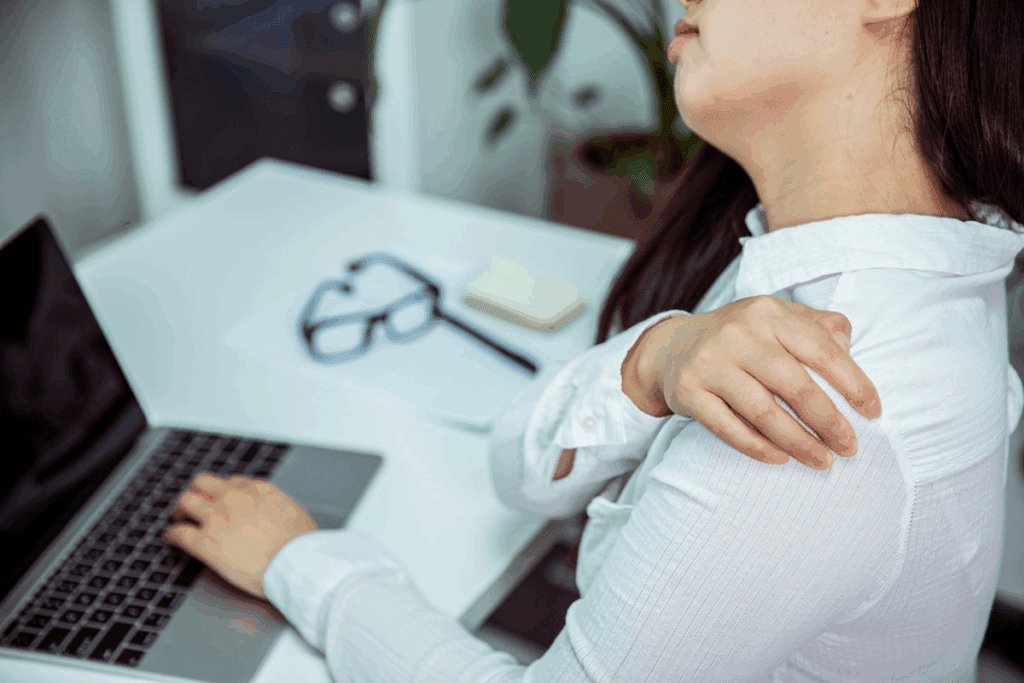
Did you know that nearly 1 in 5 people will experience shoulder pain at some point in their lives? Many are misdiagnosed with shoulder bursitis. But, several other conditions can cause similar symptoms, making it hard to get a correct diagnosis.
Patients often find out their shoulder pain isn’t from bursitis. It could be from rotator cuff injury or tendonitis. Knowing about shoulder pain complexities is key for the right treatment.Find out which Conditions Mimicking Shoulder Bursitis, including tendonitis and arthritis, and how to tell them apart.
Looking into the different shoulder-related injuries or conditions that can look like shoulder bursitis shows us. A precise diagnosis is vital for the right care.
Key Takeaways
- Shoulder bursitis is often misdiagnosed, with other conditions presenting similar symptoms.
- Rotator cuff injury and tendonitis are common conditions that can mimic shoulder bursitis.
- An accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of shoulder pain.
- Understanding the complexities of shoulder pain is essential for proper care.
- Several shoulder-related injuries or conditions can cause pain similar to shoulder bursitis.
Understanding shoulder bursitis is key to managing and treating it. It’s a condition where the bursae, fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed. These sacs help reduce friction between bones, tendons, and muscles in the shoulder joint.
What is a Bursa and Its Function
A bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac. It reduces friction between moving parts in the body. In the shoulder, bursae act as cushions, allowing for smooth movement.
The main job of a bursa is to minimize friction. This prevents irritation between moving parts.
Common Types of Shoulder Bursitis
There are several types of shoulder bursitis. The most common are:
- Subacromial bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa between the acromion and the rotator cuff tendons.
- Subdeltoid bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa between the deltoid muscle and the rotator cuff tendons.
Typical Symptoms of Shoulder Bursitis
The symptoms of shoulder bursitis vary but usually include:
- Pain or tenderness in the shoulder, specially when moving the arm.
