The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
About 1 in 10 people will get bursitis at some point. It often affects the shoulders, elbows, and hips. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and limited movement. Sometimes, bruising may also be present — but does bursitis cause bruising?
We’ll explore this question in detail and look into how bursitis, swelling, and bruising are connected. Understanding does bursitis cause bruising helps identify when discoloration is a normal symptom and when it might signal something more serious. We’ll dive into the causes and symptoms of this condition to give you a clearer picture.
Key Takeaways
- Bursitis is characterized by inflammation of the bursae, leading to pain and swelling.
- Bruising can occur in some cases of bursitis, but it’s not a universal symptom.
- The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
- Understanding the causes of bursitis is essential for effective treatment.
- Bursitis can affect various parts of the body, including the shoulders, elbows, and hips.
Understanding Bursitis: Definition and Basic Mechanism
Bursitis is when the bursae, fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints, get inflamed. It’s a common issue that can cause a lot of pain. Knowing how bursae work and how they get inflamed is key to understanding bursitis.
What Are Bursae and Their Function
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that help reduce friction between bones, tendons, and skin. They act as cushions, making it easier for joints to move smoothly. You can find bursae near major joints like the shoulders, hips, knees, and elbows.
The main job of bursae is to help joints move smoothly by reducing friction and absorbing shock. When they get inflamed, it can lead to bursitis. This causes pain and makes it hard to move.
How Inflammation Develops in Bursitis
Inflammation in bursitis can happen from repetitive motion, direct injury, or infection. Doing the same motion over and over can irritate and inflame the bursae. This leads to bursitis. Direct injury to a joint can also cause bursitis by inflaming the bursae.
In some cases, infection can cause septic bursitis, a more serious issue that needs medical help. Knowing what causes inflammation is important for managing and treating bursitis.
Does Bursitis Cause Bruising?
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
Inflammation is a big part of bursitis. It can make the area red, swollen, and warm. Inflammation can also increase blood flow, which might change the skin’s color. This color change can look like bruising.
The body’s inflammatory response in bursitis releases chemicals. These chemicals make blood vessels more open. This openness can let blood leak into the tissues, causing color changes. Even though it’s not true bruising, it can look like it.
Mechanisms That May Lead to Bruising-Like Appearance
Several things can make bursitis look like it’s bruising. One big factor is the inflammation itself, which can make the skin red and swollen. Also, swelling can stretch the skin, changing how it looks.
Minor trauma or repetitive motion can cause tiny blood vessel tears. These tears can lead to small hemorrhages, making it look bruised. We will look at how these factors work together to cause bruising-like symptoms.
In conclusion, bursitis itself might not directly cause bruising. Butthe inflammation and changes it brings can make it look like it does. Understanding these mechanisms helps in diagnosing and treating bursitis.
Common Symptoms of Bursitis
Bursitis symptoms can vary based on where and how severe it is. It usually shows a mix of signs that affect the joint or area involved.
Pain, Tenderness, and Swelling
Pain is a common symptom of bursitis. It often feels tender to the touch. Swelling also happens due to inflammation of the bursa.
The pain can be sharp or last a long time. It may get worse when you move or press on the area.
Redness and Skin Changes
Redness and warmth are common signs of inflammation. The skin might look shiny or stretched because of swelling. You might feel warmth or heat in the area, too.
| Symptom | Description |
| Pain | Often acute or chronic, worsens with movement or pressure |
| Tenderness | Sensitive to touch |
| Swelling | Resulting from inflammation of the bursa |
| Redness | Increased blood flow causes redness and warmth |
Limited Range of Motion and Functional Impact
Bursitis can make it hard to move the affected joint. This is because of pain and swelling. It can really affect your daily life and how you move around.
In bad cases, you might need to change how you do things or use special devices to help.
