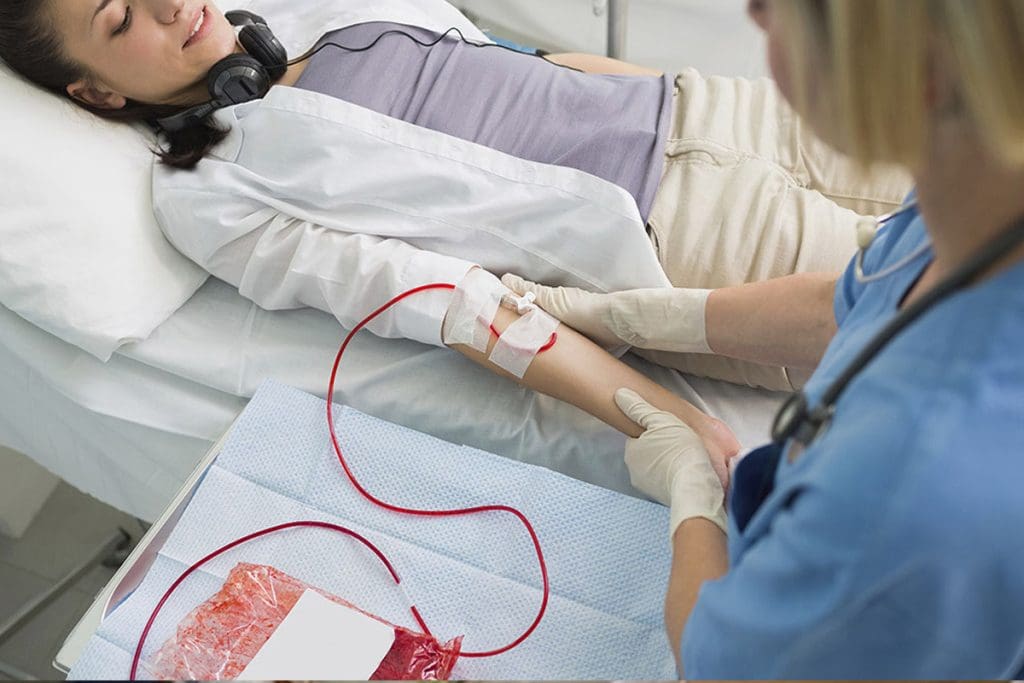
Lymphoma patients often need supportive care because of the disease and its treatments. These can harm blood cell production, causing issues like anemia and low platelet counts.
Lymphoma and its treatments can deplete blood counts, making blood transfusion for anaemia essential for many. At livhospital.com, we offer safe and innovative care. We address the need for blood transfusion for anaemia and other side effects from lymphoma treatment. In some cases, repeated blood transfusion for anaemia supports recovery and improves quality of life for patients.
Key Takeaways
- Lymphoma treatments can cause significant side effects, including anemia and low platelet counts.
- Blood transfusions are often necessary to support patients through their treatment.
- Innovative care options are available to manage treatment side effects.
- Organizations like livhospital.com are dedicated to providing safe and supportive care.
- Understanding the need for blood transfusions is key to lymphoma patient care.
Understanding Lymphoma and Its Effects on Blood Cells
Lymphoma is a cancer that harms the immune system. It affects how the body makes healthy blood cells. We’ll look at how lymphoma impacts the body, focusing on bone marrow and blood cell production.
What is lymphoma, and how does it affect the body?
Lymphoma starts in the lymphatic system, which is part of our immune system. It happens when lymphocytes grow too much. There are two main types: Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The disease can grow in lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow. When it fills the bone marrow, it stops healthy cells from being made. This leads to fewer normal blood cells.

Impact of lymphoma on bone marrow function
The bone marrow makes blood cells, like red and white blood cells and platelets. Lymphoma can get into the bone marrow and mess with its work. This can cause fewer healthy blood cells to be made.
Conditions like anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia can happen. Treatments like chemotherapy and radiation can also hurt the bone marrow’s ability to make blood cells.
How lymphoma disrupts normal blood cell production
Lymphoma mainly hurts blood cell production by affecting the bone marrow. As lymphoma cells grow in the marrow, they block the production of healthy blood cells. This can cause anemia, infections, and bleeding problems.
Understanding these effects is key to managing the disease and its treatment side effects. By knowing how lymphoma affects blood cells, doctors can make better treatment plans.
