The EVAR technique is changing how we treat aortic aneurysms. It’s a new, less invasive way to fix these problems.
The EVAR technique, or endograft repair, is now the top choice for treating aortic aneurysms. It’s known for being effective and allowing for faster recovery. Places like Liv Hospital use it because it offers personalized care and top-notch results.
Using the endograft repair technique means less pain and quicker healing times. This is compared to the old open surgery method. It shows our dedication to giving the best healthcare and support.
Key Takeaways
- EVAR technique is a minimally invasive procedure for treating aortic aneurysms.
- Endograft repair has become the primary approach due to its effectiveness.
- Reduced recovery time is a significant benefit of the EVAR technique.
- Leading medical centers trust the EVAR technique for its clinical excellence.
- Patients benefit from shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery.
Understanding Aortic Aneurysms and Their Treatment Challenges

It’s key for doctors to know about aortic aneurysms to give the best care. An aortic aneurysm happens when the aorta, the main blood vessel, gets too big. This can be very dangerous if not treated right.
What Is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)?
An Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) is when the aorta gets too big in the belly. It’s bigger than 3 cm or 50% larger than normal. The aorta carries blood to the body, and when it weakens, it can bulge. AAAs often don’t show symptoms until they burst, so early checks are important.
Risk Factors and Prevalence
Things like advanced age, smoking, hypertension, and family history can cause AAAs. Men are more likely to get them, and they’re common in people over 65. Knowing these risks helps find who needs a check-up.
AAAs are found in about 4-8% of men aged 65-75 worldwide. Many countries have screening programs to catch AAAs early. This can really help save lives.
Consequences of Untreated Aneurysms
If AAAs aren’t treated, they can burst. This causes severe internal bleeding that’s often fatal. The death rate for burst AAAs is very high. So, finding and treating them early is very important.
We need to spread the word and screen for AAAs, mainly in high-risk groups. Knowing the risks and what can happen helps us save lives.
The Evolution of Endograft Repair: A Medical Breakthrough

Endograft repair has changed how we treat aortic aneurysms. This method is less invasive than traditional surgery. It offers a safer option for patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs).
Historical Treatment Approaches
Before, treating AAAs meant open surgery. This was a big operation with a long recovery. It was risky, mainly for older people or those with other health issues.
Julio C. Palmaz was a key figure in changing this. He said, “Endovascular stenting has changed vascular surgery. It allows for less invasive treatments for complex conditions.”
“EVAR technology has changed how we treat aortic aneurysms. It’s less invasive and has shorter recovery times.”
Development of EVAR Technology
EVAR technology has improved over time. Advances in materials, imaging, and surgery have helped. Early endografts had problems with durability and accuracy. But, new designs have made them better.
Today’s endografts are more flexible and last longer. They have special features for complex aneurysms. EVAR is getting even better, opening up more treatment options.
| Year | Milestone in EVAR Development | Impact |
| 1990s | First EVAR procedures performed | Introduction of minimally invasive AAA treatment |
| Early 2000s | Advancements in endograft design | Improved durability and deployment accuracy |
| Present day | Continued innovation in EVAR technology | Expanded applications for complex aneurysms |
Current Adoption Rates in Clinical Practice
EVAR is now a common choice for treating AAAs. It’s less invasive and has fewer complications than open surgery. This makes it a preferred option for many.
Recent data shows 80-90% of AAA repairs use EVAR. This shows it’s becoming the standard treatment. As technology improves, we’ll see more use of EVAR and better results for patients.
Key Fact #1: EVAR Dominates Modern AAA Treatment
EVAR has changed how we treat AAA, becoming the top choice in vascular surgery today. More evidence shows it’s better than old-school open surgery.
Statistical Overview: 80-90% of AAA Repairs Use EVAR
More and more, EVAR is being used for AAA repairs. About 80 to 90 percent of repairs now use EVAR. This shows it’s gaining favor among doctors and patients.
A study in the Journal of Vascular Surgery found EVAR’s use has gone up over 20 years. At the same time, open surgery has gone down. This trend will likely keep growing as technology gets better and more doctors learn EVAR.
Reasons for Widespread Adoption
Several reasons explain why EVAR is so popular. It’s less invasive, causing less harm to patients than open surgery. This means fewer complications, less pain, and faster healing.
Also, EVAR is a good choice for high-risk patients. It can be done under local anesthesia, making it safer than general anesthesia.
“The minimally invasive nature of EVAR, combined with its efficacy in preventing aneurysm rupture, has made it an attractive option for both patients and clinicians.”
