Neurogenic bladder happens when the brain, spinal cord, or nerves have issues. This leads to bladder control problems. It can make daily life hard. Common reasons include multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and spinal cord injury.
Liv Hospital is dedicated to finding new ways to handle neurogenic bladder. They focus on understanding why urinary incontinence happens. This way, they hope to help patients get better.
Key Takeaways
- Neurogenic bladder is caused by brain, spinal cord, or nerve problems.
- Multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and spinal cord injury are common causes.
- Liv Hospital prioritizes innovative solutions for managing neurogenic bladder.
- Understanding the underlying causes is key to effective management.
- Neurogenic bladder significantly impacts an individual’s quality of life.
Understanding Neurogenic Bladder: When Neurology Affects Urination
The nervous system and bladder control are closely linked in a neurogenic bladder. This condition happens when neurological issues or damage affect the bladder’s normal function. It can cause problems like incontinence, urgency, and retention.
How Normal Bladder Function Works
Normal bladder function is a complex process. It involves the bladder muscle, nerves, and sphincters working together. When the bladder fills up with urine, it stretches the bladder wall.
When it’s full enough, signals go to the brain saying it’s time to pee. The brain then tells the bladder to contract and the sphincters to relax. This lets urine flow out properly.
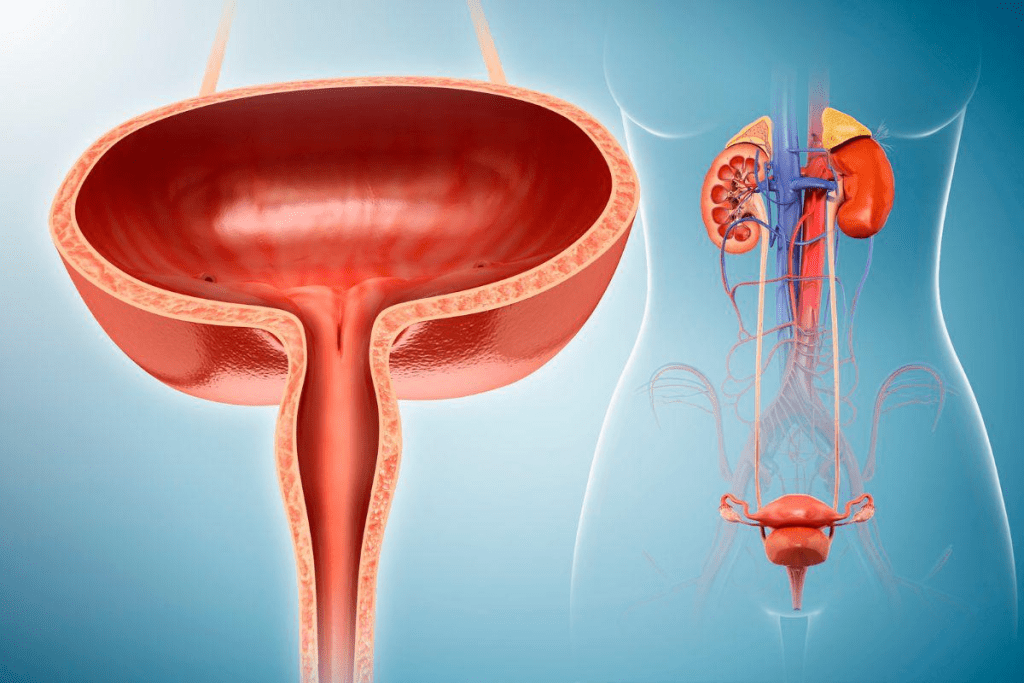
The Neural Pathways That Control Urination
The process of controlling urination uses many pathways in the nervous system. The pontine micturition center in the brainstem is key. It helps the bladder muscle contract and the sphincter relax.
Damage to these pathways, like from spinal cord injuries or diseases, can cause neurogenic bladder. Studies show sacral neuromodulation can help. It improves bladder control for 52-72% of patients.
Common Symptoms of Neurogenic Bladder
Neurogenic bladder shows itself through symptoms like urgency, frequency, incontinence, and retention. The exact symptoms depend on the neurological condition and the extent of nerve damage. For example, those with spinal cord injuries might have detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia. This is when the bladder and sphincter muscles contract together, blocking urine flow.
Knowing these symptoms is key to diagnosing and treating neurogenic bladder. Treatments like sacral neuromodulation, catheterization, and medications are chosen based on the patient’s symptoms and the cause of their condition.