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
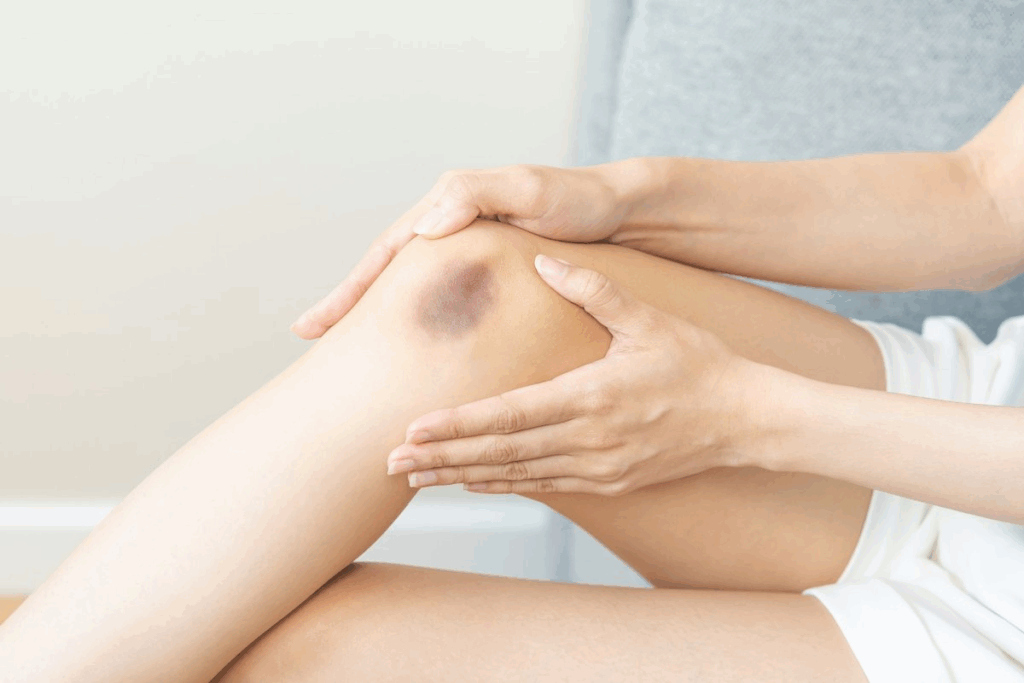
To tell bursitis apart from contusions, you need to know their key differences. Both can hurt and swell, but they start from different causes and show in different ways.
Visual Differences in Appearance
Looking at how they appear can help tell them apart. Bursitis shows up as swelling and redness near the bursa. Contusions, on the other hand, have bruising because of blood in the tissues.
Key Visual Differences:
| Characteristic | Bursitis | Contusion |
| Swelling | Localized around the bursa | Diffuse, depending on the injury |
| Bruising | Not typically present | Often present due to blood leakage |
| Redness | Common due to inflammation | Variable, may be accompanied by bruising |
Differences in Pain Patterns and Development
The pain from bursitis and contusions is different, too. Bursitis pain is usually in one spot and gets worse with movement. Contusion pain spreads out and depends on the injury’s size.
Pain patterns can provide valuable clues in telling them apart. Bursitis pain comes on slowly. Contusion pain starts right after the injury.
Signs of Bursitis vs. Bruise
To sum up, bursitis shows as swelling, redness, and pain that gets worse with movement. Bruises, on the other hand, show as discoloration from blood and pain that spreads out.
Knowing these differences is key to the right diagnosis and treatment. By looking at how they appear and the pain they cause, doctors can tell bursitis from contusions. This helps patients get the best care for their condition.
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
The shoulder joint is often affected by bursitis. Subacromial and subdeltoid bursitis are common and can cause bruising.
Subacromial Bursitis Symptoms
Subacromial bursitis happens when the bursa between the acromion and rotator cuff tendons gets inflamed. It causes pain, swelling, and a bruised look. These symptoms are worse when lifting the arm.
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
Subdeltoid bursitis occurs when the bursa under the deltoid muscle gets inflamed. It leads to pain, tenderness, and skin changes that look like bruises. The area may also show redness and swelling.
