Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik

Did you know that nearly 1 in 4 adults experience some form of joint pain or stiffness? This affects their daily lives. Learn about key types of four joint movements and their role in flexibility.
Knowing the basic types of joint mobility is key to keeping joints healthy and avoiding injuries. Flexion and extension are two main movements. They are vital for our range of motion.
The human body can do many actions thanks to the complex work of different joint action types. Learning about these movements helps us see why joint health is so important.
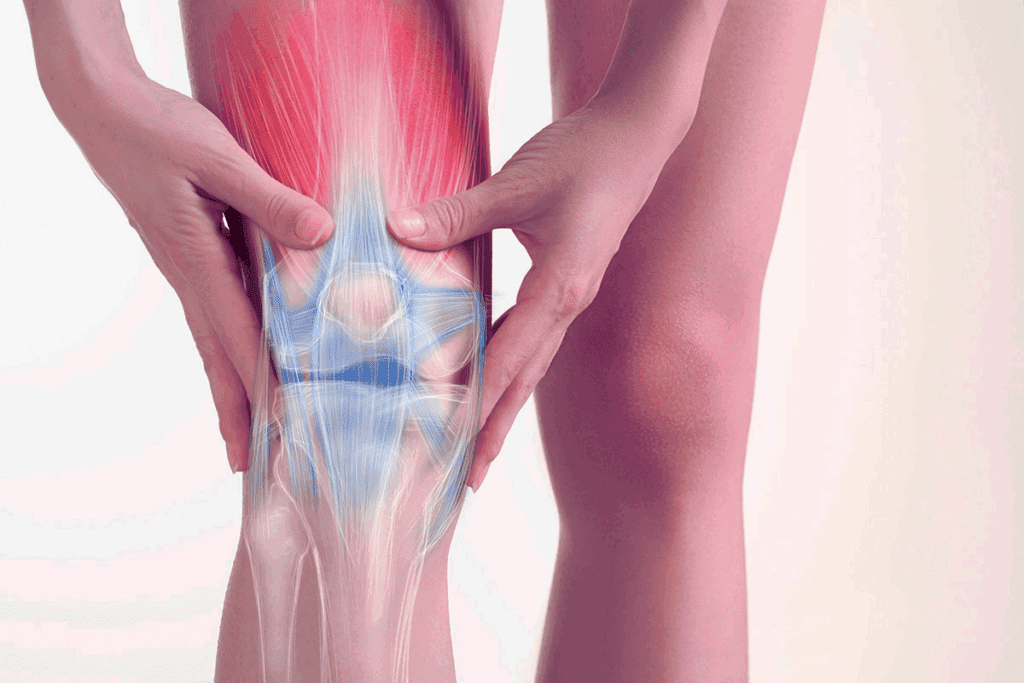
Our joints play a key role in how we move and stay flexible. Joints connect bones, allowing us to move in different ways. Knowing how joints work helps us understand human movement better.
The human body has many types of joints, each with its own role. Synovial joints are the most common and offer the most movement. They have a space filled with synovial fluid, making movement smooth.
Other joints, like cartilaginous and fibrous, move less. Cartilaginous joints have cartilage and allow slight movement. Fibrous joints are tight and move very little.
The design of a joint affects how it moves. Synovial joints are made for lots of movement. The shape of bones, ligaments, and muscles all help with mobility.
For example, ball-and-socket joints like the shoulder and hip can rotate and move in circles. Hinge joints, like the elbow, mainly bend and straighten.
Knowing how joints work is key for treating movement problems and keeping joints healthy. The right exercise and care are important.
Knowing the four basic joint movements is key to understanding human anatomy and how we move. These movements are the base for more complex actions. They are vital for keeping our joints healthy and our bodies working well.
Synovial joints are the most common and flexible joints in our bodies. They allow for a wide range of movements. The four main movements are flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
Flexion is bending, which decreases the angle between bones. Extension is straightening, which increases this angle. Abduction moves a limb away from the body’s midline. Adduction moves it towards the midline.
