Last Updated on November 17, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir

When routine blood tests show strange results, a bone marrow test can help find the cause. At Liv Hospital, we focus on you to find the source of blood problems and cancers.
Bone marrow tests, like aspiration and biopsy, are key to diagnosing blood issues and cancers. If you’re wondering what is a bone marrow test used to diagnose, it helps detect problems in blood cell production and identify various blood disorders or cancers.
Our team at Liv Hospital aims to give top-notch care with support for international patients. We know how vital accurate diagnosis is, and bone marrow testing is a big part of it.

Deep inside our bones, there’s a soft, spongy tissue called bone marrow. It’s key to our health. Bone marrow is a complex organ that helps our body make blood cells and keep our bones strong.
Bone marrow has a network of blood vessels. These include arteries, veins, and capillaries that bring it nutrients and oxygen. It has different cell types, like hematopoietic cells and stromal cells. These cells help make blood cells and support the marrow.
The main job of bone marrow is to make blood cells. It produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cells carry oxygen, fight infections, and help blood clot.
Blood cell production, or hematopoiesis, happens in the bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cells turn into different blood cell types. This process uses growth factors and cell interactions to keep our blood cell levels healthy.
Bone marrow is divided into red marrow and yellow marrow. Red marrow makes blood cells and is in bones like the hips and vertebrae. Yellow marrow is mostly fat and is in the long bones’ shafts.
Yellow marrow doesn’t make blood cells but can turn into red marrow when needed.
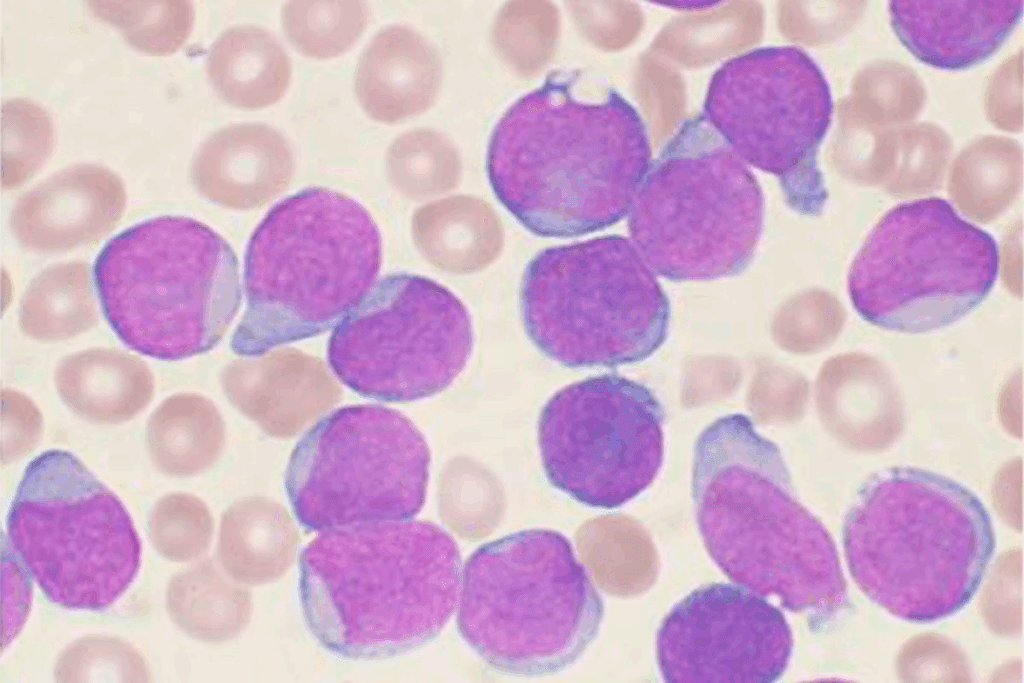
Bone marrow testing includes aspiration and biopsy. These tests help understand blood-related conditions and diseases. We’ll explore each test and how they’re used together.