Impact on Daily Activities and Movement
Both subacromial and subdeltoid bursitis can make daily tasks hard. Even simple actions like dressing or reaching overhead can hurt. Sleeping can also be uncomfortable due to pain and stiffness.
| Symptoms | Subacromial Bursitis | Subdeltoid Bursitis |
| Pain Location | Top of the shoulder, worse with arm lift | Outer shoulder, potentially radiating down |
| Visible Symptoms | Swelling, potentially bruising | Redness, swelling, bruise-like appearance |
| Impact on Movement | Limited arm lift, pain with overhead activities | Pain with arm movement, limited mobility |
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
Understanding hip bursitis is key because it can cause pain, bruising, and discomfort. This condition is when the bursae in the hip area get inflamed. It can affect your daily life and how you move.
Trochanteric Bursitis Symptoms
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
Common symptoms of trochanteric bursitis:
- Pain on the outside of the hip
- Tenderness to the touch
- Swelling or redness
- Bruising or discoloration
Iliopsoas Bursitis and Associated Skin Changes
Iliopsoas bursitis affects the bursa near the iliopsoas muscle. This muscle runs from the lower back to the femur. This condition can cause pain in the groin or hip area. It may also lead to skin changes, like bruising, because of the bursa’s location.
“The inflammation associated with iliopsoas bursitis can sometimes cause visible skin changes, including bruising, due to the bursa’s location near the surface of the skin.”
| Condition | Symptoms | Skin Changes |
| Trochanteric Bursitis | Pain on the outside of the hip, tenderness | Bruising, swelling |
| Iliopsoas Bursitis | Pain in the groin or hip area | Bruising, redness |
Effects on Mobility and Sleep
Hip bursitis, whether trochanteric or iliopsoas, can greatly affect your mobility and sleep. The pain and discomfort make it hard to move or find a comfortable position. This can lead to disturbed sleep and reduced mobility.
We recommend seeing a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. This can help alleviate symptoms and improve your quality of life.
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
The knee is a common spot for bursitis. Knowing its visual signs is key to the right diagnosis. Knee bursitis occurs when the bursae around the knee joint become inflamed. This can lead to pain, swelling, and redness.
Prepatellar Bursitis (Housemaid’s Knee)
Prepatellar bursitis, or Housemaid’s Knee, hits the bursa in front of the kneecap. It shows as swelling over the kneecap, which hurts when touched. The swelling also brings redness and warmth.
This condition often comes from kneeling a lot. People who kneel a lot for work or hobbies are more likely to get it.
Infrapatellar Bursitis (Clergyman’s Knee)
Infrapatellar bursitis, or Clergyman’s Knee, affects the bursa below the kneecap. It causes swelling and tenderness below the kneecap. This can look like other knee injuries.
This bursitis is linked to deep knee bending or hitting the area below the kneecap.
Distinguishing Knee Bursitis from Other Knee Injuries
Telling knee bursitis apart from other knee injuries is hard because symptoms can be similar. But swelling’s location and type are key. Bursitis swells around the bursa, while other injuries might spread the swelling or pain.
| Condition | Common Symptoms | Typical Causes |
| Prepatellar Bursitis | Swelling, redness, and tenderness over the kneecap | Repetitive kneeling |
| Infrapatellar Bursitis | Swelling, tenderness below the kneecap | Deep knee bending, direct trauma |
| Ligament Sprain | Pain, instability, diffuse swelling | Trauma, twisting injury |
Knowing knee bursitis and its visual signs is key to the right diagnosis and treatment. If you have ongoing knee pain or swelling, see a doctor for a check-up.
How Inflammation Affects Blood Vessels and Skin Appearance
Inflammation is key in bursitis, affecting bursae, blood vessels, and skin. It causes big changes in the affected area.
Inflammatory Response and Vascular Changes
The inflammatory process in bursitis makes blood vessels more open. This lets fluid and white blood cells leak into the tissue. It leads to swelling and changes in skin appearance.