These basic movements can be mixed to create more complex actions. For example, moving an arm in a circle involves flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction. This shows how synovial joints can do many things.
To grasp joint movements, we must understand anatomical planes and axes. The human body is divided into three main planes: sagittal, frontal, and transverse. Movements happen within these planes around specific axes.
For instance, flexion and extension happen in the sagittal plane around a frontal axis. Abduction and adduction occur in the frontal plane around a sagittal axis. Knowing these planes and axes helps us describe and study human movement accurately.
Flexion is key for everyday tasks. It lets us move in many ways, from simple gestures to complex actions.
When we bend a joint, its angle gets smaller. This is thanks to the contraction of specific muscles, called flexor muscles. For example, bending our elbow uses the biceps brachii, making the forearm and upper arm closer.
Flexion isn’t just about the main muscles. Other muscles work together for smooth movement. For elbow bending, the biceps brachii and brachialis both play a part.
Flexion is vital in our daily lives. Bending our knees to squat is a good example. It’s also what lets us lift objects towards us by bending our elbows.
Here are some common examples of flexion in daily life:
Knowing how flexion works helps us see why keeping our joints and muscles healthy is so important.
| Joint | Flexion Movement | Primary Flexor Muscle |
| Elbow | Bending the arm | Biceps brachii |
| Knee | Squatting | Hamstrings |
| Hip | Bending forward | Iliopsoas |
Extension is key for keeping our joints flexible and moving well. It’s important for everyday activities and sports. This movement helps us move freely.
Extension and flexion work together. Flexion bends our joints, while extension straightens them. This balance is essential for our joints to move fully.
For example, in a bicep curl, we bend our arm (flexion) and then straighten it (extension). This shows how extension and flexion are connected. It’s important for our muscles and joints to stay healthy.
Many muscles help with extension in our body. Some main ones are:
Working these muscles through exercises can make our extension better. It also helps prevent injuries.
By focusing on extension, we can improve our mobility. This keeps our joints healthy and functional for life.
Abduction is when a body part moves away from the midline. It’s key for many motions we do every day. It’s also important for sports and other activities.
The biomechanics of abduction involves many parts working together. Synovial joints like the shoulder and hip are key. When we move these joints, muscles pull the bones away from the midline.
“The complexity of abduction lies in its requirement for precise coordination between various muscle groups and joints,” as noted by experts in the field of orthopedic biomechanics.
Many major joints can move through abduction. These include:
Knowing what these joints can do is important. It helps doctors diagnose and treat injuries and movement problems.
Adduction is moving toward the body’s midline. It’s a key part of how we move and stay flexible. It’s important for everyday tasks and sports.
Adduction is the opposite of abduction. Abduction is moving a limb away from the midline. Adduction brings it back. This balance is key for balance and complex movements.
For example, in a jumping jack, legs move away and then back. Knowing how these movements work helps us understand our bodies better.
Many muscles and ligaments help with adduction. The main muscles depend on the joint. But they usually include:
| Muscle | Location | Function |
| Adductor Magnus | Hip | Primary adductor |
| Pectineus | Hip | Assists adduction |
| Adductor Brevis | Hip | Contributes to adduction |
Ligaments like the medial collateral ligament in the knee also support the joint during adduction.
Secondary motion types, like rotation and circumduction, are key for better joint function. These movements add complexity to our actions, making us more mobile and flexible.
It’s important to know about these secondary motions to fully understand human movement. We’ll look into rotation and circumduction, their roles in our daily lives.
Rotation is when a bone turns around a single axis. This can happen in two ways: internal (medial) rotation and external (lateral) rotation.
Internal rotation brings a limb towards the body’s center. External rotation moves it away. These movements help us do things like turn door handles or use screwdrivers.
| Rotation Type | Description | Example Activity |
| Internal Rotation | Movement towards the body’s midline | Turning a door handle |
| External Rotation | Movement away from the body’s midline | Using a screwdriver |
Circumduction is a complex movement where a limb moves in a circular path. It combines flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction in a sequence.