- Swelling or redness around the affected area.
- Limited mobility or stiffness in the shoulder joint.
These symptoms can really affect daily activities. It’s important to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Why Accurate Diagnosis Matters
Getting the right diagnosis is key to treating shoulder pain well. Shoulder pain can be tricky to figure out because of the joint’s complexity and many possible causes. We need to look at all options to make sure we get it right.
Consequences of Misdiagnosis
Misdiagnosis can significantly impact a person’s physical health, mental well-being, and overall quality of life. We must be thorough and careful when diagnosing shoulder pain to avoid these issues.
Importance of Differential Diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of shoulder pain.
An accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of shoulder pain.
“A correct diagnosis is the foundation upon which successful treatment is built.”
Medical Expert
Conditions Mimicking Shoulder Bursitis: An Overview

Common Misdiagnoses
Many conditions are often mistaken for shoulder bursitis. For example, rotator cuff injuries and tendonitis can cause similar pain and stiffness. Rotator cuff injuries damage the muscles and tendons around the shoulder. Tendonitis is inflammation of the tendons.
Similar Symptom Patterns
Many shoulder issues show similar signs like pain, swelling, and less movement. For example, shoulder impingement syndrome and adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder) can cause pain and stiffness. This makes it hard to tell them apart from bursitis without detailed tests and exams.
- Pain and swelling
- Reduced range of motion
Risk Factors for Misdiagnosis
Some factors make it more likely to misdiagnose shoulder bursitis. These include having multiple shoulder problems, not using the right imaging tests, and not doing a full exam. Also, a patient’s age and how active they are can affect how symptoms show up, making diagnosis harder.
Knowing about common misdiagnoses, similar symptoms, and risk factors helps doctors get better at diagnosing. This leads to more effective treatments for shoulder pain.
Rotator Cuff Injuries vs. Shoulder Bursitis
It’s important to know the difference between rotator cuff injuries and shoulder bursitis. Both can hurt the shoulder and cause pain. But, they have different causes and treatments.
Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
The inflammation can be sudden or long-term. Sudden inflammation comes from a quick injury. Long-term inflammation happens from doing the same thing too much.
Rotator Cuff Tears
A rotator cuff tear is when one or more tendons are torn. This can happen from a sudden injury or from doing the same thing too much over time. Common symptoms include a lot of pain, weakness, and not being able to move the arm as much.
There are two types of tears: partial-thickness and full-thickness. Partial-thickness means the tendon is not completely torn. Full-thickness means it is completely torn.
To tell the difference between rotator cuff injuries and bursitis, doctors do a thorough check-up and tests. The main differences are:
- Location of Pain: Rotator cuff injuries hurt the outside or front of the shoulder. Bursitis pain is more on the surface and over the bursa.
- Nature of Pain: Tendinitis and tears hurt more when you move or do certain activities. Bursitis pain is often constant and gets worse when you press on the bursa.
- Weakness and Limited Mobility: Tears make the arm weak and hard to move. Bursitis doesn’t usually cause this.
Tests like MRI or ultrasound can show what’s wrong by looking at the tendons and bursae.
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
Shoulder impingement syndrome happens when the rotator cuff tendons get squished or irritated. This happens as they move through the shoulder joint. It’s often mistaken for bursitis.
Mechanism of Impingement
The cause of shoulder impingement syndrome is the narrowing of space between the acromion and the humeral head. This leads to the compression of the rotator cuff tendons.
Many things can cause this compression. These include bone spurs, inflammation, or repetitive motion. Knowing these causes is key to diagnosing and treating the condition right.
Overlapping Symptoms with Bursitis
Shoulder impingement syndrome and bursitis have similar symptoms. These include pain when moving, pain at night, and less range of motion. These similarities make it hard to tell them apart.
