Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
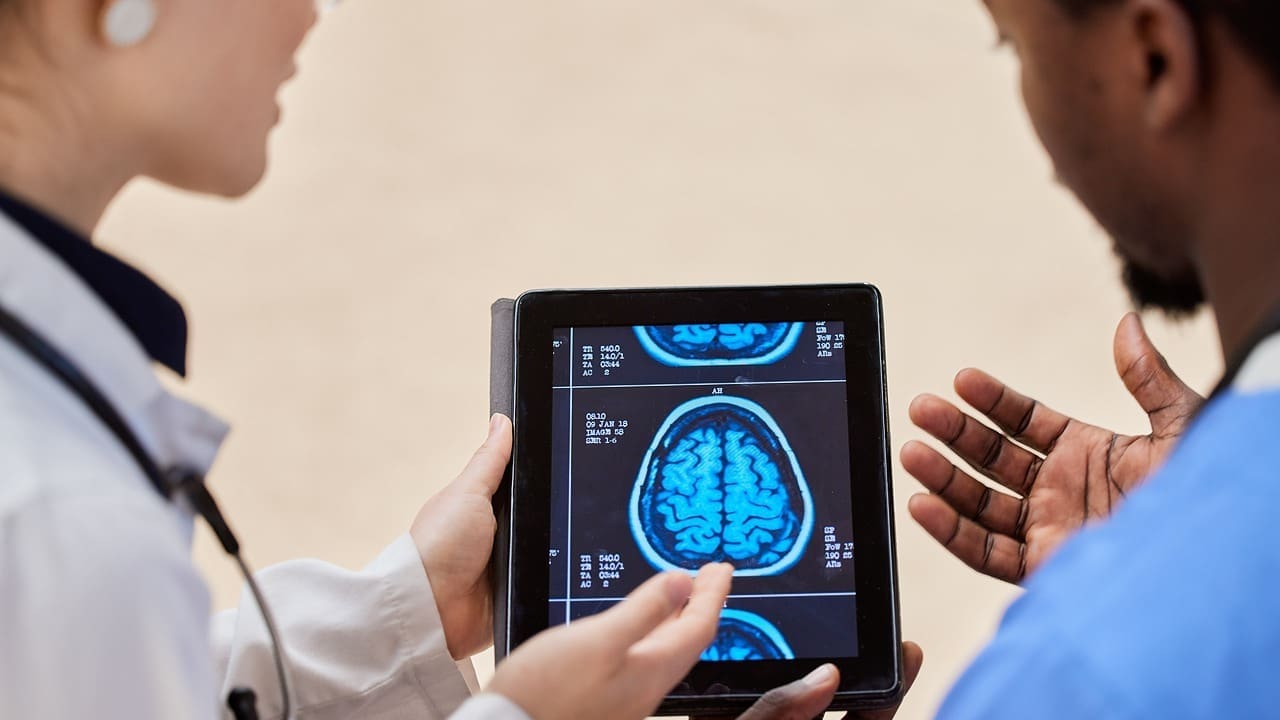
At Liv Hospital, we use the latest technology to find and treat complex health issues. MRI is key in spotting brain damage and past injuries. It’s vital for diagnosing traumatic brain injuries (TBIs).
MRI is known for its high sensitivity. It can find small injuries and damage that CT scans miss. This helps us give our patients the right treatment.
Brain imaging has changed how we diagnose and treat neurological issues. We use two main methods: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scanning. Knowing how these work helps us see their strengths and weaknesses in checking for brain damage.
MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to show brain details. It’s a safe way to see inside the brain without harmful radiation.
The MRI machine creates a strong magnetic field. This field aligns hydrogen atoms in the body. Radio waves then disturb these atoms, sending signals to the MRI for images.
MRI is great at showing different soft tissues. It uses special sequences like T1 and T2 to highlight tissue details. T2 images are best for spotting swelling and lesions.
CT scanning uses X-rays to view the brain. It’s fast and useful in emergencies.
