When a blood clot forms inside an artery, it can block blood flow. This can lead to serious medical events like heart attack, stroke, and peripheral arterial disease. At LivHospital, we know how important arterial thrombosis is for global health. Understand arterial thrombosis, its causes, symptoms, and how blood clots form in arteries.
We aim to give top-notch healthcare and support to international patients. Our team works hard to treat blood clots in arteries with great care and accuracy.
It’s key to understand the causes and symptoms of thrombosis in artery. This helps us treat it quickly and effectively. We’re here to help you through this process and provide the care you need.
Key Takeaways
- Arterial thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms inside an artery.
- It can lead to serious medical events such as heart attack and stroke.
- LivHospital provides world-class healthcare delivery for arterial thrombosis.
- Understanding the causes and symptoms is key for effective treatment.
- Our team of experts is dedicated to treating blood clots with care and precision.
What Happens When Blood Clots Form in Arteries
Arterial blood clots form quickly and can cause serious health problems. When a blood clot blocks an artery, it stops oxygen-rich blood from reaching important organs and tissues.
The Mechanism of Arterial Blood Clot Formation
An arterial blood clot forms when an artery’s inner lining gets damaged, usually because of atherosclerosis. This damage exposes collagen and tissue factor, starting a chain of events that leads to clotting.
- Platelet activation and aggregation at the site of injury
- Coagulation cascade initiation, leading to thrombin generation
- Fibrin formation, stabilizing the clot
This process is fast, often happening in just minutes. It can cause severe symptoms to appear suddenly.
How Arterial Thrombi Differ from Venous Clots
Arterial thrombi and venous clots are different in many ways. Arterial clots form in high-pressure vessels with oxygen-rich blood. Venous clots form in low-pressure veins with less oxygen.
| Characteristics | Arterial Thrombi | Venous Clots |
| Blood Flow | High pressure, oxygen-rich | Low pressure, oxygen-poor |
| Formation Speed | Rapid, often minutes | Slower, often hours or days |
| Common Causes | Atherosclerosis, injury | Stasis, hypercoagulability |
Knowing these differences is key to diagnosing and treating arterial thrombosis right.
Key Fact #1: Understanding Arterial Thrombosis and Its Immediate Effects
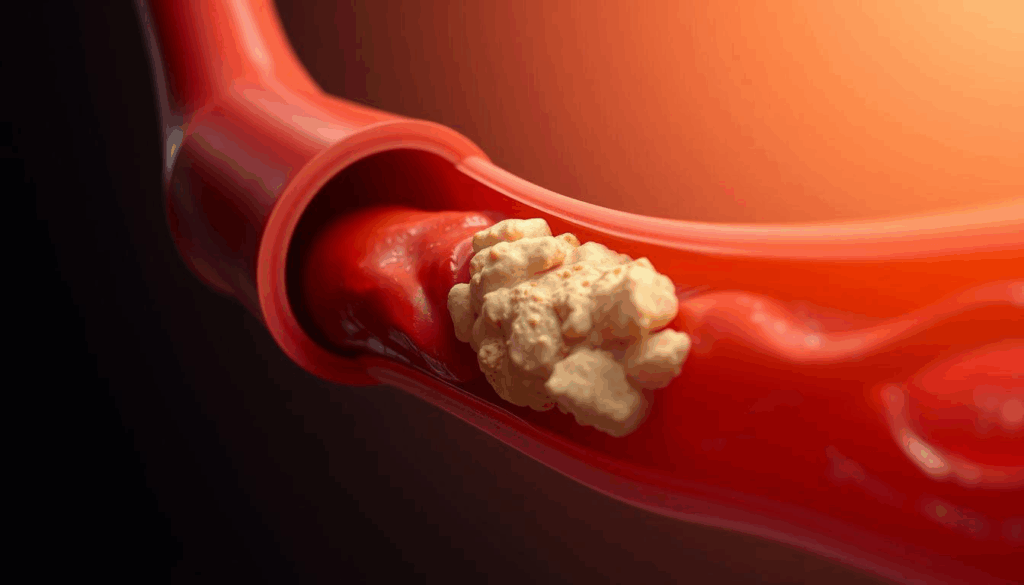
Arterial thrombosis is a serious condition where a blood clot forms in an artery. This can block blood flow to vital organs. It’s important to know about it because it can have severe effects on the body.
How Arterial Thrombosis Blocks Blood Flow
When a clot forms in an artery, it can block blood flow. This blockage can damage tissue or even cause organ failure. For example, a clot in a heart artery can cause a heart attack. A clot in a brain artery can lead to a stroke.
