Last Updated on October 20, 2025 by

When regular blood tests don’t give clear answers, a diagnostic procedure like a bone marrow biopsy is key. At Liv Hospital, we focus on making this advanced test safe and useful for you.
Getting a diagnostic test can be scary. Our team is here to give you full care. We’ll explain why you need a bone marrow biopsy and answer any questions you have.
A bone marrow biopsy is a critical tool for spotting blood disorders. It can help find issues like polycythemia vera.
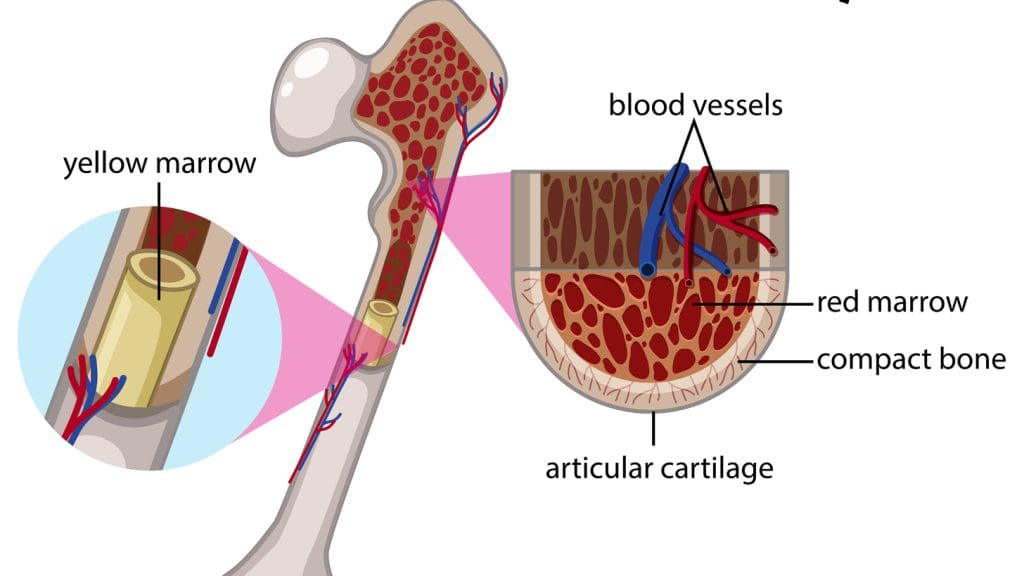
Bone marrow is key to how our bodies make blood cells and stay healthy. It’s a spongy tissue inside bones like the hips and thighbones. It’s where blood cells are produced.
Bone marrow is soft, fatty tissue inside bones. In adults, it’s mainly in the pelvis, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and long bone ends. It’s a vital organ for blood cell production and fat storage, doctors say.
Bone marrow’s main job is to make blood cells. It creates red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells fight infections, and platelets help blood clot.
The making of blood cells in bone marrow is a complex process. It involves many cell types and growth factors working together. Any problem in this process can cause health issues.
There are two main types of bone marrow: red and yellow. Red marrow makes blood cells, while yellow marrow is mostly fat. In babies, all marrow is red, but it changes to yellow as we grow older.
Knowing about the different bone marrow types and their roles helps us understand blood cell production. It shows how important bone marrow is for our health.
We do a bone marrow biopsy to get a sample for detailed checks. It’s key for spotting and tracking blood issues like cancers and anemia.
A bone marrow biopsy takes a small piece of bone marrow from bones like hips and thighbones. This tissue makes blood cells. It’s to see if there’s any odd cell growth, infection, or disease in the marrow.
The marrow has stem cells that turn into red and white blood cells and platelets. Doctors look at it to understand how these cells are doing. This helps them find problems that blood tests might miss.
There are two ways to get bone marrow samples: aspiration and biopsy. Bone marrow aspiration takes out the liquid part of the marrow to check for odd cells.
Bone marrow biopsy takes a small bone and marrow piece. It gives a detailed look at the marrow’s structure and cell making. Both are often done together for a full marrow health check.
The most common spot for bone marrow extraction is the iliac crest, the curved hip bone part. It’s chosen because it’s easy to get to and has lots of marrow.
Sometimes, the sternum or other bones might be used. But the iliac crest is the top choice because of its easy access and good marrow quality.
Bone marrow biopsies are done for many important reasons. They help doctors understand a patient’s health. These tests are key for diagnosing and tracking blood-related issues.
One main reason for a bone marrow biopsy is to find the cause of unexplained anemia. Anemia happens when there are not enough red blood cells or when these cells lack hemoglobin. This test looks at how red blood cells are made in the marrow.
Key findings in anemia diagnosis include:
Abnormal blood cell counts can point to many issues, from infections to blood cancers. A bone marrow biopsy gives a detailed look at the marrow’s blood cell production.
Leukemia and other blood cancers are big reasons for a bone marrow biopsy. The test lets doctors check for cancer cells in the marrow. This helps in diagnosing and understanding the disease’s stage.
“A bone marrow biopsy is a critical diagnostic tool in the detection and management of leukemia and other hematologic malignancies.”
For those with bone marrow diseases, regular biopsies are needed. They help track the disease’s progress and how well treatments are working. This ongoing check helps doctors adjust treatment plans.
Other reasons for a bone marrow biopsy include finding myelodysplastic syndromes, checking unexplained fevers or infections, and seeing if cancer has spread to the marrow. Each reason shows how vital bone marrow biopsies are for patient care.
