Last Updated on November 20, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
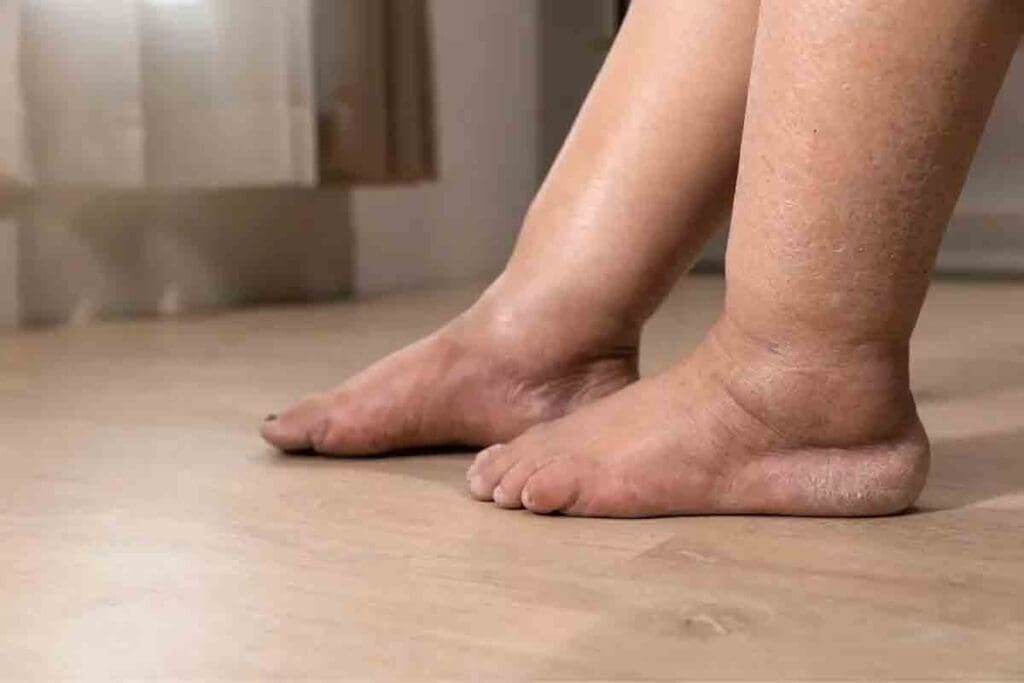
Anemia happens when the body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells or hemoglobin. This makes it hard for tissues to get enough oxygen. Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. It can also cause fluid buildup and swelling in the feet and legs, known as peripheral edema.Find out how swollen feet anemia is connected. Learn the crucial link between low hemoglobin and leg edema you need to know.
It’s important to understand how anemia and swelling are connected. At Liv Hospital, we treat anemia and related issues. We focus on finding and fixing the cause of symptoms.
Anemia affects more than just the blood. It impacts the heart and overall health. It’s a complex disorder with wide-ranging effects on the body.
Anemia means not enough red blood cells or poor quality ones. These cells carry oxygen to our tissues. There are many types, like iron deficiency and vitamin deficiency anemia. Each type needs a different treatment.
| Type of Anemia | Cause | Common Symptoms |
| Iron Deficiency Anemia | Lack of iron | Fatigue, weakness |
| Vitamin Deficiency Anemia | Deficiency in vitamin B12 or folate | Numbness, tingling in hands and feet |
Anemia puts a lot of strain on the heart. With fewer red blood cells, tissues get less oxygen. The heart works harder, which can lead to heart failure.
Heart failure makes it hard for the heart to pump enough blood. This can cause fluid buildup and swelling, or edema, in the legs and feet.
The link between anemia, heart strain, and swelling is complex. As anemia gets worse, the heart works even harder. This can make swelling worse. It’s important to understand this to manage anemia and reduce swelling.
Anemia and leg swelling are linked through complex body processes. Anemia, a lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin, affects the body in many ways. It can cause swelling in the legs.
Peripheral edema is swelling in the lower legs and feet due to fluid buildup. This happens when too much fluid stays in the leg tissues. Anemia can make this swelling worse by reducing the blood’s ability to carry oxygen.