The effects of arterial thrombosis can be severe. A clot can block the artery, stopping blood flow. This can lead to tissue death if not treated quickly.
Acute vs. Chronic Manifestations of Arterial Clots
Arterial thrombosis can happen suddenly or over time. Sudden cases have severe symptoms like pain and breathing trouble. Slow cases have milder symptoms that get worse over time.
Knowing if it’s acute or chronic helps decide how to treat it. Quick cases need fast action like clot-busting drugs or surgery. Slow cases might need ongoing treatment and lifestyle changes.
“The timely diagnosis and treatment of arterial thrombosis are critical to preventing long-term damage and improving patient outcomes.”
— Cardiologist
| Manifestation | Characteristics | Treatment Approach |
| Acute | Sudden onset, severe symptoms | Immediate medical intervention (thrombolytic therapy, surgery) |
| Chronic | Gradual onset, milder symptoms | Long-term management (anticoagulant medication, lifestyle changes) |
In conclusion, knowing about arterial thrombosis and its effects is key. Recognizing its signs can help get timely treatment. This can save lives and prevent serious health problems.
Key Fact #2: Atherosclerosis – The Leading Cause of Arterial Thrombosis
Atherosclerosis is the main cause of arterial thrombosis. It involves the buildup and rupture of plaques. These plaques are made of fat, cholesterol, and other substances.
Over time, this buildup narrows the arteries. This narrowing can lead to arterial thrombosis.
The Progressive Nature of Plaque Buildup
Atherosclerosis starts early in life. Plaque buildup happens when there’s an imbalance in lipid metabolism. This imbalance leads to lipids accumulating in the arterial walls.
Risk factors like hypertension, diabetes, and smoking make this worse.
- Endothelial dysfunction, where the inner lining of the arteries becomes impaired
- Lipid accumulation, leading to plaque formation
- Inflammation, which plays a critical role in the progression of atherosclerosis
As plaques grow, they narrow the arteries. This narrowing, or stenosis, reduces blood flow to vital organs. Symptoms vary based on where the artery is affected.
How Plaque Rupture Triggers Arterial Clot Formation
Plaque rupture is a key event that can cause an arterial thrombus. When a plaque ruptures, the lipid core is exposed. This triggers a quick clotting response.
This clot can block the artery. It can cause acute ischemic events like myocardial infarction or stroke.
The process of plaque rupture and clot formation is complex. It involves the plaque’s composition and inflammation. Understanding these mechanisms is key to preventing and treating arterial thrombosis.
- Identifying individuals at high risk of plaque rupture and arterial thrombosis
- Implementing lifestyle modifications and medical therapies to reduce risk factors
- Monitoring plaque progression and arterial health through regular check-ups and diagnostic tests
Key Fact #3: Major Risk Factors for Arterial Thrombotic Disease
Arterial thrombotic disease is influenced by several key risk factors. These can be divided into modifiable and non-modifiable factors. Knowing these risk factors is key to preventing and managing the disease.
Modifiable Risk Factors: Hypertension, Diabetes, and Smoking
Several risk factors for arterial thrombotic disease can be changed. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, damages blood vessel linings. This makes them more likely to form clots.
Diabetes also increases the risk of arterial thrombosis. It causes inflammation and damage to blood vessels. This can lead to plaque buildup and thrombosis.
Smoking is a major risk factor that damages the cardiovascular system. It also increases the risk of arterial thrombosis. Quitting smoking is a critical step in reducing this risk.
| Modifiable Risk Factor | Impact on Arterial Thrombosis |
| Hypertension | Damages blood vessel lining, increasing clot risk |
| Diabetes | Causes inflammation and vascular damage |
| Smoking | Damages cardiovascular system, increases thrombosis risk |
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Age, Gender, and Genetic Predisposition
Some risk factors can’t be changed, but knowing them helps manage risk. Age is a significant risk factor. The risk of arterial thrombosis increases with age due to plaque buildup.
Gender also plays a role. Men are generally at higher risk at younger ages than women. But, women’s risk increases after menopause.
Genetic predisposition is another non-modifiable risk factor. People with a family history of arterial thrombotic disease are at higher risk. They should be closely monitored.
Understanding both modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors helps individuals take proactive steps. Managing modifiable risk factors through lifestyle changes and medical treatment can significantly lower risk.
Key Fact #4: Recognizing Symptoms of Artery Thrombosis in Different Body Locations
It’s key to know the signs of artery thrombosis to get help fast. We’ll look at how symptoms change based on where the clot is in the body.
