
When you get a adenocarcinoma diagnosis, it can hit hard. It affects many organs, like the duodenum. Patients and families need the best chemotherapy options. At Liv Hospital, we offer top-notch healthcare and support for patients from around the world.
Adenocarcinoma chemotherapy treatment is key for glandular tumors. We aim to give you all the info on the chemotherapy drugs for adenocarcinoma.
Key Takeaways
- Chemotherapy is a mainstay in treating adenocarcinoma.
- Liv Hospital is dedicated to the latest chemotherapy drugs and cancer treatments.
- We create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
- We offer full support for international patients looking for top medical care.
- We keep improving to give patients the best results.
Understanding Adenocarcinoma and Its Treatment Landscape
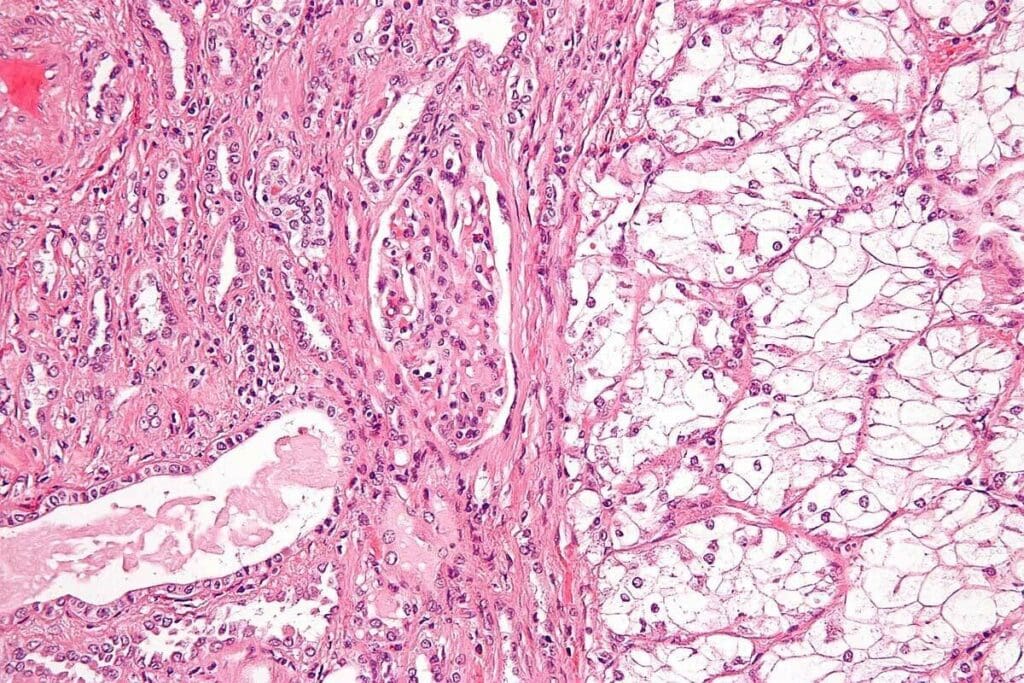
It’s important to know about adenocarcinoma to choose the right treatment. Adenocarcinoma starts in glandular tissue found in many organs.
What Defines Glandular Tumors
Glandular tumors, or adenocarcinomas, start in glandular epithelium. They can happen in places like the colon, duodenum, and more. These tumors affect how glands work by disrupting their secretions.
Adenocarcinoma cells look different under a microscope. They can look like normal cells or be very different.
Common Sites of Occurrence
Adenocarcinoma can happen in many places, each with its own challenges. Common sites include:
- The colon and rectum (colorectal adenocarcinoma)
- The duodenum (cancer duodenum)
- The pancreas (pancreatic adenocarcinoma)
- The lung (lung adenocarcinoma)
- The prostate (prostate adenocarcinoma)
Each place needs a special treatment plan. This plan considers the area’s anatomy, function, and cancer type.