Vascular Surgeon
Comparison with Traditional Open Surgical Repair
EVAR and open surgery are different in many ways. Open surgery needs a big cut in the belly, causing more pain and a longer recovery. EVAR, on the other hand, uses small cuts in the groin, causing less damage.
| Criteria | EVAR | Open Surgical Repair |
| Incision Size | Small (groin incisions) | Large (abdominal incision) |
| Recovery Time | Shorter | Longer |
| Post-operative Pain | Less | More |
| Anesthesia | Local or General | General |
The table shows EVAR’s advantages over open surgery. These benefits have made EVAR the preferred choice for AAA treatment today.
Key Fact #2: How Endograft Repair Works in EVAR Surgery
The EVAR procedure is a key part of modern vascular surgery. It uses endografts to fix aortic aneurysms. We’ll look at how this works, including the types of endografts and the important anatomical factors.
The EVAR Procedure Explained
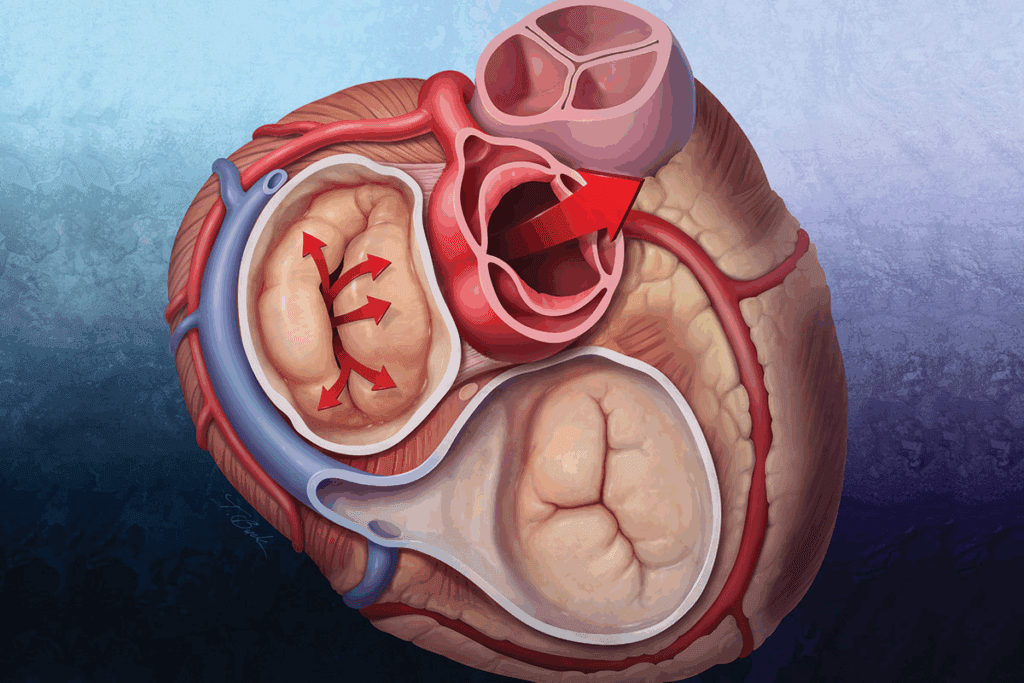
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) is a new way to treat aortic aneurysms. It involves placing an endograft in the aorta to block the aneurysm from blood flow. This stops the aneurysm from getting bigger and reduces the risk of rupture.
The process starts with accessing the femoral arteries. Then, the endograft delivery system is guided into place. Once in the right spot, the endograft is deployed. This lets blood flow through the graft, avoiding the aneurysm. This method is safer than traditional open repair.
Types of Endografts Used
There are many types of endografts for EVAR, each for different needs. The right endograft depends on the aneurysm’s size, location, and the patient’s health. Some common ones are:
- Standard infrarenal endografts for simple AAA cases
- Fenestrated and branched endografts for complex aneurysms
- Endografts with active fixation for better stability
Anatomical Considerations for Successful Deployment
For EVAR to work well, careful planning is needed. Important factors include the aortic neck’s size, length, and angle, and any iliac artery disease. CT angiography helps check these and plan the best endograft.
Getting the anatomy right is key for good EVAR results. Choosing the right endograft and deployment method is vital. This ensures the best outcome from this minimally invasive treatment.
Key Fact #3: Significant Reduction in Surgical Risks
EVAR has changed how we treat aortic aneurysms, making surgery safer for patients. This new method is key for treating abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs). It’s a safer choice than traditional open surgery.
