Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by
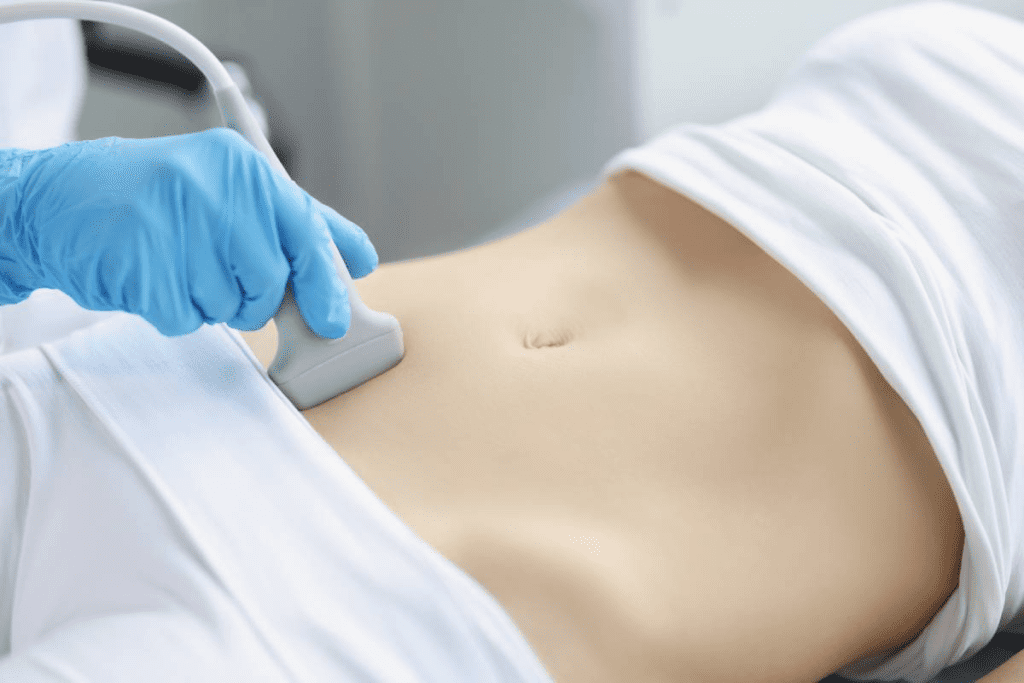
Our team uses a handheld device called a transducer. It sends high-frequency sound waves to the bladder. These waves create detailed images that help us find urinary problems and abnormalities.
This test is key for spotting issues like urinary retention and bladder stones. We aim to provide top-notch healthcare. We support patients through every step of diagnosis and treatment.
It’s important to understand how bladder ultrasounds work. They are key in urology, helping us see how the bladder works without surgery.
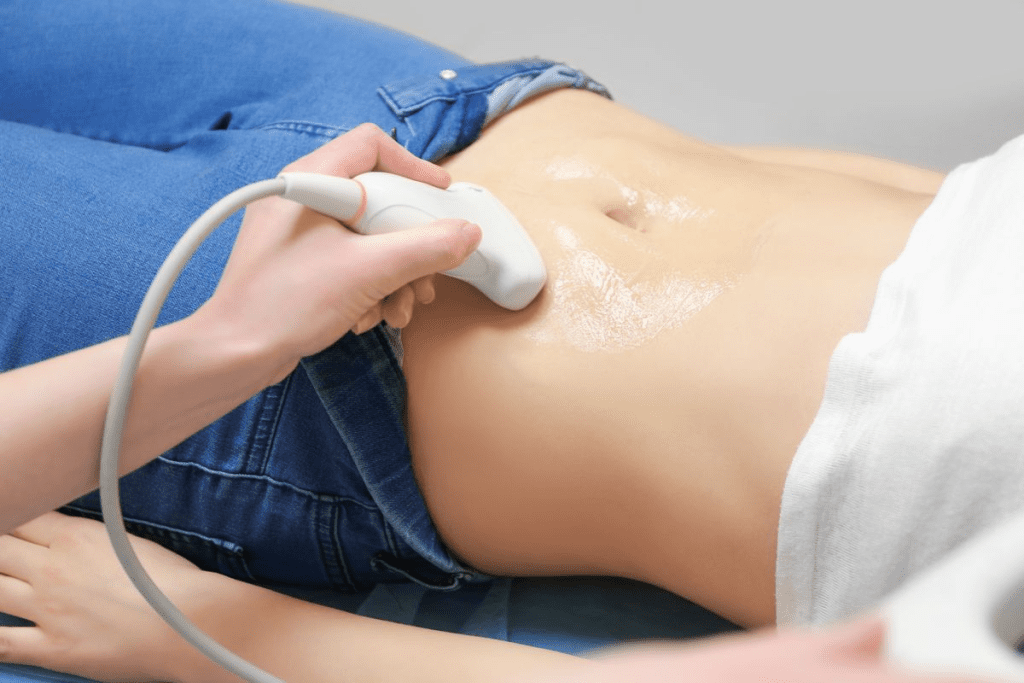
Ultrasound uses sound waves from a handheld device to see inside the bladder. This helps us find problems in the urinary system. A full bladder is needed for clear images because it moves other organs out of the way.
“A full bladder is essential for a successful ultrasound examination,” as it allows for better visualization of the bladder walls and contents. This requirement is key to accurate diagnoses and shows why getting ready for the test is important.
There are many ultrasound machines for bladder imaging, from simple to advanced. We choose the right one based on what the patient needs.
