Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
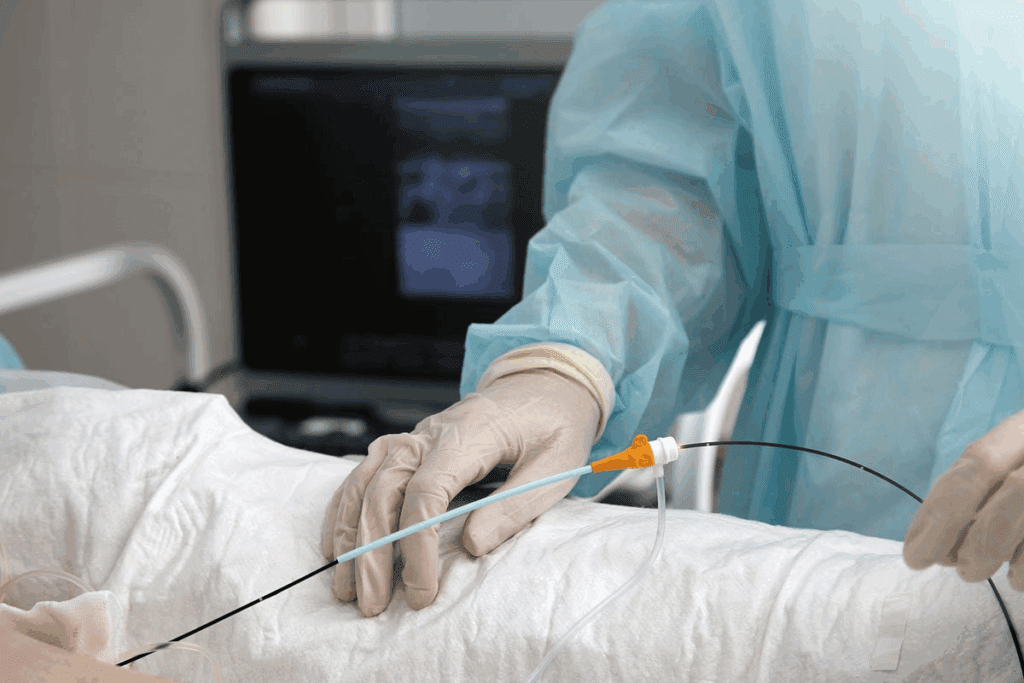
At Liv Hospital, we know how worried patients are about heart arrhythmias. Our team uses radiofrequency ablation techniques and follows international standards. This ensures the best care for your heart.
Radiofrequency ablation treats heart arrhythmias by destroying bad electrical paths in the heart. It uses controlled heat from a catheter to do this.
Learning about this treatment’s benefits and risks is key. We aim to give top-notch healthcare and support to patients from around the world.
It’s important to know about heart arrhythmias to manage their health impact. These irregular heartbeats can cause serious problems if not treated. Heart arrhythmias happen when the heart’s electrical system gets disrupted, leading to irregular heartbeats.
This disruption can cause various symptoms and serious health risks. It’s vital to understand this to take the right steps.
There are many types of cardiac arrhythmias, each with its own traits. Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is common, causing rapid and irregular heartbeats. Other types include supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and ventricular tachycardia, both serious conditions.
| Type of Arrhythmia | Description | Common Symptoms |
| Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) | Rapid and irregular heartbeats | Palpitations, shortness of breath |
| Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) | Rapid heartbeats originating above the ventricles | Rapid heartbeat, dizziness |
| Ventricular Tachycardia | Potentially life-threatening rapid ventricular beats | Dizziness, loss of consciousness |
Symptoms of heart arrhythmias vary. Common signs include palpitations, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Some might feel fatigue or chest discomfort.
It’s key to spot these symptoms early. This way, you can get medical help quickly.
“The key to managing arrhythmias is early detection and treatment. By understanding the symptoms and risks, patients can seek medical help before complications arise.”
— A Cardiologist Says
Untreated heart arrhythmias can lead to serious health issues. Stroke is a big risk, as blood clots can form in the heart and travel to the brain. Other risks include heart failure and sudden cardiac arrest.
