Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik
Bursitis affects millions worldwide, causing significant discomfort and impairing daily activities. At our clinic, we’ve seen firsthand the impact of bursitis on our patients’ lives. An orthopedic doctor for bursitis plays a key role in diagnosing and treating this condition.
Our orthopedic doctors for bursitis use advanced techniques to manage inflammation and pain. They focus on restoring joint function and improving mobility. Our clinic integrates advanced medical technologies with compassionate care to develop personalized treatment plans for each patient.
Understanding the various treatment options available is key for effective bursitis management. Our approach ensures patients get the best care, from the first consultation to full recovery.
Knowing the causes and symptoms of bursitis is key to getting the right treatment. Bursitis happens when the bursae, fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed. These sacs cushion joints and reduce friction between bones and soft tissues.
Bursitis occurs when the bursae get inflamed. This can happen due to repetitive motion, direct trauma, or infection. The inflammation causes pain, swelling, and limited mobility in the joint.
Bursitis often affects the shoulders, hips, knees, and elbows. Each area has specific bursae that can get inflamed. This leads to different symptoms and challenges in diagnosing the condition.
| Location | Common Name | Symptoms |
| Shoulder | Subacromial Bursitis | Pain when moving the arm, swelling |
| Hip | Trochanteric Bursitis | Pain on the outer hip, tenderness |
| Knee | Prepatellar or Infrapatellar Bursitis | Swelling, pain when kneeling or jumping |
| Elbow | Olecranon Bursitis | Swelling at the back of the elbow, pain |
Some people are more likely to get bursitis due to certain risk factors. These include age, job, sports, and health conditions. Knowing these risk factors helps in preventing or catching bursitis early.
By understanding bursitis causes, common spots, and risk factors, we can better grasp this condition. This knowledge is vital for seeking the right medical care.
Bursitis can make everyday tasks painful and uncomfortable. Knowing when to see a doctor is key to managing and treating it. We’ll talk about the signs that mean you need medical help, how to tell if it’s bursitis, and why seeing an orthopedic specialist is a good idea.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should see an orthopedic doctor:
These signs might mean you have a more serious issue that needs a doctor’s check-up.
Bursitis can look like arthritis or tendinitis. An orthopedic specialist can tell the difference with a detailed check-up and tests.
| Condition | Common Symptoms | Diagnostic Approach |
| Bursitis | Pain, swelling, limited mobility | Physical examination, imaging tests |
| Arthritis | Joint pain, stiffness, swelling | Medical history, imaging, blood tests |
| Tendinitis | Pain, swelling, tenderness | Physical examination, ultrasound |
Seeing an orthopedic specialist for bursitis has many advantages. They have specialized knowledge and access to advanced treatments.
An orthopedic doctor can give a precise diagnosis and create a treatment plan just for you. They might use therapies not available from a general doctor.
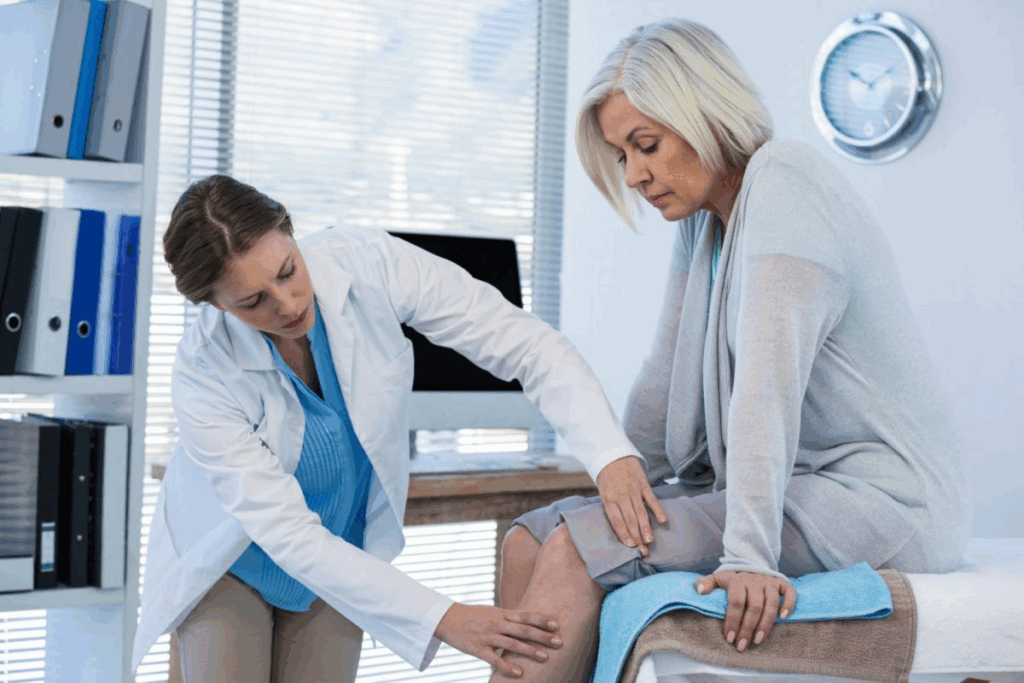

To treat bursitis, we start with a detailed diagnosis. This includes looking at your medical history, doing a physical exam, and sometimes using imaging studies. This method helps us find the cause of your symptoms and create a treatment plan just for you.