CT scans rotate an X-ray source around the patient. They capture data from many angles. This data is turned into detailed brain images.
CT scans are good at showing differences in density. They’re great for finding bleeding and bone breaks.
Understanding MRI and CT basics helps us see their value in brain injury diagnosis. Each method has its own benefits, chosen based on the situation and needed information.
MRI can show brain damage thanks to its advanced technology. It’s very good at spotting changes in brain tissue. This lets it find different kinds of brain damage.
MRI is very good at finding changes in brain tissue. It can spot many injuries and problems. This is key for seeing the difference between gray and white matter.
MRI can tell gray and white matter apart. This helps find injuries that affect these areas. It’s important for understanding how much damage there is.
MRI can also find edema and inflammation in the brain. These are often seen in traumatic brain injuries.
MRI can show many types of brain damage. Some important findings include:
MRI can spot structural problems caused by brain injuries. This is key for diagnosing and treating patients with brain damage.
In cases of traumatic brain injury, CT scans are often the first choice. They are good at finding acute hemorrhage. We use them because they quickly show how bad the injury is in emergencies.
CT scans have many benefits in acute brain trauma. Rapid assessment capabilities help make quick decisions in urgent situations.
The speed of CT scans is key in emergencies. It lets doctors quickly find and treat serious problems.
CT scans are great at finding acute intracranial hemorrhage. This makes them very useful at first in checking for traumatic brain injuries.
While CT scans are great for acute trauma, they have some downsides. They’re not as good at finding small brain injuries.
CT scans might not show small changes or tiny lesions well. Other imaging like MRI can see these better.
CT scans can also have problems in the posterior fossa. This can hide important details in that area.
We know CT scans are very useful in acute brain trauma. But, their limits show we need a full imaging plan. This might include different types of scans to get a clear diagnosis and plan treatment.
Choosing between MRI and CT scans for traumatic brain injury depends on several factors. These include the need for speed, the level of detail needed, and patient-specific considerations.
In emergency situations, quick diagnosis is key. CT scans are faster and more available than MRI scans. They are often the first choice for acute traumatic brain injury.
CT scans are favored in emergency triage for their speed. They can quickly spot acute hemorrhages and fractures. This quick assessment is vital for immediate care.
While CT scans are quick, MRI is better for certain brain injuries. MRI is great for soft tissue damage. It can spot subtle injuries that CT might miss.
The choice between MRI and CT depends on the injury stage and patient factors.
For acute injuries, CT scans are used first. They’re fast and good at finding immediate threats like hemorrhage. For subacute or chronic injuries, MRI is better. It shows a wider range of injuries and brain tissue details.
Some patients can’t have MRI due to metal implants or pacemakers. CT is safer for them. But, MRI is safer for those with radiation exposure history.
| Imaging Modality | Speed | Detail | Preferred Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| CT Scan | Fast | Good for bone and acute hemorrhage | Acute injury, emergency situations |
| MRI | Slower | Excellent for soft tissue and subtle injuries | Subacute or chronic injuries, detailed assessment |
MRI can now show tiny brain injuries that were hard to see before. It’s better than CT scans at finding these small problems. This helps doctors understand brain damage more fully.
MRI is great at spotting tiny blood spots and small bruises in the brain. These small injuries can really affect how a person feels and acts. MRI’s skill in finding them is key for the right treatment.
Special MRI scans, like Gradient Echo and Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging (SWI), are super good at finding these tiny blood spots. They make it easier for doctors to see how bad the brain damage is.
Finding tiny blood spots in the brain is very important. It shows that the injury might be worse than it seems. This info helps doctors decide the best treatment and predict how well a patient will do.
MRI is also great at spotting changes in white matter and axonal injury. These are common in brain injuries and can affect thinking and memory. Accurate diagnosis is key for good care.
Diffuse axonal injury (DAI) is a serious brain injury that MRI can find. DAI patterns can be different, but MRI can spot even small changes in brain tracts.