Coronary Artery Thrombosis: Signs of a Blood Clot in the Heart
A blood clot in the heart’s arteries can cause a heart attack. Look out for these symptoms:
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: A feeling of tightness in the chest that might spread to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
- Shortness of Breath: Feeling like you can’t catch your breath, even when sitting or lying down.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Feeling sick to your stomach or vomiting, which might be mistaken for something less serious.
- Lightheadedness or Dizziness: Feeling like you might pass out or are dizzy.
- Cold Sweat: Breaking out in cold sweat.
If you have these symptoms, get medical help right away. Quick action can greatly improve your chances of recovery.
Cerebral Arterial Thrombosis: Warning Signs of Stroke
A clot in the brain’s arteries can lead to a stroke. Watch for these signs:
- Sudden Numbness or Weakness: Feeling numb or weak on one side of your body, like your face, arm, or leg.
- Confusion or Trouble Speaking: Having trouble speaking or understanding what others say.
- Vision Disturbances: Sudden vision problems in one or both eyes.
- Dizziness or Loss of Balance: Feeling dizzy or having trouble walking.
- Severe Headache: A sudden, severe headache with no clear cause.
Spotting these symptoms early and getting medical help fast can save your life.
Arterial Clot in Leg: Symptoms of Peripheral Arterial Disease
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a blockage in leg arteries. Look out for these symptoms:
- Pain or Discomfort: Pain in your legs or hips when you walk or exercise, which goes away when you rest.
- Numbness or Weakness: Feeling numb or weak in your legs.
- Coldness: One leg feeling colder than the other.
- Sores or Wounds: Sores or wounds on your legs or feet that don’t heal well.
Knowing these symptoms can help you get medical help quickly. This can prevent serious problems like losing a limb.
We stress the importance of recognizing these symptoms and getting medical help right away. Early treatment can greatly improve outcomes for those with artery thrombosis.
Key Fact #5: Diagnostic Approaches for Detecting Arterial Blood Clots
Diagnosing arterial thrombosis is a detailed process. It uses non-invasive imaging and lab tests. Accurate diagnosis is key for quick treatment and management.
Non-Invasive Imaging Techniques
Non-invasive imaging is vital for spotting arterial blood clots. Ultrasound and CT scans are top choices. They help see the arteries and find clots or blockages.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to show artery images, spotting clots and checking blood flow.
- CT Angiography: Mixes CT tech with dye for clear artery pictures, spotting clots and narrowing.
Laboratory Tests for Thrombosis Risk Assessment
Laboratory tests are key for checking thrombosis risk and finding arterial clots. They look at blood clotting factors and find possible causes of thrombosis.
Some important tests are:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Finds blood component issues that might show thrombosis.
- Coagulation Studies: Tests like PT and aPTT check how well blood clots.
- D-Dimer Test: Measures D-dimer, a sign of clot breakdown, showing thrombosis.
Key Fact #6: Treatment Strategies for Arterial Thrombosis
Arterial thrombosis treatment needs a mix of medical strategies. These aim to open up blocked blood flow and stop more clots. The right treatment depends on the clot’s size, location, and the patient’s health.
Antiplatelet and Anticoagulant Medications
Antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs are key in treating arterial thrombosis. Antiplatelet drugs like aspirin and clopidogrel stop platelets from sticking together. Anticoagulants, including warfarin and NOACs like rivaroxaban, slow down blood clotting. This reduces the chance of more clots forming.
Doctors often mix these medicines. They pick the best ones based on the patient’s risk factors and the clot’s details.
Thrombolytic Therapy for Acute Arterial Clots
Thrombolytic therapy quickly dissolves acute clots. It uses drugs to activate the body’s clot-dissolving system. This treatment is urgent, used in emergencies like stroke or severe limb ischemia.
Surgical and Endovascular Interventions
Sometimes, surgical or endovascular interventions are needed. Surgery might include removing the clot or bypassing the blocked area. Endovascular methods, like angioplasty and stenting, use small tools to open the artery.
| Treatment Option | Description | Indications |
| Antiplatelet Medications | Prevent platelet aggregation | Primary and secondary prevention of arterial thrombosis |
| Anticoagulant Medications | Inhibit coagulation cascade | Prevention of clot growth and recurrence |
| Thrombolytic Therapy | Dissolve acute clots | Acute ischemic stroke, severe limb ischemia |
| Surgical/Endovascular Interventions | Restore blood flow | Significant arterial occlusion, failed medical therapy |
Choosing the right treatment depends on many factors. These include the patient’s symptoms, the clot’s location and size, and any other health issues. A mix of treatments often works best to manage arterial thrombosis.