Bone marrow aspiration removes fluid and cells from your bone marrow. It’s key for checking the marrow’s cell types. Aspiration lets us see the marrow’s cell structure, helping spot blood disorders.
To do this test, a needle is put into the hip bone to get marrow fluid. Then, the sample is looked at under a microscope for any cell issues.
A bone marrow biopsy takes a small bone and marrow piece. It gives a detailed look at the marrow’s structure and cells. A biopsy is great for a detailed marrow look.
The biopsy sample is studied to check the marrow’s health. It looks for any fibrosis, infiltration, or other problems.
“Bone marrow biopsy is an essential diagnostic tool that provides valuable information about the bone marrow’s cellular and structural integrity.”
Aspiration and biopsy are often done together. This way, both the marrow’s cells and structure are checked.
| Procedure | Description | Primary Use |
| Bone Marrow Aspiration | Removes fluid and cells from the bone marrow | Analyzing cellular composition |
| Bone Marrow Biopsy | Removes a piece of bone and bone marrow | Examining marrow structure and cellularity |
| Combined Procedures | Both aspiration and biopsy were performed together | Comprehensive assessment of bone marrow health |
Knowing about bone marrow tests helps doctors make better diagnoses and treatment plans.
Bone marrow tests are key for checking the bone marrow’s health and blood cell production. They help find and track conditions that affect the bone marrow and blood cell making. Doctors say, “Bone marrow tests can find the causes of blood problems and some cancers.”
These tests have many uses and are very important for patient care. They let doctors see how well the bone marrow makes blood cells.
Bone marrow tests mainly help diagnose and track bone marrow and blood disorders, and some cancers. They are key to checking the bone marrow’s health and its blood cell-making ability.
Bone marrow tests are also used to check abnormal blood cell counts. Doctors can find the cause of blood cell production problems by looking at the bone marrow.
Abnormal blood cell counts can come from many things, like bone marrow issues, infections, and some medicines. These tests help find the main cause, leading to better treatment plans.
Bone marrow tests also help find cellular and genetic problems in the bone marrow. This info is key for diagnosing and planning treatments.
By studying bone marrow cell genetics, doctors can spot genetic changes linked to blood disorders and cancers. This genetic info helps guide treatments and predict outcomes.
“The analysis of bone marrow samples provides critical information about the presence of genetic abnormalities and their impact on blood cell production.”
In summary, bone marrow tests are essential for understanding the bone marrow’s health and blood cell production. Knowing how these tests work helps patients and doctors deal with blood-related issues better.
Doctors often use bone marrow tests to understand a patient’s health better. They do this when the first tests don’t show clear results or hint at a problem. The choice to do a bone marrow test depends on a patient’s symptoms and first test results.
Doctors order bone marrow tests to check unexplained blood count abnormalities. If blood tests show odd cell counts, a bone marrow test can find the cause. This is key for diagnosing issues with blood cell production.
For example, a low red blood cell count might mean a problem with making or losing red blood cells. Odd white blood cell counts could point to infections, autoimmune diseases, or bone marrow problems.
Doctors also test bone marrow when they suspect blood disorders like leukemia, lymphoma, or multiple myeloma. These conditions need a bone marrow check to confirm and see how far the disease has spread.
A bone marrow test gives vital information on the disorder’s type and how severe it is. This helps doctors plan the best treatment. For leukemia, for example, it shows the leukemia type and its genetic details, which are key for treatment.
Another reason for bone marrow tests is to monitor treatment effectiveness for blood cancers and other disorders. By checking the bone marrow before, during, and after treatment, doctors see how well it’s working.
This info is essential for tweaking treatment plans. For instance, if someone with leukemia is getting chemotherapy, a bone marrow test after can show if the cancer is gone or if more treatment is needed.
Bone marrow testing is key to finding blood cancers like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. These cancers hit the blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic system. Accurate diagnosis is vital for good treatment. We’ll see how bone marrow tests help diagnose these conditions.