The first step is an initial consultation. We gather information about your symptoms. We want to know when they started, how bad they are, and what makes them better or worse. This helps us understand your condition and find possible causes.
A detailed physical exam is key to diagnosing bursitis. We check the affected area for signs of inflammation, tenderness, and swelling. We also check your range of motion and do specific tests to see if we can reproduce your symptoms. This helps confirm the diagnosis.
In our orthopedic assessment, we might use special tests to check the bursae and surrounding tissues. These tests help us tell if it’s bursitis or something else that’s causing your symptoms. This ensures we get the diagnosis right.
Experts say a detailed diagnostic process is vital for treating bursitis. This shows how important it is to thoroughly check and diagnose the condition.
By looking at your medical history, doing a physical exam, and sometimes using imaging studies, we can accurately diagnose bursitis. Then, we can suggest the best treatment options for you.
Diagnostic imaging is key in finding bursitis. It helps orthopedic doctors make the right treatment plans. We use different imaging methods to see if bursitis is present and to check for other possible causes of pain.
X-rays are often the first choice for checking bursitis. They’re great for finding bone problems like fractures. But, they might not show the bursa itself. Yet, X-rays help rule out other pain causes like osteoarthritis or fractures.
It’s important to know that X-rays are just the start. More tests might be needed for a full check-up.
MRI scans give a closer look at soft tissues, like the bursa. They’re great for seeing how bad the inflammation is and if tendons or ligaments are hurt. When we’re not sure or thinking about surgery, MRI scans are often recommended.
Ultrasound imaging is also useful for finding bursitis. It lets us see the bursa and nearby tissues live. Ultrasound can also help with treatments like injections. It’s popular because it’s safe and doesn’t use radiation.
As orthopedic doctors, we pick the best imaging for each patient. This way, we can make sure we’re treating the right problem. And we can create a treatment plan that really works for each person.
“Choosing the right imaging for bursitis is very important. It helps us give the best treatment and improve how patients feel.”
Joint fluid aspiration is a procedure that helps patients with bursitis. It removes fluid from the joint to ease pressure and reduce swelling.
The patient is placed in a way that makes it easy to reach the joint. The area is cleaned and a local anesthetic might be used to lessen pain. A sterile needle and syringe are used to take out the fluid from the bursa.
The whole process is quick and done in an outpatient setting. You might feel some pressure or discomfort, but it’s short-lived.
The fluid taken out is analyzed to find out what’s causing bursitis. This test can show if there’s an infection, crystal buildup, or other issues in the joint.
Looking at the fluid helps doctors see if there are bacteria, crystals, or other problems. This helps them decide on the best treatment.
Removing extra fluid from the bursa can greatly reduce swelling and pressure. This makes the joint less painful and more mobile.
It also helps the bursa heal by creating a better environment for recovery.
| Benefits | Description |
| Diagnostic Clarity | Fluid analysis helps in identifying the cause of bursitis, guiding treatment. |
| Therapeutic Relief | Removing excess fluid reduces inflammation and relieves pressure. |
| Improved Mobility | Reducing inflammation and pressure improves joint mobility. |
Orthopedic doctors often start with non-surgical treatments for bursitis. They help patients choose the best options. Knowing these methods helps patients understand their treatment plans better.
Resting the affected area is a key first step. Changing how you do things can also help. This might mean taking breaks or avoiding certain activities.
Ice and heat therapy are simple yet effective methods for managing bursitis symptoms. Ice reduces inflammation, while heat relaxes muscles and improves blood flow.
Compression and elevation are additional techniques used to manage bursitis. Compression reduces swelling, while elevation aids in reducing inflammation by improving venous return.
Using compression bandages or sleeves and elevating the affected limb above the level of the heart can significantly alleviate symptoms.
Protecting the affected joint is key in managing bursitis. This involves using protective equipment and adopting techniques that minimize strain on the joints.
