A cardiac stress test is a common medical test. It checks how well the heart works when you’re active. It looks at heart rate, blood pressure, and electrical activity.
During a stress test, patients walk on a treadmill or pedal a stationary bike to increase the heart’s workload. This helps see how the heart functions under stress. The treadmill stress test duration can vary depending on a patient’s age, fitness level, and medical condition, but most tests last between 10 and 15 minutes of active exercise. Understanding how long the test takes”and why”is important for preparing and ensuring accurate heart health results.
Key Takeaways
- A cardiac stress test evaluates heart function during physical activity.
- The test measures heart rate, blood pressure, and electrical activity.
- It helps diagnose and monitor heart conditions.
- The test duration can vary based on individual health and fitness levels.
- Understanding the test’s significance is vital for heart health assessment.
Understanding Cardiac Stress Tests
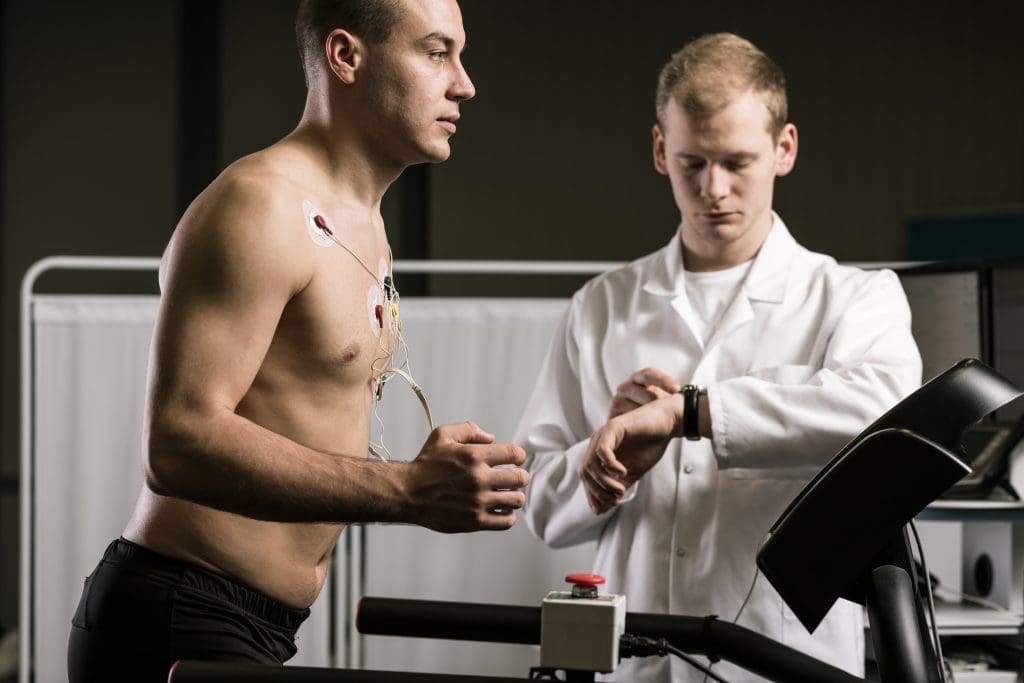
A cardiac stress test, also known as a stress test or treadmill test, checks how well the heart works when it’s under stress. This test is key for finding and checking heart problems.
Definition and Purpose of Stress Testing
The main goal of stress testing is to see how the heart performs under stress. This stress is usually from exercise or medicine. It helps spot heart issues like coronary artery disease and arrhythmias by watching the heart’s electrical activity and blood flow.
A cardiologist, says, “Stress tests are very important for checking a patient’s heart health and finding the best treatment.” The test shows how well the heart can handle more work. This helps find problems early.
Why Physicians Order Stress Tests
order heart stress tests for many reasons. They use them to figure out chest pain, see how bad heart disease is, and check if treatments are working. They also help find out a patient’s risk for heart problems and create a good exercise plan.