The legs are more likely to swell because gravity pulls on the blood flow. Anemia reduces oxygen to tissues, harming the heart and blood vessels. This makes fluid stay in the legs.
| Factors Contributing to Edema in Anemia | Description |
| Reduced Blood Viscosity | Fewer red blood cells mean thinner blood, causing fluid to leak into tissues. |
| Compensatory Mechanisms | The body tries to make up for anemia by pumping more blood, leading to fluid buildup. |
| Neurohormonal Activation | Neurohormonal pathways get activated, causing blood vessels to widen and hold more fluid. |
It’s important to understand how anemia and leg swelling are connected. By treating anemia, people can lower their risk of swelling in the legs. This improves their overall health and well-being.
Anemia can start a chain of responses that may cause fluid retention. It’s important to understand how anemia and swelling are connected, mainly in the legs and feet.
Anemia lowers blood viscosity because there are fewer red blood cells. This makes blood flow more and increases shear stress on blood vessel walls. The body might try to fix this by changing how it handles blood volume or pressure.
The lower viscosity also makes it harder to keep blood pressure and flow right. The heart has to work harder because of the lack of red blood cells. This can change cardiac output.
When anemia lasts a long time, the body tries to keep tissues oxygenated. It does this by making the heart pump more and by changing where blood goes. These changes help, but can also cause fluid to stay in the body.
The kidneys are key in managing fluid balance by controlling sodium and water. In anemia, they might not work properly, leading to more fluid retention.
Neurohormonal pathways are key in how the body reacts to anemia. The RAAS gets activated, which means more aldosterone. This hormone helps keep sodium and water in the body, leading to more fluid retention and swelling.
The sympathetic nervous system also gets involved. It can cause blood vessels to narrow and make RAAS work even harder. This makes fluid retention worse.
Knowing how anemia leads to fluid retention and swelling is important. It helps us understand the complex ways anemia, body responses, and hormones work together. This knowledge is key to treating edema in anemic patients.
It’s important to understand how anemia affects the body, like causing swollen feet and ankles. Anemia makes the body change how it handles blood flow and pressure.
Anemic patients often have their heart pump more blood. This is because their blood doesn’t carry as much oxygen. Increased cardiac output helps tissues get enough oxygen. But it can also change blood flow and pressure.
Anemia also makes blood flow easier. With fewer red blood cells, blood is less thick. This means blood can flow more freely. But it can also cause swelling in the feet and ankles.
Blood pressure can change in anemic patients. Some might have hypotension, while others might have normal or high blood pressure. Knowing these changes helps manage symptoms.
| Hemodynamic Parameter | Change in Anemia | Clinical Implication |
| Cardiac Output | Increased | Compensatory mechanism for reduced oxygen-carrying capacity |
| Vascular Resistance | Reduced | Contributes to edema due to increased blood flow to the lower extremities |
| Blood Pressure | Variable | Can be hypotensive, normotensive, or hypertensive depending on compensatory mechanisms |
Iron deficiency is a common nutritional disorder. It can cause swelling in the legs. This happens when the body doesn’t have enough iron to make hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
Iron deficiency anemia comes from not getting enough iron or not absorbing it well. It can also be caused by chronic blood loss, pregnancy, or certain diseases. When iron is low, the body can’t transport oxygen well, leading to changes in the body.
Iron deficiency anemia makes blood less thick. This means blood flows more easily and can leak into tissues. This leakage causes swelling or edema.
Iron deficiency leads to edema in several ways. First, it reduces oxygen to tissues, making blood vessels leaky. This allows fluid to move into the spaces between cells. Second, the body tries to make up for less oxygen by pumping more blood. This can cause fluid to stay in the body, leading to swelling.
Iron is also key for healthy blood vessels and the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system helps remove excess fluid. Without enough iron, these systems don’t work right, making edema worse.
Many studies have looked at how iron deficiency affects swelling. They found that iron supplements can help reduce swelling in some people. For example, a study in the Journal of Clinical Anesthesia showed iron therapy helped patients with restless legs syndrome.
Another study found that people with iron deficiency anemia were more likely to have swelling in their legs and feet. This shows how important it is to treat iron deficiency to prevent swelling.