Key Differentiating Factors
There are a few ways to tell shoulder impingement syndrome apart from bursitis. These include:
- The specific location of pain
- The presence of pain during specific movements
- Imaging findings from X-rays or MRIs
| Characteristics | Shoulder Impingement Syndrome | Bursitis |
| Primary Cause | Compression of rotator cuff tendons | Inflammation of the bursa |
| Common Symptoms | Pain during movement, pain at night | Pain, swelling, reduced mobility |
| Diagnostic Clues | Specific movements exacerbate pain | Tenderness over the bursa |
Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
Adhesive capsulitis, also known as frozen shoulder, causes a lot of shoulder stiffness and pain. We will look at its stages, how it’s different from shoulder bursitis, and the risk factors.
Stages of Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder goes through three stages: freezing, frozen, and thawing. In the freezing stage, pain and stiffness get worse. The frozen stage brings a big drop in shoulder movement, but pain starts to lessen. The thawing stage sees movement slowly coming back.
- Primary Difference: Frozen shoulder hurts the joint capsule, leading to stiffness and reduced mobility.
- Symptom Variation: The pain in frozen shoulder is often more diffuse compared to the localized pain of bursitis.
Risk Factors and Associations
Some things make you more likely to get frozen shoulder. These include:
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are more at risk.
- Immobilization: Not moving your shoulder for a long time can cause it.
- Other Medical Conditions: Conditions like thyroid disorders, heart disease, and Parkinson’s disease also raise the risk.
Knowing these risk factors helps in spotting frozen shoulder early. This makes it easier to treat it, differentiating it from other shoulder problems like bursitis.
Labral Tears and SLAP Lesions
Understanding labral tears and SLAP lesions is key to treating shoulder pain. These injuries harm the labrum, a cartilage around the shoulder socket. They can cause a lot of pain and limit movement.
Anatomy of the Labrum
The labrum is a cartilage ring around the shoulder socket. It helps keep the joint stable and allows for smooth movement. It’s attached to the glenoid rim and deepens the socket, improving the fit of the humeral head.
Types of Labral Injuries
Labral injuries vary in type and severity. The most common include:
- Labral Tears: These are tears in the labrum caused by trauma, overuse, or wear and tear.
- SLAP Lesions: SLAP stands for Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior. These are specific tears at the labrum’s top, where the biceps tendon attaches.
Distinctive Clinical Features
Labral tears and SLAP lesions have unique symptoms. These can help doctors diagnose them. Common symptoms are:
- Pain when lifting the arm overhead or during throwing
- A clicking or catching feeling in the shoulder
- Less strength and range of motion
- Pain from lifting or rotating the arm
To accurately diagnose labral tears and SLAP lesions, doctors need a thorough evaluation. This includes a detailed medical history, physical exam, and imaging like MRI.
Shoulder Arthritis Conditions
The shoulder joint can get arthritis in different ways, like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis. These can make a lot of pain and stiffness. This can really affect how you live your day-to-day life.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is when the cartilage in the shoulder joint wears down. This makes bones rub against each other, causing pain and less movement. Symptoms include pain when moving, stiffness, and a grinding feeling in the joint.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is when the body’s immune system attacks the shoulder joint. This leads to pain, swelling, and can damage the joint badly over time. Treatment often includes medicines to reduce inflammation and slow the disease.
Post-traumatic Arthritis
Post-traumatic arthritis happens after a shoulder injury, like a fracture or dislocation. It causes degenerative changes in the joint over time. It’s similar to osteoarthritis but is caused by the injury.
Arthritis and bursitis can both cause shoulder pain, but they are different. Arthritis causes joint pain and stiffness, while bursitis is inflammation of the bursae, with more localized pain. Doctors use imaging and a detailed check-up to tell them apart.
Doctors say, “Knowing why your shoulder hurts is key to fixing it.” Getting the right diagnosis helps doctors treat the right problem. This makes patients feel better.
Biceps Tendon Disorders
An accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of shoulder pain.
Tendinitis of the Biceps Tendon
Doing things that make you lift or move your arm up can make it worse. It’s important to get it checked out to know for sure it’s tendinitis.
Rupture of the Biceps Tendon
A biceps tendon rupture means the tendon tears. This can happen suddenly or slowly over time. You might see a “Popeye” bulge in your arm.
Signs of a rupture include sharp pain and a noticeable bulge. Knowing the difference between a rupture and other problems is key for treatment.