Ultrasound is better than other tests because it’s safe and doesn’t use radiation. It’s also quick, often giving results right away.
Using ultrasound has made patient care better by avoiding more invasive tests. As technology improves, ultrasound will play an even bigger role in diagnosing urological issues.
Getting a bladder scan is easy and doesn’t hurt. It helps us understand how your bladder works. We’re here to help you through every step of the process.
To get accurate results, you need a full bladder for your bladder scan procedure. Drink water about an hour before. A full bladder for a sonogram is key to clear images.
Our team will tell you exactly how to prepare for your bladder test. This way, you’ll know what to expect.
During the bladder scan procedure, you’ll lie on a table. A gel will be applied to your pelvic area. Then, a transducer will take pictures of your bladder.
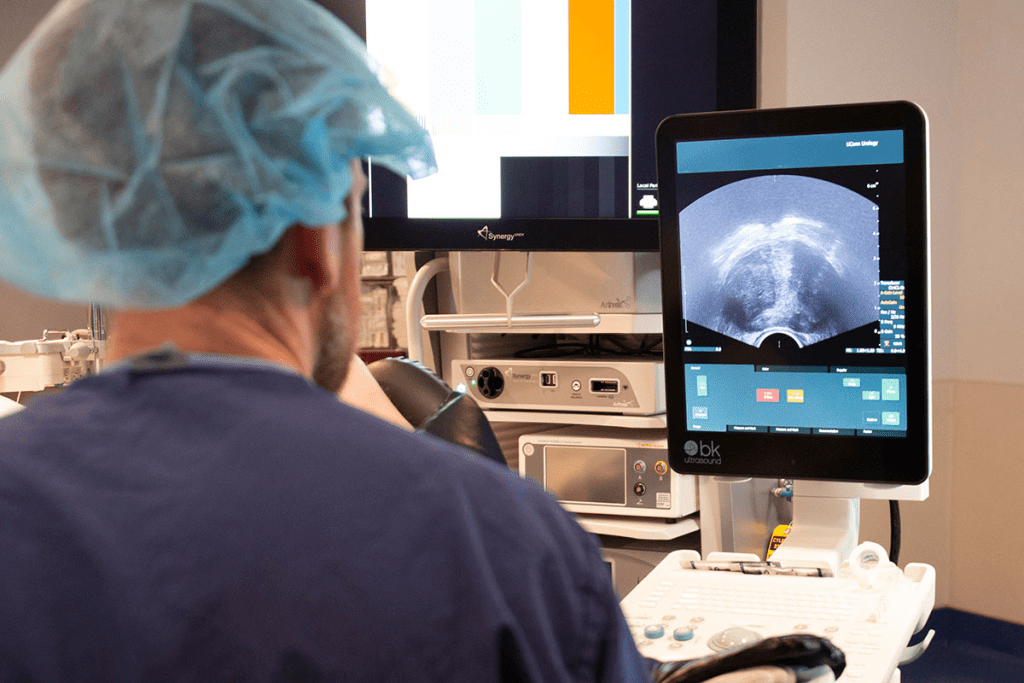
The technician will move the transducer to get different views of your bladder. These will be shown on a monitor. You might need to change positions or hold your breath for a few seconds.