Treatment Approaches Overview
Treatment for adenocarcinoma depends on several things. These include where the cancer is, how far it has spread, and the patient’s health. Treatments can be surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, or a mix of these.
| Treatment Modality | Description | Common Applications |
| Surgery | Removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue | Early-stage adenocarcinomas in various sites |
| Chemotherapy | Use of drugs to kill cancer cells | Advanced or metastatic adenocarcinomas |
| Radiation Therapy | Use of high-energy rays to kill cancer cells | Localized adenocarcinomas, often in combination with surgery or chemotherapy |
Knowing about these treatments is key for patients and doctors. It helps make informed decisions about adenocarcinoma care.
Adenocarcinoma Chemotherapy Treatment: Principles and Evolution
The treatment of adenocarcinoma has seen big changes with new chemotherapy methods. It’s important to know the history and current ways of treating this disease.
Historical Development of Chemotherapy Approaches
Chemotherapy has been key in fighting adenocarcinoma for many years. At first, treatments were not very specific and harmed both cancer cells and healthy cells. But, as we learned more about cancer, treatments got better and more focused.
Many things have helped chemotherapy get better. Advances in technology, understanding cancer better, and finding new targets have all played a part. Now, treatments are more effective and safer for patients.
Current Treatment Goals and Response Assessment
Today, the main goals of chemotherapy for adenocarcinoma are to control the tumor, improve survival, and make life better for patients. Doctors check how well treatment is working by looking at the patient, using imaging, and doing lab tests.
Checking how well treatment is working is very important. It helps doctors decide if they need to change the treatment plan. The Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) are often used to make these checks standard.
| Treatment Goal | Assessment Criteria | Clinical Significance |
| Tumor Response | RECIST criteria | Evaluating treatment effectiveness |
| Survival Rate | Overall survival, progression-free survival | Assessing long-term outcomes |
| Quality of Life | Patient-reported outcomes, symptom management | Improving patient care and well-being |
The Balance of Efficacy and Toxicity
Finding the right balance between treating cancer and avoiding harm to healthy cells is a big challenge. Chemotherapy aims to kill cancer cells but can also hurt other cells.
To reduce harm, doctors carefully choose which chemotherapy to use, how much, and when to give it. They also use supportive care to help patients deal with side effects.
Understanding how chemotherapy has evolved helps us see the effort to improve treatment for adenocarcinoma. This knowledge is key to better patient care.
Paclitaxel: A Frontline Agent for Adenocarcinoma
Paclitaxel is a key chemotherapy drug for fighting adenocarcinoma. We’ll look at how it works, its uses, and how it’s given to patients.
Mechanism of Action and Cell Cycle Disruption
Paclitaxel stops cancer cells from growing by stabilizing microtubules. This disrupts the cell cycle, causing cell death. A study on the National Center for Biotechnology Information website highlights its importance in cancer treatment.
It works by binding to microtubules, stopping them from breaking down. This stops cell division and leads to cell death. This is why it’s so effective against fast-growing cancer cells.
Clinical Applications Across Adenocarcinoma Types
Paclitaxel is effective against many adenocarcinomas, like lung, breast, and ovarian cancers. It’s a key part of chemotherapy for these cancers.
Its use varies based on the cancer type and stage. For example, in lung cancer, it’s often used with other drugs or targeted therapies.
| Adenocarcinoma Type | Paclitaxel Use | Common Combinations |
| Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | First-line and second-line treatment | Carboplatin, bevacizumab |
| Breast Cancer | Adjuvant and metastatic disease treatment | Trastuzumab, doxorubicin |
| Ovarian Cancer | First-line and recurrent disease treatment | Carboplatin, gemcitabine |
Administration Protocols and Patient Management
Paclitaxel is given through an IV, with doses adjusted for each patient. This includes body size and kidney function.
Doctors use supportive care to manage side effects. This includes premeds to prevent allergic reactions. They also watch for nerve damage and low blood counts.
Cisplatin: Platinum-Based Therapy for Advanced Adenocarcinoma
Cisplatin is a key treatment for advanced adenocarcinoma. It uses a platinum-based method to fight cancer cells. This drug is used to treat many cancers, including adenocarcinoma.
DNA Crosslinking and Cancer Cell Death Pathways
Cisplatin works by causing DNA crosslinking, which kills cancer cells. It does this by binding to DNA, creating adducts that block DNA repair. This leads to cell death. Its ability to crosslink DNA makes it effective against fast-growing cancer cells.
