Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik
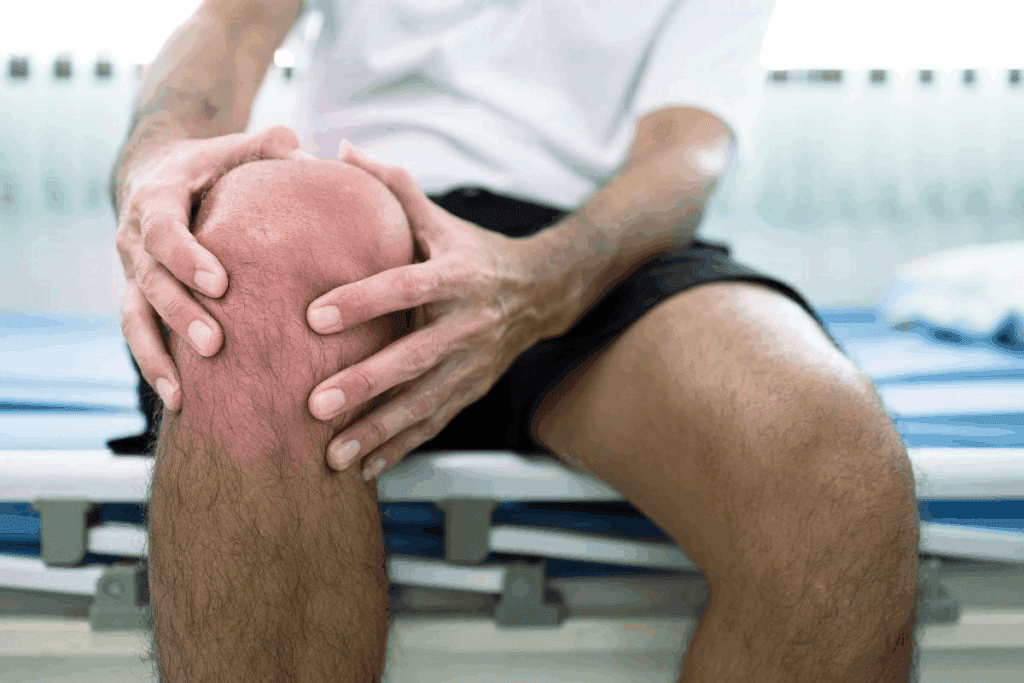
Did you know that nearly 1 in 5 adults in the United States suffers from some form of arthritis? Many of these people are also at risk of developing bursitis. This shows how important it is to understand the link between these two conditions.
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis raise the risk of bursitis. It’s key to know the causes, symptoms, and treatments for these conditions.

Arthritis is not just one disease. It’s a term for many conditions that affect joints and tissues. We’ll look at the main types of arthritis, their characteristics, and how they impact joints.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common arthritis type. It’s caused by cartilage and bone degeneration. It mainly affects hips, knees, spine, and hands.
The degeneration leads to pain, stiffness, and less mobility. Age, obesity, injuries, and genetics play big roles in OA.
Wear and tear on joints over time causes OA. As we age, cartilage wears down, causing bone pain. Staying healthy and exercising gently can help prevent it.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease. It attacks the joint lining, causing inflammation and pain. RA often affects hands, feet, wrists, and knees. Although the precise cause of rheumatoid arthritis remains unclear, both genetic and environmental factors may contribute significantly.
RA is different from OA because it’s systemic and has autoantibodies. It can cause serious joint damage if not treated. Treatment includes medicines to reduce inflammation and prevent damage.
There are other notable arthritis types:
Each type of arthritis has its own challenges. Knowing these differences is key to effective treatment.
Arthritis includes many conditions, each with its causes and effects. Understanding these helps us develop better treatment plans.
To understand bursitis, we need to know about bursae and their role in joint movement. Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs. They reduce friction between bones, tendons, and ligaments. This allows joints to move smoothly without pain.
Bursae are key in joint movement. They reduce friction and act as cushions between bones, tendons, and ligaments. This is very important in areas where tendons or ligaments rub against bony parts.
There are many bursae in our bodies, each with its own job. For example, the subacromial bursa in the shoulder helps the rotator cuff tendons move smoothly over the acromion.
Bursitis can happen in different parts of the body. It often occurs in areas with a lot of movement or pressure. Common places include:
Bursitis happens for many reasons, like repetitive motion, direct trauma, infection, or inflammatory diseases. Knowing these causes helps in preventing and treating bursitis.
| Cause | Description |
| Repetitive Motion | Using a joint over and over can irritate the bursa, causing inflammation. |
| Direct Trauma | A fall or hit to a joint can irritate the bursa and cause bursitis. |
| Infection | Bacterial infection in the bursa can lead to severe bursitis. |
| Inflammatory Conditions | Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis can make bursitis more likely. |
Understanding the relationship between arthritis and bursitis requires careful consideration of their complexities. It involves both direct and indirect factors. We will look at how arthritis can lead to bursitis.