The whole bladder scan procedure takes 15 to 30 minutes. Most people find it very comfortable. The need to hold your urine might cause some discomfort, but it shouldn’t hurt.
Bladder ultrasounds are key in checking bladder health. They look at both the structure and how it works. This tool helps doctors understand the bladder’s shape and how well it functions.
Ultrasound shows a normal bladder anatomy as smooth and thin. It also checks if the bladder is shaped right. Doctors look for any signs of problems in the bladder wall.
Knowing the bladder’s capacity is vital. Bladder ultrasounds measure how much urine the bladder holds. This helps find issues like not being able to hold urine or needing to go too often.
The post-void residual (PVR) volume is also important. It shows how much urine is left after you pee. Ultrasound can check this without needing to insert anything. It helps see if the bladder is emptying right.
Ultrasound helps doctors find and treat many bladder problems. It’s a key tool in urology today.
Bladder ultrasounds are key in spotting urinary retention and blockages. They give us important info on bladder health. We use this tech to check how well the bladder works and find problems that might cause urinary issues.
Urinary retention can show up in two main ways: acute or chronic. Acute urinary retention means you can’t urinate suddenly and need quick medical help. Chronic urinary retention is when you can’t fully empty your bladder over time.
Ultrasounds help tell these apart by looking at how much urine is left after you try to pee. This helps us see how bad the retention is and what treatment is best. It’s also key for keeping an eye on patients with long-term retention, helping us tweak their care as needed.
Bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) happens when urine can’t flow out because of a blockage. This is often because of an enlarged prostate or other blockages. Ultrasounds can spot BOO by looking at how thick the bladder wall is and finding any oddities in the bladder or prostate.
Signs of BOO include a thick bladder wall, high PVR volumes, and odd urine flow patterns. By looking at these signs, we can figure out if someone has BOO. Then, we can suggest treatments to help with symptoms and improve how well you pee.
Detrusor underactivity is when the muscle that makes the bladder contract doesn’t work right. This can cause you to not empty your bladder fully and lead to retention. Ultrasounds help us check if this is happening by looking at how well the bladder contracts and measuring PVR volumes.
By studying these, we can spot detrusor underactivity and plan treatments to help your bladder work better. This can make your symptoms better and improve your overall bladder function.
Bladder ultrasounds are key in spotting many bladder problems. They let doctors see the bladder and its areas in real-time. This helps find any oddities.
Bladder ultrasounds are great at finding bladder tumors and cancer. They use sound waves to show the bladder wall clearly. This helps spot tumors and see how big and where they are.
Spotting bladder cancer early is key to treating it well. Bladder ultrasounds are a big help in this.
Ultrasounds also find bladder stones and calcifications well. These hard spots can hurt and cause trouble with urination. Ultrasound shows where and how big these stones are, helping decide how to treat them.
Bladder ultrasounds can also spot bladder diverticula and other wall issues. Diverticula are like pouches in the bladder wall. They can cause trouble with urination and infections. Ultrasound helps see how big and what effect these pouches have.