Medication is key in managing bursitis symptoms. It helps improve life quality for those affected. The goal is to reduce inflammation, ease pain, and help the joint or area function better.
Oral anti-inflammatory meds are often the first choice for bursitis. Ibuprofen or naproxen reduce inflammation and pain. It’s important to follow the dosage and talk to an orthopedic specialist to avoid side effects.
Topical treatments, like creams, gels, or patches, are applied directly to the skin. They offer localized relief from pain and inflammation. These are great for those who can’t take oral meds or have sensitive stomachs.
Managing pain is vital in treating bursitis. Anti-inflammatory meds are used, along with acetaminophen or stronger pain relievers when needed. Orthopedic specialists create a personalized pain management plan for each patient.
| Medication Type | Primary Use | Examples |
| Oral Anti-inflammatory | Reduce inflammation and pain | Ibuprofen, Naproxen |
| Topical Treatments | Localized pain and inflammation relief | Creams, Gels, Patches |
| Pain Management | Manage pain | Acetaminophen, Stronger pain relievers |
Corticosteroid injections are a common treatment for bursitis. Orthopedic specialists use them to reduce inflammation and ease pain. This helps patients with bursitis feel better.
Corticosteroid injections put anti-inflammatory medicine right into the bursa. This helps to lessen swelling and pain. It also helps the joint move better.
Benefits of Corticosteroid Injections:
Orthopedic specialists use ultrasound to guide injections. This method ensures the medicine goes exactly where it’s needed. It makes the treatment more effective.
Patients usually see a big drop in pain and swelling after the injections. But, like any treatment, there can be side effects. These include temporary pain, skin thinning, and very rarely, infection.
| Expected Results | Potential Side Effects |
| Reduced inflammation | Temporary pain at injection site |
| Effective pain relief | Skin thinning |
| Improved joint mobility | Infection (rare) |
How often you get injections depends on how bad your bursitis is and how well you respond to treatment. Usually, you can get injections every few months. But, there’s a limit to how many you can have to avoid long-term side effects.
It’s important to stick to your treatment plan and talk to your orthopedic specialist about any worries.
Orthopedic doctors often recommend physical therapy for bursitis treatment. It’s a key part of getting better and moving normally again. A good physical therapy plan can really help those with bursitis.
Mobility and stretching exercises are key in physical therapy for bursitis. They help improve joint movement and reduce stiffness. Gentle stretching keeps or improves range of motion, lowering irritation risk.
We suggest doing these exercises often as part of your recovery.
Strengthening exercises are also vital in physical therapy for bursitis. They make the muscles around the joint stronger, providing more support. We make these programs fit each patient’s needs, ensuring they’re safe and effective.
Manual therapy techniques are another important part of physical therapy for bursitis. These include massage and joint mobilization. A skilled therapist uses these to help heal and reduce pain.
Manual therapy breaks up adhesions, improves blood flow, and aids in recovery.
Progressing in rehabilitation is key to a successful physical therapy program for bursitis. We watch how you’re doing and adjust your plan as needed. Our goal is to help you get back to your usual activities, improving function and preventing future problems.
Physical therapy is essential in managing bursitis, helping patients recover and regain function. We’re dedicated to providing care that meets each patient’s unique needs.
Surgery is an option when bursitis doesn’t get better with other treatments. It can help ease pain and improve joint function for some people.
If other treatments like medicine and physical therapy don’t work, surgery might be needed. It’s also considered for those with recurring bursitis, a lot of pain, or trouble moving.
Key factors that may lead to surgical consideration include:
A bursectomy removes the inflamed bursa. It can be done with open surgery or less invasive methods. The choice depends on the bursa’s size and location, and the patient’s health.
The bursectomy procedure typically involves:
Arthroscopic bursectomy is a minimally invasive method. It has smaller incisions, less damage, and quicker recovery. These surgeries are often done on an outpatient basis.
Advantages of minimally invasive surgery include:
After surgery, patients need to rest and follow a rehabilitation program. This helps regain strength and mobility. Managing pain is also important.
Post-surgical recovery may involve:
Understanding surgical options for bursitis helps patients make informed choices. We work with patients to find the best surgical approach for their needs.
It’s important to know about the different types of bursitis to manage and treat them well. Bursitis can happen in many joints, each with its own set of problems. We’ll look at the most common types, like shoulder, hip, knee, and elbow bursitis.
Shoulder bursitis, or subacromial bursitis, affects the bursa between the acromion and the rotator cuff tendons. It causes pain and tenderness, mainly when you move your arm up. Treatment includes physical therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs, and sometimes corticosteroid injections.
