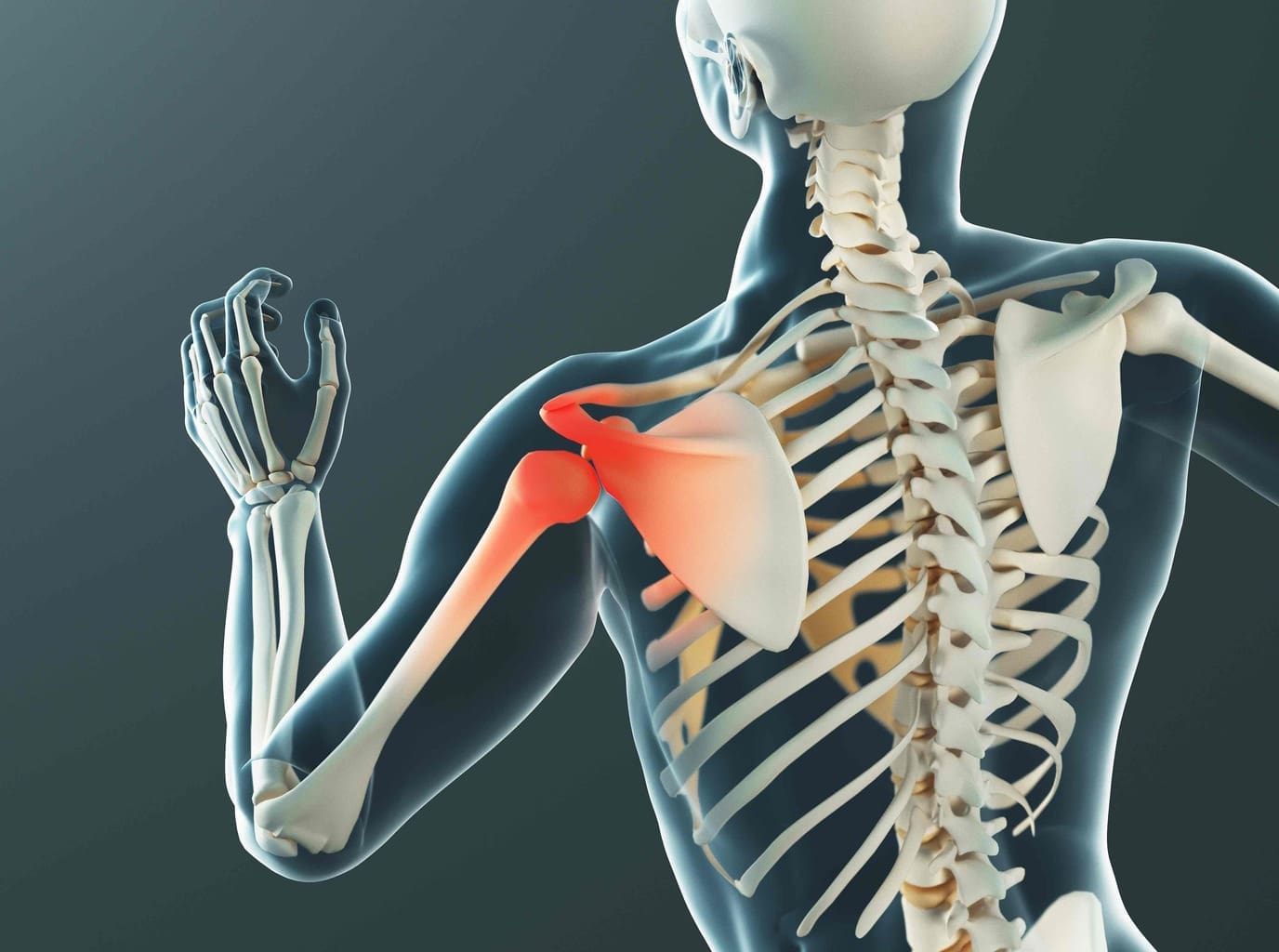
At Liv Hospital, we know how complex anatomic shoulder replacement can be. We focus on giving top-notch care to patients from around the world. This surgery replaces a damaged or arthritic shoulder joint with a new one. It aims to make the shoulder work like it should again and reduce pain.
We’ll share key facts about this surgery. You’ll learn about its definition, parts, and how it’s done. We’ll use photos and X-rays to help you understand. Knowing about the anatomy and how imaging works is key for those looking for advanced medical care.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the basics of anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty.
- The importance of imaging in shoulder replacement surgery.
- Components of anatomic shoulder replacement.
- The surgical process and what to expect.
- Restoring normal function and alleviating pain.
What Is Anatomic Shoulder Replacement and Who Needs It?
For those with severe shoulder arthritis, anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty is a hopeful option. This surgery replaces the damaged joint with artificial parts that look like the real thing.
Definition and Purpose of Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
Anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty aims to fix the shoulder’s natural shape. It swaps out the humeral head and glenoid with fake ones. The goal is to ease pain, boost function, and improve life quality for those with severe arthritis.