Knowing these risks shows why it’s important to get medical help if symptoms don’t go away or get worse. Treating arrhythmias early can greatly reduce the risk of these serious problems.
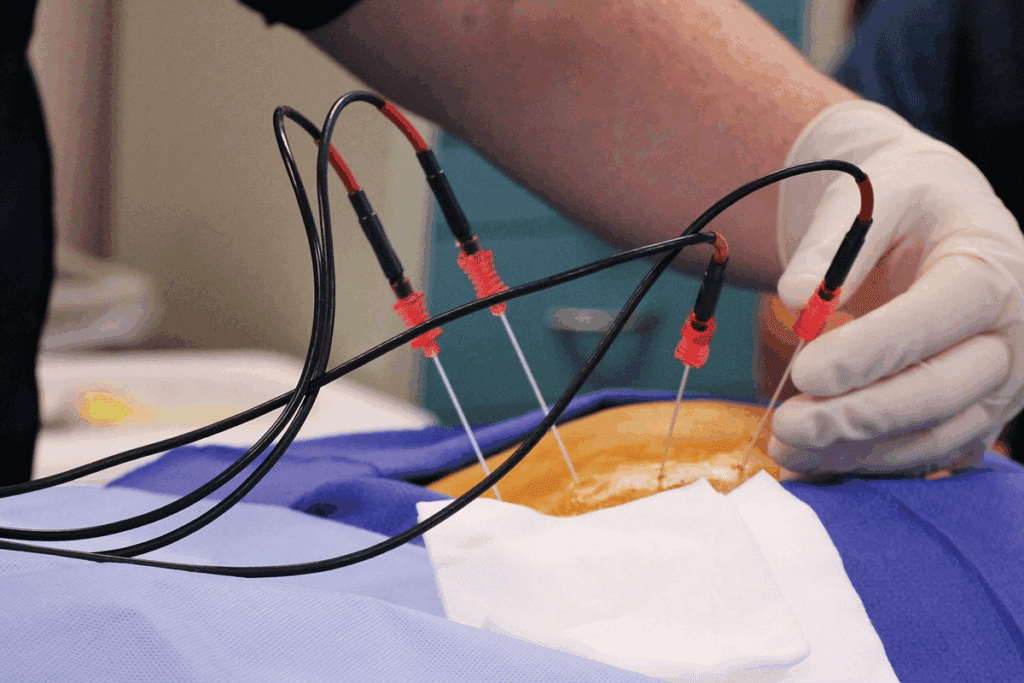
Radiofrequency ablation surgery is a leading treatment for arrhythmias. It uses electrical energy to fix irregular heart rhythms. This method targets specific heart areas causing the problems.
This surgery uses radiofrequency energy to heat heart tissue. This creates a scar that stops bad electrical signals. A catheter, guided by imaging, delivers this energy.
First, the heart’s electrical system is mapped to find the problem. Then, the catheter sends radiofrequency energy to the bad tissue. This energy makes lesions that stop the bad signals.
Radiofrequency ablation has grown a lot over time. It started with simple cases but now treats complex ones like atrial fibrillation. New tools like 3D mapping systems and contact force sensing technology make it safer and more precise.
| Technological Advancements | Impact on Radiofrequency Ablation |
| 3D Mapping Systems | Enhanced precision in locating abnormal heart tissue |
| Contact Force Sensing Technology | Improved safety by ensuring optimal catheter contact |
| Robotic Catheter Navigation | Increased maneuverability and accuracy during the procedure |
Understanding radiofrequency ablation for heart arrhythmias is key. This method has become popular for treating different arrhythmias.
Radiofrequency ablation is minimally invasive. It doesn’t require open-heart surgery. Instead, small incisions are made for catheters to reach the heart tissue.
Catheter ablation works well for some arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation. Success depends on the arrhythmia and the patient’s health.
The procedure is done under local anesthesia. Patients stay awake. This reduces risks and speeds up recovery.