“The cardiac stress test is a cornerstone in the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular diseases, providing insights that guide treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes.”
Conditions Diagnosed Through Stress Testing
Stress testing helps find many heart problems, including:
- Coronary artery disease
- Arrhythmias
- Heart valve problems
- Cardiac ischemia
Understanding a stress test result helps make better treatment plans. This improves patient care and results.
Types of Cardiac Stress Tests
Cardiac stress tests are designed to check how well the heart works under stress. They help find and manage heart disease. These tests show how the heart performs during physical activity.
Exercise Stress Tests
Exercise stress tests are the most common. You walk on a treadmill or bike while your heart is monitored. This test checks how your heart handles the extra blood and oxygen needed during exercise.
Nuclear Stress Tests
Nuclear stress tests use exercise or medicine and nuclear imaging. A tiny amount of radioactive material is given to see how well your heart gets blood. It’s great for spotting areas where blood flow is low.
Pharmacological Stress Tests
Pharmacological stress tests are for those who can’t exercise well. Medicine is given to make the heart work like it does during exercise. This test is often paired with nuclear imaging or echocardiography.
Stress Echocardiograms
Stress echocardiograms use ultrasound to look at the heart before and after stress. can see how well the heart muscle works. They can also find any problems that might mean coronary artery disease.
Knowing about the types of cardiac stress tests helps patients understand their diagnostic journey. Each test has its own purpose and gives important info about the heart’s stress performance.
The Treadmill Stress Test Protocol
The treadmill stress test is key in checking heart health. It uses a set plan to test how well the heart works when stressed. The goal is to see how the heart handles more intense exercise.
Bruce Protocol
The Bruce protocol is a top choice for these tests. It makes the treadmill go faster and steeper every few minutes. This method is great for checking how well the heart works.
Modified Bruce Protocol
For those who can’t handle the full Bruce test, there’s a modified version. It starts easier and gets harder, fitting better for people with health issues.
Naughton Protocol
The Naughton protocol is used for those needing a slower increase in exercise. It has smaller steps up in intensity compared to the Bruce protocol.
Other Common Protocols
Other tests like the Balke and ramping protocols are also used. The right one depends on the patient’s health, the test’s purpose, and the doctor’s choice.
Knowing about these protocols helps patients get ready for their tests. It also lets them know what to expect during the test.
How Long Does a Stress Test Take: Complete Procedure Timeline
The time it takes for a stress test can vary. It includes several key parts that affect its length. “A stress test usually takes 1-2 hours,” medical experts say. This includes getting ready and recovering afterwards.
Pre-Test Preparation Time
Before starting the test, there’s a lot to do. This includes setting up equipment, explaining the test, and making sure safety measures are in place. Preparation takes about 15-30 minutes.
Exercise Portion Duration
The exercise part of the test is very important. It lasts 10-15 minutes. During this time, the patient’s heart rate is watched while they exercise on a treadmill. The workout gets harder to reach the right heart rate.
Recovery Period
After exercising, the patient needs time to rest. This is when their vital signs are checked as they calm down. This period can be 5-15 minutes, depending on how fast their heart rate goes back to normal.
Total Time Commitment
Adding up preparation, exercise, and recovery, a stress test usually takes 1-2 hours. It’s important for patients to plan ahead. The exact time can change based on the patient and the test’s details.
A cardiology expert notes, “Knowing the whole process and being ready can really help. It makes the experience less stressful for the patient.”
Average Treadmill Time by Age Group
The time you can stay on a treadmill during a stress test changes with age. This change is because of your fitness, health, and how your heart works as you get older.
Performance Expectations for 20-40 Year Olds
People between 20 and 40 usually do well on treadmill tests. A healthy man in this age can last 9 to 12 minutes. Women usually last 8 to 11 minutes.
Performance Expectations for 40-60 Year Olds
Those aged 40 to 60 tend to do less well on treadmill tests. This is because they naturally get less fit and may have health problems. Men might last 7 to 9 minutes, and women 6 to 8 minutes.