The Connection Between Lymphoma Treatments and Blood Transfusion Needs
Lymphoma treatments often affect blood cell production. This makes blood transfusions a key part of care. These treatments aim to kill cancer cells but can harm the bone marrow’s ability to make blood.
Chemotherapy’s Impact on Blood Cell Production
Chemotherapy targets fast-growing cells, including cancer and some healthy bone marrow cells. This can lower the production of red and white blood cells and platelets.
- Anemia: Fewer red blood cells can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
- Neutropenia: Fewer white blood cells raise the risk of infections.
- Thrombocytopenia: Fewer platelets can lead to bleeding and bruising.
These issues often need blood transfusions to fix blood cell counts and ease symptoms.
Effects of Radiation Therapy on Bone Marrow
Radiation therapy can also harm bone marrow if the area treated includes active marrow.
It can damage bone marrow stem cells, reducing blood cell production. The damage’s extent depends on the radiation dose and area.

CAR T-cell Therapy and Transfusion Requirements
CAR T-cell therapy is a new treatment for some lymphomas. It removes T-cells, changes them to fight cancer, and then puts them back in.
This therapy can cause cytokine release syndrome (CRS), a serious side effect. It can drop blood cell counts, needing blood transfusions.
It’s important for patients to know about blood transfusion needs with lymphoma treatments. Knowing the risks helps manage care and avoid complications.
Common Blood Disorders Requiring Blood Transfusion for Anemia in Lymphoma Patients
Lymphoma patients often face blood disorders that need medical help, like blood transfusions. These issues can really affect their quality of life and treatment results. We’ll look at the blood disorders linked to lymphoma and how transfusions help manage them.
Severe Anemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Severe anemia is a big problem for lymphoma patients. It happens when there are not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. This can be due to the lymphoma itself or treatments like chemotherapy.
Symptoms include feeling very tired, weak, and short of breath. To tackle severe anemia, doctors often give blood transfusions. This boosts the red blood cell count and helps tissues get enough oxygen.
Thrombocytopenia and Bleeding Risks
Thrombocytopenia, or low platelet count, is common in lymphoma patients. It raises the risk of bleeding, from small bruises to serious hemorrhages. Causes include the lymphoma or its treatment affecting the bone marrow.
To manage severe thrombocytopenia, doctors might give platelet transfusions. But it’s also key to watch for bleeding risks and offer supportive care.
Low Hemoglobin Levels and Their Consequences
Low hemoglobin levels are a sign of anemia, which can be serious for lymphoma patients. It makes it hard for the body to carry oxygen. This can cause fatigue, lower physical performance, and even worsen heart problems.
Regular checks on hemoglobin levels and quick action with blood transfusions can help. This way, patients can better cope with their treatment.
In summary, blood disorders like severe anemia, thrombocytopenia, and low hemoglobin are big worries for lymphoma patients. Knowing about these issues and how blood transfusions help is key for good care.
Recognizing the Signs That You Need a Blood Transfusion
Knowing when you need a blood transfusion is key for lymphoma patients. It’s important to understand when a transfusion is needed during treatment.
Physical Symptoms Indicating Transfusion Necessity
Some physical signs show you might need a blood transfusion. These include:
- Fatigue and weakness that make daily tasks hard
- Shortness of breath, even when you’re not doing much
- Dizziness or feeling lightheaded, which can lead to falls
- Pale skin is a sign of low hemoglobin levels
As one expert says,
“Fatigue is one of the most common symptoms reported by patients with anemia, which is a frequent indication for blood transfusion in lymphoma patients.”
These symptoms can really affect your life. So, it’s important to catch them early and act fast.
Laboratory Values That Trigger Transfusion Decisions
Laboratory tests help decide if you need a blood transfusion. Important values include:
- Hemoglobin levels: Low hemoglobin means you might need a transfusion
- Platelet count: If your platelet count is low, you might need a transfusion
- White blood cell count: Sometimes, low counts can also mean you need a transfusion
We watch these values closely to decide if you need a transfusion. The American Society of Hematology says decisions are based on how you’re feeling and your lab results.
Emergency Situations Requiring Immediate Transfusion
Some situations need a blood transfusion right away. These include:
- Severe bleeding from an injury or procedure
- Acute anemia from quick blood loss or hemolysis
- Life-threatening conditions that need quick action
In emergencies, quick action is vital. We make these cases a priority to get you the blood products you need fast.