Radiofrequency ablation has a shorter recovery time than surgery. Patients can get back to normal in a few days. This is great for those who can’t take long hospital stays.
These facts show radiofrequency ablation’s benefits for heart arrhythmias. As technology improves, so will patient outcomes.
Exploring these facts shows that radiofrequency ablation is a promising treatment. It helps patients make informed choices about their heart health.
Understanding the catheter ablation process is key for those considering it for heart arrhythmias. The steps are important and our team will guide you through them.
Before starting, our team checks if you’re right for the procedure. They look at your medical history, current meds, and do tests like echocardiograms or electrocardiograms.
On the day, you’ll get specific instructions on what to eat, drink, and take. An IV line will be put in for meds and fluids during the procedure.
The process starts with a thin, flexible tube (catheter) inserted through a vein. Advanced imaging like fluoroscopy helps our cardiologist guide it to your heart.
Once in, the catheter is moved through your heart to find the arrhythmia source. This is done with great care to target the right spot.
With the catheter in place, our cardiologist maps your heart’s electrical system. This step finds the arrhythmia’s cause for targeted treatment.
The map is made by recording heart electrical activity. This info is key for finding and treating the arrhythmia source.
After finding the problem spots, radiofrequency energy is used to treat them. This energy destroys the abnormal heart tissue causing the arrhythmia.
The energy is controlled to only treat the right areas. This helps avoid harming healthy tissue.
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
| Pre-Procedure Preparation | Evaluation and preparation before the procedure | Medical history review, medication management, necessary tests |
| Catheter Insertion and Navigation | Insertion of catheter through a vein and navigation to the heart | Use of imaging techniques like fluoroscopy, and precision in catheter placement |
| Mapping the Heart’s Electrical System | Creating a detailed map of the heart’s electrical activity | Recording electrical activity, identifying arrhythmia sources |
| Delivering Radiofrequency Energy | Ablation of abnormal electrical pathways | Controlled delivery of energy, minimizing risk to healthy tissue |
Catheter ablation is a key treatment for many heart rhythm disorders. It improves patient outcomes. This method is vital for arrhythmias that don’t respond to medication or other treatments.
Atrial fibrillation is a common heart rhythm disorder. It causes rapid and irregular heartbeats. AFib treatment with catheter ablation involves creating lesions in the heart tissue to block abnormal electrical signals. Studies show it can greatly improve symptoms and quality of life for AFib patients.
A 2019 study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found catheter ablation better than medication in reducing AFib recurrence.
Supraventricular tachycardia is a rapid heartbeat from above the ventricles. SVT can cause symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Catheter ablation targets the heart area causing the abnormal rhythm.
“Catheter ablation has become a first-line treatment for many patients with SVT, with a high success rate and low risk of complications.” An Expert Cardiologist
Ventricular tachycardia is a serious condition with rapid heartbeats from the ventricles. In some cases, catheter ablation can be used to treat VT by destroying the abnormal electrical pathway. This is key for patients who haven’t responded to medication or have had significant side effects.
| Arrhythmia Type | Characteristics | Ablation Success Rate |
| Atrial Fibrillation | Irregular, rapid heartbeats | 60-70% |
| Supraventricular Tachycardia | Rapid heartbeats from above ventricles | 90-95% |
| Ventricular Tachycardia | Rapid heartbeats from ventricles | 50-80% |
| Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome | Accessory electrical pathway | 95-99% |
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome is a rare condition with rapid heartbeats. Catheter ablation is highly effective in treating WPW by destroying this extra pathway, often providing a cure for the condition.
Understanding the different arrhythmias treated with catheter ablation helps patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions.
RF catheter ablation has seen big improvements thanks to new techniques. These advancements make the procedure more precise and safe. They help patients with heart arrhythmias get better results.
3D mapping systems are a big step forward in RF catheter ablation. They give a clear view of the heart’s layout. This helps doctors place the catheter exactly right.
By mapping the heart’s electrical paths, doctors can find and fix problems better. This leads to better treatment for patients.