Ultrasounds also hint at inflammation or infection in the bladder. We look for signs like thick bladder walls or stuff in the bladder. These signs tell us what tests or treatments are needed next.
In short, bladder ultrasounds are a powerful tool for finding many bladder problems. They help us give the best care to patients with bladder issues.
During a bladder ultrasound, we check several key parameters. These insights are vital for understanding bladder health. They help us diagnose and manage urological issues.
Bladder wall thickness is a key measurement in a bladder ultrasound. If the wall is too thick, it might mean bladder problems like obstruction or overactivity. We look at the wall thickness to spot issues that need attention.
A normal bladder wall is usually 3 to 5 mm thick when it’s empty. But this can change based on the person’s health and other factors. By checking the wall thickness, we learn a lot about the bladder’s health and how it works.
Assessing bladder weight is another important part of a bladder ultrasound. This helps us find issues like bladder hypertrophy, often caused by blockages or other problems. We use this info to understand how severe the condition is and plan the right treatment.
To calculate bladder weight, we use special ultrasound software. It looks at the bladder’s size and wall thickness. This is key for diagnosing and treating bladder function problems.
The detrusor muscle is essential for bladder function. We examine its thickness and how well it contracts during a bladder ultrasound. This helps us find out if there are problems causing urinary symptoms or other bladder issues.
By looking at the detrusor muscle, we can spot issues like underactivity or overactivity. These problems can really affect a person’s life. Knowing this helps us create a treatment plan that fits the individual’s needs.
We use bladder ultrasound in many ways to help patients. It’s a key tool for making quick decisions. It gives us real-time info to guide our actions.
Bladder ultrasound is key to placing catheters correctly. Accurate catheterization is vital, like in surgeries or for urinary issues. It helps avoid problems and makes patients more comfortable.
Ultrasound helps check if treatments are working. For urinary retention, it tracks how much urine is left after voiding. This lets doctors adjust treatments for better results.
Ultrasound is also used for LUTS. It looks at bladder thickness and the amount of urine left after voiding. This helps find the cause of symptoms and plan better treatments.
After acute urinary retention, ultrasound checks bladder function. It looks at bladder size and muscle activity. This helps predict if problems will come back and plan for follow-up care.
In summary, bladder ultrasound has many uses in healthcare. It helps doctors make better decisions and improve patient care.
Bladder ultrasounds are key in urology today. They help check bladder health without surgery. At Liv Hospital, we see how vital they are and aim to offer top-notch care.
These ultrasounds have changed urology for the better. They use new tech to help patients more than ever before. This means we can give better care and see better results.
We’re all about top healthcare at Liv Hospital. Our use of the latest ultrasound tech shows our dedication to our patients. We’re here to make sure you get the best care in urology.
A bladder ultrasound is a test that uses sound waves to see the bladder. It checks the bladder’s shape and how it works. It looks for problems like tumors, stones, or diverticula, and checks for blockages or retention.
A full bladder is needed for a clear view of the bladder. It helps see any issues and measure the bladder’s size and how much urine is left after you pee.
The bladder scan usually takes a few minutes. It can take longer if there are more things to check.
A bladder ultrasound is usually painless. You might feel a bit of discomfort from the full bladder or the probe. But this is usually short and mild.
Yes, it can spot bladder tumors and cancer. It looks for changes in the bladder wall and inside. But a biopsy is needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Bladder ultrasound is non-invasive and doesn’t use radiation. It gives real-time images. It’s quick and easy, making it a great tool for urology.
Yes, it can measure the bladder wall thickness. This is important for checking bladder health. Thick walls can mean problems like blockages or weak muscles.
Ultrasound findings help doctors decide on treatments. They check how well treatments work and look at symptoms. It helps in managing patients and making care plans.
Ultrasound is key in finding urinary retention. It measures how much urine is left after peeing. This helps diagnose and manage retention.
Yes, it can find bladder stones or calcifications. It’s good at spotting these problems. They can cause symptoms or blockages.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!