Mortality Rate Comparisons
Research shows EVAR lowers death rates during and right after surgery. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials found a big drop in 30-day death rates for EVAR patients. This makes EVAR a top choice for many vascular surgeons and patients.
Reduced Operative Complications
EVAR also cuts down on surgery problems. Its minimally invasive approach lowers risks of infections, bleeding, and breathing issues. This leads to better short-term results, quicker recovery, and shorter hospital stays.
Impact on High-Risk Patient Populations
EVAR helps those at high risk for open surgery. It’s safer for patients with severe heart or lung disease. This makes EVAR a lifesaver for those who might not get surgery.
EVAR has opened up more treatment options for aortic aneurysm patients. It improves their outcomes and quality of life. As technology gets better, EVAR will keep getting safer and more effective.
Key Fact #4: The Economic Impact of EVAR Procedures
EVAR procedures have changed how we treat aortic aneurysms. They also have big economic effects. It’s important for healthcare providers, patients, and others to know about these financial impacts.
Current Market Size
The EVAR vascular procedure market is valued at about $2.5 billion in 2025. This shows how widely EVAR is used and trusted for treating aortic aneurysms.
Projected Growth Rate
The EVAR market is set to grow by 5-7% each year until 2033. This growth comes from more older people, more aortic aneurysms, and better EVAR technology.
Factors Driving Market Expansion
Several factors are making the EVAR market grow:
- More aortic aneurysms in older people
- Better EVAR devices and methods
- More people choosing less invasive surgeries
- More money spent on healthcare and insurance for EVAR
To understand the market better, let’s look at the current and future sizes:
| Year | Market Size (USD Billion) | Growth Rate (%) |
| 2025 | 2.5 | – |
| 2030 | 3.2 | 5.5 |
| 2033 | 4.1 | 6.2 |
The economic effects of EVAR procedures are far-reaching. They impact the healthcare economy, patient outcomes, and quality of life. As the market grows, it’s key to keep an eye on these trends and their future implications for treating aortic aneurysms.
Key Fact #5: Patient Recovery and Clinical Outcomes
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) has changed how we treat abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs). It greatly improves patient recovery and clinical outcomes. Patients see many benefits that make their lives better.
Shorter Hospital Stays and Recovery Times
EVAR makes hospital stays much shorter. Patients recover faster than with traditional surgery. A study in the Journal of Vascular Surgery found EVAR patients stay 2-3 days, compared to 7-10 days for open repair.
“The minimally invasive nature of EVAR contributes to faster recovery times, allowing patients to return to their normal activities sooner,” says a leading vascular surgeon.
Reduced Readmission Rates
EVAR also lowers readmission rates. A meta-analysis showed EVAR patients have much lower readmission rates. This means they have a smoother recovery.
Long-term Surveillance Requirements
EVAR brings many benefits but needs long-term monitoring. This is to watch for complications like endoleaks. Regular imaging studies are key to ensure the endograft works right. We suggest a detailed surveillance plan to catch any problems early.
Quality of Life Improvements
Studies prove EVAR boosts patients’ quality of life. The quick recovery and lower risk of problems make patients happier and healthier. A patient shared, “After EVAR, I was back on my feet quickly. I could enjoy my retirement without worrying about surgery.”
So, EVAR not only improves health outcomes but also makes life better for patients with AAAs.
Key Fact #6: Advanced Techniques in Endovascular AAA Repair
New endografts and techniques have changed how we treat AAA. They offer safer and more effective ways to repair aortic aneurysms. We’re always looking for new ways to tackle the tough challenges of aortic aneurysms.
Fenestrated and Branched Endografts
Fenestrated and branched endografts are big steps forward in EVAR. They let us treat more complex aneurysms safely. These special endografts have precise openings or branches for the patient’s arteries, keeping blood flow to important organs.
These advanced devices help more people get EVAR, even if their aneurysms were hard to treat before. Studies show they work well and give good results for the right patients.
Solutions for Complex Anatomical Challenges
Before, EVAR was hard for complex aneurysms. But now, new endografts and techniques make it possible. They help with short or angled necks, tough aortas, and tricky branch vessels.
Fenestrated endografts solve problems with short necks by fitting around the renal arteries. Branched endografts keep blood flowing to vital organs when the aneurysm touches the aortic branches.
Emerging Techniques and Applications
The field of endovascular AAA repair is growing fast. New techniques and tools are being developed to improve results. Next-generation endografts are getting better at flexibility, durability, and sealing.