Performance Expectations for 60+ Year Olds
People over 60 usually don’t last as long on treadmill tests. This is because their heart health and fitness decline with age. They might last 5 to 7 minutes, depending on their health and fitness.
Gender Differences in Test Duration
Men generally last longer on treadmill tests than women, across all ages. But, fitness level, health, and hormones also play a role.
| Age Group | Average Treadmill Time for Males (minutes) | Average Treadmill Time for Females (minutes) |
| 20-40 | 9-12 | 8-11 |
| 40-60 | 7-9 | 6-8 |
| 60+ | 5-7 | 5-7 |
Factors Affecting Stress Test Duration
Stress test duration varies based on several factors. These include physical fitness and existing medical conditions. Knowing these can help you prepare better for your test.
Physical Fitness Level
Your physical fitness level greatly affects how long you can last on a treadmill stress test. Fitter people usually do better and last longer. Regular cardio exercise boosts endurance, helping with the test.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Underlying medical conditions can greatly impact your test duration. Heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory issues can affect your performance. It’s important to share your medical history with your doctor before the test.
Medications
Certain medications can change your test results and how long it lasts. For example, beta-blockers can reduce heart rate during exercise, possibly shortening the test. Always tell your doctor about any medications you’re taking.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors like anxiety and stress also play a role. High stress or anxiety can make the test shorter. Deep breathing and visualization can help manage these feelings.
Understanding what affects stress test duration can help you prepare better. Always follow your doctor’s advice and share any medical information to ensure a safe test.
Preparing for Your Treadmill Stress Test
Getting ready for a treadmill stress test is key. It involves diet, mental state, and more. Being well-prepared helps get accurate test results, giving insights into heart health.
Dietary Restrictions
Follow dietary tips before the test. Avoid heavy meals and caffeine for 2-3 hours beforehand. This prevents discomfort during the test.
Choose light, balanced meals with complex carbs, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Drinking water is important, but don’t drink too much right before the test.
Medication Adjustments
Tell your doctor about any medicines you’re taking. Some, like beta-blockers, might need to be changed or stopped. Always listen to your doctor about medication changes.
Clothing and Footwear Recommendations
Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothes and sturdy shoes for exercise. Don’t wear sandals or flip-flops. Comfortable clothes help you focus on the test.
Mental Preparation
Mental readiness is as important as physical. Knowing what to expect can lower anxiety. Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing or visualization.
Arriving early to do paperwork helps you relax before the test starts.
What to Expect During the Test
Knowing what to expect during a treadmill stress test can make you feel less anxious. It’s a test to see how well your heart works when you’re stressed, usually by exercising.
Initial Setup and Monitoring Equipment
First, you’ll be hooked up to some monitoring gear. You’ll have ECG electrodes on your chest to watch your heart’s electrical signals. Also, a blood pressure cuff will track your blood pressure. This setup is key for getting accurate results during the test.
Starting the Exercise
The test starts with a slow pace on the treadmill. You’ll start walking, and the speed and incline will get harder as you go. This is to stress your heart and see how it performs.
Increasing Difficulty Levels
The treadmill gets harder as you keep going. It might go faster or get steeper. The aim is to get your heart rate up to a certain level. The person running the test will keep an eye on you and adjust the treadmill as needed.
When and Why the Test Ends
The test ends when you hit your target heart rate, show signs of distress, or finish the set plan. It might stop if you have chest pain, can’t breathe well, or if your blood pressure gets too high. The whole test usually takes between 7 to 14 minutes, including the time to recover.
Signs of a Successful Stress Test Completion
Knowing the signs of a successful stress test can help understand heart health. A test is seen as successful when it meets certain criteria. This shows the heart works well under stress.
Target Heart Rate Achievement
Reaching the target heart rate is key to a successful test. This rate is based on age and fitness. Achieving this target heart rate shows the heart can handle physical stress well. A cardiology expert says, “Reaching the target heart rate is vital. It lets us check the heart’s function under stress.”