“Cisplatin’s efficacy in treating various cancers, including adenocarcinoma, is largely attributed to its ability to form DNA crosslinks, which inhibit cancer cell proliferation.”
Efficacy Profile in Different Adenocarcinoma Subtypes
Cisplatin’s effectiveness in treating adenocarcinoma differs by subtype. Clinical trials have shown that cisplatin-based chemotherapy improves survival in advanced adenocarcinoma patients. It’s used in lung, stomach, and ovarian adenocarcinomas.
- Cisplatin is often a first-line treatment for advanced ovarian adenocarcinoma.
- In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), cisplatin-based chemotherapy improves survival.
- Cisplatin is also used in gastric adenocarcinoma, often with other drugs.
Toxicity Management and Supportive Care
Cisplatin is effective but can cause serious side effects like kidney damage, hearing loss, and nerve damage. Managing these side effects is key to ensuring patients can handle the treatment. Hydration and protective agents help reduce these effects.
Personalized care is vital in managing cisplatin side effects. Each patient reacts differently to chemotherapy. Tailoring care to each patient’s needs helps maximize treatment benefits while reducing side effects.
Oxaliplatin: Optimizing Treatment for Gastrointestinal Adenocarcinomas
Oxaliplatin is a key drug in treating gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas. It’s a third-generation platinum-based chemotherapy. This drug has greatly improved treatment for cancers in the colon and duodenum.
Molecular Mechanisms and Advantages Over Other Platinum Agents
Oxaliplatin works by creating platinum-DNA adducts. These adducts block DNA replication and transcription, killing cancer cells. It has a different activity and toxicity profile than earlier platinum agents like cisplatin.
Its diaminocyclohexane (DACH) carrier ligand gives it unique properties. These properties make it more effective against certain tumors.
Oxaliplatin can also overcome resistance to other platinum compounds. This makes it a vital part of chemotherapy for gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas.
Specific Applications in Colorectal and Cancer of the Duodenum
Oxaliplatin is a mainstay in colorectal cancer treatment. It’s often used with fluoropyrimidines and other drugs. The FOLFOX regimen, which includes oxaliplatin, is a standard first-line treatment for advanced colorectal cancer.
Oxaliplatin also shows promise in treating duodenal adenocarcinomas. These rare tumors are challenging to treat. Using oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy has improved outcomes for some patients.
Managing Unique Neurotoxicity Profiles
Oxaliplatin’s side effects include neurotoxicity, which can cause neuropathy. The acute form is often cold-induced paresthesia or dysesthesia. Chronic neurotoxicity can lead to lasting sensory problems.
Managing this neurotoxicity is complex. It involves adjusting doses, pausing treatment, and using neuroprotective agents. These strategies help keep patients’ quality of life high while treating their cancer.
| Treatment Aspect | Oxaliplatin | Cisplatin |
| Molecular Mechanism | Forms platinum-DNA adducts with DACH carrier ligand | Forms platinum-DNA adducts without DACH ligand |
| Primary Use | Gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas, colorectal cancer | Various cancers, including testicular, ovarian, and lung |
| Notable Toxicity | Neurotoxicity, cold-induced neuropathy | Nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, neurotoxicity |
Irinotecan: Targeting Resistant and Refractory Adenocarcinomas
Irinotecan is a key chemotherapy drug for treating hard-to-treat adenocarcinomas. It works by stopping topoisomerase I, an enzyme cancer cells use to copy their DNA. This makes it great for adenocarcinomas that don’t respond to other treatments.
We’ll look at how irinotecan works, its role in second-line and salvage therapy, and how to handle its side effects. Knowing this helps us understand how irinotecan can help patients with tough adenocarcinoma cases.
Topoisomerase I Inhibition and DNA Damage
Irinotecan’s power comes from stopping topoisomerase I. This enzyme is key for cancer cells to copy their DNA. By blocking it, irinotecan causes DNA damage, leading to cancer cell death. This is very useful for treating adenocarcinomas that are resistant to other drugs.
Second-Line Applications and Salvage Therapy
Irinotecan is often used when first treatments don’t work for adenocarcinomas. It’s very effective in treating colorectal adenocarcinomas, used alone or with other drugs. It’s also used in salvage therapy for patients who have tried many treatments before.