It’s important to know the signs of a blood transfusion. This includes physical symptoms, lab values, and emergency situations. It helps us give the best care to lymphoma patients.
The Blood Transfusion Process for Lymphoma Patients
The blood transfusion process is key in lymphoma care. It gives patients the blood components they need. Lymphoma patients may need blood transfusion for anaemia to deal with complications from their disease or treatment.
Types of Blood Products Commonly Used
For lymphoma patients, transfusions often include red blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Red blood cells are given as a blood transfusion for anaemia or low hemoglobin. They improve oxygen delivery to tissues. Platelets are given to prevent or treat bleeding, while plasma helps with clotting issues.
According to Lymphoma Action, knowing about these blood products, especially blood transfusion for anaemia, is key to patient care.
Special Considerations for Lymphoma Patients
Lymphoma patients often need irradiated blood products to avoid a serious complication. Irradiation stops lymphocytes from growing, preventing this complication. For many, repeated blood transfusion for anaemia ensures stability and prevents severe fatigue.
Duration and Frequency of Transfusions
A blood transfusion for anaemia can take 1 to 4 hours, depending on the product and the patient’s health. How often transfusions happen depends on the patient’s response and overall condition. Patients may require ongoing blood transfusion for anaemia throughout their treatment journey.
What to Expect During a Transfusion Procedure
During a blood transfusion for anaemia, patients are watched closely for any bad reactions. The transfusion goes through a vein in the arm. Some discomfort might happen, but it’s usually minor.
“Receiving a blood transfusion for anaemia was a much more straightforward process than I expected. The medical staff were very supportive and monitored me closely throughout.”
Getting a blood transfusion for anaemia can seem scary, but it’s safe and can save lives with the right care.
Conclusion: The Vital Role of Blood Transfusions in Lymphoma Care
Blood transfusions are key in managing lymphoma treatment side effects. A blood transfusion for anaemia helps improve patient outcomes, boosts energy, and reduces symptoms linked to low hemoglobin. These transfusions are vital for treating anemia and reducing bleeding risks, making life better for patients.
They are a big part of lymphoma care, helping patients face treatment challenges. Even though there are worries about their effect on life span, the benefits of blood transfusion for anaemia in handling treatment side effects are clear. Knowing how important blood transfusion for anaemia is in lymphoma treatment can ease worries about safety and need.
Patients can better understand their treatment by knowing when they need a blood transfusion for anaemia and how it works. As we keep improving lymphoma care, transfusions will keep being a key part in getting the best results for patients.
FAQ
Why do lymphoma patients need blood transfusions?
Lymphoma patients often need blood transfusions because the disease affects their bone marrow. This leads to a decrease in blood cell production. Treatments like chemotherapy and radiation can make this worse, causing severe anemia and other blood disorders.
What are the signs that you need a blood transfusion?
Signs you might need a blood transfusion include feeling very tired, short of breath, or dizzy. Low hemoglobin levels and thrombocytopenia are also indicators. In emergencies like severe bleeding, a transfusion is needed right away.
How long does a blood transfusion take?
The time it takes for a blood transfusion varies. It depends on the type and amount of blood being given. Transfusions can last from a few hours to several hours. How often you need one depends on your health and treatment plan.
What types of blood products are used for lymphoma patients?
Lymphoma patients may get different blood products. Red blood cells help with anemia. Platelets are for thrombocytopenia. Sometimes, irradiated blood is given to prevent graft-versus-host disease, like after CAR T-cell therapy.
Do blood transfusions shorten your life?
While blood transfusions are lifesaving, they can cause iron overload and other issues with repeated use. Yet, the benefits of transfusions in supporting patients through treatment usually outweigh the risks when managed well.
Why would someone need irradiated blood?
Irradiated blood is for patients at risk of graft-versus-host disease. This includes those having CAR T-cell therapy, stem cell transplantation, or those with severely weakened immune systems.
What is the role of blood transfusions in managing low hemoglobin levels?
Blood transfusions are key in managing low hemoglobin levels. They increase red blood cells, improving oxygen delivery to tissues. This helps alleviate symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath.
Why do people need a blood transfusion after chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy can lower blood cell production by affecting the bone marrow. Blood transfusions are needed to replace red blood cells, platelets, or other components lost due to chemotherapy.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2020). Transfusion-Associated Graft-Versus-Host Disease. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534241/