Anemia is when you don’t have enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. It comes in different types, some causing swelling in the feet and ankles. Knowing about these types helps manage symptoms and treat the root cause.
Iron deficiency anemia is very common and can cause swelling. Without enough iron, your body can’t make enough hemoglobin. This means less oxygen gets to your tissues, leading to fluid buildup and swelling, mainly in your legs. Iron supplements are often needed to fix both the anemia and swelling.
A study in a medical journal found that iron deficiency anemia is linked to swelling. It shows how important iron is for keeping blood vessels healthy.
“Iron is key for blood vessel health. Without it, blood vessels can leak, causing swelling.”
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) happens when your immune system attacks your red blood cells. This leads to their destruction. Swelling can occur as your body tries to compensate and possibly due to heart failure. Treating AIHA includes immunosuppressive drugs and sometimes blood transfusions.
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder affecting hemoglobin production. It makes red blood cells sickle-shaped. This can block small blood vessels, causing swelling in your extremities. Managing sickle cell anemia includes pain relief, staying hydrated, and sometimes blood transfusions.
Pernicious anemia is caused by a lack of vitamin B12, often due to poor absorption. It’s less directly linked to swelling than iron deficiency anemia, but it can cause serious health issues. These include neurological problems and fatigue. Treatment involves vitamin B12 injections to fix the absorption problem.
In summary, different anemias can cause swollen feet and ankles in various ways. Knowing the specific type and its effects is key to managing and treating it effectively.
Anemia can cause swelling in the feet and ankles. It also brings other symptoms. Knowing these signs is key to diagnosing and treating anemia.
Swelling in the feet, ankles, and legs is common with anemia. This swelling is usually the same on both sides. The skin might look pale or even blue because of the anemia.
People with anemia may also feel tired, weak, and short of breath. They might get dizzy, have cold hands and feet, or have headaches. These symptoms happen because anemia makes it hard for tissues and organs to get enough oxygen.
Swelling can be a sign of serious anemia. If you also feel very tired, have chest pain, or can’t breathe well, get help right away. Severe anemia can cause serious health problems if not treated quickly.
| Symptom | Description | Severity Indicator |
| Swelling in Feet and Ankles | Bilateral swelling, often accompanied by skin pallor | Mild to Severe |
| Fatigue | Persistent feeling of tiredness or weakness | Mild to Severe |
| Shortness of Breath | Difficulty breathing or feeling winded even at rest | Moderate to Severe |
Knowing these symptoms and what they mean can help you get the right medical care. This can prevent serious problems from anemia.
Swollen ankles can be a sign of many health problems. Finding the cause is key. Anemia might be one reason, but other issues can look similar.
Many health issues can make your legs and ankles swell. These look like anemia symptoms. Some of these include:
These conditions can make your legs swell like anemia does. So, a detailed check-up is very important.
To figure out if anemia is causing swelling, doctors look for certain signs. These include:
Doctors use these tests together to find out if anemia is causing your swollen ankles.
To find out if anemia is causing swollen ankles, doctors use many tests. They look at lab tests, imaging, and physical exams. This helps them figure out what’s going on.
Blood tests are key to spotting anemia. They check for things like:
These tests tell doctors a lot about anemia. They help decide how to treat it.
Imaging tests also play a big role. They help find the cause of anemia or related problems. Some common tests are:
A detailed physical exam is also important. It checks how bad the swelling is and looks for signs of anemia. These signs include:
Doctors use these signs to decide on more tests and treatment.
Managing anemia-related swelling legs needs a full plan. It must tackle the anemia and the fluid buildup. This approach is key to easing symptoms and improving life for those with anemia and swollen ankles.
The first step is to fix the anemia’s root cause. This might mean changing diets, taking supplements, or undergoing other treatments. For example, iron deficiency anemia gets treated with iron pills, while vitamin deficiency anemia might need B12 shots.