This movement is seen in joints like the shoulder and hip. It’s vital for wide-range activities, like throwing or swimming.
Understanding and keeping these secondary motions healthy boosts our mobility. Regular exercise and joint care are key to keeping our joints working well.
The upper body’s joints work together to allow for a wide range of movements. From simple gestures to complex actions, these movements are key for daily activities. Knowing how these movements work is important for keeping our joints healthy.
The shoulder complex is known for its amazing mobility. It can move in many ways, like bending, straightening, and rotating. This is thanks to the teamwork of many joints and muscles.
As an orthopedic specialist noted, “The complexity of the shoulder joint makes it both highly versatile and particularly vulnerable.” This shows how vital it is to understand and care for the shoulder complex.
“The complexity of the shoulder joint makes it both highly versatile and particularly vulnerable.” This highlights the importance of understanding and maintaining the health of the shoulder complex.
The elbow, wrist, and hand work together to offer a wide range of movements. The elbow helps bend and straighten the arm. The wrist allows for movements like bending and rotating, helping adjust hand position.
The hand, with its detailed structure, can make precise movements and grasp objects. The coordination between these joints is key for tasks needing precision, like writing or playing music.
It’s clear that keeping our upper body joints moving well is essential for mobility and function. By understanding these movements, we can see why taking care of our joints is so important.
Effective lower body joint movements are key to mobility, balance, and physical ability. The hip, knee, and ankle joints work together. They help us move in many ways for daily tasks and sports.
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint. It’s vital for supporting our body weight and for power in movements like walking, running, and jumping. Its design allows for many motions, like bending, straightening, moving outward, and rotating.
Key Functions of the Hip Joint:
The knee is more than a simple hinge joint. It’s a complex structure with bones, ligaments, and muscles. It helps us bend and straighten our knee. It also absorbs shock and supports our body weight.
| Knee Movement | Primary Muscles Involved | Function |
| Flexion | Hamstrings | Bending of the knee |
| Extension | Quadriceps | Straightening of the knee |
Understanding the knee’s mechanics is important. It helps us see its role in our body’s function. It’s also key for creating good plans when we get knee injuries.
Spinal joint movements are key to our mobility and posture. The spine has different segments, each adding to its flexibility and stability.
The spine is split into three main parts: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar. Each part moves differently.
Knowing these differences helps keep our spine healthy and prevents injuries.
Core stability is key for healthy spinal movement. The core muscles, like the abs and back, support the spine during movements.
Good core stability makes the spine stable, lowers injury risk, and improves posture.
| Spinal Region | Primary Movements | Key Characteristics |
| Cervical | Flexion, Extension, Rotation | Highly flexible, supports head movement |
| Thoracic | Rotation, Limited Flexion/Extension | Stabilized by rib cage, less flexible |
| Lumbar | Flexion, Extension | Weight-bearing, significant flexibility |
Understanding spinal joint movements and core stability shows how complex human mobility and posture are.
Evaluating range of motion is key for healthcare pros to see how well joints move. It helps spot any problems early. This is a big part of checking a person’s health.
Getting the right measurements is vital for diagnosing and treating joint issues. It tells us a lot about joint health. This info helps us make better treatment plans.
There are two main types of range of motion: active and passive. Active range of motion is when a person moves a joint on their own. Passive range of motion is when someone else moves the joint without the person’s effort.
Knowing the difference is important for checking how well a joint works. For example, if active and passive ranges don’t match, it might mean muscle weakness or nerve problems.
Many tools and ways are used to measure range of motion. Goniometers, inclinometers, and digital devices are some examples. A goniometer is often used to measure joint angles, giving a precise look at how much a joint can move.
Healthcare pros also use other methods like looking and feeling the joint. These methods, along with tools, help us get a full picture of joint movement.
By accurately checking and measuring range of motion, we can create better treatment plans. This helps improve joint mobility and overall health.
It’s important to know about joint movement disorders to keep our joints healthy. These disorders can make it hard to move and cause pain. This can really change how we live our lives.
