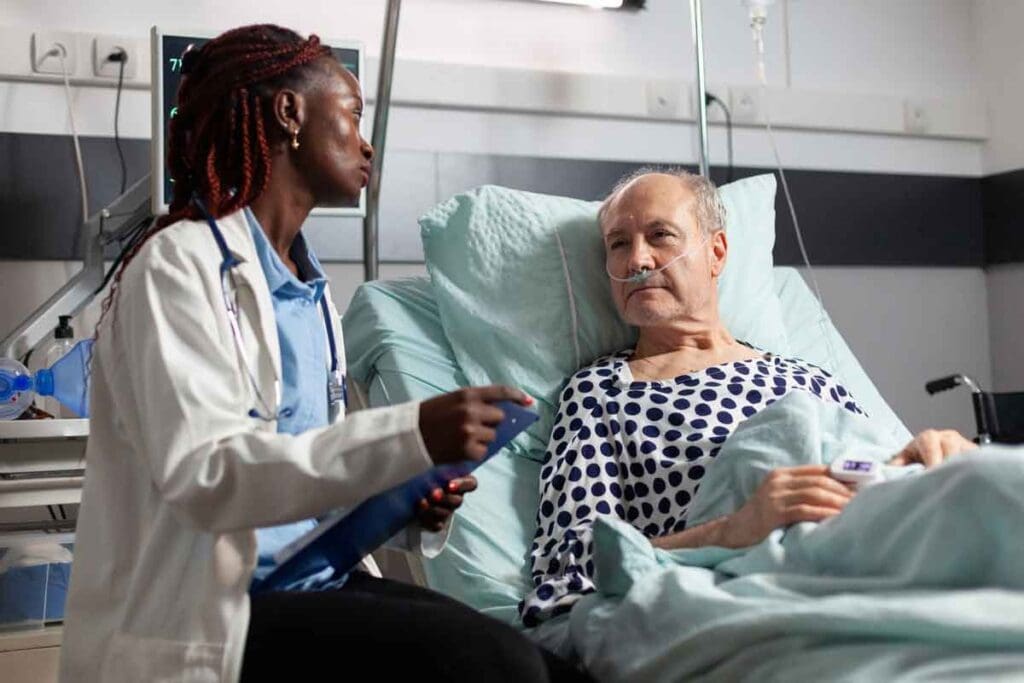
Sickle cell disease is a serious inherited blood disorder. It’s caused by a mutation in the HBB gene. This leads to sickle-shaped red blood cells. It’s a chronic genetic disorder that can be fatal, with high mortality rates worldwide.
Many people don’t realize how deadly sickle cell disease can be. It’s important to know its mortality rates and prognosis. This knowledge helps in providing better care. Liv Hospital’s patient-centered approach has greatly improved survival rates for those with the disease.
Key Takeaways
- Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder that affects red blood cells.
- Mortality rates for sickle cell disease vary globally and regionally.
- Understanding prognosis is key for effective care.
- Liv Hospital’s approach has improved survival rates.
- Patient-centered care is vital for managing the disease.
Understanding Sickle Cell Disease: A Genetic Blood Disorder
It’s important to understand the genetic roots of sickle cell disease. This disorder affects the hemoglobin in red blood cells, making them sickle-shaped. This shape makes it hard for the cells to carry oxygen, leading to health problems.
The Genetic Basis of Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease comes from a mutation in the HBB gene. This gene is key for making the beta-globin part of hemoglobin. The mutation creates sickle hemoglobin, or HbS, which causes red blood cells to deform under low oxygen.
This disease is inherited in a specific way. A person needs two copies of the mutated HBB gene, one from each parent, to have the disease.
“Sickle cell disease is a prime example of a genetic disorder where understanding the molecular basis has led to significant advances in diagnosis and treatment.”
This knowledge has been key in creating tests and treatments.
Different Types and Their Severity
Sickle cell disease has several types, each with its own level of severity. The most severe is sickle cell anemia (HbSS), where a person has two HbS genes. Other types, like HbSC disease and HbS beta-thalassemia, are less severe but can also cause health problems.
- HbSS (Sickle Cell Anemia): The most severe form, characterized by frequent episodes of pain and increased risk of infections and organ damage.
- HbSC Disease: Generally milder than HbSS, but can also cause health issues, including vision problems and increased risk of certain infections.
- HbS Beta-Thalassemia: The severity can vary depending on whether the individual has one or no normal beta-globin gene.