Learn more about anemia and its causes at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
| Treatment Approach | Description | Example |
| Dietary Changes | Increasing intake of specific nutrients | Consuming iron-rich foods for iron deficiency anemia |
| Supplementation | Taking supplements to correct deficiencies | Iron supplements for iron deficiency anemia |
| Medical Treatments | Treating underlying conditions causing anemia | Vitamin B12 injections for pernicious anemia |
It’s important to manage fluid retention to reduce swelling. This can be done through lifestyle changes like elevating legs, cutting down on salt, and staying active. Sometimes, diuretics are needed to get rid of extra fluid.
There are many medicines for treating anemia and swelling. For example, ESAs help make more red blood cells in some anemias. Also, treatments like iron pills or B12 shots are key in managing anemia.
Knowing the treatment options for anemia that cause swollen legs is vital. By tackling the anemia and fluid buildup, people can see big improvements in swelling and other symptoms.
To prevent anemia and swelling, we need to make several changes. These include eating right, staying active, and making lifestyle adjustments. By doing these things, we can lower our chances of getting anemia and swelling in our feet.
Eating a balanced diet is key to avoiding anemia. Foods high in iron, vitamin B12, and folate are very important. Iron is found in red meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and fortified cereals. Vitamin B12 is in animal products, and folate is in leafy greens, legumes, and citrus fruits.
| Nutrient | Food Sources | Importance |
| Iron | Red meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, fortified cereals | Essential for hemoglobin production |
| Vitamin B12 | Animal products, fortified plant-based milk | Critical for red blood cell formation |
| Folate | Leafy greens, legumes, citrus fruits | Necessary for preventing megaloblastic anemia |
Staying active helps improve blood flow and lowers swelling risk. Walking, cycling, or swimming are good choices. It’s important to avoid too much strain and talk to a doctor before starting new exercises if you have health issues.
Putting your legs up helps reduce swelling by improving blood flow. Wearing compression stockings or sleeves also helps. These methods are great for people who are on their feet a lot or have jobs that involve standing or sitting for long periods.
Keeping an eye on anemia symptoms and acting early is vital. Regular blood tests can check for anemia and its causes. Catching it early means we can treat it quickly, avoiding serious problems and improving our quality of life.
By making these changes part of our daily lives, we can lower our risk of anemia and swelling. It’s about eating right, staying active, and watching for signs of anemia. This proactive approach can make a big difference.
Managing anemia well is key to avoiding swollen feet and leg edema. We’ve looked into how anemia and edema are connected. We’ve seen how different types of anemia can cause fluid buildup and swelling, mainly in the legs.
It’s important to catch anemia early and treat it. This helps prevent its effects, like swollen feet. By fixing the root cause of anemia, people can lower their chance of getting edema. This means making healthy food choices, staying active, and sometimes taking medicine.
Knowing how anemia and edema are linked helps people manage their health better. They should watch for swelling signs and see a doctor if it gets worse. Handling anemia well not only boosts health but also makes life better by reducing swelling in the feet and legs.
Yes, anemia can cause swelling in the feet and ankles. This is due to fluid retention and changes in blood circulation.
Yes, low iron levels, like in iron deficiency anemia, can lead to swelling. This is because of decreased blood viscosity and other changes.
Iron deficiency anemia, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, sickle cell anemia, and pernicious anemia can cause swelling. This is in the feet and ankles.
Anemia can make the heart work harder. This can lead to heart failure and fluid retention, causing swelling.
Symptoms include swelling in the lower extremities. You may also feel tired, weak, and have trouble breathing.
Doctors use blood tests, lab evaluations, imaging studies, and physical exams. They look for the cause of swelling.
Treatment focuses on the underlying anemia. It also involves managing fluid retention and edema. Medications may be used too.
Yes, making dietary changes and staying active can help. Elevating and compressing the legs and monitoring can also prevent swelling.
Severe swelling with fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath is a sign of severe anemia. You should seek medical help right away.
Yes, heart failure, kidney disease, and liver disease can also cause swelling. It’s important to get a proper diagnosis.
Yes, anemia can cause leg swelling. This is due to fluid retention and changes in blood circulation.
Yes, anemia can contribute to peripheral edema. This is more common in the lower extremities due to fluid retention and other changes.
Yes, anemia can cause swollen ankles. This is due to fluid retention and changes in blood circulation.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!