Distinguishing Features from Bursitis
Biceps tendon issues and bursitis can both hurt your shoulder. But they are different. Bursitis is when the bursae, which are fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed.
| Condition | Primary Symptoms | Common Causes |
| Biceps Tendinitis | Pain in the front of the shoulder, tenderness | Repetitive motion, overuse |
| Biceps Tendon Rupture | Sudden, severe pain, possible deformity | Severe injury, wear and tear |
| Bursitis | Pain, swelling, limited mobility | Repetitive motion, direct blow |
To figure out what’s wrong, doctors look at your symptoms, medical history, and might use imaging. Knowing the difference is important for the right treatment.
Referred Pain Sources
Referred pain from different areas can make diagnosing shoulder pain tricky. It’s important to remember that shoulder pain might not always come from the shoulder. It could be coming from somewhere else.
Cervical Radiculopathy
Cervical radiculopathy happens when a nerve in the neck gets inflamed or damaged. This can cause pain in the shoulder. It’s often due to a herniated disk or bone spur in the neck.
Symptoms include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arm or shoulder. Accurate diagnosis is key to tell it apart from shoulder bursitis.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is when nerves or blood vessels get compressed between the collarbone and first rib. This can lead to shoulder and arm pain. It might be caused by physical trauma, anatomical issues, or repetitive motion.
Physical therapy is often a big part of treating TOS.
Cardiac Referred Pain
Cardiac conditions can sometimes cause pain in the shoulder. This is common in heart attacks, where pain spreads to the left shoulder or both. While rare, it’s a serious condition that needs quick medical attention.
Gallbladder Disease
Gallbladder disease, like cholecystitis, can also cause pain in the right shoulder. This happens because the gallbladder and shoulder share nerve roots. People with gallbladder disease might have severe abdominal pain, nausea, and fever, along with shoulder pain.
Traumatic Shoulder Conditions
Traumatic shoulder conditions are tricky to diagnose because they can look like bursitis. Injuries to the shoulder can lead to various conditions that need quick diagnosis and treatment.
Shoulder Fractures
Shoulder Dislocations and Instability
Shoulder dislocations happen when the humeral head slips out of the glenoid cavity. This can cause instability and make dislocations happen again. Recurrent instability really affects a person’s life, so it’s important to diagnose and treat it right. We’ll look at the different kinds of instability and how to treat them.
Acromioclavicular Joint Injuries
It’s important for healthcare providers to understand traumatic shoulder conditions well. This helps them make the right diagnosis and treatment plans. By knowing the specific traits of these conditions, we can help patients get better faster and avoid more problems.
Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder
Understanding calcific tendinitis is key to treating shoulder pain. It’s a condition where calcium builds up in the tendons of the shoulder. This can cause a lot of pain and feel like other shoulder problems, like bursitis.
Formation of Calcium Deposits
The exact reason for calcific tendinitis isn’t known. But it’s thought to be due to tendon wear and tear and how the body heals. Calcium deposits in the tendons, like in the rotator cuff, cause inflammation and pain.
“The formation of calcium deposits is a complex process that may be influenced by various factors, including age, tendon health, and metabolic conditions,” as noted in medical literature.
Acute vs. Chronic Presentations
Calcific tendinitis can be either acute or chronic. The acute form comes on suddenly with severe pain and inflammation. The chronic form starts more slowly with pain and stiffness.
- Acute calcific tendinitis needs quick medical help because of the intense pain.
- Chronic calcific tendinitis might need ongoing care, like physical therapy and pain management.
Comparison with Bursitis Symptoms
Telling these conditions apart is important for the right treatment. A detailed diagnosis, including scans, is often needed to find the cause of shoulder pain.
Diagnostic Approaches for Shoulder Pain
Identifying the cause of shoulder pain requires a detailed approach. This involves clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and lab tests.
Clinical Examination Techniques
Our first step is a thorough clinical exam. We check the shoulder’s range of motion, strength, and tenderness. Specific maneuvers like the Neer test help pinpoint pain causes.
We also look at the patient’s medical history and perform a physical assessment. This helps us find any underlying conditions that might be causing the pain.
