They’re not good for seeing herniated discs but help with spinal alignment and disc height.
“The use of X-ray imaging as a preliminary assessment can guide further diagnostic steps, though it is not definitive for herniated disc diagnosis.”
Diagnostic imaging is vital for herniated disc diagnosis. Knowing MRI, CT scans, and X-rays’ strengths and limits helps doctors make better decisions for patients.
Advanced imaging techniques are key in diagnosing herniated discs. They help confirm the diagnosis and show how severe the condition is. These methods give detailed pictures of the spine. This lets doctors see the disc and the areas around it.
A myelogram is a special test that uses dye in the spinal canal. It helps doctors see the spinal cord and nerve roots. This test is good for people who can’t have an MRI or have complex spine shapes.
It shows where the spinal cord or nerve roots might be compressed or irritated.
Discography is a technique used to find the cause of disc pain. It involves putting dye into the disc to check its health. This test is helpful for people with many disc problems.
Electrophysiological studies are key in finding out if you have a herniated disc. They check how well nerves and muscles work. This helps doctors see how much damage a herniated disc has caused.
These studies add to what images show, giving a clearer picture of what’s going on. This is really helpful when images don’t match up with how the patient feels.
Electromyography (EMG) is a way to see how muscles work by looking at their electrical activity. It’s used to find out if muscles are damaged because of a herniated disc.
An EMG test uses a small needle to record muscle electrical activity. If the patterns are off, it might mean there’s nerve damage or muscle injury. This helps doctors decide on the best treatment.
Nerve conduction studies (NCS) are also important for diagnosing herniated discs. They check how well nerves send signals. This helps find out if nerves are damaged or being squished.
NCS work by sending a small electrical signal to a nerve and recording how it responds. This test shows where and how bad the nerve damage is. It’s key for making a good treatment plan.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose | Key Findings |
| Electromyography (EMG) | Measures muscle electrical activity | Abnormal patterns indicating nerve damage or muscle injury |
| Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) | Measures nerve signal speed and strength | Identifies nerve damage or compression, determining location and severity |
Diagnosing a herniated disc is a detailed process. It uses clinical checks, medical history, and advanced imaging. We’ll explain how these steps help diagnose herniated discs fully.
Diagnosing a herniated disc involves several steps. We look at clinical findings, patient history, and imaging results. Diagnostic criteria include specific tests and images that show a herniated disc.
When deciding on treatment, we assess the disc’s size, the nerve root affected, and how symptoms impact daily life. This detailed check helps doctors choose the best treatment.
It’s important to rule out other conditions that might cause similar symptoms. We look at possibilities like degenerative disc disease or spinal stenosis. These can mimic symptoms of a herniated disc.
Differential diagnosis means looking at many possible causes for symptoms. We consider the patient’s age, medical history, and symptoms. For example, older patients might have degenerative changes, while younger ones might have herniated discs from injury or overuse.
By carefully following these steps, we can accurately diagnose herniated discs. This ensures patients get the right care for their needs.
Understanding radiculopathy and sciatica is key for proper diagnosis and treatment. Radiculopathy is when nerve roots get compressed or irritated. This can cause pain, numbness, or weakness along the nerve’s path. Sciatica is a type of radiculopathy that affects the sciatic nerve, running from the lower back to the legs. Accurate assessment of these conditions is vital for choosing the right treatment.
To check for nerve root compression, we use both clinical assessment and imaging. Clinically, we look for signs like pain, muscle weakness, or decreased reflexes. The straight leg raise test is often used to check for sciatic nerve irritation.
Diagnostic imaging, like MRI, is also important. It helps us see the compressed nerve root and find the cause, like a herniated disc.
It’s important to tell sciatica apart from other leg pain causes. Sciatica pain goes along the sciatic nerve, but other issues like peripheral artery disease can look similar. A detailed history and physical exam, along with tests, help figure out the real cause.
For example, vascular claudication pain comes on when walking and goes away with rest. Sciatica pain is often constant and gets worse with certain movements.
Diagnosing herniated discs needs a deep understanding of cervical and lumbar spine imaging. The choice of imaging depends on the spinal area, symptoms, and medical history.
Imaging is key in diagnosing herniated discs. The approach varies between the cervical and lumbar spine.
The cervical spine has unique challenges due to its complex anatomy. It houses vital structures like the spinal cord and vertebral arteries. For cervical spine herniated disc evaluations, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is often chosen. It’s great for showing soft tissues like discs, nerves, and the spinal cord.
Getting the cervical spine imaging right is critical. It helps in making accurate diagnoses and guiding treatment.