The severity of sickle cell disease can differ a lot among people. This is because of genetic factors and the environment. Knowing these differences is key to managing the disease well.
Is Sickle Cell Fatal? Understanding the Life-Threatening Nature

Sickle cell disease has many serious aspects. It can cause sudden and long-term problems. These issues can be deadly if not treated right away.
Acute Life-Threatening Complications
Acute problems from sickle cell disease can happen fast. They can be very dangerous. These include:
- Acute chest syndrome, a condition that can lead to respiratory failure
- Stroke, which can result from the sickling of red blood cells in blood vessels
- Severe infections, mainly those caused by encapsulated bacteria
- Splenic sequestration, where red blood cells accumulate in the spleen
Acute chest syndrome is very dangerous. It can quickly lead to breathing problems. Symptoms include chest pain, cough, and trouble breathing, often with fever and an abnormal chest X-ray.
Chronic Progressive Damage
Chronic damage is another serious part of sickle cell disease. Over time, sickling can harm different organs. This includes:
- The kidneys, potentially resulting in chronic kidney disease
- The liver, leading to dysfunction and potentially cirrhosis
- The heart, contributing to conditions such as pulmonary hypertension
Chronic kidney disease is a big worry. It can lead to needing dialysis or a transplant.
Risk Factors That Increase Mortality
Some factors can make sickle cell disease more deadly. These include:
- A history of severe or recurrent acute chest syndrome
- Previous stroke or other significant cerebrovascular events
- High levels of certain biomarkers indicative of inflammation or organ damage
A study in a medical journal found something important. “Early identification and management of these risk factors are key to lowering death rates in sickle cell disease.”
“The management of sickle cell disease needs a full approach. This includes prevention, quick treatment of acute problems, and ongoing checks for chronic damage.”
Understanding sickle cell disease helps doctors manage it better. This can lessen its deadly effects.
Global Burden of Sickle Cell Disease Mortality
Sickle cell disease has a big impact on death rates worldwide. It’s a major health issue, affecting millions and causing many deaths each year.
Worldwide Annual Death Toll
About 7.74 million people live with sickle cell disease globally. The number of deaths from it is high, with many reported every year. A study by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation shows it’s more deadly than thought, stressing the need for better awareness and care.
It’s hard to know the exact death toll from sickle cell disease worldwide. But it’s clear it has a big impact, mainly in areas with poor healthcare access.
Geographic Distribution of Mortality
The death rate from sickle cell disease varies by region. It’s more common in some areas, like sub-Saharan Africa, where the disease-causing gene is more common.
In these areas, poor healthcare and other health issues make the disease’s impact worse. Countries with better healthcare systems see lower death rates thanks to better care and treatments.
Key regions affected by sickle cell disease include:
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- India
- Middle East
- Parts of South America
Knowing the global impact of sickle cell disease is key to fighting it. We need effective strategies to lower death rates and improve life for those with the disease.
Sickle Cell Disease Mortality in the United States
Sickle cell disease in the U.S. shows different patterns in death rates by age and ethnicity. It’s a big health problem, with death rates affected by age, race, and ethnicity.
Current Death Rates and Statistical Trends
Recent studies show sickle cell disease is a major killer in the U.S. Most deaths happen in adults aged 25 to 54. Death rates have stayed mostly the same, with some changes due to better medical care and population shifts.
Statistical trends indicate progress in lowering death rates with better healthcare. Yet, some groups face higher death rates. This shows the need for focused efforts and better healthcare access for these communities.
Age Distribution of Fatalities
Deaths from sickle cell disease in the U.S. show a worrying trend. Most deaths are among adults aged 25 to 54. This means the disease hits hard during people’s working years.
This age group’s mortality is due to disease complications like organ failure, acute chest syndrome, and stroke. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing these outcomes.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Outcomes
Racial and ethnic disparities in sickle cell disease outcomes are clear in the U.S. People of African descent face higher death rates than others.
These disparities come from genetic, socioeconomic, and healthcare access factors. It’s vital to tackle these issues to lower sickle cell disease mortality.
The data highlight the need for ongoing research, better healthcare access, and targeted efforts. These are essential to lessen sickle cell disease’s impact on at-risk groups.
Leading Causes of Death in Sickle Cell Disease Patients
It’s important to know what causes death in sickle cell disease patients. This disease affects how the body makes hemoglobin, leading to abnormal red blood cells. These cells can cause serious health problems, including acute and chronic issues that can be deadly.