Arthritis and bursitis are closely related. Arthritis often leads to bursitis. Direct connections include the inflammation in arthritis that can spread to bursae, causing inflammation and bursitis.
Indirect connections involve the mechanical changes and compensatory movements due to arthritis. These changes can put extra stress on bursae, leading to inflammation.
Mechanical factors are key in bursitis development in arthritis patients. As arthritis progresses, it can cause joint deformities and alter biomechanics. This leads to increased stress on bursae.
For example, in osteoarthritis of the hip, degenerative changes can alter gait patterns. This places extra stress on the trochanteric bursa, potentially causing trochanteric bursitis.
Compensatory movement patterns in arthritis patients also contribute to bursitis. These altered movements can cause repetitive strain on specific bursae, leading to inflammation and pain.
Understanding the relationship between arthritis and bursitis requires careful consideration of their complexities.
Osteoarthritis is a disease that wears down joints. It causes inflammation that can lead to bursitis. This happens when cartilage breaks down, causing bones to rub against each other.
As osteoarthritis worsens, it affects the bursae around joints. Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints. They help reduce friction between bones and soft tissues.
This can cause bursitis, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joint.
People with osteoarthritis often change how they move to avoid pain. These changes might help in the short term but can irritate bursae over time.
For instance, changing how you walk can stress bursae in your hips or knees. Moving your shoulders or elbows differently can also irritate bursae in these areas.
It’s important to understand how osteoarthritis, movement changes, and bursitis are connected. This knowledge helps in finding effective treatments for both arthritis and bursitis.
Understanding the relationship between arthritis and bursitis requires careful consideration of their complexities.
Rheumatoid arthritis causes an abnormal immune response, leading to inflammation. This inflammation can hit various parts of the body. It affects the synovial tissues around joints and bursae.
The inflammatory process in RA involves cytokines and other mediators. These cause swelling, pain, and damage to tissues.
Key inflammatory mechanisms include:
Systemic inflammation from RA can harm bursae. Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints. They reduce friction between bones and soft tissues. Inflammation in bursae is called bursitis.
The effects of systemic inflammation on bursae include:
Understanding the relationship between arthritis and bursitis requires careful consideration of their complexities.
Arthritis can cause bursitis in many joints. Each joint has its own challenges. We’ll look at how arthritis leads to bursitis in the shoulder, hip, and knee. We’ll also talk about the specific types of bursitis in these areas.
Understanding the relationship between arthritis and bursitis requires careful consideration of their complexities.
Symptoms include pain when moving the shoulder, like during overhead activities. You might also feel tenderness when touched. Treating this condition means tackling both the bursitis and the arthritis.
Trochanteric bursitis is common in the hip, often tied to arthritis. The trochanteric bursa is near the greater trochanter of the femur. Inflammation here can cause pain on the outer hip. Trochanteric bursitis often occurs in those with osteoarthritis of the hip, due to joint degeneration and altered biomechanics.
Treatment includes physical therapy, anti-inflammatory meds, and sometimes injections to reduce inflammation.
The knee is also affected by arthritis-induced bursitis, like prepatellar bursitis. This condition involves inflammation of the bursa in front of the patella. It’s common in those who kneel a lot. While not only caused by arthritis, prepatellar bursitis can get worse with it, as the inflammation can irritate the bursa.
Symptoms include swelling and pain at the front of the knee. To manage it, protect the knee, use anti-inflammatory measures, and treat any underlying arthritis.
Chronic arthritis and bursitis are tough on joints over time. These conditions affect joint function and get worse if not managed well.
These conditions can really hurt joint function. The ongoing inflammation can damage cartilage, create scar tissue, and reduce motion. This leads to more pain and stiffness.
As joints get worse, doing everyday tasks becomes harder. This shows why early treatment and good management are key.
Both chronic arthritis and bursitis get worse if not treated. Many things can make them progress faster, like age, genetics, and lifestyle.
| Factor | Impact on Disease Progression |
| Age | Increased susceptibility to joint degeneration |
| Genetic predisposition | Higher risk of developing severe arthritis |
| Lifestyle factors | Obesity and lack of exercise can exacerbate symptoms |
Knowing these factors helps create better treatment plans. These plans should tackle symptoms and the root causes of chronic arthritis and bursitis.
Understanding these conditions’ effects and progression is vital. It highlights the need for thorough management to protect joint health over time.
