Last Updated on November 20, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
At Liv Hospital, we are dedicated to top-notch healthcare. We support international patients fully. Sickle cell disease management has made big strides, giving patients new hope. Leading-edge therapies and patient-centered care are changing the game in effective disease management.
The field of sickle cell anemia treatment has grown a lot. Hydroxyurea is a key treatment. But newer drugs like L-glutamine, voxelotor, and crizanlizumab are adding more benefits. They help improve patients’ lives.

Living with sickle cell anemia means always managing the condition. It’s a genetic disorder caused by a single mutation in the β-globin gene. This leads to abnormal hemoglobin and red blood cells shaped like sickles, not disks.
Sickle cell anemia is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. This means a person needs two defective copies of the β-globin gene to have the condition. Carriers have one normal and one defective gene. They don’t show all symptoms but can pass the mutated gene to their kids.
Symptoms of sickle cell anemia vary but often include pain episodes. These are caused by sickled red blood cells blocking blood vessels. Other issues include anemia, increased infection risk, and possible organ damage.
Some patients face acute chest syndrome, a serious condition needing quick medical help. For more on managing sickle cell disease, visit
Managing sickle cell anemia requires a detailed plan. This includes medicines like hydroxyurea to reduce pain crises. Sickle cell disease specialists play a key role in creating care plans. They use the latest treatment of sickle cell anemia and sickle cell drugs to enhance patients’ lives.
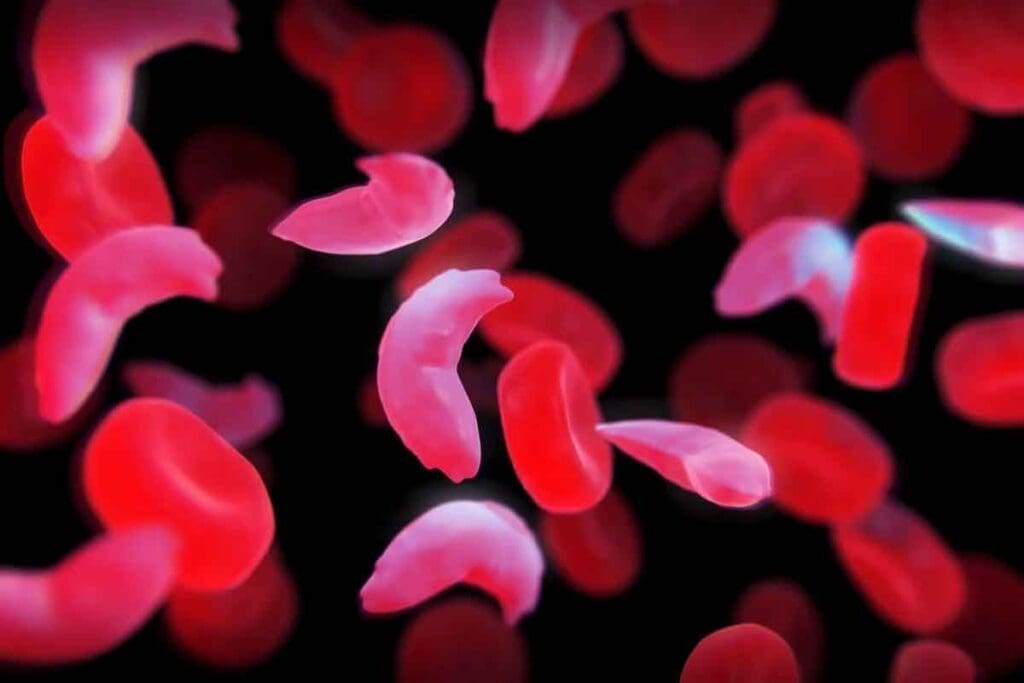
In recent years, treating sickle cell anemia has changed a lot. We now focus on finding cures, not just managing symptoms. This change comes from new medical technologies and a better understanding of the disease.
Before, sickle cell anemia treatment mainly aimed to ease symptoms and prevent problems. Doctors used pain meds, blood transfusions, and antibiotics to fight infections. But now, we have treatments that aim to fix the disease itself.
New treatments like bone marrow transplantation and gene therapy offer hope. They are promising for those with severe cases of the disease.