Acute Chest Syndrome
Acute chest syndrome (ACS) is a big problem for sickle cell disease patients. It shows up as a new lung issue on X-rays, often with fever, breathing trouble, or chest pain. ACS can quickly get worse, leading to serious breathing problems that can be fatal.
Stroke and Cerebrovascular Complications
Stroke is a major killer in sickle cell disease. The disease can cause strokes by blocking or bursting blood vessels. Quick treatment is key to avoid serious harm or death from a stroke.
Infections and Sepsis
People with sickle cell disease are more likely to get infections because their spleen doesn’t work right. These infections can turn into sepsis, a deadly condition. Sepsis is a big reason why these patients die.
Organ Failure and Multiple Organ Dysfunction
Long-term damage from sickle cell disease can harm organs like the kidneys, heart, and lungs. This damage can lead to organ failure, which is a big reason for death. Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) is a severe condition that can happen when organs fail, making death more likely.
| Cause of Death | Description | Impact on Mortality |
| Acute Chest Syndrome | Characterized by new pulmonary infiltrate, often with fever or respiratory symptoms. | High risk of respiratory failure. |
| Stroke and Cerebrovascular Complications | Includes ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes due to sickling of red blood cells. | Significant morbidity and mortality. |
| Infections and Sepsis | Increased risk due to hyposplenism; can lead to life-threatening sepsis. | Major cause of mortality. |
| Organ Failure and Multiple Organ Dysfunction | Progressive organ damage from chronic hemolysis and vaso-occlusive crises. | Contributes to high mortality rates. |
Sickle Cell Anemia: The Most Severe and Potentially Deadly Variant
Sickle cell anemia is the most severe form of SCD. It has high mortality rates and severe complications. This genetic disorder affects hemoglobin production, causing abnormal red blood cells.
Why HbSS Has Higher Mortality Rates
HbSS is the most severe form of SCD. It happens when you inherit two abnormal hemoglobin genes, one from each parent. This leads to more abnormal hemoglobin, causing red blood cells to sickle more often and severely.
The higher mortality rates associated with HbSS are also due to more severe complications. Patients with HbSS face severe anemia, pain episodes, and increased infection risk. These can be life-threatening if not managed well.
Specific Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia leads to many complications that affect life quality and expectancy. Some major complications include:
- Acute chest syndrome, a condition that can lead to respiratory failure
- Stroke and other cerebrovascular events
- Severe infections and sepsis due to spleen dysfunction
- Organ damage, including to the kidneys, liver, and heart
These complications are life-threatening and need immediate medical attention to prevent long-term damage.
Comparing Death Rates Across Different Variants
Comparing death rates across SCD variants shows HbSS has a significantly higher rate. Studies show that HbSS has a higher risk of death than other SCD forms, like HbSC or HbSβ+ thalassemia.
The severity of the disease and complication frequency are key factors. While other variants may have milder symptoms, HbSS has severe manifestations and a higher risk of life-threatening events.
In conclusion, sickle cell anemia is the most severe and potentially deadly variant of SCD. Its high mortality rates are due to its severe nature and complications. Understanding these differences is vital for managing patient expectations and developing treatment plans.
Life Expectancy and Survival Rates for Sickle Cell Patients
Thanks to better medical care, sickle cell disease patients are living longer. In the past, life expectancy was much lower. Now, thanks to new treatments, many are living into their forties and beyond.
Historical Improvements in Survival
Years ago, sickle cell disease often led to death in early childhood. But, advances in medical care have greatly increased life expectancy. Newborn screening and treatments like hydroxyurea have helped a lot.
These changes mean sickle cell patients are living longer. What was once a death sentence in the early twenties is now a chance to live into the forties. This shows how well modern treatments work.
Early diagnosis and good care are key to survival. Also, access to specialized care and managing complications are very important. These factors help determine how long a patient can live.
Prognosis and Quality of Life with Sickle Cell Disease
The outlook for sickle cell disease patients varies a lot. This depends on healthcare access and disease severity. Knowing these factors helps manage hopes and improve life quality.
Factors That Influence Long-Term Prognosis
Many things affect the long-term outlook for sickle cell disease patients. These include:
- Access to Complete Care: Regular doctor visits and specialized care can greatly help.
- Disease Severity: How often and how bad the crises are matters a lot.
- Presence of Complications: Issues like organ damage or stroke can make things worse.
- Genetic Factors: Some genetic traits can change how the disease progresses and reacts to treatment.