It’s important to know how arthritis changes how joints work. This helps prevent bursitis in those affected. Arthritis can make joints move differently, putting more stress on the tissues around them.
Arthritis can lead to several changes in how joints work, including:
To avoid overusing joints and lower the chance of bursitis, arthritis patients can do a few things:
By understanding how arthritis affects joints and taking steps to prevent overuse, patients can lower their risk of bursitis. This helps keep their joints healthier.
It’s important to know the symptoms of arthritis and bursitis together. This helps in managing and treating them well. When both conditions are present, it’s a complex situation that needs careful attention.
Understanding the relationship between arthritis and bursitis requires careful consideration of their complexities.
Both conditions can cause swelling, but it’s different in each. Arthritis swelling is inside the joint, while bursitis swelling is around it. Joint stiffness is common, often after resting or being inactive.
Understanding the relationship between arthritis and bursitis requires careful consideration of their complexities.
Understanding each condition’s unique aspects and how they interact is vital. This way, patients can get the right treatment.
To diagnose arthritis-related bursitis, we use a detailed approach. This includes both clinical evaluation and diagnostic testing. We know how complex this condition is. So, we focus on accurate diagnosis for the best treatment.
A thorough physical exam is the first step. We check the affected joint carefully. This includes feeling tenderness and checking how well the joint moves.
We also do special tests to see if the symptoms come back. For example, in the shoulder, we might do the Neer or Hawkins-Kennedy test. These tests help us see if arthritis is causing the bursitis.
Imaging studies are key to confirming the diagnosis. We often use X-rays to look for signs of arthritis. This includes checking for joint space narrowing or osteophytes.
For a closer look, we might use ultrasound or MRI. These can show us the inflamed bursa and any other problems. They help us see the extent of the bursitis and any joint inflammation.
Laboratory tests help find the cause of arthritis-related bursitis. We check for inflammation markers in the blood. This helps us rule out other conditions.
In some cases, we take fluid from the bursa for analysis. This can confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment.
| Diagnostic Method | Purpose | Key Findings |
| Physical Examination | Assess joint tenderness and mobility | Tenderness, limited range of motion |
| X-rays | Evaluate joint for arthritis signs | Joint space narrowing, osteophytes |
| Ultrasound/MRI | Visualize inflamed bursa and associated pathology | Bursa inflammation, tendon pathology |
| Laboratory Tests | Identify underlying cause and inflammation | Elevated ESR/CRP, infection signs |
Treating arthritis and bursitis needs a plan made just for each person. It often includes medicine, changes in lifestyle, and sometimes surgery.
Many medicines can help with both arthritis and bursitis. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to lessen pain and swelling. Sometimes, corticosteroid injections are given to treat inflamed bursae or joints.
Physical therapy is key for managing arthritis and bursitis. It includes exercises to improve joint movement, strengthen muscles, and lessen pain.
“Physical therapy is essential in maintaining joint function and reducing pain in patients with arthritis and bursitis.”
Expert Opinion
Physical therapy for arthritis and bursitis includes:
If other treatments don’t work, surgery might be needed. Surgery can be simple or complex, depending on the case.
Knowing all the treatment options helps doctors create a plan that fits each patient’s needs. This approach can lead to better results.
Arthritis patients can greatly benefit from protecting their joints. This helps manage symptoms and prevents bursitis, a condition of inflammation in the bursae.
Using ergonomic strategies in daily life is key. It reduces joint stress. Adjusting your workspace for good posture and using tools that reduce strain are important.
For example, keeping your monitor at eye level and using ergonomic handles can help. These actions reduce strain on your neck and wrists.
Proper body mechanics are vital for joint protection. Being mindful of posture and movement helps avoid unnecessary joint stress.
When lifting, bend at the knees to distribute weight evenly. Avoid twisting and use leg muscles to stand up. These actions protect your joints.
| Proper Body Mechanics | Benefits |
| Bending at the knees when lifting | Reduces strain on the back |
| Avoiding twisting motions | Minimizes stress on joints |
| Using leg muscles to stand up | Protects joints from excessive strain |
Assistive devices are essential for joint protection. They reduce strain on compromised joints. Tools like jar openers and reachers to walkers and wheelchairs are examples.
These devices improve daily life for arthritis patients. They make tasks easier and less painful. For instance, walkers reduce knee and hip joint strain when walking.
Examples of Assistive Devices:
By using these strategies, arthritis patients can protect their joints. This reduces bursitis risk and improves their quality of life.
Making lifestyle changes is key to managing arthritis and bursitis. These changes can help reduce symptoms and improve life quality.
An anti-inflammatory diet is vital for managing both conditions. Eating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and sardines, can help. Also, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provide antioxidants and fiber.