Finding white matter changes and axonal injury is very important for knowing how a patient will do in the long run. By understanding the extent of these injuries, doctors can predict cognitive outcomes and plan better treatments.
About 80% of brain injuries, like concussions, can’t be seen on MRI or CT scans. This makes diagnosing them hard. It’s a big problem because it means many people with invisible brain injuries might not get the right treatment.
Concussions can hurt brain function without changing its structure. Metabolic disruption without visible damage is common. Doctors have to rely on how the patient feels and their history to diagnose.
Even if scans don’t show damage, it doesn’t mean there’s no injury. Changes in how the brain works can happen without visible damage. This affects how the brain functions.
Tests that check brain function are key in diagnosing concussions. They help link symptoms to possible brain problems, even if scans look normal.
It’s hard to spot early brain injuries because of imaging tech limits. The temporal evolution of injury visibility means some injuries might not show up right away.
How visible brain injuries are on scans can change over time. Some injuries become clearer as they progress, while others stay hidden.
Scientists are looking into emerging biomarkers to spot invisible brain injuries. These markers could help find damage that scans miss.
As we learn more about brain injuries, we see the need for a detailed approach to diagnose and treat them.
The timing of MRI after brain trauma is very important. It affects how well we can diagnose and treat. We suggest using MRI as a follow-up for patients with ongoing or unclear neurological issues.
Studies show MRI works best within a certain time frame after brain injury. The best time can change based on the injury’s type and severity.
After a brain injury, MRI images can change. Some injuries might show up more clearly as swelling goes down.
Each brain injury type needs a different MRI timing. For example, subtle injuries might need a later MRI for accurate spotting.
Following up with imaging is key for tracking brain injury progress and adjusting treatments. MRI is used for follow-ups to see how healing is going and catch any complications early.
The need for MRI follow-ups varies with injury severity and patient health. Short-term monitoring is often needed for acute injuries. Long-term monitoring might be needed for more subtle or chronic cases.
Sequential imaging lets us see how the brain changes over time. It gives us important insights into recovery and helps us make better care decisions.
MRI technology has changed neurology by finding past brain injuries. We use MRI to see old brain injuries, like scar tissue or shrinking areas. This helps us understand a patient’s brain history and plan treatments.
Brain trauma can cause scar tissue. MRI is great at finding this scar tissue.
Gliosis is a brain reaction to damage. MRI scans show specific patterns of gliosis. Spotting these patterns helps us see the extent of past injuries.
Encephalomalacia, or brain softening, is a sign of injury. MRI can spot this damage in the brain.
Brain atrophy, or shrinking, can show past trauma. MRI lets us check for this atrophy.
By looking at MRI scans, we can find where the brain has shrunk. This is a key sign of past injury.
It’s important to tell apart atrophy from trauma and aging. MRI helps us make this distinction. This is key for correct diagnosis and treatment.
| MRI Findings | Indication |
|---|---|
| Scar Tissue | Past Brain Injury |
| Gliosis Patterns | Reactive Change to CNS Damage |
| Encephalomalacia | Brain Softening Due to Injury |
| Brain Atrophy | Historic Trauma or Aging |
Advanced MRI techniques have changed how we look at brain damage. They give us detailed views of injury extent. These methods help us understand the brain’s complex changes after trauma.
DTI is a top-notch MRI method. It checks the health of white matter tracts. This is key for seeing how much brain damage there is.
DTI lets us look at white matter tracts. These tracts are vital for brain function. Damage here can lead to big problems with thinking and doing things.
DTI gives us numbers on fiber damage. This helps doctors figure out how bad the injury is.
fMRI looks at how brain networks change after injury. It shows how brain function shifts.
fMRI shows changes in brain connections. It tells us how brain damage affects overall brain activity.
This method finds brain areas that help out when others are damaged. It’s useful for planning rehab.
Susceptibility-weighted imaging spots hemosiderin, signs of old bleeding. It’s very useful in checking for brain injury from trauma.
Choosing between MRI and CT scans is a key part of neuroimaging. The decision depends on the situation, the patient’s health, and what the doctor needs to see.
