When bones slip out of their normal position, the resulting injury impacts mobility and quality of life. Immediate medical attention is critical—not just to realign the joint but to manage intense discomfort during recovery. We prioritize solutions that balance rapid pain relief with long-term healing strategies. Discover the best drug for dislocation pain and inflammation management.
Treatment begins with professional realignment, followed by immobilization to protect the affected area. Pain management plays a central role, with options ranging from localized numbing agents to oral medications. The choice depends on factors like injury severity, medical history, and the complexity of the reduction process.
For example, minor finger injuries might require only ice and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory tablets. Larger joints like shoulders or hips often demand stronger medications during realignment procedures. Collaboration between patients and healthcare teams ensures tailored approaches that address both physical needs and safety concerns.
Key Takeaways
- Pain management strategies vary based on joint location and injury complexity
- Medical professionals determine medication plans during the realignment process
- Individual health factors influence drug selection and dosage
- Immediate care focuses on stabilization before long-term recovery
- Combination therapies often provide optimal relief during treatment phases
- Follow-up care minimizes risks of complications or reinjury
Understanding Dislocation: Definitions and Types
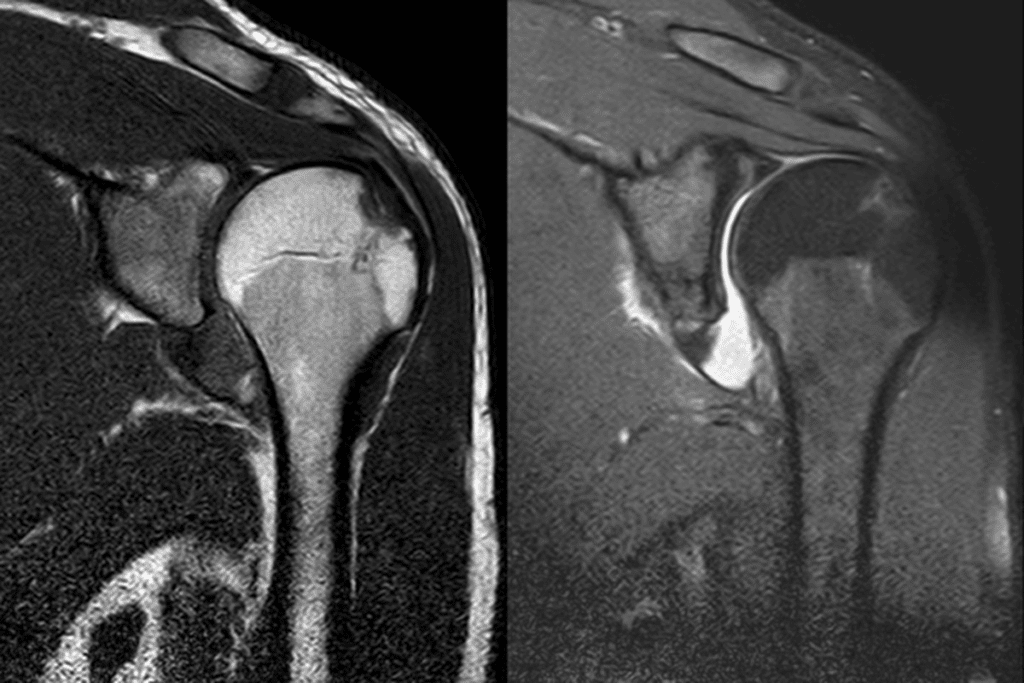
Injuries affecting joint alignment demand precise medical classification for optimal care. We categorize these issues based on how far bones shift from their natural positions and the resulting damage to surrounding tissues.
Complete Separation vs. Partial Shifting
When bones fully disconnect within a joint, this constitutes a complete dislocation. Subluxations occur when partial alignment remains. “The distinction guides treatment intensity,” notes orthopedic specialist. “Full separations often involve more complex tissue damage.”
Associated injuries like fractures or tendon tears frequently accompany major dislocations. These complications influence both recovery timelines and pain management strategies. Smaller joints may show less visible swelling but still require careful assessment.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Key symptoms include sudden loss of mobility, visible deformity, and pain intensifying with movement. Numbness or tingling suggests possible nerve compression – a red flag requiring urgent care. We prioritize these indicators when evaluating injury severity.
Different body parts present unique challenges. Finger joints might appear only slightly bent, while shoulder displacements often cause pronounced swelling. Early symptom documentation helps clinicians tailor medication plans effectively.
Understanding these fundamentals empowers patients to describe their experiences accurately. This collaboration ensures appropriate treatment – whether simple anti-inflammatories or advanced pain control methods – matches each situation’s demands.
Exploring Causes and Risk Factors
Joint displacements often stem from high-impact activities or unexpected trauma. We analyze patterns to identify why certain groups face elevated risks and how injury origins shape treatment decisions.