“The heart rate response to exercise is a critical component of the stress test, providing valuable information about cardiovascular health.”
Cardiology Expert
Metabolic Equivalent (MET) Levels
Metabolic equivalent (MET) levels are also important. They show how much energy an activity uses. A higher MET level achieved during the test means better heart fitness. For example, reaching 10 METs or more shows good heart health.
Symptoms vs. Duration Considerations
Reaching the target heart rate and high MET levels are important. But, not feeling bad during the test is also key. The test is considered successful if the individual completes it without experiencing concerning symptoms like chest pain or dizziness. How long the test lasts also matters. A longer test usually means better heart health.
In summary, a successful stress test shows a few things. It means reaching the target heart rate, high MET levels, and no bad symptoms. These signs together give a full picture of heart health.
Understanding Stress Test Results
Stress tests are key to checking heart health. They show how well the heart works under stress. use this info to find problems and choose the right treatment.
Normal vs. Abnormal Findings
Stress test results can be normal or abnormal. Normal results mean the heart is okay under stress. Abnormal results might show heart issues. These can include chest pain, breathing trouble, or irregular heartbeats.
Knowing if results are normal or abnormal is very important. A normal test means low heart disease risk. But an abnormal test might need more tests or doctor visits.
ECG Changes During Exercise
ECG changes are a big part of stress test results. ECG monitoring tracks the heart’s electrical activity before, during, and after exercise. Big changes can mean heart disease or other heart issues.
Heart Rate Recovery Metrics
Heart rate recovery is key to heart health. Heart rate recovery is how fast the heart rate goes back to normal after exercise. A slow recovery can mean a higher risk of heart disease.
| Heart Rate Recovery Time | Interpretation |
| Less than 12 beats per minute | Normal |
| 12-22 beats per minute | Borderline |
| More than 22 beats per minute | Abnormal |
Exercise Capacity Interpretation
Exercise capacity is measured in METs. METs show how well someone can do physical activities. A higher MET score means better heart health.
- Low exercise capacity (<5 METs): High risk
- Moderate exercise capacity (5-8 METs): Moderate risk
- High exercise capacity (>8 METs): Low risk
Special Considerations for Seniors and Treadmill Testing
Seniors need special care during treadmill tests because of age-related changes. As people get older, their physical abilities and health can affect how well they do on a treadmill test.
Modified Protocols for Older Adults
Older adults can’t handle the usual Bruce Protocol in treadmill tests. So, modified protocols are used for them. These changes might include:
- Reduced initial intensity
- Slower increase in exercise intensity
- Shorter test time
These adjustments make sure the test is safe and works well for older adults.
Safety Precautions
Keeping seniors safe during treadmill tests is key. Several safety precautions are taken:
| Safety Measure | Description |
| Continuous Monitoring | Watching vital signs and ECG readings all the time during the test. |
| Emergency Preparedness | Having emergency gear and trained people ready. |
| Pre-Test Screening | Checking the patient’s medical history before the test. |
Alternative Testing Options
For seniors who can’t do a regular treadmill test, alternative testing options are there. These include:
- Pharmacological stress tests
- Stress echocardiograms
- Nuclear stress tests
These options let check heart function without needing to run on a treadmill.
Improving Your Stress Test Performance
To do better on a treadmill stress test, you need to work on cardiovascular conditioning and change your lifestyle. These steps can really boost your endurance and test scores.
Cardiovascular Conditioning Strategies
Good cardiovascular health is key for a stress test success. Start with regular aerobic activities like fast walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming. Try to do at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of intense exercise each week.
Adding interval training to your routine can also help. This method mixes high-intensity workouts with rest periods. It makes your heart work better and boosts your stamina.
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing your lifestyle can also help your stress test results. Eat a healthy diet full of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean meats. Stay away from tobacco products and drink less alcohol.
Also, sleep well and manage stress. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night. Try stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga to keep your stress levels down.