Leukemia is a blood and bone marrow cancer with too many white blood cells. Bone marrow tests are key to finding leukemia. They check the bone marrow’s cells and spot odd ones. There are many leukemia types, each needing its own treatment.
Tests like bone marrow aspiration and biopsy tell us the leukemia type and stage. This info is key for treatment planning. It shows how far the disease has spread and how well treatment is working.
Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, part of the immune system. Bone marrow tests are important for lymphoma staging and checking if it’s in the bone marrow. This info helps predict the disease’s outcome and pick the right treatment.
Lymphomas are split into Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin types, with many subtypes. Bone marrow testing shows if the bone marrow is involved. This affects the treatment plan and disease management.
Multiple myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells in the bone marrow. Diagnosing multiple myeloma often means bone marrow testing. It checks plasma cell levels and genetic issues in these cells. It also looks at bone damage from myeloma cells.
Diagnosing and managing multiple myeloma depend on bone marrow test results. These tests show myeloma cell characteristics and chromosomal issues. This info helps decide treatment and track disease response.
Bone marrow tests are key for spotting non-cancerous issues that mess with blood cell production. These problems can really affect a person’s quality. Getting a correct diagnosis through bone marrow tests is key to managing and treating these conditions well.
Aplastic anemia happens when the bone marrow can’t make enough blood cells. This leads to tiredness, infections, and bleeding issues. Bone marrow tests show if aplastic anemia is present by checking for low blood cell production.
Other anemias, like iron deficiency anemia, can also be checked through bone marrow tests. But it’s not as common.
To diagnose aplastic anemia, doctors look at the bone marrow’s cell count and blood cell health. This condition can be caused by toxins, some medicines, and viruses.
Bone marrow infections, like osteomyelitis, can be found through bone marrow tests. These infections happen when bacteria or fungi get into the bone marrow, causing inflammation and damage. The test finds out what’s causing the infection and how bad it is.
Sometimes, bone marrow infections come from a body-wide infection or when pathogens directly get into the bone. Quick diagnosis and treatment are important to avoid lasting harm.
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a rare, serious condition where the immune system gets too active. In HLH, the bone marrow gets filled with abnormal immune cells that destroy blood cells. This leads to severe blood cell shortages. Bone marrow tests are key for spotting HLH by finding hemophagocytic cells.
HLH can be either genetic or caused by infections, autoimmune diseases, or cancers. Quick diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage this condition well.
Learning about the bone marrow test can ease your worries. We’ll cover how to prepare, what happens during the test, and how they manage pain and anesthesia.
There are steps to take before a bone marrow test. Following your doctor’s advice is key to a smooth process.
The bone marrow test has several steps. It usually takes 30 to 60 minutes.
Pain control is important during the test. Local anesthesia numbs the area where the needles go in.
You might feel sore or uncomfortable after. This can be managed with over-the-counter pain meds. Your doctor will tell you how to handle any pain.
Knowing what to expect can help you prepare for the bone marrow test. If you have questions, talk to your healthcare provider.
Understanding a patient’s blood cell health is key. This is done by analyzing bone marrow samples in a lab. The samples come from bone marrow aspiration or biopsy.
Cytological examination looks at the cells in the bone marrow sample. It helps identify cell types, their shape, and any issues. We use special stains to see these cells under a microscope. This helps diagnose diseases like leukemia or lymphoma.
Histological assessment examines the bone marrow tissue structure. It looks at how cells are arranged and if there’s scarring. This gives us important information about the bone marrow’s health. It helps diagnose conditions like myelofibrosis.
Advanced tests are used to further analyze bone marrow samples. These include flow cytometry, cytogenetic analysis, and molecular testing. These methods help find specific genetic issues or markers. They’re vital for diagnosing and managing blood disorders.
By combining cytological, histological, and advanced tests, we get a full picture of bone marrow health. This detailed approach is key to accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Bone marrow tests are usually safe, but there are risks and complications. It’s important to know about these to make good choices.