Recent discoveries have changed how we treat sickle cell anemia. Gene editing, like CRISPR/Cas9, is a big step forward. It lets us fix the genes that cause the disease, which could cure it.
Another key advance is targeted therapies. For example, voxelotor helps hemoglobin carry more oxygen. This reduces painful crises.
| Treatment Approach | Description | Potential Benefits |
| Bone Marrow Transplantation | Replaces diseased bone marrow with healthy marrow | Potential cure for severe sickle cell anemia |
| Gene Therapy | Modifies or replaces the gene causing sickle cell anemia | Potential cure by correcting genetic defect |
| Targeted Therapies (e.g., Voxelotor) | Improves hemoglobin function | Reduces frequency of painful crises |
These new treatments are a big step forward. As research keeps going, we’ll see even more ways to manage and cure sickle cell anemia.
As we look into treatments for sickle cell disease, it’s key to know what a “cure” means. Finding a cure is not simple, mainly because sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder.
A cure usually means getting rid of the disease completely. This would mean fixing the genetic problem that causes sickle cell disease. It would stop the production of sickled red blood cells.
Right now, treatments like hydroxyurea and new drugs help manage the disease. They lessen symptoms and prevent serious problems. But they don’t fix the genetic issue at the root of the disease.
It’s vital to know the difference between treatment and cure. Treatments help manage the disease, ease symptoms, and stop serious issues. A cure would fix the disease’s cause.
| Aspect | Treatment | Cure |
| Purpose | Manage symptoms and prevent complications | Correct the genetic cause, eliminating the disease |
| Examples | Hydroxyurea, L-Glutamine, Voxelotor | Bone Marrow Transplantation, Gene Therapy |
| Outcome | Improved quality of life, reduced crises | Normal health, no further treatment needed |
Even though treatments have made managing sickle cell disease better, there are hopes for more. Things like bone marrow transplants and gene therapy are being looked into. They aim to fix the disease’s genetic cause for good.
Hydroxyurea is key in treating sickle cell anemia. It helps lower pain crisis frequency and boosts patient health. It’s a trusted treatment in clinics for its proven results.
Hydroxyurea boosts fetal hemoglobin production. Fetal hemoglobin is less prone to sickling. This means fewer red blood cells can sickle, reducing pain crises and other sickle cell disease issues.
Key Benefits:
Studies show hydroxyurea cuts down pain crises in sickle cell anemia patients. This makes life better for those with the condition.
Hydroxyurea’s benefits are wide-ranging:
Hydroxyurea is mostly safe but can cause myelosuppression. This lowers blood cell counts. It’s vital to check blood counts often to manage these risks.
Monitoring Requirements:
Knowing hydroxyurea’s benefits and side effects helps doctors use it better. This leads to better health outcomes for patients with sickle cell anemia.
L-Glutamine (Endari) is a promising treatment for sickle cell disease. It helps reduce oxidative stress, a major problem in the disease. This stress causes red blood cells to sickle and leads to painful crises.
L-Glutamine works by lowering oxidative stress in sickle red blood cells. It increases reduced glutathione, a key antioxidant. This helps protect cells from damage.
Clinical studies have shown L-Glutamine can cut down on pain crises. This makes life better for those with sickle cell disease.
Studies have found L-Glutamine (Endari) has many benefits. It leads to fewer hospital visits for pain and improves patients’ overall health. The reduction in oxidative stress helps manage symptoms and may slow disease progression.
Patients often see a decrease in symptoms. This is key for keeping them independent and reducing medical needs.
Healthcare providers usually suggest a specific dose of L-Glutamine (Endari). The standard is 5 grams (one packet) twice daily, with food or liquid. It’s important for patients to stick to the recommended dose and way of taking it.
L-Glutamine is usually safe, but side effects like nausea or constipation can happen. It’s good to have a healthcare provider watch for any issues and adjust treatment if needed.
Voxelotor, also known as Oxbryta, is a big step forward in treating sickle cell disease. It’s part of a new wave of treatments that get to the root of the problem. Voxelotor improves how hemoglobin works, which is key to managing sickle cell anemia.
Voxelotor works by sticking to hemoglobin, making it better at grabbing oxygen. This means more oxygen gets to our tissues and organs. It also means fewer sickling events happen. By modifying hemoglobin function, voxelotor lessens anemia and might lower the chance of sickle cell disease complications.