The Rising Popularity of Shoulder Replacement Surgery
Shoulder replacement surgery, like anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty, is getting more popular. This is thanks to better surgery methods and more people dealing with shoulder issues. Total shoulder arthroplasty for arthritis is now a common choice.
| Year | Number of Shoulder Replacement Surgeries |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 12,000 |
| 2015 | 20,000 |
| 2020 | 35,000 |
Key Differences from Reverse Shoulder Replacement
Anatomic shoulder replacement is different from reverse shoulder replacement. Anatomic is for those with intact rotator cuff muscles. Reverse is for those without. The right choice depends on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s advice.
Understanding Shoulder Anatomy and Pathology
To understand anatomic shoulder replacement, we must first know the normal anatomy and common shoulder problems. The shoulder is made up of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. These work together to allow for a wide range of motion.
Normal Shoulder Joint Structure
The shoulder joint, or glenohumeral joint, is a ball-and-socket joint. The humeral head fits into the glenoid cavity of the scapula. This design lets the shoulder move in many directions.
The rotator cuff, made of four muscles and their tendons, helps keep the shoulder stable. It also helps with movement.
Common Pathologies Leading to Shoulder Replacement
Several conditions can lead to the need for shoulder replacement surgery. These include severe osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and avascular necrosis. These cause a lot of pain and make it hard to move.
Severe fractures or rotator cuff problems can also require shoulder replacement. Knowing about these conditions helps doctors choose the best treatment. This includes anatomic shoulder replacement to improve function and reduce pain.
The Components of Anatomic Shoulder Replacement
Anatomic shoulder replacement uses key parts to match the natural shoulder. It needs a deep understanding of the shoulder’s complex structure. This includes the components used in the replacement.
The Humeral Component: Metal Ball and Stem
The humeral component has a metal ball and a stem. The stem goes into the humerus bone. This setup allows for smooth movement with the glenoid component, just like the natural shoulder.
The metal ball is made from strong materials like cobalt-chromium or titanium. This ensures it lasts long and doesn’t wear out easily.
The Glenoid Component: Polyethylene Socket
The glenoid component is a polyethylene socket that replaces the shoulder’s natural socket. It works with the humeral component for smooth movement. The glenoid is placed to fit the patient’s anatomy well, for better function and less risk of problems.
Materials and Design Advancements
New materials and designs have made anatomic shoulder replacement better. Modern implants are more durable and last longer. They have innovative materials and coatings that help the bone grow around them, reducing the chance of the implant coming loose.
Advanced imaging techniques and 3D printing help plan and customize the components. This leads to better results for patients.
Pre-Operative Planning and Patient Selection
Getting ready for anatomic shoulder replacement surgery is key to success. This process includes important steps to help our patients get the best results.
Diagnostic Imaging Requirements
Imaging is a big part of getting ready for surgery. We use X-rays and other tools to check the shoulder joint. This helps us see how damaged it is and plan the surgery.
Patient Factors Affecting Surgical Decisions
What affects our decisions to operate includes the patient’s health and bone quality. We also look at any other health issues that might impact the surgery or recovery. This detailed look helps us tailor the surgery to each patient’s needs.
When Anatomic Replacement Is Not Recommended
Not every patient is a good fit for anatomic shoulder replacement. We carefully check each case to find the best treatment. Severe bone loss or certain health issues might mean a different treatment is needed.
By looking at these factors and using advanced imaging, we make sure our patients get the right care for their condition.
The Anatomic Shoulder Replacement Surgical Procedure
Surgeons follow a detailed process for anatomic shoulder replacement surgery. They need to know the shoulder’s anatomy well. This ensures the shoulder works naturally after surgery.
The Deltopectoral Approach and Incision
The deltopectoral approach is a common method for this surgery. It involves an incision between the deltoid and pectoralis muscles. This approach balances good exposure with less tissue damage, helping surgeons work precisely.
They plan the incision to look good and reduce scarring. The incision’s length depends on the patient’s body and the surgery’s complexity.
Step-by-Step Surgical Technique
The surgery starts with exposing the shoulder through the deltopectoral approach. Then, the surgeon dislocates the humeral head and prepares the damaged areas for the prosthetics.
The metal ball and stem of the humeral component are implanted next. The stem goes into the humeral canal, and the ball is attached. After that, the polyethylene socket of the glenoid component is placed in the glenoid cavity. The surgeon makes sure both parts fit right and are secure.
The technique requires careful attention to detail. Surgeons use planning, navigation, and their skills to get the best results. They aim to keep the surrounding tissues intact, like the rotator cuff, to maintain shoulder function.
Visual Guide to Anatomic Shoulder Replacement X-rays
X-rays are key in anatomic shoulder replacement for surgeons and patients. They give vital info about the shoulder before, during, and after surgery.
Pre-Operative X-rays: What Surgeons Look For
X-rays before surgery show the shoulder’s condition. We look for joint damage, bone loss, and deformities. This helps plan the surgery.
Immediate Post-Operative X-rays: Normal Appearance
Right after surgery, X-rays check the prosthetic’s position. We look for complications like fractures or misaligned implants. A good X-ray shows the components are in place.
Long-term Follow-up Imaging: What to Expect
Long-term X-rays check the implant’s durability and the joint’s health. We look for stable implants without loosening or wear. Any issues are watched closely.