Most people don’t have big problems after a bone marrow test. You might feel some pain, bruising, or swelling. These usually go away in a few days.
Doctors often use ways to help with pain to make you more comfortable.
Even though they’re rare, serious problems can happen. These include infections, too much bleeding, nerve damage, or reactions to anesthesia.
Following your doctor’s advice after the test can help avoid these issues. If you notice anything strange, call your doctor right away.
Some people might not be good candidates for bone marrow tests. This includes those with severe bleeding problems, active infections, or heart or lung issues.
Talking to your doctor about your health is key to figuring out if you should have the test.
Knowing the risks of bone marrow tests helps you make smart choices. Always talk to your doctor about any worries you have.
Understanding the recovery process after a bone marrow test is key. We’ll guide you through the essential steps for a smooth recovery. This will help you heal comfortably.
Your healthcare provider will give you specific care instructions after the test. You should avoid strenuous activities and keep the bandage dry for 24 hours. Following these instructions carefully is vital to prevent complications and promote healing.
Discomfort or pain at the test site is common after a bone marrow test. Your doctor may suggest over-the-counter pain relievers. It’s essential to monitor your pain levels and report any severe or worsening pain to your healthcare provider.
Knowing when to seek medical attention is important. Contact your doctor if you have increased pain, swelling, redness, or drainage at the test site, or if you have a fever. Being vigilant about these signs can help prevent serious complications.
By following the care instructions and watching for signs of complications, you can recover with confidence. Our team is here to support you every step of the way.
Your bone marrow test results give you important health insights. They help find blood-related disorders like cancers and infections. They also show how the bone marrow is doing.
When your bone marrow sample is checked, it’s either normal or not. Normal findings mean your bone marrow cells are healthy. But, abnormal findings might show a disorder, like cancer or a blood cell issue.
Abnormal results can show up in different ways. This includes:
How long it takes to get your bone marrow test results varies. It can be a few days to weeks. This depends on the test’s complexity and the lab’s work pace.
Your doctor will tell you when to expect your results. They’ll also explain what they mean for your health.
If your results show something’s off, your doctor might suggest more tests. This could be more bone marrow tests or imaging. They aim to confirm the diagnosis or get more details.
Understanding your bone marrow test results is key to managing your health. Your doctor will help you make sense of them. They’ll also tell you what to do next in your care plan.
Bone marrow testing is key in diagnosing many health issues. It gives detailed information about the bone marrow and blood cells. These tests help spot and track diseases, like blood cancers and other non-cancerous conditions.
Doctors use the data from these tests to choose the right treatment.
In short, bone marrow testing is a vital tool for doctors. It helps them diagnose and manage many health problems. Patients should know how important these tests are for their care.
A bone marrow test helps find many health issues. It looks at the cells and genes in the bone marrow. This includes blood cancers, anemia, and infections.
Bone marrow tests use aspiration and biopsy. These methods take a sample of bone marrow for lab checks.
Bone marrow aspiration gets a liquid sample. A biopsy takes a small bone piece with marrow for study.
Doctors use these tests to check blood counts and find blood disorders. They also check if treatments are working.
Yes, they are key in finding blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma. They look for abnormal cells and genes.
These tests might hurt a bit, but doctors use anesthesia to lessen the pain. They also help with pain after the test.
Side effects include pain, bruising, bleedinggBut serious issues like infection and nerve damage are rare.
Results come in a few days for basic tests. More detailed tests take longer.
A normal result means the bone marrow looks healthy. But an abnormal result could mean cancer or anemia.
Yes, you need to prepare. This includes stopping some medicines, getting a ride, and following a diet.
People with bleeding disorders need careful thought. Sometimes, they might not be able to have the test because of bleeding risks.
To feel better, follow the care instructions. This might include taking pain meds, resting, and watching for any complications.
Lee, A., et al. (2008). Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy: Techniques and Analysis. Hematology, 13(4), 230–237.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!