Joint health is complex. It involves many things, like inflammation and how our brain controls movement. These factors can cause different disorders that affect how we move our joints.
Conditions like arthritis can really hurt our joint mobility. Arthritis is a group of diseases that cause pain and swelling in the joints. We’ll look at how these conditions affect movement and what treatments are available.
Neurological conditions can greatly affect how we control our joint movements. Diseases like Parkinson’s disease and stroke can make it hard for the brain to control movement. This can lead to stiffness, tremors, and limited mobility.
Diagnosing and treating these conditions need a team effort. This team includes neurologists, physical therapists, and other healthcare experts.
Keeping joints healthy is a big challenge that needs many strategies. It’s key for moving well and feeling good. We’ll look at ways to keep joints in top shape.
Physical therapy is key for better joint movement. Physical therapists use many methods like manual therapy and exercises. They also use heat and cold to help with pain and movement.
Manual therapy is hands-on to make joints move better and feel less stiff. It includes techniques like joint mobilization and manipulation. Physical therapists also give exercises to make muscles stronger around the joint. This helps with support and stability.
Stretching and strengthening are key for joint health. Stretching makes joints more flexible and moves better. Strengthening exercises build muscle support around the joint. This lowers injury risk and boosts function.
Good stretching can ease stiffness and improve joint movement. It includes static and dynamic stretches. Strengthening focuses on exercises for the muscles around the joint. This improves stability and function.
Using these methods together can greatly improve joint function. It’s important to work with health experts to create a plan that meets your needs and goals.
Understanding how joints move is key to better athletic performance and injury prevention. Joint movements are vital in sports and exercise. They affect how well we do and our injury risk.
To succeed in sports, it’s important to improve movement patterns. Knowing how joints move helps athletes perform better and stay injury-free. Good movement patterns help athletes reach their peak while keeping them safe from harm.
Improving movement patterns helps athletes perform better and stay safe. This requires good training, conditioning, and technique.
Preventing injuries is key in sports and exercise. Right joint mechanics help lower injury risk. Knowing how joints move and keeping them healthy helps prevent injuries.
“Proper joint mechanics are essential for preventing injuries and ensuring optimal performance in sports and exercise.”
Some ways to prevent injuries include:
By using these strategies, athletes can lower their injury risk and keep their joints healthy.
Keeping our joints moving well is key at every stage of life. We’ve seen how flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction are vital for our daily life and health. Knowing about these movements helps us protect our joints.
Each joint in our body, from the shoulders to the hips, allows us to move in many ways. Understanding how our joints work helps us see why exercise, good posture, and avoiding injuries are so important.
Adding stretching and strengthening exercises to our routine can boost joint health. This is even more critical as we get older. It lets us stay active, move freely, and keep our independence for years to come.
The four key joint movements are flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction. These movements help keep joints healthy and support various activities.
Flexion is bending a joint, making the angle between bones smaller. Extension is straightening a joint, making the angle between bones larger.
Synovial joints are key for movement. They allow for flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, and circumduction. This is thanks to their structure and synovial fluid.
Anatomical planes and axes help us understand joint movement. They include the sagittal, frontal, and transverse planes and their axes. These help describe the body’s movements.
Assessing and measuring range of motion is vital. It helps evaluate joint mobility and spot movement disorders or pathologies. This info guides targeted treatments.
Common issues include inflammatory conditions like arthritis and neurological impacts from stroke or spinal cord injury. Knowing these conditions helps keep joints healthy.
Physical therapy, like stretching and strengthening, boosts joint function. It improves mobility, reduces pain, and promotes better movement.
Core stability is key for healthy spinal movement. It provides a stable base for the spine to move. This stability prevents injuries and supports optimal movement.
Joint movements are vital for exercise and sports. Optimizing movement and keeping joints mobile are key for success and injury prevention.
Keeping joints mobile is essential for health and well-being. It allows for easy daily activities, prevents injuries, and supports optimal movement.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!