Predictors of Better Outcomes
Even with sickle cell disease’s challenges, some things lead to better results. These include:
- Early Diagnosis and Action: Finding the disease early helps start treatments sooner, improving life quality.
- Effective Management of Symptoms: Handling pain crises and symptoms well helps with daily life.
- Preventive Care: Getting regular shots and antibiotics lowers infection risks.
Managing Expectations and Planning for the Future
It’s key to manage hopes and plan for the future with sickle cell disease. This means:
- Creating a Personalized Care Plan: Working with doctors to make a plan just for you.
- Staying Informed: Keeping up with new treatments and research.
- Building a Support Network: Connecting with loved ones and support groups.
By knowing what affects prognosis and taking action, sickle cell disease patients can better their life quality. They can also manage their condition well.
Childhood vs. Adult Mortality in Sickle Cell Disease
It’s important to know how sickle cell disease affects children and adults differently. This genetic disorder changes how the body makes hemoglobin, leading to sickle-shaped red blood cells. These cells can cause many health problems.
Pediatric Mortality: Causes and Prevention
Children with sickle cell disease face serious risks like acute chest syndrome, stroke, and infections. These can be deadly and need quick medical help.
- Acute Chest Syndrome: A big risk for kids, it shows up as a new lung problem on X-rays.
- Stroke: Kids with sickle cell are more likely to have strokes, which can harm their brains.
- Infections: Kids are more prone to infections because their immune systems are not fully grown and sickle cell affects their spleen.
To prevent these problems, kids should get regular check-ups, vaccines, and penicillin to stop infections.
Transition to Adult Care: A Critical Period
When kids with sickle cell disease grow up, they face a big change. They might not get the care they need, which can lead to serious issues.
“The transition to adult care is a vulnerable time for patients with sickle cell disease, requiring coordinated efforts from healthcare providers to ensure continuity of care.”
Good transition programs can help. They should include education, counseling, and support to keep patients safe and healthy.
Adult-Specific Mortality Concerns
Adults with sickle cell disease have their own risks, like organ damage, chronic pain, and mental health problems. These can really hurt their quality of life and how long they live.
- Organ Damage: The disease can harm organs like the kidneys, liver, and heart over time.
- Chronic Pain: Adults often deal with ongoing pain from sickle cell crises, which can make life hard.
- Mental Health: The long-term effects of sickle cell disease can lead to depression and anxiety.
Dealing with these issues needs a full care plan. It should cover both the body’s health and the mind.
The Impact of Early Diagnosis on Survival Rates
Early diagnosis has changed how we manage sickle cell disease, leading to better survival rates. Newborn screening programs are key in this success. They help doctors catch and treat the disease early.
Newborn Screening Programs and Their Effectiveness
Newborn screening for sickle cell disease is common in many places, like the United States. It lets doctors start care right away. This cuts down on serious problems and boosts long-term health.
Key benefits of newborn screening include:
- Early identification of affected individuals
- Prompt initiation of preventive care
- Education for families on managing the condition
Preventive Interventions in Early Childhood
Preventive steps are vital in managing sickle cell disease. Early childhood is when these steps are most important. Some key actions include:
- Penicillin prophylaxis to prevent infections
- Regular follow-up with a hematologist
- Education on signs of complications and when to seek medical help
How Early Detection Changes Long-Term Outcomes
Early detection and preventive steps greatly improve long-term health for sickle cell disease patients. They lower the risk of serious problems. This leads to better survival rates and a better quality of life.
| Outcome | Early Diagnosis | Late Diagnosis |
| Survival Rate | Improved | Reduced |
| Complication Rate | Lower | Higher |
| Quality of Life | Enhanced | Reduced |
In conclusion, early diagnosis through newborn screening is vital. It boosts survival rates and improves life quality for sickle cell disease patients. Early intervention makes a big difference.
Treatment Advances and Their Effect on Reducing Mortality
New treatments have greatly helped lower death rates in Sickle Cell Disease patients. The way we manage Sickle Cell Disease has changed a lot. Now, we focus more on helping patients live longer and better lives.
Standard Treatments and Their Impact on Survival
For Sickle Cell Disease, treatments like pain relief, blood transfusions, and antibiotics are key. These help manage the disease and increase chances of survival. Early treatment and full care are very important in cutting down death rates.
For example, regular blood transfusions can lower the risk of stroke and other serious problems. Also, antibiotics are essential in fighting off infections, a big killer in SCD patients.