Injuries from Contact Sports and Accidents
Contact sports like football and basketball account for 38% of shoulder dislocations in athletes under 25. Collisions and abrupt directional changes stress joints beyond their natural limits. “These scenarios often require immediate pain control to facilitate safe joint repositioning,” explains sports physician.
Motor vehicle crashes generate forces strong enough to displace multiple joints simultaneously. Such cases typically involve complex tissue damage, demanding tailored medication plans. Emergency teams prioritize rapid-acting analgesics to stabilize patients during transport.
Recreational activities and workplace incidents also contribute significantly. Falls from heights frequently cause hip or knee displacements, particularly among older adults. We assess each situation’s energy impact to determine appropriate pain relief strategies.
- High-impact sports triple dislocation risks compared to non-contact activities
- Multi-joint injuries occur in 22% of car accident trauma cases
- Pre-existing joint weaknesses increase vulnerability during physical strain
Understanding these causes helps medical teams select medications that match injury severity. Quick recognition of trauma patterns enables faster, more effective treatment decisions.
Diagnostic Approaches and Imaging Tests

Accurate diagnosis forms the foundation of effective joint injury management. Physicians combine physical assessments with advanced imaging tests to create personalized treatment plans. This approach ensures safe medication choices and targeted recovery strategies.
The Role of X-Rays, CT, and MRI
X-rays remain the primary tool for confirming bone displacement. They reveal fractures needing specialized care while guiding anesthesia decisions. “Quick imaging prevents unnecessary movement during joint realignment,” states ER nurse practitioner Alicia Cho.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) excels at showing ligament tears or cartilage damage. These details help doctors adjust pain management timelines. For complex cases involving shattered bones, computed tomography (CT) scans provide 3D views that inform surgical planning.
When Immediate Medical Evaluation is Needed
Seek emergency care if numbness accompanies visible deformity – this signals potential nerve damage. Multi-joint injuries or high-impact trauma often require simultaneous imaging and stabilization.
Emergency teams prioritize rapid scans to rule out life-threatening complications. Imaging results directly influence sedation levels and medication types during procedures. Through precise diagnostics, we ensure every treatment step supports both immediate relief and long-term joint health.
Choosing the Best Drug for Dislocation
Effective pain management during joint realignment requires careful medication selection tailored to each situation. We consider injury complexity, procedure type, and individual health factors to ensure safe, targeted relief.
Pain Relievers and Anti-inflammatory Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen reduce swelling and discomfort in minor cases. For severe pain, short-term opioid use helps patients tolerate reduction procedures. “Balancing immediate relief with long-term safety guides our medication choices,” explains pain management specialist.
Oral options work well for stable injuries needing closed reduction. Intravenous administration provides faster action during emergency treatments. We monitor responses closely to adjust dosages and prevent side effects.
Anesthesia and Sedative Options in Reduction Procedures
Local anesthetics numb specific areas for finger or toe adjustments. Lidocaine injections allow precise pain control without systemic sedation. Larger joints often require intravenous medications to relax muscles and ease bone repositioning.
General anesthesia becomes essential for open reductions involving surgical incisions. Anesthesiologists combine fast-acting sedatives with pain blockers to maintain comfort. Recovery teams then transition patients to oral medications as healing progresses.
We prioritize clear communication about each option’s benefits and risks. This collaborative approach ensures patients receive appropriate care at every treatment stage.
Non-Surgical Treatments and Closed Reduction Techniques
Modern care strategies focus on restoring joint function without invasive procedures. Our approach combines immediate stabilization with targeted recovery plans designed to promote natural healing.
Applying the PRICE Method
The PRICE protocol (Protection, Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) forms the foundation of early treatment. “This method reduces swelling by up to 40% in the first 48 hours,” notes physical therapist. We recommend applying ice packs for 15-minute intervals during initial days post-injury.
Compression wraps help control inflammation while protecting vulnerable tissues. Elevation minimizes fluid buildup, particularly crucial for ankle or wrist injuries. Patients typically maintain this routine for 3-5 days before progressing to active recovery.
Immobilization with Splints and Slings
After successful realignment, proper support prevents re-injury. Custom splints keep joints stable during healing phases. For shoulder displacements, slings limit arm movement while encouraging proper blood flow.
Most patients wear these devices for 2-4 weeks depending on injury severity. We combine immobilization with gentle stretching exercises once swelling subsides. Regular follow-ups ensure adjustments align with recovery progress.
Avoid strenuous activities during the first week to protect the realigned joint. Gradual return to daily activities begins after splint removal, guided by your care team’s recommendations. Consistent adherence to these protocols significantly improves long-term mobility outcomes.
Surgical Interventions and Open Reduction
When non-surgical methods can’t realign joints, operating room procedures become essential. We prioritize precision and safety during these complex interventions, ensuring damaged tissues receive proper attention. Advanced imaging guides every step to minimize risks and optimize outcomes.
