Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
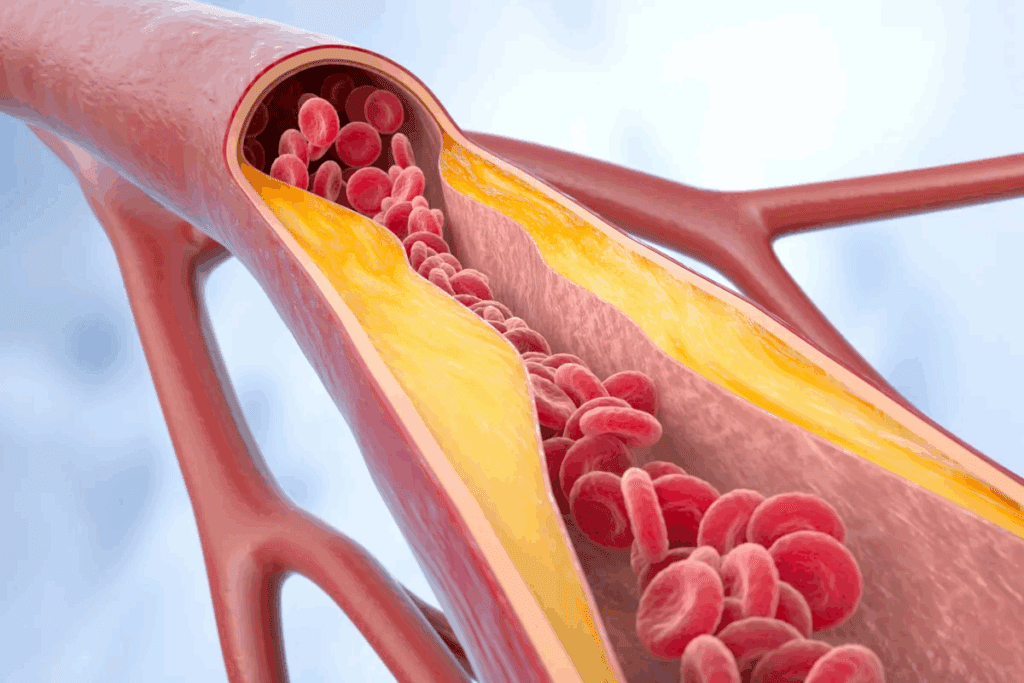
Learn the arteriosclerosis definition, its causes, symptoms, and how it affects blood vessels.
Arteriosclerosis is when the arteries get hard. This can cause serious heart problems. We will look into what arteriosclerosis is and how it affects the body.
This term covers several types, like atherosclerosis and arteriolosclerosis. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatments for arteriosclerosis is key to keeping your heart healthy.

Arteriosclerosis is a group of conditions that harden and lose elasticity in arteries. It includes many different changes that affect how arteries work.
Arterial hardening comes from complex changes in cells and molecules. Important factors are inflammation, damage to the inner lining of arteries, and buildup of lipids and calcium. These changes make arteries less flexible and harder to move blood through.
Looking into arteriosclerosis shows it’s caused by many things. Genetics, lifestyle, and the environment all play a role in how it develops and grows.
Arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis are often confused, but they’re not the same. Atherosclerosis is when plaques build up inside arteries. Arteriosclerosis is a wider term that includes hardening of arteries, like arteriolosclerosis and vascular sclerosis.

Arteriosclerosis comes in several forms, each with its own traits and health impacts. Knowing these differences is key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Atherosclerosis is the most common arteriosclerosis type. It’s marked by plaque buildup in artery walls. This plaque is made of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and blood substances. Over time, it can harden or burst, causing blood clots that block blood flow.
Key features of atherosclerosis include:
Arteriolosclerosis is when arteriole walls thicken. This can cut down blood flow to important organs. It’s often linked to high blood pressure and diabetes.