Signs of Possible Complications on X-rays
X-rays are also key for spotting complications in shoulder replacement. Signs include loosening implants, bone loss, or dislocation. Catching these early helps patients get the best results.
Recovery and Rehabilitation Timeline
Recovery from anatomic shoulder replacement needs a special rehab plan for each patient. This helps regain strength, mobility, and reach the best results.
Hospital Stay and Immediate Post-Surgical Phase
Patients usually stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 days after surgery. We focus on managing pain and starting to move around. Effective pain control is key for a smooth recovery. We use medicines and other methods to help with this.
Physical Therapy Protocols and Progression
Physical therapy starts soon after surgery and goes on for months. The first steps are passive range of motion exercises to avoid stiffness and aid healing. Later, active exercises help strengthen the shoulder muscles.
Our rehab plan includes:
- Early mobilization to prevent stiffness
- Strengthening exercises for the rotator cuff and other shoulder muscles
- Progressive resistance exercises to improve strength and function
Milestones in Recovery
Patients will hit certain milestones during their recovery. These are:
- Regaining range of motion
- Improving strength
- Returning to daily activities
Return to Daily Activities and Sports
Most people can get back to their daily life in 3 to 6 months. Return to sports or heavy lifting is usually allowed after 6 months. This is when the shoulder is strong and mobile enough.
Throughout recovery, sticking to the rehab plan is vital for the best results. This way, patients can regain a lot of function and improve their life quality.
Potential Risks and Complications
Anatomic shoulder replacement is a common and effective surgery. But, it also has risks and complications. Knowing about these risks is important for making the right choice.
Infection and Implant Loosening
Two big risks are infection and implant loosening. Infection can happen, and you should watch for signs like pain, redness, or fever. Implant loosening means the artificial parts can come loose over time, causing pain and possibly needing more surgery.
Instability and Dislocation
Instability and dislocation are also possible. The shoulder joint can easily dislocate if the muscles and tissues don’t heal well or if there’s trauma.
Rotator Cuff Failure
The rotator cuff is key for shoulder movement and stability. Rotator cuff failure after surgery can cause pain and less function, possibly needing more surgery.
Long-term Wear and Revision Surgery
Prosthetics can wear out over time. This means the parts of the anatomic shoulder replacement might need to be replaced. This is why regular check-ups with your doctor are important.
Knowing about these risks helps patients make better choices. It’s about weighing the surgery’s benefits against the possible downsides. Being informed is key to choosing the right path for your treatment.
Conclusion: Outcomes and Future of Anatomic Shoulder Replacement
Anatomic shoulder replacement has changed how we treat shoulder arthritis and other conditions. This surgery replaces the damaged joint with prosthetic parts that look like the real thing.
Patients have seen big improvements in pain and how well they can move. New surgical methods and better implants keep making this surgery even better.
Looking ahead, we’ll see even more progress in shoulder surgery. New materials and technologies will make prosthetics last longer and work better. This means patients will get even better results and move more naturally.
At our institution, we’re all about top-notch healthcare for everyone. Our skilled orthopedic surgeons work hard to give patients the best care. They aim for the best results for those getting anatomic shoulder replacement.
What is anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty?
Anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty is a surgery. It replaces the damaged shoulder joint with artificial parts. These parts look like the natural shoulder.
How does anatomic shoulder replacement differ from reverse shoulder replacement?
Anatomic shoulder replacement works for those with a good rotator cuff. Reverse shoulder replacement is for those with damaged rotator cuffs or other conditions.
What are the components used in anatomic shoulder replacement?
It uses a metal ball and stem for the humeral component. The glenoid component is a polyethylene socket.
What diagnostic imaging is required before anatomic shoulder replacement surgery?
Before surgery, X-rays and sometimes CT or MRI scans are needed. They check the shoulder and surrounding tissues.
What are the possible complications of anatomic shoulder replacement?
Complications can include infection, loosening, instability, dislocation, and rotator cuff failure. These are among the possible issues.
How long does it take to recover from anatomic shoulder replacement surgery?
Recovery time varies. Most can do daily activities in months. Full recovery might take a year or more.
What is the role of physical therapy in the recovery process?
Physical therapy is key. It helps patients regain strength, mobility, and function in the shoulder after surgery.
Can I expect to return to sports or heavy activities after anatomic shoulder replacement?
Many can go back to sports or heavy activities. It depends on the activity and the condition of the tissues.
How do X-rays help in monitoring the success of anatomic shoulder replacement?
X-rays check the implant’s position and integrity. They also look for signs of complications like loosening or wear.
What advancements have improved the outcomes of anatomic shoulder replacement?
Better materials, design, and surgical techniques have improved results. These advancements have helped patients more.
References
- PMC. (n.d.). Techniques to address humeral bone insufficiency during total shoulder arthroplasty with a nonspherical humeral head and inlay glenoid. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5676003
- Orthobullets. Total Shoulder Arthroplasty for Arthritis. Retrieved from https://www.orthobullets.com/approaches/12171/total-shoulder-arthroplasty-for-arthritis