New imaging methods like fusion imaging and 3D reconstruction are also being used. They help plan and do procedures better, making sure the endografts are placed right and the results are good.
| Technique | Description | Benefits |
| Fenestrated Endografts | Endografts with precise fenestrations for branch vessels | Preserves blood flow to vital organs, expands EVAR eligibility |
| Branched Endografts | Endografts with branches for complex aortic anatomies | Enables treatment of aneurysms involving critical branches |
| Advanced Imaging | Use of fusion imaging and 3D reconstruction | Enhances procedural precision and success assessment |
Key Fact #7: Challenges and Limitations of Endograft Repair
Endograft repair has changed how we treat aortic aneurysms. Yet, it comes with its own set of challenges. It’s important to know these limitations to better care for our patients.
Anatomical Restrictions
One big challenge is the anatomy of the aorta. The shape and size of a patient’s aorta can affect how well the endograft works. Sometimes, we need special endografts like fenestrated or branched endografts for a better fit.
Endoleaks and Other Complications
Endoleaks are a big worry. They happen when blood leaks back into the aneurysm sac. Studies show we need to watch for them closely and sometimes do more to fix them. Other issues like graft migration and endograft failure can also affect how well the repair lasts.
A study on the National Center for Biotechnology Information website stresses the need for ongoing checks to catch and manage these problems early.
Long-term Durability Concerns
How well endografts last over time is a big concern. As we keep improving the technology, we learn more about their long-term performance. Issues like material wear and device migration are areas we’re studying and working on.
Patient Selection Considerations
Choosing the right patients for endograft repair is key. We look at the patient’s health, the size and location of the aneurysm, and the aorta’s shape. By carefully picking patients, we can improve results and lower risks.
In summary, endograft repair has been a game-changer for treating aortic aneurysms. But, we must face its challenges and limitations head-on. This way, we can keep making patient care better and safer.
Conclusion: The Future of Aortic Aneurysm Treatment
Exploring endograft repair using the EVAR technique shows it’s changing aortic aneurysm treatment. This minimally invasive method is leading the way. The future of treating aortic aneurysms depends on EVAR’s growth.
EVAR has already brought many benefits. It lowers surgical risks and speeds up recovery. As technology gets better, EVAR will help more patients with complex issues.
Innovations in endograft design and deployment are driving EVAR’s growth. This means EVAR will likely stay a top choice for treating abdominal aortic aneurysms. It offers a safer, more effective option than traditional surgery.
Our study shows EVAR technology will keep improving. This will lead to better results for patients and more treatment options for those at risk of rupture.
FAQ
What is EVAR and how does it differ from traditional open surgical repair for aortic aneurysms?
EVAR, or Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair, is a new way to treat aortic aneurysms. It’s different from open surgery, which needs a big cut in the belly. EVAR uses small cuts in the groin to put in a graft, guided by images. This makes recovery faster and safer.
What are the benefits of choosing EVAR over open surgical repair for AAA treatment?
EVAR has many advantages. It lowers death rates and reduces complications. Patients also stay in the hospital less and recover quicker. It’s great for people at high risk who can’t have open surgery.
What are the risks and possible complications of EVAR?
EVAR is mostly safe, but there are risks. These include leaks, graft movement, and needing more surgery. Some body shapes can make it hard to place the graft. You also need to watch it for a long time to catch any problems early.
How is patient recovery after EVAR, and what are the typical outcomes?
Recovery from EVAR is faster than open surgery. Patients often leave the hospital sooner and feel better faster. But, they need to keep an eye on the graft for life to catch any issues early.
What advancements have been made in EVAR technology to address complex aneurysms?
New EVAR tech has made it possible to treat more complex aneurysms. This includes grafts that can handle tricky blood vessels. These advances help more people get treated with EVAR.
What is the current market size for EVAR procedures, and what is the projected growth rate?
The EVAR market is about $2.5 billion now and growing. It’s expected to grow 5-7% by 2033. This growth is due to more people needing treatment and better technology.
How does EVAR impact the treatment of high-risk patient populations?
EVAR has opened up new treatment options for high-risk patients. These patients were once too risky for open surgery. EVAR reduces risks and complications, making it safer for them.
What are the long-term surveillance requirements after EVAR?
After EVAR, it’s important to keep an eye on the graft. This means regular scans to check for leaks or movement. This helps catch any problems early and ensures the graft keeps working well.
Can EVAR be used for all types of aortic aneurysms?
EVAR is a good choice for many aneurysms, but not all. It depends on the size, location, and health of the patient. Some aneurysms need special grafts or open surgery is better.
References
- Paravastu, S. C., Jayarajasingam, R., Cottam, R., Palfreyman, S. J., Michaels, J. A., & Thomas, S. M. (2014). Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, *2014*(1), CD004178. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10799965/





