Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
When you get a headache or see things blurry, it worries you. At Liv Hospital, we know it’s key to spot brain cyst signs early. This helps us act fast.
A brain cyst can lead to debilitating headaches, feeling sick, and blurry vision. If you’re having these issues, you should see a doctor right away.
We aim to give top-notch healthcare to everyone, including international patients. Our team focuses on you, making sure you get the right treatment for brain cysts.
Cystic formations in the brain are fluid-filled sacs. They can be either benign or malignant. This affects brain function differently. These formations can appear in various parts of the brain. This leads to a range of symptoms and health concerns.
Brain cysts are filled with fluid and may have a membrane or wall. They can be congenital or develop due to trauma, infection, or tumors.
Brain cysts are quite common. Many people have them without major symptoms. But, when symptoms do appear, they can greatly affect daily life.
Distinguishing between benign and malignant cysts is key. Benign cysts are non-cancerous and don’t spread. Malignant cysts, on the other hand, are cancerous and can grow into surrounding brain tissue.
Knowing the type of cystic formation in the brain is vital. It helps determine the right treatment and management plan.
It’s important to know about the different brain cysts for the right treatment. These cysts vary by location, makeup, and other traits. We’ll look at the most common ones, their special features, and symptoms.
Arachnoid cysts are benign fluid-filled lesions found between the brain or spinal cord and the arachnoid membrane. They often don’t cause symptoms but can if they press on nearby nerves. Research shows they’re rare, making up about 1% of brain masses.
Colloid cysts are benign tumors in the third ventricle that might block CSF flow. They have a gelatinous center and are lined with a single layer of cells. Symptoms include headaches, memory issues, and, in severe cases, hydrocephalus.
Dermoid and epidermoid cysts are congenital lesions from ectodermal inclusions during neural tube closure. Dermoid cysts have hair and sebaceous secretions, while epidermoid cysts are filled with keratin debris. Both can cause symptoms due to their size or if they rupture.
Pineal and pituitary cysts are fluid-filled lesions in the pineal and pituitary glands. Pineal cysts usually don’t cause symptoms but can lead to hydrocephalus or Parinaud’s syndrome. Pituitary cysts might be found by chance or cause hormonal issues if they press on the gland.
Each brain cyst type has its own traits and effects on patients. Getting the right diagnosis and treatment is key to avoiding problems and improving health.
Cysts in the frontal lobe can lead to changes in thinking, feeling, and behavior. This is because the frontal lobe plays a key role in these areas. It helps with making decisions, planning, and solving problems. It also affects personality and how we interact with others.
The frontal lobe is a major part of the brain. It handles complex thinking tasks and personality traits. It’s divided into areas, each with its own job. The prefrontal cortex is key for complex thinking and showing our personality.
A cyst in the frontal lobe can make it hard to focus, remember things, and make decisions. People might find it tough to plan and solve problems. Symptoms can include:
Cysts in the frontal lobe can also change how a person acts and feels. These changes can be hard for the person and their family. Some common changes are:
Knowing about these changes is important. It helps in managing the condition and supporting those affected.
When you have persistent or severe headaches, it’s normal to worry about brain cysts. Headaches can be signs of many things, including brain cysts. Knowing what your headaches are like can help figure out if they might be from a brain cyst.
Headaches from brain cysts can be different. They can be persistent and progressive, getting worse over time. The pain might be in one spot or all over, depending on the cyst’s size and where it is.
It’s important to tell cyst-related headaches apart from tension or migraine headaches. Cyst-related headaches are usually more severe. They might also come with other symptoms like weakness or numbness.
“Headaches that are persistent, severe, or accompanied by other neurological symptoms warrant medical evaluation.”
Brain cysts can sometimes cause headaches due to increased pressure inside the skull. These headaches might feel worse in the morning and get better as the day goes on. They can also make you feel sick to your stomach and cause vomiting.
If your headaches are sudden, severe, or come with other scary symptoms like confusion or trouble speaking, get help right away. Quick medical check-ups are key to make sure you don’t have a serious problem.
Brain cysts can lead to vision issues like blurred vision, double vision, and loss of peripheral vision. These problems happen when a cyst presses on or disrupts the visual pathway. This pathway includes the eyes, optic nerves, and brain areas that handle visual information.
People with brain cysts often face various visual problems. Blurred vision is common, caused by pressure on the optic nerves or visual pathway. Double vision, or diplopia, occurs when the cyst impacts nerves controlling eye movement. Some also experience a loss of peripheral vision, making it hard to see objects or movement on the sides.
The visual pathway is complex, involving the eyes, optic nerves, optic chiasm, optic tracts, and the brain’s visual cortex. A brain cyst can disrupt this pathway at different points, based on its location. For example, a cyst near the optic nerves can lead to vision loss or disturbances in one or both eyes. A cyst affecting the optic chiasm can cause specific vision loss patterns, like bitemporal hemianopsia.
Vision changes from brain cysts can be gradual or sudden. Progressive vision loss happens slowly as the cyst grows or changes. On the other hand, sudden vision changes occur quickly, often due to a sudden increase in cyst size or pressure. Sudden vision loss is a medical emergency that needs immediate care.