Multiple Sclerosis and Bladder Dysfunction
The link between multiple sclerosis and bladder issues is a big concern for both patients and doctors. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease that harms the central nervous system. It causes many symptoms, including problems with bladder control.
Effects on Bladder Control
MS can seriously affect bladder function because it damages the central nervous system. It can cause a neurogenic bladder, where you can’t control when you pee. This happens because the nerves between the bladder and the brain don’t work properly.
The way MS affects bladder control varies from person to person. Some might feel the need to pee a lot or pee too little. Others might not be able to hold their pee, leading to bladder incontinence. This can really lower their quality of life.
Common Urinary Symptoms in MS Patients
Many people with MS face urinary problems, affecting 40% to 90% of them. These issues include:
- Urinary urgency
- Frequency
- Nocturia (waking up many times at night to pee)
- Bladder incontinence
- Difficulty starting to pee
- Not emptying the bladder fully
Impact on Quality of Life
Urinary symptoms from MS can really hurt a person’s quality of life. Bladder dysfunction can make people stay away from social events. They might worry about accidents or needing to pee too often. These issues can also make them feel anxious or depressed.
It’s important to manage bladder problems to improve life for those with MS. This means using medicine, changing how you live, and sometimes using special devices.
Parkinson’s Disease and Urinary Complications
Parkinson’s disease often causes urinary problems, making life harder for patients. This neurodegenerative disorder impacts not just motor skills but also autonomic functions like bladder control.
Mechanisms of Bladder Dysfunction in Parkinson’s
Bladder issues in Parkinson’s stem from the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the brain. These neurons are key to motor control. Their loss disrupts bladder control, leading to symptoms like urgency and frequency.
Detrusor overactivity is a big problem, where the bladder muscle gets too active. This causes a sudden need to urinate. It’s often paired with detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia, where the bladder and urethral sphincter don’t work together properly, making urination harder.
“Urinary dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease significantly impacts the quality of life, necessitating a thorough management plan that covers both neurological and urological aspects.”
Progression of Bladder Symptoms with Disease Advancement
As Parkinson’s disease gets worse, urinary symptoms get more severe. Research shows that 37% to 72% of patients face urinary issues, with more as the disease progresses.
- Urgency and frequency are common symptoms.
- Nocturia, or nighttime urination, disrupts sleep.
- Incontinence can happen later, affecting dignity and quality of life.
Challenges in Management
Dealing with urinary problems in Parkinson’s is tough. It’s because of the mix of neurological decline and bladder issues. Treatment often needs a team effort, including medicine, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery.
One big challenge is finding the right balance. Some Parkinson’s meds can make urinary problems worse.
Post-Stroke Bladder Control Issues
Stroke can affect more than just movement and speech. It can also impact bladder control. Many survivors face challenges with urinary continence, affecting their daily lives.
Types of Urinary Dysfunction After Stroke
Stroke survivors may deal with different urinary dysfunction types. Common problems include:
- Urinary incontinence
- Urinary retention
- Overactive bladder
- Neurogenic bladder
These issues arise from the brain’s damage affecting bladder control. The severity and type can vary greatly among survivors.
Correlation Between Stroke Location and Bladder Symptoms
The brain area hit by the stroke can affect bladder symptoms. Studies show that certain brain areas are linked to specific urinary problems.
- Frontal lobe strokes can disrupt bladder control signals.
- Brainstem strokes often cause severe urinary issues.
Recovery Patterns and Long-term Prognosis
Recovery from bladder control issues post-stroke varies. Some see improvement, while others face ongoing urinary dysfunction.
Recovery depends on several factors:
- Stroke severity
- Stroke location
- Rehabilitation success
Knowing these factors helps set realistic goals and plan treatments for bladder control issues post-stroke.
Spinal Cord Injury and Its Effects on Bladder Function
It’s important to understand how spinal cord injuries affect bladder function. These injuries can lead to bladder problems in 70-84% of people. The severity of the injury determines the type of bladder issue.
Types of Bladder Dysfunction Based on Injury Level
The level and completeness of a spinal cord injury determine bladder dysfunction. People with injuries above T6-T7 often face autonomic dysreflexia. This is a serious condition that can be caused by bladder issues or other problems below the injury.
A medical expert says, “Managing neurogenic bladder in spinal cord injury patients needs a detailed approach. This includes considering the injury level, its completeness, and the patient’s health.”
“The bladder and the spinal cord are closely linked. Damage to the spinal cord can cause big problems with bladder control.”