In emergencies, like severe brain injuries, picking the right scan is urgent. CT scans are often first because they’re fast and easy to find.
Triage algorithms help decide which scan to use. For example, those with serious head injuries usually get CT scans. This is because they can quickly spot bleeding.
In emergencies, weighing risks and benefits is key. CT scans have radiation, but they’re fast and can save lives. This makes them worth the risk.
Each patient’s situation affects the choice between MRI and CT. Some patients, like those with metal implants, can’t have MRI.
Age and health conditions also matter. Kids and pregnant women often get MRI instead of CT to avoid radiation.
Younger patients worry about radiation. MRI is safer for them in non-emergency cases.
| Imaging Modality | Emergency Use | Radiation Exposure | Patient Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| CT Scan | Yes, for acute trauma | Yes | Quick, widely available |
| MRI | Limited, due to longer scan times | No | Better for soft tissue, no radiation |
At Liv Hospital, we’re all about top-notch brain imaging services. We aim to set a new benchmark in diagnostic care. Our focus is on providing detailed solutions for patients with brain injuries or disorders.
We use multimodal imaging protocols to get a full picture of the brain. This method combines different imaging techniques. It helps us spot even the smallest changes in brain tissue and find damage.
Our protocols include various MRI sequences like Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging (SWI). These give us deep insights into the brain’s structure and function.
We match imaging results with clinical assessments for accurate diagnoses. This approach helps us create treatment plans that meet each patient’s needs.
Our brain imaging services meet international standards and evidence-based guidelines. We stick to established protocols for brain injury assessment. This ensures our patients get the best care possible.
| Imaging Technique | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| MRI | Brain anatomy and function | High-resolution images, sensitive to soft tissue changes |
| DTI | White matter tractography | Detailed visualization of white matter tracts |
| SWI | Detection of microbleeds and iron deposits | High sensitivity to small hemorrhages and iron deposits |
Medical imaging is getting better, and MRI is playing a big role in finding brain damage. MRI can spot tiny changes in the brain. This makes it key for diagnosing and checking traumatic brain injuries.
New MRI techniques like Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging are making diagnosis better. Also, using algorithms to read medical images could change how we use them in medicine.
At Liv Hospital, we aim to give top-notch healthcare to everyone, including international patients. We use the latest in brain imaging and follow international standards. MRI will keep being a major player in understanding brain injuries, working with CT and other tech.
The future of brain injury imaging looks bright. MRI and CT are getting better, which means we’ll be able to diagnose and treat better. This will help patients get the best care possible.
Yes, MRI can spot old brain injuries. It shows changes like scar tissue and brain shrinkage. We use special MRI methods to see how bad the injury is.
MRI is better at finding brain damage than CT scans. CT scans are quicker but MRI gives more details. This is important for seeing small injuries.
Yes, small brain bleeds can be missed on CT scans. MRI is better at finding these tiny injuries. It’s a key tool for spotting them.
Yes, MRI can find traumatic brain injuries. It looks for damage like white matter changes and scar tissue. This helps us understand the injury better.
The best time for an MRI after brain trauma varies. It depends on the injury’s severity and the patient’s health. Usually, it’s done within 48 hours. Follow-up scans help track the patient’s recovery.
Yes, MRI can find damage from a concussion. It looks for changes in brain function and white matter. Advanced MRI techniques help us see the extent of the injury.
Liv Hospital uses MRI and CT scans together for brain damage assessment. We follow international standards and use new diagnostic methods. This ensures accurate diagnoses and care for our patients.
CT scans struggle with finding small brain injuries. MRI is better at spotting these injuries. It’s more sensitive to subtle damage.
We employ advanced MRI techniques like diffusion tensor imaging and functional MRI. These help us understand brain tissue changes and injuries in detail.
In emergencies, the choice between MRI and CT depends on the patient’s condition. CT scans are quicker and used first. MRI is used for more detailed evaluation and follow-up.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!