Certain vision problems need immediate medical attention. These include:
As one medical expert noted,
“Prompt evaluation is key for those with sudden or severe vision changes. Timely action can greatly improve outcomes.”
Brain cysts can cause a range of neurological symptoms. These depend on where and how big the cyst is. Knowing about these symptoms is key to understanding their impact on a person’s life.
Balance and coordination issues are common with brain cysts. If a cyst is near the cerebellum, it can make walking and doing small tasks hard. People might have ataxia, which means they can’t walk steadily or coordinate their movements well.
Seizures and epileptic episodes can happen if a cyst is near brain areas that control movement. The chance of seizures depends on the cyst’s size, location, and how much it irritates the brain.
Speech and language problems can occur if a cyst affects areas like Broca’s or Wernicke’s areas. This can lead to dysarthria (trouble speaking clearly) or aphasia (trouble understanding or speaking).
Cysts near memory centers, like the hippocampus, can cause memory and thinking problems. People might find it hard to remember new things, learn, or recall past events.
| Symptom | Description | Possible Location of Cyst |
|---|---|---|
| Balance and Coordination Problems | Difficulty walking, maintaining posture, and performing fine motor tasks | Cerebellum or its connections |
| Seizures and Epileptic Episodes | Seizures or convulsions | Near or involving areas responsible for motor control |
| Speech and Language Difficulties | Difficulty articulating words or understanding/producing language | Broca’s or Wernicke’s areas |
| Memory and Cognitive Changes | Difficulty forming new memories, learning, or recalling past events | Hippocampus or temporal lobe |
It’s important to know about these symptoms to diagnose and treat brain cysts well. We’ll look at diagnosis and treatment options next.
Brain cyst symptoms can show up in different ways for adults and kids. It’s important to know these differences to get the right treatment. We’ll look at how symptoms change between ages and what it means for care.
Adults and kids with brain cysts have different symptoms. Adults might get headaches, vision issues, and changes in thinking. Kids might see delays in growth, be more irritable, or not grow as expected. Knowing these differences helps in giving the right care.
Brain cysts in kids can slow down growth and development. They might not reach milestones on time, have trouble learning, or act differently. Finding and treating these early is key to avoiding lasting problems.
Older adults with brain cysts might show symptoms like memory loss, trouble walking, or needing to urinate often. These can be mistaken for other age-related issues. A detailed check-up is needed to find the real cause.
The outlook for brain cysts varies with age. Kids and adults usually do better than older adults, who might have other health issues making treatment harder.
“Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve outcomes for brain cyst patients, no matter their age,”
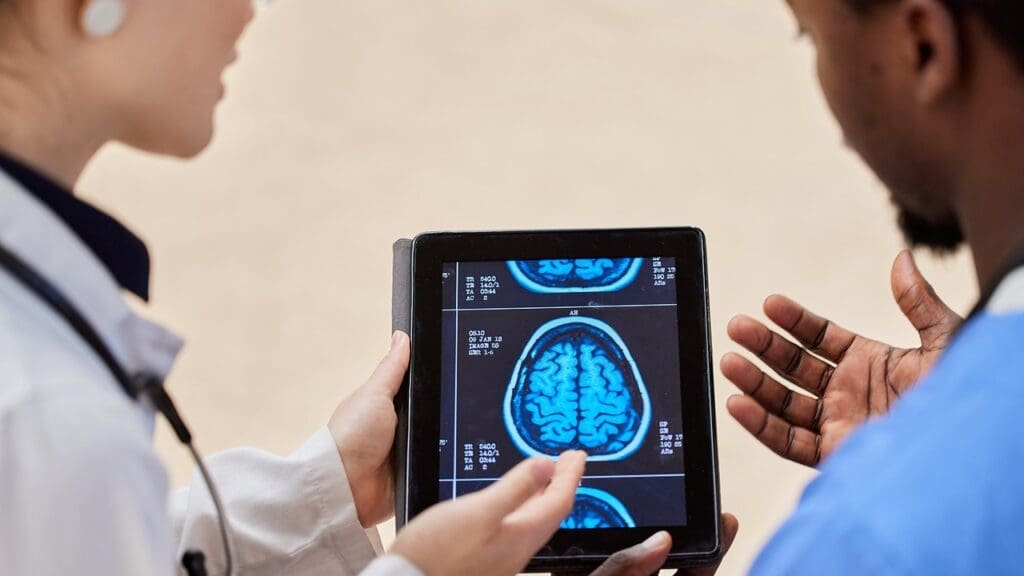
Doctors use advanced imaging to find brain cysts. They look at images and do a physical check-up to diagnose.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is key for finding brain cysts. It shows the cyst’s size, where it is, and what it looks like. MRI is great for seeing soft tissues, like the cyst’s shape and how it fits with other brain parts.
Computed Tomography (CT) scans also help find brain cysts. They spot big cysts and those that push on the brain or cause fluid buildup. CT scans can’t see soft tissues as well as MRI, but they find calcium in cysts or walls.
Radiologists check images for brain cysts for certain things. They look at the cyst’s size, where it is, and how it looks on different scans. They also see how the cyst affects the brain and if there are other problems.