The benefits of irinotecan include:
- Improved tumor response rates
- Prolonged progression-free survival
- Potential for improved overall survival
Predicting and Managing Gastrointestinal Toxicity
Irinotecan is effective but can cause serious side effects like diarrhea and neutropenia. Healthcare providers must be able to predict and manage these side effects well.
Strategies for managing these side effects include:
- Prophylactic use of anti-diarrheal medications
- Close monitoring of blood counts to prevent neutropenia
- Dose adjustments based on patient tolerance
- Supportive care measures to manage symptoms
By understanding how to reduce these side effects, we can help patients stay on their treatment plans and get the best results.
Pemetrexed: Precision Treatment for Non-Squamous Adenocarcinomas
Pemetrexed is a key treatment for non-squamous adenocarcinomas. It targets specific types of cancer cells. This makes it a vital part of treating certain adenocarcinoma subtypes.
Multi-Targeted Antifolate Mechanism
Pemetrexed works by blocking several enzymes in folate metabolism and DNA synthesis. It targets thymidylate synthase, dihydrofolate reductase, and glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase. This multi-targeted approach helps stop cancer cells from growing.
It stops the production of nucleotides needed for DNA replication. This makes pemetrexed very effective against fast-growing tumors, like some adenocarcinomas.
Lung Adenocarcinoma: First-Line and Maintenance Therapy
Pemetrexed is very effective against non-squamous lung adenocarcinoma. It’s often used with platinum-based chemotherapy as a first-line treatment. It also works well as maintenance therapy, improving survival and stopping tumor growth in patients who haven’t progressed yet.
Studies show pemetrexed improves outcomes in lung adenocarcinoma. It’s a valuable treatment option for this specific cancer type.
Biomarker-Guided Patient Selection
Pemetrexed works best when certain biomarkers are present. For example, low thymidylate synthase expression means better response to pemetrexed. Biomarker-guided patient selection helps find the right patients for pemetrexed treatment.
Using biomarkers in treatment decisions makes pemetrexed more effective. This personalized approach is key to modern cancer treatment.
Breakthrough Combinations: Chemotherapy with Immunotherapy
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy together are changing how we treat adenocarcinoma. This mix has shown great promise in helping more patients. It works well for different types of adenocarcinoma.
Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy: Doubling Survival Rates
Pembrolizumab with chemotherapy is a strong treatment for some adenocarcinoma types. Studies show it can make patients live longer than with chemotherapy alone.
For example, in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with adenocarcinoma, this combo can double survival rates. It’s a big win for some patients.
Mechanisms of Synergy Between Treatment Modalities
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy work well together. Chemotherapy helps by making more tumor antigens and improving how the immune system sees them. This makes the immune system stronger against cancer.
Immunotherapies like pembrolizumab help the immune system fight cancer better. Adding chemotherapy makes this effect even stronger. It’s a powerful way to fight tumors.
Patient Selection for Combination Approaches
Not every adenocarcinoma patient is right for this combo treatment. Choosing the right patients is key. It depends on the tumor type, genetic makeup, and how well the patient is doing.
Tests like PD-L1 expression help pick the best candidates. Genetic mutations also play a role in choosing the right treatments.
| Patient Characteristics | Ideal for Combination Therapy | Considerations |
| PD-L1 Positive | Yes | High likelihood of response to immunotherapy |
| EGFR Mutation | Variable | May require targeted therapy consideration |
| High Tumor Mutational Burden | Yes | Increased likelihood of neoantigen expression |
As we learn more, we’ll refine who gets this combo treatment. This could help more adenocarcinoma patients in the future.
Research Advances Toward a Cure for Adenocarcinoma
Medical science is making big strides in treating adenocarcinoma. This means better treatments and maybe even a cure. Research is getting better at understanding adenocarcinoma, leading to new ways to fight it.
Northwestern University’s Findings on Celecoxib Combinations
Northwestern University has found that mixing celecoxib with chemotherapy can be very effective.Research shows this combo can make treatments work better and lower the chance of resistance. Celecoxib’s anti-inflammatory effects help chemotherapy work even better.