The skin may look red, swollen, and warm. Inflammation can also make new blood vessels, which are fragile and can bleed. This might cause bruising or a bruised look.
Why Inflammation Can Mimic Bruising
Inflammation in bursitis can make the skin look bruised. Increased blood flow and vascular permeability cause fluid and blood cells to build up. This makes the skin look discolored.
Chemical mediators released during inflammation can break down blood components. This leads to pigments that discolor the skin. Sometimes, the skin looks bruised without actual bruising.
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
Inflammation in bursitis changes blood flow, affecting skin appearance. Increased blood flow makes the skin red and warm. Decreased blood flow makes it pale or cool.
New blood vessels formed by inflammation can be fragile and bleed easily. Understanding how inflammation affects blood vessels and skin is key to diagnosing and treating bursitis. This helps healthcare professionals manage the condition effectively.
Diagnosing Bursitis vs. Actual Bruising
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
Physical Examination Techniques
Diagnosing bursitis starts with a physical examination. Doctors check for tenderness, swelling, and how well the area moves. They use special tests to find bursitis, like feeling for tenderness and checking for pain when moving.
For shoulder bursitis, doctors might test the subacromial space. They check for pain when lifting the arm. These physical examination techniques help tell bursitis apart from bruising.
Imaging Tests for Accurate Diagnosis
Even with a physical exam, imaging tests are key to confirming bursitis. Ultrasound and MRI show the bursae and tissues around them. They spot inflammation and fluid, signs of bursitis.
These tests help diagnose bursitis and rule out other issues like fractures or tendinitis. They can also find complications like calcification.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to seek medical attention is vital. Look for severe pain, big swelling, or trouble moving. If symptoms don’t get better or get worse, see a doctor.
Watch for signs of infection like redness, warmth, or fever with swelling. Quick medical attention helps avoid problems and treat bursitis properly.
Treatment Options for Bursitis With Bruising-Like Symptoms
Dealing with bursitis that looks like bruises is a challenge. It’s important to know how to treat it. We aim to reduce swelling, ease pain, and get the joint working right again. We’ll look at different ways to manage bursitis, from simple steps to more serious treatments.
Conservative Treatment Approaches (RICE Method)
The RICE method is a top choice for treating bursitis. It stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Rest stops further irritation, Ice cuts down on pain and swelling, Compression reduces swelling, and Elevation lowers blood flow to lessen swelling.
Using the RICE method can really help. For example, ice wrapped in a cloth for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, can ease pain and swelling.
Medical Interventions and Medications
If simple treatments don’t work, doctors may step in. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often given to lessen pain and swelling. In serious cases, corticosteroid shots might be needed to help.
Physical therapy is also key. It keeps the joint moving and strengthens the muscles around it. Sometimes, draining the bursa is done to remove extra fluid.
Recovery Timeline and Expectations
The time it takes to get better from bursitis depends on how bad it is and the treatment. Usually, with the right care, symptoms start to get better in a few weeks. But it’s important to be patient and stick to the treatment plan to fully recover.
Knowing what to expect during recovery helps manage the condition better. It’s vital to keep up with doctor visits to adjust the treatment as needed.
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
To avoid the discomfort of bursitis, it’s essential to adopt preventive measures that protect your joints. We will explore several strategies that can help reduce the risk of developing bursitis.
Proper Exercise Techniques and Warm-up
One of the key factors in preventing bursitis is adopting proper exercise techniques. This includes warming up before engaging in physical activities and gradually increasing the intensity of your workouts. A well-structured warm-up routine can significantly reduce the strain on your joints.
- Start with light cardio to increase blood flow.
- Perform dynamic stretches to loosen the muscles around the joints.
- Gradually increase the intensity of your workout.
Protective Equipment for Joint Protection
Using protective equipment is another key aspect of bursitis prevention. Whether you’re engaging in sports or performing repetitive tasks, protective gear can help cushion your joints and reduce the risk of inflammation.
Examples of protective equipment include knee pads, elbow pads, and supportive braces. These tools can provide additional support and protection to vulnerable areas.