Sometimes, more tests are needed to check a brain cyst. These might include scans with contrast, functional MRI, or even a biopsy if the diagnosis is unclear.
Symptomatic brain cysts need timely and right treatment to ease symptoms and avoid complications. The treatment choice depends on the cyst’s size, location, and the patient’s health.
For small, asymptomatic, or mildly symptomatic cysts, watching and monitoring might be the best first step. This means regular imaging like MRI or CT scans to check the cyst’s size and symptoms. We suggest follow-up imaging every 6 to 12 months, adjusting as needed based on the cyst and patient’s health.
Surgery is considered when the cyst is big, symptomatic, or causing a lot of pressure. There are different surgical methods:
| Surgical Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Craniotomy and cyst removal | Complete removal of the cyst | Invasive, longer recovery time |
| Endoscopic cyst fenestration | Minimally invasive, shorter recovery | Risk of incomplete drainage |
| Stereotactic aspiration | Precise, minimally invasive | Risk of cyst reaccumulation |
While surgery is often needed for many brain cysts, medication is key in managing symptoms. For example, antiepileptic drugs help with seizures, and corticosteroids reduce swelling and inflammation. We customize medication plans for each patient, adjusting as needed based on symptom control and side effects.
New treatments for brain cysts are being researched. New methods include advanced imaging for precise procedures and exploring new drugs to prevent cysts from coming back. We are committed to keeping up with these advancements to provide our patients with the best care.
It’s important to know about the possible problems with brain cysts. Most are harmless and don’t show symptoms. But, some can cause serious health issues.
Several things can make brain cyst complications worse. The size and where the cyst is matter a lot. Also, how healthy you are plays a big role.
Big cysts or ones in important brain spots can cause big problems.
Hydrocephalus is a serious issue with brain cysts. It’s when too much cerebrospinal fluid builds up in the brain. This can make you feel sick, give you headaches, and mess with your vision.
In some cases, brain cysts can cause serious problems. These include seizures, brain damage, and problems with thinking. Getting medical help fast is key to avoiding these issues.
The chance of dying from a brain cyst depends on several things. This includes the type and where the cyst is, and your health. While rare, some cysts can be deadly if not treated right.
| Complication | Risk Factors | Potential Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrocephalus | Large cysts, critical location | Increased intracranial pressure, brain damage |
| Increased Intracranial Pressure | Cyst size, location, patient health | Headaches, nausea, vision problems |
| Seizures | Cyst location, size | Cognitive impairment, brain damage |
It’s important to know when brain cyst symptoms need quick medical help. Brain cysts might have mild symptoms, but some situations are urgent.
Some symptoms are serious and could be life-threatening. Look out for severe headache, sudden vision changes, and seizures. If you see these, get medical help right away.
Brain cysts that cause increased intracranial pressure or hydrocephalus need emergency care. Symptoms like confusion, trouble walking, and losing consciousness are urgent.
When you see a doctor, tell them about your symptoms, medical history, and past diagnoses. This helps doctors make the best plan for you.
After emergency care, follow-up visits are key. They help track your progress and adjust treatment if needed. This might include more tests and talks with specialists.
Living with brain cysts can be tough, but knowing about it helps a lot. Studies show that 12.1% of breast cancer patients get cystic brain metastases. Younger patients and those with aggressive cancer types are more likely to get these cysts.
The outlook for brain cysts depends on several things. This includes the cyst’s size, location, and how well treatment works. Research shows that cystic brain metastases are harder to treat than solid ones. For more details, check out studies on Oncotarget.
Knowing what to expect long-term is key for those with brain cysts. By staying informed and working with doctors, patients can face the challenges better. This helps improve their life quality.
A brain cyst is a fluid-filled sac in the brain. It can be harmless or cancerous. We treat different types, like arachnoid, colloid, and dermoid cysts.
Yes, a brain cyst can lead to headaches. This happens when there’s too much pressure inside the skull. We check if your headaches are from a cyst.
A frontal lobe cyst can affect thinking and emotions. It might make it hard to make decisions or control feelings. We look at how it affects your daily life.
We use MRI and CT scans to find brain cysts. These tests show where, how big, and what kind of cyst it is. Sometimes, we need more tests to know more.
For brain cysts, we might watch and wait, or do surgery. We also use medicine. We’re always looking for new ways to help our patients.
Yes, a brain cyst can be dangerous. It can cause too much pressure or other serious problems. We treat it quickly to avoid serious issues.
Severe headaches, sudden vision changes, and seizures are urgent signs. We tell you when to get help fast and what to tell doctors.
Symptoms can change with age. Kids and adults have different needs. We tailor care to meet each patient’s unique situation.
The future looks different for everyone with brain cysts. It depends on the cyst’s size, location, and how well it’s treated. We support our patients to manage their condition and improve their lives.
Yes, cerebral cysts and brain cysts mean the same thing. They’re fluid-filled sacs in the brain. We use both terms to describe this condition.
Yes, a brain cyst can affect your vision. It might cause blurry or double vision, or make it hard to see on the sides. We treat these vision issues.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!