Hydroxyurea and Disease-Modifying Therapies
Hydroxyurea is a therapy that helps reduce painful crises and may lower the risk of other issues. Studies have shown it can make a big difference in survival for adults with SCD.
New treatments like voxelotor are also being looked into. They aim to improve hemoglobin levels and reduce hemolysis. These treatments give SCD patients new hope for better outcomes.
Curative Approaches: Stem Cell and Gene Therapy
Stem cell transplantation and gene therapy could be cures for Sickle Cell Disease. Stem cell transplantation replaces the patient’s bone marrow with healthy marrow from a donor, effectively curing the disease.
Gene therapy tries to fix the genetic problem that causes SCD. Recent breakthroughs in gene editing, like CRISPR/Cas9, show promise in early studies. They could offer a cure for SCD.
The following table summarizes the key treatment advances and their impact on reducing mortality in Sickle Cell Disease:
| Treatment | Impact on Mortality | Key Benefits |
| Standard Treatments (Pain Management, Blood Transfusions, Antibiotics) | Reduced risk of infections and other complications | Improved survival rates, better disease management |
| Hydroxyurea | Reduced frequency of painful crises, improved survival | Decreased risk of complications, improved quality of life |
| Stem Cell Transplantation | Potential cure, significantly improved survival | Elimination of SCD symptoms, cure |
| Gene Therapy | Potential cure, correction of genetic defect | Long-term cure, elimination of SCD symptoms |
In conclusion, new treatments for Sickle Cell Disease have been key in lowering death rates. From basic treatments to new options like stem cell and gene therapy, these advances bring hope for better lives for patients.
Conclusion: The Changing Landscape of Sickle Cell Disease Mortality
The way we view sickle cell disease mortality is changing. Thanks to better medical care, more people are living longer. This has greatly reduced the number of deaths.
It’s important to know the genetic basis and types of sickle cell disease. This knowledge helps us tackle its deadly nature. The world faces a big challenge with SCD mortality, with big differences in outcomes depending on where you are.
There’s a clear trend of fewer deaths from SCD, mainly in places with top-notch medical care. Early detection, prevention, and new treatments are key to this positive change.
As doctors and researchers keep working, the outlook for SCD patients is getting better. The question “is sickle cell deadly” is slowly getting a less scary answer. This is thanks to the progress in managing the disease.
FAQ
Is sickle cell disease fatal?
Sickle cell disease can be fatal. The risk depends on the disease’s type and severity. It also depends on the quality of medical care received.
Can sickle cell disease kill you?
Yes, it can. Life-threatening complications like acute chest syndrome, stroke, and infections can occur. These can be deadly if not managed well.
What is the mortality rate for sickle cell disease?
The death rate varies worldwide. In the U.S., people with sickle cell anemia often die between 40 to 50 years old.
How does sickle cell anemia affect life expectancy?
It can shorten life expectancy. But, thanks to better medical care, some live into their 50s and 60s.
What are the leading causes of death in sickle cell disease patients?
Deaths are often due to acute chest syndrome, stroke, infections, and organ failure. These can be caused by infections, dehydration, and environmental factors.
Can early diagnosis improve survival rates for sickle cell disease?
Yes, it can. Early detection through newborn screening helps. It allows for early interventions and preventive measures like vaccinations and antibiotics.
What is the impact of hydroxyurea on mortality rates in sickle cell disease?
Hydroxyurea can lower death rates. It reduces painful crises, acute chest syndrome, stroke risk, and other complications.
Are there any curative approaches for sickle cell disease?
Yes, there are. Stem cell and gene therapy are being developed. They show promise in clinical trials, aiming to improve survival and quality of life.
How does the transition to adult care affect mortality rates in sickle cell disease?
The transition to adult care is critical. It can increase the risk of complications and death. This is due to changes in healthcare providers and treatment plans.
What are the predictors of better outcomes in sickle cell disease?
Better outcomes depend on early diagnosis, proper medical care, treatment adherence, and a healthy lifestyle. Avoiding smoking and maintaining a healthy weight are key.
Can sickle cell disease be managed to improve quality of life?
Yes, it can. Proper medical care and lifestyle changes help manage the disease. This reduces the risk of complications and death, improving quality of life.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). Data and statistics on sickle cell disease. https://www.cdc.gov/sickle-cell/data/index.html




