The lumbar spine has its own diagnostic needs for herniated discs. MRI is the top choice for lumbar disc herniations. But, CT scans and X-rays might be used too, based on the situation. The straight leg raise test is also helpful for lumbar disc herniation checks, alongside imaging.
Understanding the unique needs for diagnosing cervical and lumbar spine herniations helps doctors. They can make better diagnoses and create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
Spine specialists are key in finding out what’s wrong with herniated discs and creating treatment plans. They are experts at looking at complex spinal problems.
If you’re feeling pain that won’t go away or is really bad, see a spine specialist. Key indicators include:
These experts can tell how serious the problem is and suggest tests to find out more.
Diagnosing herniated discs involves a team effort. This team includes:
Together, they give a full picture of what’s going on. This leads to better diagnoses and treatment plans. This team effort makes sure patients get care that fits their needs.
Herniated discs are tricky to diagnose. Their symptoms can look like other health issues. This makes it key to get the right diagnosis for proper treatment.
Many conditions can seem like herniated discs. This can lead to wrong diagnoses. These include:
To get it right, doctors need to look at your medical history, do a physical check, and use imaging tests.
| Condition | Similarities to Herniated Disc | Distinguishing Features |
| Degenerative Disc Disease | Pain and stiffness in the back | Gradual onset, absence of radiculopathy |
| Spinal Stenosis | Numbness and pain in the legs | Typically affects older adults, worsens with walking |
| Piriformis Syndrome | Sciatica-like symptoms | Pain worsens with hip rotation, no neurological deficits |
Doctors use both clinical checks and advanced imaging to tackle these challenges.
Diagnostic findings are key in choosing the right treatment for herniated discs. After a diagnosis, we create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
The findings help we understand how severe the herniation is and its impact on the patient. This info is vital for deciding between non-surgical and surgical options.
Imaging studies like MRI or CT scans give us detailed info about the herniated disc. We use this to decide the best treatment plan.
For example, a big herniation might need surgery, while a small one could be treated with physical therapy and pain meds.
The choice between non-surgical and surgical treatments depends on several factors. These include the severity of symptoms and the patient’s health. Conservative approaches often include physical therapy and pain management.
Surgical options are considered when non-surgical treatments don’t work. The decision to have surgery depends on the patient’s condition and preferences.
Getting a correct diagnosis is key for those with herniated discs. It affects how treatment is planned and how well it works. We’ve looked at the signs and symptoms of a herniated disc and how doctors confirm it.
Diagnosing a herniated disc involves several steps. These include looking at medical history, doing a physical exam, and using imaging tests. Knowing what causes and affects herniated discs helps doctors create the right treatment plans for each person.
In short, diagnosing a herniated disc needs a detailed approach. This includes clinical checks and advanced imaging. By focusing on accurate diagnosis, we help people get the right treatment. This relieves their symptoms and improves their life quality.
A herniated disc happens when the soft center of the disc leaks out. This usually happens because of wear and tear, injury, or sudden strain. It causes discomfort and nerve compression.
Common symptoms include pain that spreads to the limbs, numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, and limited mobility. These symptoms vary based on the location and severity of the herniation.
To diagnose a herniated disc, doctors look at your medical history, do a physical exam, and check your nerves. They might also use MRI, CT scans, or X-rays to see the extent of the herniation.
The straight leg raise test is a way to check for sciatic pain and nerve irritation. It involves lifting the affected leg to a certain angle. This helps doctors diagnose herniated discs.
A myelogram is used when other tests don’t give clear results. It’s an advanced imaging technique that shows the spinal canal and nerve roots in detail. It helps confirm pain sources or assess complex cases.
EMG and nerve conduction studies check nerve and muscle function. They help diagnose herniated discs by finding nerve damage or compression. They also show how much nerve root involvement there is.
Herniated discs in the cervical spine can cause neck pain, arm pain, or numbness. Those in the lumbar spine usually cause lower back pain, sciatica, or leg pain. Each area has different diagnostic considerations and treatment options.
See a spine specialist if you have persistent or severe symptoms, red flag symptoms, or if treatments don’t work. They can give a detailed evaluation and provide multidisciplinary care.
Diagnostic findings show the severity and location of the herniation. They help decide between conservative treatments like physical therapy and pain management, or surgery. The choice depends on the extent of nerve compression and symptoms.
Diagnosing herniated discs can be tricky. It’s hard to tell them apart from other conditions like spinal stenosis or degenerative disc disease. A thorough diagnostic approach is needed to make sure you get the right diagnosis.
Yes, herniated discs can be misdiagnosed. To avoid this, use a combination of a detailed medical history, physical exam, and advanced imaging. Also, getting a specialist’s evaluation when needed can help.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!