Key Fact #7: The COVID-19 Connection to Arterial Thrombosis
The COVID-19 pandemic has shown a link between the virus and a higher risk of arterial thrombosis. Understanding how COVID-19 affects our heart health is key. The virus can change how our blood clots, raising the risk of blood clots.
Hypercoagulability in COVID-19 Patients
People with COVID-19 often have a higher chance of blood clotting. This is because the virus causes a strong inflammatory response. This response starts the blood clotting process, making arterial thrombosis more likely.
Why does this happen? It’s because of damaged blood vessels, more clotting factors, and less ability to break down clots. Knowing this helps us find ways to lower the risk of blood clots in COVID-19 patients.
Prevention and Management Strategies
To stop and manage blood clots in COVID-19 patients, we need a few steps. Anticoagulant therapy is used to prevent blood clots. But, we must adjust the treatment based on each patient’s risk.
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
| Anticoagulant Therapy | Use of medications to prevent blood clot formation | Reduces risk of arterial thrombosis |
| Monitoring Coagulation Parameters | Regular assessment of blood clotting factors | Enables early detection of hypercoagulability |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Promoting healthy lifestyle choices | Supports overall cardiovascular health |
By using these methods, doctors can lower the risk of blood clots in COVID-19 patients. This helps improve their health outcomes.
Prevention Strategies: Reducing Your Risk of Thrombus in Artery
Preventing arterial thrombosis is a mix of healthy living, medical care, and new ways to prevent it. Knowing and using these methods can lower your risk of artery blockages.
Lifestyle Modifications for Arterial Health
Keeping a healthy lifestyle is key to avoiding artery blockages. Eat a balanced diet with lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains. Cut down on fats and cholesterol.
Also, physical activity like walking boosts heart health and lowers thrombosis risk.
Quitting smoking is also essential, as it greatly increases artery blockage risk. Staying away from secondhand smoke and keeping a healthy weight also help your arteries.
Medical Management of Risk Factors
Managing medical risks is vital to prevent artery blockages. This means controlling high blood pressure with meds and lifestyle changes. It also means keeping diabetes under control and treating high cholesterol with statins.
People with heart disease or at high risk might get antiplatelet or anticoagulant medications. Regular check-ups with doctors are key to adjusting treatments.
Emerging Preventive Approaches
New ways to prevent artery blockages are being researched. This includes novel anticoagulants that are safer and studying genetic factors that might increase risk.
Conclusion: Taking Proactive Steps Against Arterial Thrombosis
Understanding arterial thrombosis and its prevention is key. We’ve looked into its causes, symptoms, and how to treat it. This knowledge helps people take action against it.
Knowing the risks, like atherosclerosis and smoking, helps make better choices. We stress the need to manage these risks with treatment and lifestyle changes.
At LivHospital, we offer top-notch care for those with arterial thrombosis. Our team creates custom plans for each patient. This ensures they get the best support.
Combining healthcare and personal effort is vital in fighting arterial thrombosis. Together, we can lower its occurrence and better outcomes for patients.
FAQ
What is arterial thrombosis?
Arterial thrombosis is when a blood clot forms in an artery. This can block blood flow to important organs and tissues.
What are the main causes of arterial thrombosis?
The main cause is atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in arteries. Hypertension, diabetes, and smoking also increase the risk.
How does arterial thrombosis differ from venous thrombosis?
Arterial thrombosis happens in arteries and often leads to heart attacks or strokes. Venous thrombosis is in veins and can cause deep vein thrombosis.
What are the symptoms of arterial thrombosis?
Symptoms depend on where the clot is. Chest pain is common in heart attacks. Stroke symptoms can occur in the brain. Limb pain or numbness can happen in the limbs.
How is arterial thrombosis diagnosed?
Doctors use ultrasound and CT scans to see clots. Blood tests check for clotting factors.
What are the treatment options for arterial thrombosis?
Doctors use medicines to stop clots. For big clots, they might use surgery or special procedures to open up the artery.
Can COVID-19 increase the risk of arterial thrombosis?
Yes, COVID-19 can make blood clot more easily. People with COVID-19 need careful medical care to avoid this.
How can I reduce my risk of developing arterial thrombosis?
Eating well, exercising, and not smoking helps. Managing blood pressure and diabetes is also key.
What is the role of atherosclerosis in arterial thrombosis?
Atherosclerosis is the main cause. It leads to plaque buildup and can cause clots when the plaque ruptures.
Are there any non-modifiable risk factors for arterial thrombosis?
Yes, age, gender, and genetics are non-modifiable risks. People with these risks need to stay alert and get regular check-ups.
References
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2022). Arterial Thrombosis. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/arterial-thrombosis