Characteristics of arteriolosclerosis:
Vascular sclerosis is a term for different arteriosclerosis types, including medial arterial calcification. Arthrostenosis, while not a direct arteriosclerosis type, refers to joint stiffening. Yet, in vascular health, it’s sometimes linked to blood vessel stiffening or narrowing.
The table below outlines the main arteriosclerosis types and their characteristics:
| Type | Characteristics | Risk Factors |
| Atherosclerosis | Plaque buildup in large and medium-sized arteries | High cholesterol, hypertension, smoking |
| Arteriolosclerosis | Thickening of arteriolar walls | Hypertension, diabetes |
| Medial Arterial Calcification | Calcification of the medial layer of arteries | Age, diabetes, kidney disease |
Knowing these types is vital for creating effective treatment plans and managing the condition well.
Arteriosclerosis is caused by many risk factors. Some can be changed through lifestyle. Knowing these factors is key to preventing and managing the disease.
Several risk factors can be changed. These include high cholesterol, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, and obesity. By controlling these, people can lower their risk of arteriosclerosis.
High cholesterol causes plaque buildup in arteries, making them hard and narrow. Hypertension strains the arteries, speeding up hardening. Diabetes damages blood vessels and nerves that control the heart.
Some risk factors can’t be changed, but knowing them is important. Age is a big risk factor, as arteriosclerosis risk grows with age. Family history also matters; those with a family history are more likely to get it.
Also, genetic predispositions affect how the body handles lipids and responds to risks. Knowing these helps in making a prevention plan that fits you.
Arteriosclerosis often starts quietly, but knowing its signs is key. As it gets worse, symptoms can show up. These depend on the arteries and how severe the disease is.
In the early stages, arteriosclerosis might not show symptoms. But some people might feel:
These early signs can be hard to notice and might seem like other issues. It’s important to watch for them and see a doctor if they don’t go away or get worse.
As arteriosclerosis gets worse, symptoms can get clearer. They often match the arteries affected:
Spotting these symptoms is key to getting the right medical help.
If you notice any of these, get help right away:
Quick medical check-ups can greatly improve treatment and prevent serious issues. If you’re feeling mild or ongoing symptoms, talk to your doctor for a full check-up and advice.
Healthcare professionals use many methods to diagnose arteriosclerosis. These include physical exams, lab tests, and imaging studies. This detailed approach helps find out how much the arteries are hardened. It also guides the treatment needed.
A thorough physical exam is the first step. We look for signs like weak or absent pulses in the limbs. We also check for abnormal heart sounds and evidence of poor circulation. These signs can show if arteriosclerosis is present and how severe it is.
We also check for risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. Finding these risk factors helps us create a good treatment plan.
Laboratory tests are key in diagnosing arteriosclerosis. These tests measure biomarkers that show the disease’s presence and how it’s progressing. Some important tests include:
Imaging studies are vital for seeing how much arteriosclerosis affects different organs. Common imaging techniques include:
These methods help doctors accurately diagnose arteriosclerosis. They can see how severe it is and create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Managing arteriosclerosis needs a mix of lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and sometimes surgery. Each person’s situation is different. So, treatment plans are made to fit their specific needs and how severe their condition is.
Changing your lifestyle is often the first step against arteriosclerosis. Eating a diet full of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean meats is key. Also, regular exercise like walking is important.
Quitting smoking and managing stress through meditation or yoga can also help a lot. Quitting smoking and managing stress are big steps in fighting the disease.
As “The American Heart Association emphasizes the importance of lifestyle changes in managing cardiovascular diseases, including arteriosclerosis.” Making these lifestyle changes can slow down the disease and lower the risk of heart problems.
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, medicine might be needed. We might suggest:
These medicines can help manage symptoms, slow the disease, and lower the risk of serious problems.
In severe cases, surgery or interventional procedures might be needed. We might look at:
These methods can improve blood flow, ease symptoms, and prevent serious issues.
Dealing with arteriosclerosis requires a detailed plan. By combining lifestyle changes, medicines, and sometimes surgery, we can manage the condition well. This approach can greatly improve a person’s quality of life.