Realistic Expectations for Improvement
Setting realistic expectations is important when trying to improve your stress test results. Bettering your heart health and endurance takes time, usually weeks or months.
Talk to your doctor to make a plan that fits your health and goals. They can suggest safe and effective ways to improve your performance.
When a Treadmill Stress Test May Be Terminated Early
The safety of the patient is always the top priority. A treadmill stress test might end early if the patient shows concerning symptoms. Several factors can prompt this decision.
Concerning Symptoms During Testing
During a treadmill stress test, watch for symptoms that mean it’s time to stop. These symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Severe shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Severe fatigue
- Pain or discomfort in the legs or arms
If any of these symptoms show up, the test will likely end early to keep the patient safe.
Significant ECG Changes
Electrocardiogram (ECG) changes are key during a stress test. Big changes can show heart problems under stress. For example:
- ST-segment depression or elevation
- T-wave inversion
- Arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia
Blood Pressure Abnormalities
Abnormal blood pressure during exercise can also cause an early stop. This includes:
- Hypertensive response (very high blood pressure)
- Hypotensive response (low blood pressure)
- Failure of blood pressure to rise with increasing exercise intensity
These signs can point to heart problems.
Patient Request or Inability to Continue
At times, a patient might want to stop the test due to discomfort. Or, if they can’t keep going because of physical issues, the test will end early.
In summary, ending a treadmill stress test early is a careful decision. It’s based on the patient’s symptoms, ECG changes, blood pressure, and comfort. Keeping the patient safe is the main goal.
Conclusion
Knowing how long you’ll last on a treadmill stress test is key. This article has covered everything you need to know about cardiac stress tests. It includes what they are, why they’re done, and the different types.
It’s important to remember that your age, fitness level, and health can affect how long you’ll last. We talked about the Bruce Protocol and other common tests. We also looked at how to prepare for the test and what to do after.
In short, knowing about treadmill stress tests can help you prepare better. It helps you understand what to expect and how to do your best. By understanding the factors that affect your test, you can improve your experience.
FAQ
What factors affect stress test duration?
Many things can change how long a stress test takes. These include how fit you are, any health issues, your meds, and your mindset. All these can affect your test results.
What is the average treadmill time for different age groups?
Younger people usually do better on treadmill tests than older ones. Men often do better than women, too.
When is a treadmill stress test terminated early?
A treadmill stress test can stop early if you have bad symptoms or heart changes. It can also stop if your blood pressure gets too high or if you can’t keep going.
How can I improve my stress test performance?
To do better on a stress test, work on your heart health. Make lifestyle changes and set achievable goals for improvement.
Can seniors undergo treadmill testing?
Yes, seniors can do treadmill tests. But, they might need special safety steps and tests because of health issues.
How are stress test results interpreted?
Stress test results are checked for normal or abnormal signs. This includes heart rate changes and how well you exercise. These clues help understand your heart health.
What are the signs of a successful stress test completion?
A successful stress test shows you reached your heart rate goal. You also need to meet certain metabolic levels. And, you should finish without bad symptoms or heart changes.
What happens during a stress test?
During a stress test, you’ll be hooked up to monitoring gear. You’ll exercise on a treadmill that gets harder. You’ll be watched for symptoms and heart changes until it ends.
How do I prepare for a treadmill stress test?
To get ready for a treadmill stress test, follow certain diet rules. Also, adjust your medications as told. Wear comfy clothes and shoes. And, get mentally ready for the exercise.
What are the different types of cardiac stress tests?
There are many types of cardiac stress tests. These include exercise stress tests, nuclear stress tests, and stress echocardiograms. Each has its own purpose.
How long does a stress test take?
A stress test usually takes about 1-2 hours. This includes getting ready, exercising, and resting afterwards.
What is a stress test?
A stress test, also known as an exercise stress test or treadmill test, checks how well the heart works when you’re active. It’s done by exercising on a treadmill.