It’s important to avoid foods that can trigger inflammation. This includes processed meats, sugary drinks, and refined carbs. Drinking plenty of water is also key for healthy joints.
Exercise is essential for managing arthritis and bursitis. Low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and yoga are good. They help keep joints mobile and strong without too much strain.
It’s important to make an exercise plan that fits your needs. For those with severe pain, start with gentle stretches and then move to more active exercises. Getting advice from a healthcare professional or physical therapist can help create a good plan.
Keeping a healthy weight is important for joint health. Extra weight can make joint pain worse and speed up wear and tear, mainly in hips, knees, and spine.
Eating well and exercising regularly can help keep a healthy weight. Even a small amount of weight loss can make a big difference in symptoms and joint function.
In recent years, we’ve seen big steps forward in treating arthritis-related bursitis. This brings new hope to those dealing with these tough conditions. Research is helping us understand arthritis and bursitis better. This leads to new ways to treat them together.
Biological therapies have changed how we treat arthritis. They’re also showing promise in treating bursitis linked to arthritis. These treatments focus on specific molecules that cause inflammation. This makes them more effective at reducing inflammation and slowing disease growth.
“The use of biological agents represents a significant shift in our treatment paradigm, allowing us to target the underlying causes of inflammation.” This method not only helps symptoms but also might cut down on the need for other medicines.
Regenerative medicine, like PRP injections and stem cell therapy, is being explored for bursitis treatment. These methods aim to heal and grow back the damaged bursa. Early studies show they can help with pain and function in bursitis patients.
New physical therapy methods are also key in managing arthritis-related bursitis. These focus on improving joint movement, strengthening muscles, and boosting function. Techniques like manual therapy and exercises are designed for arthritis and bursitis patients. They help manage symptoms and prevent joint damage.
“Physical therapy is a cornerstone in the treatment of arthritis-related bursitis, improving symptoms and quality of life.”
By using these new advances, healthcare providers can give better care to those with arthritis-related bursitis. This leads to better results and a better life for patients.
If you’re dealing with ongoing or severe joint pain, knowing when to see a doctor is key. Joint pain can signal many issues, like arthritis or bursitis. These need the right diagnosis and treatment.
Choosing when to go to the doctor can be tough. But knowing certain signs can guide your decision.
Some symptoms mean you should see a doctor right away. These include:
As the
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons says, “Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve outcomes for patients with joint pain.”
| Red Flag | Possible Cause | Action Required |
| Severe Pain | Advanced arthritis or bursitis | Seek immediate medical care |
| Swelling or Redness | Infection or inflammation | Consult a healthcare professional |
| Instability | Ligament or tendon damage | Visit an orthopedic specialist |
Finding the right doctor for joint pain is important. You might need to see:
Ask your primary care doctor for recommendations or check with your insurance for in-network specialists.
Understanding Understanding the relationship between arthritis and bursitis requires careful consideration of their complexities.etter joint health. This article has shown how arthritis can cause bursitis and the treatments available.
Conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can lead to bursitis. To manage these, a mix of medicines, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes is needed.
Protecting joints and taking preventive steps can lower bursitis risk. New treatments like biological therapies and regenerative medicine offer hope.
As we learn more about arthritis and bursitis, a detailed treatment plan is vital. It helps keep joints healthy and improves life quality.
Yes, arthritis can lead to bursitis. The inflammation and wear and tear from arthritis can irritate the bursae. This causes mechanical stress on the joints.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints. The pain gets worse with movement. You might also find it hard to move your joints as much.
Doctors use physical exams, X-rays, or MRI scans to diagnose it. They also do lab tests to find out why the joints are inflamed and the bursae are irritated.
Treatments include medicines like anti-inflammatory drugs. Physical therapy helps keep the joints moving. Surgery is an option when other treatments don’t work.
Use ergonomic tools and follow proper body mechanics. Assistive devices can also help protect your joints and reduce stress on the bursae.
Yes, eating anti-inflammatory foods and exercising right can help. Keeping a healthy weight also reduces joint stress and inflammation.
New treatments include biological therapies and regenerative medicine. There are also advanced physical therapy methods. These aim to tackle the root causes of both conditions.
See a doctor if you have severe pain, sudden swelling, or if your symptoms get worse. It’s important to find a specialist for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Osteoarthritis can cause bursitis by wearing down the joints. This changes how the joint moves and can irritate the bursae, causing inflammation.
Yes, rheumatoid arthritis can lead to bursitis. The inflammation from the autoimmune disease can affect the bursae, causing inflammation.
Overusing joints in arthritis can cause bursitis. The changed mechanics of the joint due to arthritis put extra stress on the bursae. This leads to irritation and inflammation.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!