Studies on voxelotor have been very encouraging. They show it can boost hemoglobin levels and cut down on hemolysis markers. People taking voxelotor have seen significant improvements, like fewer pain crises. The main benefits from these trials are:
Voxelotor is taken orally, once a day. Adults and teens over 40 kg should take 1,500 mg. It’s important to keep an eye on hemoglobin levels and liver function tests. Doctors should watch for any bad side effects and change the dose if needed.
Here are some important things to remember about voxelotor treatment:
Crizanlizumab, known as Adakveo, is a big step forward in treating sickle cell disease. It targets the main cause of vaso-occlusive crises. This treatment offers new ways to manage sickle cell disease effectively.
Crizanlizumab blocks P-selectin, a key molecule in sickled red blood cells sticking to the endothelium. This action reduces vaso-occlusive crises. It’s given intravenously once a month, making it easy for patients to follow.
Administering crizanlizumab is simple. The dose and frequency are set to work well while keeping side effects low. Doctors watch patients closely during and after the infusion to ensure safety.
Studies show crizanlizumab cuts down on vaso-occlusive crises in sickle cell disease patients. This means fewer painful episodes for patients. It greatly improves their quality of life, helping them live more active and productive lives.
| Treatment | Frequency of Vaso-Occlusive Crises | Pain Episode Reduction |
| Crizanlizumab (Adakveo) | Reduced frequency | Significant reduction in pain episodes |
| Placebo | No significant change | Minimal reduction |
Doctors look at many factors before starting crizanlizumab. They consider the patient’s medical history, how often and how severe the crises are, and what treatments they’ve tried before. Choosing the right patients is key to safe and effective treatment.
Talking about possible side effects and monitoring needs is also important. While most patients tolerate it well, some may experience side effects. Regular checks help manage these issues quickly.
Bone marrow transplantation might cure sickle cell disease for some patients. This method replaces the patient’s bone marrow with healthy one. It could stop the disease’s symptoms and problems.
The bone marrow transplant process for sickle cell disease patients has several steps:
The success of bone marrow transplantation in treating sickle cell disease depends on several things. These include the patient’s age, health, and if a good donor is found. Studies show that:
Even though bone marrow transplantation can cure, it comes with risks. Possible complications include:
Recovering from bone marrow transplantation needs close monitoring and support. Patients should be ready for a long recovery. This might involve:
We stress that bone marrow transplantation is a complex process. It’s important to weigh the benefits and risks. For some, it’s a hopeful way to cure sickle cell disease.
Gene therapy has changed how we treat sickle cell disease. It makes targeted changes to the genome to cure diseases. For sickle cell, it aims to fix the genetic issue causing the condition.
Recently, the FDA approved several gene therapies for sickle cell disease. These therapies modify stem cells outside the body and then transplant them back. Two notable examples are exagamglogene autotemcel (exa-cel) and LentiGlobin.
Exa-cel, approved in 2023, uses CRISPR-Cas9 to edit the BCL11A gene. This boosts fetal hemoglobin and reduces sickling of red blood cells. LentiGlobin introduces a functional HBB gene into stem cells, enabling normal hemoglobin production.
CRISPR-Cas9 is key in making gene therapies for sickle cell disease. It precisely edits the faulty HBB gene. This involves isolating stem cells, editing them with CRISPR-Cas9, and then reinfusing them after conditioning.
CRISPR-Cas9’s precision allows for targeted correction of the genetic defect. This could cure the disease. Other technologies, like base editing and prime editing, are also being explored for their precision in treating sickle cell disease.
Clinical trials show promising results for gene therapy in sickle cell disease. Patients have seen fewer crises and better hemoglobin levels. But, long-term monitoring is key to understanding treatment durability and any long-term side effects.
Research aims to improve gene therapy safety and effectiveness. This includes better conditioning regimens and gene editing. As the field grows, we expect more advancements in treating sickle cell disease.
Managing sickle cell disease needs a team effort. It’s not just about treating symptoms. It’s about caring for the whole person, including their physical, emotional, and social needs.
A team of specialists is key to managing sickle cell disease. They work together to ensure the best care for patients. Key players include:
Coordinated treatment brings many benefits to sickle cell disease patients. Healthcare providers can:
It also helps cut healthcare costs by reducing emergency visits and hospital stays.