Contact force sensing technology is another key improvement. It lets doctors see how hard the catheter is pressing on the heart. This is important for effective treatment without harming the heart.
Studies show this technology makes treatments more successful. It also lowers the chance of problems coming back.
| Technology | Benefits | Impact on Procedure |
| 3D Mapping Systems | Precise visualization of heart anatomy, accurate catheter positioning | Improved success rates, reduced procedural time |
| Contact Force Sensing | Real-time monitoring of catheter-tissue contact | Enhanced efficacy, reduced risk of complications |
| Robotic Catheter Navigation | Enhanced precision, stability, and control | Improved outcomes, reduced operator fatigue |
Robotic catheter navigation is a new and exciting area. It makes procedures more precise and controlled. This leads to better results and fewer risks.
It also helps doctors work for longer without getting tired. This means they can do more complex treatments with ease.
As technology keeps getting better, we’ll see even more progress. This will lead to even better care for patients with heart arrhythmias.
Cardiac radiofrequency ablation offers many benefits, improving symptoms and quality of life. It has changed how we treat heart arrhythmias. Patients can now take back control of their health.
This procedure greatly reduces arrhythmia symptoms. It targets and removes the cause of abnormal heart rhythms. Patients often see a big drop in symptoms like palpitations and shortness of breath.
Studies show that catheter ablation improves symptoms and quality of life. It lets patients do their normal activities again with more confidence.
Successful radiofrequency ablation can also cut down on medication use. Many patients need fewer or no drugs after the procedure. This not only boosts quality of life but also lowers the risk of drug side effects.
Cardiac radiofrequency ablation can also lower the risk of stroke and heart failure. Untreated arrhythmias can lead to these serious conditions. For example, atrial fibrillation increases stroke risk. Successful ablation can reduce this risk, providing long-term heart health benefits.
The initial cost of radiofrequency ablation might seem high. But, it can be cost-effective in the long run. It reduces the need for ongoing medical care and medication, saving money over time.
Let’s look at a table comparing costs. It shows how radiofrequency ablation can save money compared to long-term medication management.
| Cost Component | Radiofrequency Ablation | Long-term Medication Management |
| Initial Procedure Cost | $15,000 – $20,000 | $0 |
| Annual Medication Costs | $0 (post-procedure) | $1,000 – $3,000 |
| Follow-up Care (First Year) | $1,000 – $2,000 | $500 – $1,000 |
| Total First Year Cost | $16,000 – $22,000 | $1,500 – $4,000 |
| Annual Cost After First Year | $0 – $500 | $1,000 – $3,000 |
The table shows that while radiofrequency ablation costs more upfront, it saves money in the long run. This makes it a cost-effective option for many patients.
Radiofrequency ablation, like any medical procedure, comes with risks and complications. It’s generally safe, but knowing these risks is key to making good treatment choices.
Most people don’t face big problems after radiofrequency ablation. Minor issues might include:
These issues usually go away in a few days. Following your doctor’s post-procedure care is important to avoid these problems.
Though rare, serious complications can happen. These might include:
Talking to your cardiologist about your risk factors is essential to understand your situation.
Some factors can raise the risk of complications. These include:
Knowing these risk factors helps your healthcare team prepare. Talking about your medical history and concerns with your cardiologist is vital.
Being aware of risks and complications helps patients make informed choices. Working with your healthcare team is key to reducing these risks.
Following the recovery process is key. It’s important to follow the post-procedure instructions carefully. This helps avoid complications and ensures the best results from your radiofrequency ablation procedure.
After the procedure, patients are watched in a recovery room for a few hours. Medical staff check vital signs and look for bleeding or issues at the catheter site. This waiting period is critical for catching any early problems.
After discharge, patients are told to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities. They should also avoid bending over for a few days. It’s best to not drive or operate heavy machinery for at least 24 hours. These steps help prevent bleeding or hematoma at the catheter site.
Follow-up appointments are vital for post-procedure care. These visits help us check the heart’s rhythm and overall health. We may do tests like electrocardiograms (ECGs) to see how the heart is doing and adjust treatment plans if needed.