It’s important to know the complications of arteriosclerosis to manage the disease well. Arteriosclerosis can cause severe problems, affecting many parts of the body. This can really lower your quality of life.
Arteriosclerotic heart disease is a big problem caused by arteriosclerosis. It happens when the heart’s blood supply arteries get blocked by plaque. This can cause:
When arteriosclerosis affects the brain’s blood supply arteries, it leads to:
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is another issue caused by arteriosclerosis. It narrows arteries, reducing blood flow to limbs. Symptoms include:
Other problems can be kidney disease and aneurysms. It’s key to manage arteriosclerosis well to avoid these issues and keep your heart healthy.
Managing arteriosclerosis requires smart choices about diet, exercise, and stress. It’s not easy, but the right steps can greatly improve your life.
Eating right is key to managing arteriosclerosis. Focus on foods full of nutrients but low in bad fats, cholesterol, and salt. Eat lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins to help.
Here are some diet tips:
“A healthy diet is not just about cutting out certain foods, but also about incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods that support overall cardiovascular health.”
Exercise keeps your heart healthy. Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise, or a mix of both, each week. Good choices include brisk walking, cycling, and swimming.
Managing stress is also critical. Stress can worsen arteriosclerosis. Try meditation, deep breathing, and yoga to lower stress.
| Exercise Type | Benefits | Examples |
| Aerobic Exercise | Improves cardiovascular health, reduces blood pressure | Brisk walking, jogging, cycling |
| Resistance Training | Builds muscle, improves metabolism | Weight lifting, bodyweight exercises |
| Flexibility Exercises | Enhances flexibility, reduces injury risk | Yoga, stretching exercises |
Regular health checks are essential for managing arteriosclerosis. Keep an eye on blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar. Regular visits to your doctor can catch problems early.
Dealing with arteriosclerosis is tough, but support helps a lot. Join online or in-person support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges.
Also, get advice from health experts, nutritionists, and fitness coaches. They can offer personalized tips for you.
Arteriosclerosis is a big problem for heart health. Knowing its causes, signs, and symptoms is key to catching it early. Eating right and exercising can help a lot in preventing heart issues.
Preventing arteriosclerosis is very important. Knowing what increases your risk helps you take action. Doctors may also use medicines or surgery to help manage it.
Combining healthy living, medical care, and support can make a big difference. Regular check-ups are also essential. This way, we can catch any changes early and act fast. Working with doctors is the best way to manage arteriosclerosis and stay healthy.
Arteriosclerosis is when arteries get hard. This can cause heart problems. It includes atherosclerosis, arteriolosclerosis, and vascular sclerosis.
Arteriosclerosis is a wide term for artery hardening. Atherosclerosis is a specific case of it, caused by plaque buildup. They’re often mixed up, but atherosclerosis is a part of arteriosclerosis.
Risk factors include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and smoking. Age and family history also play a role.
Symptoms vary based on where the arteries are affected. Early signs might be mild discomfort. Severe pain or organ damage can happen later.
Doctors use physical exams, lab tests, and imaging to diagnose arteriosclerosis. It’s a detailed process.
Treatment starts with lifestyle changes. Then, doctors might prescribe medicine or surgery. It depends on the person’s situation.
Yes, it can be prevented or managed. Eating well, exercising, managing stress, and regular check-ups help.
Complications include heart disease, brain problems, and peripheral artery disease. These are serious issues.
Managing it involves lifestyle changes, medical care, and support. It’s a team effort.
Vascular sclerosis is when blood vessels harden. It’s a form of arteriosclerosis.
Arteriolosclerosis is when small arteries thicken. It’s a type of arteriosclerosis.
Yes, arthrostenosis is linked to vascular sclerosis, which is a form of arteriosclerosis.
Libby, P., & Hansson, G. K. (2019). Inflammation in atherosclerosis: From pathophysiology to practice. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 74(10), 1376-1398. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7089587/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!