Overcoming Treatment Resistance Mechanisms
One big challenge in treating adenocarcinoma is when treatments stop working. Scientists are working on new ways to beat this problem. They’re looking at new drugs and understanding how resistance happens to make treatments more effective.
| Strategy | Description | Potential Benefit |
| Targeted Therapies | Drugs designed to target specific molecular markers | Improved efficacy and reduced side effects |
| Combination Therapies | Using multiple agents to attack the tumor from different angles | Reduced risk of resistance and improved outcomes |
| Novel Drug Delivery Systems | Advanced delivery methods to enhance drug concentration at the tumor site | Better tumor control and reduced systemic toxicity |
Novel Drug Delivery Systems and Targeted Approaches
New ways to deliver drugs are a big step forward in treating adenocarcinoma. These methods aim to get drugs right to the tumor, cutting down on side effects. Ideas like nanoparticles and local injections are being tested to make treatments more effective.
As we keep exploring new ways to fight adenocarcinoma, the hope for a cure grows. By combining new treatments with a deeper understanding of the disease, we’re getting closer to better patient outcomes and a better life for those affected.
Conclusion: The Future of Adenocarcinoma Treatment
The treatment for adenocarcinoma is changing fast. This is thanks to new ways in chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and combining treatments. Drugs like Paclitaxel, Cisplatin, Oxaliplatin, Irinotecan, and Pemetrexed are key in fighting adenocarcinoma, including duodenum cancer.
New research is finding better ways to treat adenocarcinoma. Mixing immunotherapy with old treatments is showing great promise. This gives patients new hope. We are dedicated to sharing the latest news and support for those with adenocarcinoma.
We expect better results and more treatment choices as research goes on. Our goal is to give top-notch care and keep up with the latest in adenocarcinoma treatment.
FAQ
What is adenocarcinoma, and how does it affect different parts of the body?
Adenocarcinoma is a cancer that starts in glandular tissue. This tissue is in many organs, like the colon and duodenum. The treatment depends on where it is, how far it has spread, and other details.
What are the common chemotherapy drugs used to treat adenocarcinoma?
Common drugs for treating adenocarcinoma include paclitaxel, cisplatin, oxaliplatin, irinotecan, and pemetrexed. These drugs target cancer cells in different ways.
How does paclitaxel work in treating adenocarcinoma?
Paclitaxel stops cancer cells from growing by disrupting their cell cycle. It’s a key drug for treating many types of adenocarcinoma.
What is the role of cisplatin in treating advanced adenocarcinoma?
Cisplatin is a drug that damages DNA in cancer cells, causing them to die. It’s used for treating several types of adenocarcinoma.
How does oxaliplatin optimize treatment for gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas?
Oxaliplatin works better than some other drugs because of its unique action. It’s effective against colorectal and duodenal cancers.
What is the mechanism of action of irinotecan in targeting resistant and refractory adenocarcinomas?
Irinotecan stops topoisomerase I, causing DNA damage. It’s used when other treatments fail for adenocarcinoma.
How does pemetrexed work in precision treatment for non-squamous adenocarcinomas?
Pemetrexed targets several pathways, making it good for treating certain adenocarcinomas, like lung cancer. It’s used in first-line and maintenance therapy.
What are the benefits of combining chemotherapy with immunotherapy in treating adenocarcinoma?
Combining chemotherapy with immunotherapy has improved survival rates. It’s being tested in many clinical trials.
What are the latest research advances in achieving a cure for adenocarcinoma?
Researchers are looking at new combinations, like celecoxib with chemotherapy. They’re also working on overcoming resistance and finding new ways to deliver drugs.
How is cancer of the duodenum treated with chemotherapy?
Duodenal cancer is often treated with oxaliplatin. This drug has shown to be effective against gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas.
What are the treatment approaches for adenocarcinoma chemotherapy treatment?
Treatment for adenocarcinoma varies based on location, stage, and other factors. It may include a mix of chemotherapy drugs and other therapies.
References
- Amjad, M. T. (2023). Cancer Chemotherapy – StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564367/

