Complications: Infections, Reflux, and Kidney Damage
People with spinal cord injuries face higher risks of urinary problems. These include infections, vesicoureteral reflux, and kidney damage. Regular checks and proper management are key to avoiding these issues. For example, using catheters to manage bladder issues is common, but it must be done carefully to avoid infections.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a big worry because they can lead to serious problems.
- Vesicoureteral reflux can cause kidney damage if not managed well.
- Kidney damage is a long-term risk from chronic bladder problems and related issues.
Psychological Impact of Neurogenic Bladder in SCI
The emotional impact of neurogenic bladder on those with spinal cord injuries is significant. Losing bladder control can make people feel embarrassed, isolated, and depressed. Supportive care and counseling are vital for managing these feelings and challenges.
“Living with a urogenic bladder means big lifestyle changes,” says a healthcare worker. “But with the right support and management, people can have fulfilling lives.”
Treatment Approaches for Neurological Bladder Disorders
Liv Hospital focuses on new treatments for neurogenic bladder. Managing neurogenic bladder means using a mix of treatments. Each one is chosen based on the person’s needs.
Medication Options
Medicines are key in treating a neurogenic bladder. Anticholinergics and beta-3 adrenergic agonists help control the bladder. The right medicine depends on the cause and the patient’s health.
Sacral Neuromodulation
Sacral neuromodulation is a new treatment. It uses electrical impulses to help the bladder work properly. It’s good for those with trouble holding urine or an overactive bladder.
Catheterization Techniques
Catheterization is a common treatment for a neurogenic bladder. Intermittent catheterization helps empty the bladder. It lowers the chance of infections and kidney problems.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery might be needed for some cases of neurogenic bladder. Surgeries can help with drainage, spasms, or other issues. Surgery is considered after other options are tried.
Managing a neurogenic bladder needs a plan made just for the person. Using different treatments helps patients control their bladder better. This improves their quality of life.
Conclusion: Living With Neurogenic Bladder
Living with a neurogenic bladder means you need a detailed plan to manage symptoms and improve life quality. This condition often comes with neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and spinal cord injuries. It affects how you control your bladder, making daily life challenging.
To manage it well, you need to make lifestyle changes, use medical treatments, and sometimes undergo surgery. Knowing what causes neurogenic bladder and using a plan made just for you can help control your bladder. This way, you can feel better overall.
Handling a neurogenic bladder correctly can make life better for those dealing with it. It’s key for people with this condition to team up with doctors to create a treatment plan that works best for them. This ensures they can manage bladder control issues effectively.
FAQ
What is a neurogenic bladder?
Neurogenic bladder is a condition where a person has trouble with bladder control. This is due to a brain, spinal cord, or nerve problem.
What are the common symptoms of neurogenic bladder?
Common symptoms include urinary incontinence and urinary retention. Other symptoms are frequent urination and bladder spasms.
How does multiple sclerosis affect bladder control?
Multiple sclerosis can damage the nerves that control the bladder. This leads to symptoms like urge incontinence, frequency, and urinary retention.
What are the urinary complications associated with Parkinson’s disease?
Parkinson’s disease can cause urinary urgency, frequency, and urge incontinence. This is due to the degeneration of neurons that control bladder function.
How does a spinal cord injury affect bladder function?
A spinal cord injury can cause a neurogenic bladder. Symptoms include urinary retention, incontinence, and bladder spasms.
What are the treatment options for a neurogenic bladder?
Treatment options include medication and sacral neuromodulation. Other options are catheterization and surgical interventions.
Can sacral neuromodulation help manage neurogenic bladder?
Yes, sacral neuromodulation is a treatment that can help manage a neurogenic bladder. It regulates bladder function.
Why is it hard to manage bladder control after a stroke?
Managing bladder control after a stroke is challenging. This is due to varying degrees of nerve damage and urinary dysfunction.
What is the impact of neurogenic bladder on quality of life?
Neurogenic bladder can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. It causes emotional distress, social isolation, and decreased independence.
How can I manage bladder pressure and discomfort?
Managing bladder pressure and discomfort may involve lifestyle changes. This includes dietary modifications, pelvic floor exercises, and medication.
References
- Choi, E. H., & Na, H. Y. (2009). The role of sacral neuromodulation in the treatment of neurogenic bladder. Korean Journal of Urology, 50(12), 1145“1150. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2757193/
- Lund, A., & Hansen, T. B. (2019). Bladder dysfunction following stroke. International Journal of Clinical Practice, 73(1), e13271. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/ijcp.13271
- Ostergard, D. R. (2016). Management of the neurogenic bladder in spinal cord injury. Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine, 39(5), 579“587. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10790268.2016.1188351