Finding the right treatment center is vital for getting the best care. Specialized centers offer:
| Service | Description | Benefit |
| Multidisciplinary Teams | Teams including hematologists, genetic counselors, and pain specialists | Comprehensive care addressing all aspects of the disease |
| Advanced Treatment Options | Access to latest treatments including gene therapy and new medications | Improved patient outcomes and quality of life |
| Patient Support Services | Services such as counseling, social work, and patient education | Enhanced patient and family support |
When looking for a treatment center, consider their experience with sickle cell disease. Also, look at the services they offer and patient satisfaction ratings.
Sickle cell trait is different from sickle cell disease but needs special care. People with the trait are usually healthy. Yet, they should know about family planning and health precautions.
The main difference between sickle cell trait and disease is how severe they are. People with the trait have one abnormal gene but usually don’t have the disease’s severe symptoms.
But, they might face some issues during intense workouts or at high altitudes. Knowing these differences is key to managing the trait well.
Genetic counseling is very important for family planning with sickle cell trait. If both parents carry the trait, there’s a 25% chance their child will have sickle cell disease.
Genetic counseling helps parents understand the risks and options. This way, they can make informed choices about their family.
| Risk Scenario | Probability | Outcome |
| Both parents are carriers | 25% | Child has sickle cell disease |
| One parent is a carrier, the other has sickle cell disease | 50% | Child has sickle cell disease |
| One parent is a carrier, the other is normal | 50% | Child is a carrier |
People with sickle cell trait are usually healthy but need to take some precautions. They should drink plenty of water, avoid too much exercise, and be careful at high altitudes.
Key Precautions:
By following these tips, people with sickle cell trait can stay healthy. They can also make smart choices about their health and family planning.
The treatment for sickle cell disease is changing fast. We now have old treatments like Hydroxyurea and new ones like gene therapy. This makes the future look bright.
New treatments like L-Glutamine and Voxelotor focus on different parts of the disease. Bone marrow transplants and gene therapy might cure some patients. More research is needed to find even better treatments.
Researchers are working hard to find a cure for sickle cell disease. We’ve made a lot of progress, but we need to keep funding research. This will help us use these new treatments fully.
We’re dedicated to giving top-notch care to patients from around the world. Keeping up with the latest in sickle cell treatment is key. This way, we can offer the best care possible.
New treatments for sickle cell anemia include hydroxyurea and L-glutamine (Endari). Voxelotor (Oxbryta), crizanlizumab (Adakveo), bone marrow transplantation, and gene therapy are also available. These options aim to reduce symptoms and prevent complications.
There’s no sure cure for sickle cell disease yet. But treatments like bone marrow transplantation and gene therapy might cure it. We explain the difference between treatment and cure in our article.
Hydroxyurea boosts fetal hemoglobin production. This reduces pain crises and other complications. It’s a key treatment for many patients.
L-glutamine (Endari) lowers oxidative stress. This helps reduce pain crises and improves life quality for patients.
Voxelotor (Oxbryta) makes hemoglobin hold onto oxygen better. This improves oxygen delivery to tissues, reducing vaso-occlusive crises.
Crizanlizumab (Adakveo) cuts down vaso-occlusive crises in sickle cell patients. It targets specific molecules involved in the disease.
Bone marrow transplantation might cure sickle cell disease for some patients. It’s risky and requires careful selection and monitoring.
Gene therapy for sickle cell disease looks promising. Several FDA-approved options are available. They aim to fix the genetic defect, potentially curing the disease.
Compassionate care is key for sickle cell disease. A team of specialists ensures patients get the right treatment. This improves their quality of life.
People with the sickle cell trait usually don’t need treatment. But they should know about genetic implications for family planning. They might need special care during medical procedures or extreme activities.
Yes, research is exploring new treatments. Gene editing and other innovative therapies are being studied. It’s important to stay updated for patients and healthcare providers.
The best medication varies by patient. Hydroxyurea is often first, but L-glutamine, voxelotor, and crizanlizumab might be used too. It depends on the patient’s needs and history.
Look for centers with experienced hematologists and teams. We offer tips on finding these centers in our article.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!