Ergonomic Adjustments for Daily Activities
Making ergonomic adjustments in your daily activities can also play a significant role in preventing bursitis. This involves ensuring that your workspace and daily routines are set up to minimize strain on your joints.
- Adjust your workstation to promote good posture.
- Take regular breaks to stretch and move around.
- Use ergonomic tools and furniture designed to reduce joint strain.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily life, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing bursitis and associated discomfort.
When Bruising With Bursitis Indicates a More Serious Condition
Bruising with bursitis might mean a serious problem that needs quick medical help. Bursitis itself is usually not a big worry. But bruising could mean a more serious issue.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Attention
Some symptoms with bruising from bursitis need quick doctor visits. These include:
- Increasing pain or swelling
- Redness or warmth around the affected area
- Decreased mobility or function
- Fever or chills
- A history of trauma or recent surgery
Spotting these signs early is key to avoiding bigger problems.
Potential Complications of Untreated Bursitis
Ignoring bursitis can cause serious issues. These include:
- Chronic pain and inflammation
- Permanent damage to the affected joint or bursa
- Infection, which can spread to other parts of the body
- Reduced range of motion and functionality
Knowing these risks shows why seeing a doctor is important if symptoms don’t get better.
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
Bursitis with bruising might worry about joint damage. Bursae help reduce friction and cushion joints. Bursitis can harm joint function and cause lasting damage if not treated properly.
It’s vital to watch for these risks and work with doctors to protect joint health.
Conclusion
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
Bursitis causes inflammation in the bursae, leading to symptoms that look like bruises. This happens because of the inflammation’s effect on blood vessels and skin. We’ve talked about different types of bursitis, like shoulder, hip, and knee, and their symptoms.
The connection between bursitis and bruising is intricate and shaped by a variety of factors.
FAQ
Does bursitis cause bruising?
Bursitis can cause bruising or a bruised look because of inflammation and more blood flow. But, how much bruising you see can change based on who you are and the type.
What are the common symptoms of bursitis?
Symptoms of bursitis include pain, tenderness, swelling, redness, and trouble moving. The exact symptoms depend on where and how bad the bursitis is.
How can I differentiate between bursitis and a contusion?
Bursitis and contusions look and feel different. Bursitis shows swelling, redness, and warmth. Contusions have a more focused bruise.
Can shoulder bursitis cause bruising?
Yes, shoulder bursitis, like subacromial and subdeltoid, can cause bruising. This is due to inflammation and more blood flow.
What are the symptoms of hip bursitis?
Hip bursitis, like trochanteric and iliopsoas, causes pain, tenderness, swelling, and bruising. It affects the outer hip or groin, making it hard to move and sleep.
Can knee bursitis cause visual symptoms like bruising?
Yes, knee bursitis, like prepatellar and infrapatellar, can show swelling, redness, and bruising. This might look like other knee injuries.
How does inflammation in bursitis affect blood vessels and skin appearance?
Inflammation in bursitis can change the blood flow and the skin’s appearance. This might cause bruising or a bruised look.
What are the treatment options for bursitis with bruising-like symptoms?
Treatments for bursitis with bruising symptoms include the RICE method, medical help, and medicines. These help reduce inflammation and ease symptoms.
How can I prevent bursitis and associated discomfort?
To prevent bursitis, use proper exercise, wear protective gear, and make ergonomic changes. These steps help avoid bursitis and discomfort.
When should I seek medical attention for bursitis symptoms?
See a doctor if you have severe pain, swelling, redness, or bruising. Also, if symptoms get worse or bother your daily life.
Can bruising with bursitis indicate a more serious underlying condition?
Yes, bruising with bursitis might mean a serious issue like an infection or joint damage. You should get medical help right away.
References
- Reid, D. (2016). The management of greater trochanteric pain syndrome: A systematic literature review. Journal of Orthopaedics, *13*(1), 15–28. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4761624/