It’s important for patients to know when to seek medical help. Symptoms like increased bleeding, chest pain, shortness of breath, or fever need emergency care. Also, watch for signs of infection at the catheter site, like redness, swelling, or drainage. Being alert to these signs can help address them quickly.
When thinking about radiofrequency ablation for heart arrhythmias, it’s key to know the success rates and long-term outcomes. The treatment’s success depends a lot on the type of arrhythmia.
Radiofrequency ablation works differently for each arrhythmia. For example, it’s more effective for supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) than for atrial fibrillation (AFib). Here are some important stats:
Many things can affect how well radiofrequency ablation works. These include:
Knowing these factors helps set realistic goals and improve results.
Even though radiofrequency ablation is often very effective, arrhythmias can come back. The chance of recurrence depends on the type of arrhythmia and the patient. Sometimes, a second procedure is needed for lasting success.
Studies show that successful radiofrequency ablation greatly improves long-term quality of life. Patients often see fewer symptoms, better exercise ability, and less need for medication.
Those who have successful ablation tend to have better health and happiness overall.
Deciding if radiofrequency ablation is right for you means looking at your health and past treatments. It’s a big choice that needs careful thought. You should think about how bad your symptoms are, if other treatments worked, and your overall health.
Radiofrequency ablation is for people who haven’t gotten better with medicine or have very bad symptoms. Ideal candidates have certain heart rhythm problems like atrial fibrillation. These can be treated well with this procedure.
We look at many things to see if you’re a good fit for radiofrequency ablation. We consider your heart problem, medical history, and any treatments you’ve tried before.
Choosing between radiofrequency ablation and medicine depends on your situation. For some, ablation might be a better choice. For others, medicine might be the best option.
We think about the good and bad of each choice. We look at how bad your symptoms are, how they affect your life, and possible risks. Ablation vs. medication is a choice you should talk about with a cardiologist.
If you’re thinking about radiofrequency ablation, ask your cardiologist important questions. You might want to know about risks and benefits, expected results, and how it will affect your life.
It’s important to know about costs and insurance for radiofrequency ablation. Check with your insurance to see what’s covered and what you’ll have to pay for.
Cost considerations include the procedure, hospital stay, follow-up care, and any needed medicines. We can help you understand these costs and guide you through the financial side of treatment.
The future of treating heart arrhythmias is looking bright. New techniques in catheter ablation are on the horizon. These include better energy sources and mapping systems.
These improvements will make the procedure safer and more effective. This means more arrhythmias can be treated. Atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, and ventricular tachycardia are some examples.
Research is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. We’re excited for the future of treating heart arrhythmias. With these advancements, patients worldwide will receive better care.
Radiofrequency ablation surgery treats heart arrhythmias. It uses heat from a catheter to destroy bad electrical paths in the heart.
It offers many benefits. These include feeling better, living better, needing less medicine, and less chance of stroke or heart failure.
It treats many arrhythmias. These include atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome.
First, you prepare for the procedure. Then, a catheter is inserted and guided. It maps the heart’s electrical system and uses radiofrequency energy to destroy bad tissue.
Risks include bleeding, damage to the heart or blood vessels, infection, or stroke. Some people are at higher risk.
You’ll be closely watched right after. You’ll have to rest and follow up with doctors. You’ll learn about signs of trouble, like bleeding, chest pain, or shortness of breath.
Success depends on the arrhythmia type. Some, like supraventricular tachycardia, have higher success rates. Your health and the doctor’s skill also play a part.
It’s best for those who haven’t responded to medicine or have severe symptoms. Talk to a cardiologist to see if it’s right for you, considering your situation and insurance.
New advancements include better energy sources and mapping systems. There’s also contact force sensing and robotic navigation. These aim to make the procedure safer and more effective.
Radiofrequency energy heats and destroys bad heart tissue. It’s delivered through a catheter, guided by advanced imaging.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). Radiofrequency Ablation Surgery 7 Key Facts About Heart. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10460603/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!