Imaging Modalities
Imaging studies are key to confirming the diagnosis. We use imaging modalities like X-rays, ultrasound, and MRI to see the shoulder’s structures.
- X-rays show bone issues, like fractures or osteoarthritis.
- Ultrasound checks for soft tissue injuries, like rotator cuff tears.
- MRI gives detailed images of bone and soft tissue, helping diagnose labral tears or tendonitis.
Laboratory Tests
In some cases, lab tests are needed to rule out underlying conditions. We might test for inflammatory markers or diagnose rheumatoid arthritis through blood tests.
By combining clinical exam results, imaging studies, and lab tests, we can accurately find the cause of shoulder pain. Then, we can create a treatment plan.
When to Seek Medical Help
It’s important to know when you need to see a doctor for shoulder pain. Knowing the signs can help your treatment work better and improve your health.
Red Flag Symptoms
Some symptoms mean you should see a doctor right away. These include:
- Severe shoulder pain that doesn’t get better with rest
- Swelling, bruising, or deformity around the shoulder
- Can’t move the shoulder or arm
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arm or hand
- Shoulder pain with chest pain or trouble breathing
Choosing the Right Specialist
Finding the right doctor for shoulder problems is key. You might need to see:
- An orthopedic surgeon for surgery
- A rheumatologist for inflammatory or autoimmune issues
- A physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R) specialist for non-surgical treatments
Your primary care doctor can help find the right specialist for you.
What to Expect During Evaluation
At your first visit, the specialist will:
- Ask about your medical history and symptoms
- Do a detailed physical check of your shoulder
- Order tests like X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound
- Talk about possible diagnoses and treatments with you
Being ready with your symptoms and medical history can make the visit smoother.
Knowing when to get medical help and what to expect can help you deal with shoulder pain better. It can lead to a better outcome for you.
Conclusion
Figuring out what’s causing shoulder pain is key. This helps doctors give the right treatment. Knowing the signs of shoulder bursitis and other similar issues helps doctors make better plans for treatment.
By focusing on finding the right diagnosis, we can help patients more. This means better care for those with shoulder bursitis and similar issues.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of shoulder bursitis?
Shoulder bursitis symptoms include pain, swelling, and trouble moving the shoulder.
Doctors use a mix of clinical exams, imaging, and lab tests to diagnose shoulder bursitis. This helps rule out other conditions that might cause similar symptoms.
What are the consequences of misdiagnosing shoulder bursitis?
If shoulder bursitis is misdiagnosed, treatment won’t be right. This can make recovery take longer and increase the risk of complications.
What are some conditions that can be misdiagnosed as shoulder bursitis?
Rotator cuff injuries, tendonitis, shoulder impingement syndrome, labral tears, and arthritis can be mistaken for shoulder bursitis. This is because they share similar symptoms.
How can rotator cuff injuries be differentiated from shoulder bursitis?
Doctors can tell rotator cuff injuries apart from shoulder bursitis with a detailed exam and imaging studies.
Shoulder impingement syndrome happens when the rotator cuff tendons get compressed or irritated. This causes pain and limited mobility. It’s different from shoulder bursitis because of its unique cause.
Frozen shoulder goes through stages like pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. It’s different from shoulder bursitis because of its distinct stages and symptoms.
Can referred pain from other areas be mistaken for shoulder bursitis?
Yes, pain from other areas like the cervical spine, thoracic outlet, heart, or gallbladder can feel like shoulder pain. This can make it seem like shoulder bursitis.
What are the red flag symptoms that require immediate medical attention for shoulder pain?
Severe pain, sudden symptoms, trauma, or signs of infection are red flags. They mean you need to see a doctor right away.
How can I choose the right specialist for my shoulder condition?
Look for a specialist in orthopedics or sports medicine. Make sure they have experience with shoulder conditions.
What can I expect during the evaluation process for shoulder pain?
The evaluation will include a detailed exam, imaging studies, and lab tests. These help find the cause of your shoulder pain.
Reference
- Carlier, J., Flemming, D., de Moura, M., & Bousquet, M. (2024). Evidence-based approach to the shoulder examination for subacromial bursitis and rotator cuff tears: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 25, 41. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39702033/