When Surgery Becomes Necessary
Our teams recommend surgical solutions when manual adjustments fail or injuries involve multiple complications. Common scenarios include:
- Bone fragments blocking proper joint alignment
- Severe ligament tears compromising stability
- Recurrent displacements despite immobilization
An orthopedic surgeon explains: “Open reduction allows direct visualization – crucial for addressing hidden damage that scans might miss.” Associated fractures often require simultaneous stabilization during these procedures.
Steps in the Open Reduction Process
Surgical teams follow strict protocols in the operating room. Anesthesia specialists first administer general anesthesia through IV lines or masks. Surgeons then make precise incisions to access displaced bones and repair surrounding tissues.
| Procedure Phase | Key Actions | Duration |
| Preparation | Sterile draping, anesthesia induction | 25-40 mins |
| Reduction | Bone realignment, fracture fixation | 1-3 hours |
| Closure | Layered sutures, wound dressing | 30-45 mins |
Post-surgical care includes specialized pain control methods. Nerve blocks and monitored medication systems help patients recover comfortably. We schedule follow-up imaging to confirm proper healing and adjust rehabilitation plans as needed.
Comprehensive Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation transforms recovery from joint injuries into lasting mobility. We design programs that rebuild strength while preventing secondary complications. Our approach evolves with your healing progress, ensuring tissues regain flexibility without risking reinjury.
Post-Treatment Recovery Strategies
Early movement prevents joint stiffness while promoting blood flow. For shoulder injuries, gentle rotations begin within 3-5 days to avoid frozen joint syndrome. We gradually reduce pain medications as swelling decreases, maintaining comfort during activities.
Muscle preservation requires daily engagement. Isometric exercises maintain tone without straining healing joints. Therapists monitor progress weekly, adjusting plans based on tissue response. Older patients often need modified routines to prevent contractures.
Exercises to Restore Joint Function
Range-of-motion drills start with passive movements before advancing to resistance training. Shoulder recovery incorporates pendulum swings and wall walks. These activities rebuild coordination while protecting repaired tissues.
Strengthening phases introduce light weights after 14 days for most joints. Balance exercises improve proprioception – crucial for preventing repeat injuries. We time exercise intensity to match pain reduction milestones, ensuring steady progress without setbacks.
Consistent therapy sessions yield optimal results when paired with home routines. Our teams provide visual guides for daily practice, empowering patients to take charge of their recovery time. Follow-up assessments confirm restored mobility and muscle balance.
FAQ
What medications help manage dislocation pain?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen effectively reduce pain and swelling. For severe cases, doctors may prescribe short-term opioids or administer local anesthesia during joint realignment. Always follow dosage guidelines to avoid complications.
How does dislocation differ from subluxation?
Dislocation involves complete separation of bones in a joint, while subluxation refers to partial misalignment. Both damage surrounding tissues, but dislocations often require urgent closed reduction to restore normal positioning and prevent nerve damage.
What symptoms indicate a dislocated joint?
Visible deformity, intense pain, swelling, and inability to move the joint are primary signs. Numbness or pale skin near the injury suggests potential blood vessel or nerve damage, requiring immediate emergency care.
Are contact sports a major risk for dislocations?
Yes. Activities like football, hockey, and rugby frequently cause shoulder or knee dislocations due to high-impact collisions. Proper protective gear and conditioning reduce risks of ligament tears and joint instability.
Which imaging tests diagnose dislocations accurately?
X-rays confirm bone alignment after injury. For soft tissue assessment, MRI scans evaluate ligament tears, while CT scans detect subtle fractures. These tests guide treatment plans for complex cases.
When should I seek emergency care for a dislocation?
Seek immediate help if the joint appears deformed, movement is impossible, or numbness develops. Delaying treatment increases risks of chronic instability or compromised blood flow to the area.
Are sedatives used during joint realignment?
Yes. Medications like propofol or midazolam help relax muscles and minimize pain during closed reduction. Medical teams monitor vital signs to ensure patient safety throughout the procedure.
How does the PRICE method aid recovery?
A: Protect, Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation reduce swelling and stabilize the joint post-injury. Combine this with immobilization using splints for optimal healing during initial days.
When is surgery required for joint dislocation?
Surgery becomes necessary for recurrent dislocations, fractures involving the joint socket, or severe ligament tears. Open reduction realigns bones, while repairs to muscles or nerves address long-term stability.
What rehabilitation exercises restore joint function?
Physical therapy focuses on gentle range-of-motion exercises, progressing to strength training with resistance bands. Low-impact activities like swimming rebuild mobility without straining healing tissues.
Reference
- National Library of Medicine. (2024, June 17). Dislocation. MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470595/ — See section on “You may be given medicine …” MedlinePlus
MedlinePlus. (2024, September 16). Dislocations. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. https://medlineplus.gov/dislocations.html — Highlights that treatment “might include … medicine” as part of joint-dislocation care.


