Hip bursitis, or trochanteric bursitis, is inflammation of the bursa near the greater trochanter of the femur. It leads to pain on the outer hip, getting worse with activities like running or cycling. Treatment includes rest, ice, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Knee bursitis can be prepatellar (housemaid’s knee) or infrapatellar (clergyman’s knee), affecting the bursae around the kneecap. Prepatellar bursitis causes swelling and pain in front of the knee, often from kneeling. Infrapatellar bursitis affects the area below the kneecap. Treatment involves protecting the knee, using protective gear, and sometimes aspiration of the bursa.
Elbow bursitis, or olecranon bursitis, involves swelling and inflammation of the bursa at the back of the elbow. It can result from direct trauma or repetitive motion. Symptoms include swelling and pain when bending the elbow. Management includes protecting the elbow, using compression, and sometimes aspiration or corticosteroid injections.
In conclusion, managing different types of bursitis needs a tailored approach. This depends on the joint involved and the symptoms. By understanding each type, we can offer more effective treatment and relief.
Orthopedic specialists say preventing bursitis needs a mix of lifestyle changes and protective steps. Knowing and using these methods can lower your chance of getting bursitis. It also helps keep your joints healthy.
Making ergonomic changes is a big part of prevention. It means adjusting how you do things to avoid putting too much strain on your joints. For example, setting up your workspace to keep your body straight can help prevent bursitis in your shoulders and neck.
Small changes, like using an ergonomic chair or adjusting your computer monitor, can help a lot. It’s important to check your work and home spaces for ways to make them more ergonomic.
Exercise is good for your joints, but doing it right is key to avoiding bursitis. Orthopedic experts say it’s important to learn and use the right exercise form. This means warming up, using the right gear, and not pushing too hard.
Wearing protective gear and padding is also vital. For people who are at risk, like athletes or those who kneel a lot, it helps protect their joints. This can include knee pads, elbow pads, or other gear for specific activities.
It’s important to pick the right protective gear for the job. Make sure to use it correctly to get the most benefit.
Keeping your joints healthy over time is key to preventing bursitis. This means staying at a healthy weight, drinking plenty of water, and exercising regularly but correctly. Eating a diet full of nutrients that support your joints, like omega-3s and antioxidants, is also good.
“Maintaining healthy joints through a balanced lifestyle is key to preventing bursitis and ensuring long-term mobility and comfort.”
By adding these prevention strategies to your daily life, you can lower your risk of bursitis. This helps you keep your joints healthy and enjoy better mobility and comfort.
Orthopedic care is key in managing bursitis and getting joints to work right again. Seeing an orthopedic doctor for bursitis helps patients get treatments that fit their needs.
Managing bursitis well means using a mix of treatments. This includes rest, ice, and physical therapy. It also includes advanced treatments like corticosteroid injections and sometimes surgery. Orthopedic care offers many ways to ease symptoms, help healing, and stop future problems.
When you see an orthopedic specialist, you learn more about your condition. You get a treatment plan made just for you. This helps you get better and keeps your joints healthy for a long time.
Bursitis is when the bursae, fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed. These sacs cushion joints and reduce friction. It happens due to repetitive motion, direct trauma, or infection. This leads to pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
Doctors diagnose bursitis by looking at your medical history and doing a physical exam. They might use X-rays, MRI scans, or ultrasound imaging. They might also take fluid from the bursa for analysis.
Bursitis often affects the shoulder, hip, knee, and elbow. Each area has specific bursae that can get inflamed. This is due to repetitive motion or direct trauma.
Non-surgical treatments include rest, ice and heat, compression, and elevation. You can also protect your joints. Oral anti-inflammatory drugs and topical treatments are used too. Corticosteroid injections and physical therapy are also options. Sometimes, surgery is needed.
Corticosteroid injections reduce inflammation by putting steroids directly into the bursa. This helps a lot with pain and swelling. Using ultrasound to guide the injection makes it more accurate.
Physical therapy is key in managing bursitis. It improves joint mobility and strengthens muscles. It includes exercises and manual therapy tailored to your bursitis type.
Yes, you can prevent or reduce the risk of bursitis. Use ergonomic modifications, proper exercise techniques, and protective equipment. Keeping your joints healthy long-term helps too.
Surgery is considered when other treatments don’t work. It’s needed when bursitis affects your daily life. Surgery options include removing the inflamed bursa.
Seeing an orthopedic specialist offers specialized care. They have advanced treatment options for your bursitis. They provide complete care, from diagnosis to rehabilitation, improving your outcome.
To manage flare-ups, use ice or heat, compression, and elevation. Modify activities to avoid strain. Stick to your medication and physical therapy to control symptoms.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!