A bone marrow test is often needed to accurately diagnose certain anemia types. Anemia happens when there aren’t enough healthy red blood cells. This makes it hard for the body to get enough oxygen. While many anemia cases can be diagnosed with blood tests, some need a closer look at the bone marrow.
Some anemia types need a bone marrow test for diagnosis. These include:
These conditions often need a bone marrow biopsy to find the cause and how far it has spread.
Standard tests for anemia include complete blood counts (CBC) and iron studies. But, if these tests don’t give clear results, a bone marrow test might be suggested. This is true if there’s a suspicion of bone marrow failure or a process that’s affecting the marrow.
We might also suggest bone marrow testing if there are unexplained low blood cell counts. Or if the blood test results don’t match the patient’s symptoms.
A bone marrow test can give us key information about anemia. It lets us see how blood cells are made and mature in the marrow. Through aspiration and biopsy, we can check cell numbers, find abnormal cells, and spot any problems like fibrosis.
The insights from bone marrow testing help us choose the right treatment. This personalized approach can greatly improve patient results.
Understanding myelodysplastic syndromes and other blood disorders starts with a bone marrow biopsy. This test gives us key insights into diagnosis and treatment.
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are disorders with poorly formed blood cells. Bone marrow biopsies are key for diagnosing MDS. They let us see the bone marrow’s cells and find any problems.
The biopsy is checked for dysplastic cells, marrow cell count, and genetic issues. This info helps us know the MDS type and plan treatment.
Beyond MDS, bone marrow analysis is key for other blood disorders. This includes leukemia, lymphoma, and aplastic anemia.
A bone marrow biopsy gives a detailed look at the bone marrow’s cells. This helps us find the cause of symptoms and plan treatment.
| Blood Disorder | Characteristics | Diagnostic Findings in Bone Marrow Biopsy |
|---|---|---|
| Myelodysplastic Syndromes | Dysplastic blood cells, ineffective hematopoiesis | Dysplastic cells, abnormal cellularity |
| Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Rapid proliferation of myeloid blasts | Presence of myeloid blasts, often >20% |
| Aplastic Anemia | Failure of bone marrow to produce blood cells | Hypocellular marrow, absence of hematopoietic cells |
Cytogenetic testing is a big part of bone marrow analysis. It looks at the genetic material of bone marrow cells. This helps find chromosomal issues linked to blood disorders.
By studying the genetic makeup of bone marrow cells, cytogenetic testing aids in diagnosing MDS and leukemia. It also helps predict treatment outcomes.
We use cytogenetic testing to understand blood disorder pathology better. This helps us create targeted and effective treatments.
The bone marrow biopsy procedure has several key steps. Healthcare professionals follow these steps to get accurate and safe results. This test is key for diagnosing and monitoring blood-related disorders like anemia and leukemia.
Before starting, patients go through some steps. Medical evaluations check their health and look for risks. They also tell their doctor about any medicines they take, which might need to change.
To reduce pain, local anesthesia is used. The patient lies on their stomach or side, depending on the biopsy site. The posterior iliac crest, a part of the pelvis, is the most common site.
The bone marrow aspiration comes first. A needle is inserted, and a syringe takes out a small bone marrow sample. This sample goes to the lab for analysis. It helps check the bone marrow cells’ health.
Next, a bone marrow biopsy is done with a bigger needle. It gets a core sample of bone marrow, giving more detailed info. This sample also goes to the lab for further study.
Knowing the bone marrow biopsy steps helps patients prepare and understand recovery. It’s important to follow the doctor’s advice and ask questions to clear up any worries.
Learning how to prepare for a bone marrow biopsy can make you feel less anxious. We’ll show you the steps to make the process smooth and successful.
We will do some medical checks before your bone marrow biopsy. This is to make sure you’re ready for the procedure. These checks might include:
These steps help us lower risks and make sure the biopsy is safe.
Telling us about your medications is key. Some might need to be changed or stopped before the biopsy. This includes:
We’ll tell you how to handle your medications before the biopsy.
On the day of your bone marrow biopsy, remember to:
It’s okay to have questions before a bone marrow biopsy. We encourage you to ask us about:
We’re here to give you the info and support you need.
Recovering from a bone marrow biopsy involves several important steps. Knowing what to expect can ease your worries and make the healing process easier.
After the biopsy, you’ll go to a recovery area. Medical staff will watch over you and check your vital signs. They might give you medicine to ease any pain or discomfort.
It’s key to follow the care instructions from your healthcare team.
Managing pain is a big part of recovery. You might feel some pain or discomfort at the biopsy site. This can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain meds. Your doctor might give you stronger pain relief if needed.
It’s important to follow the recommended dosage of your pain medication. If you have severe or ongoing pain, tell your healthcare provider right away.
It’s best to avoid hard activities, heavy lifting, and bending for a few days. You can usually go back to your normal activities in a day or two. But, listen to your body and don’t overdo it. Resting and avoiding hard activities will help prevent complications.
While complications from a bone marrow biopsy are rare, it’s important to know the signs of a problem. Call your doctor if you have increasing pain, swelling, or redness at the biopsy site, fever, or unusual bleeding. Being careful about your recovery and getting medical help when needed is key to a good outcome.
By understanding what to expect during recovery and following your healthcare team’s advice, you can reduce discomfort and complications. This will help you recover smoothly from your bone marrow biopsy.
It’s important for patients and doctors to know about the risks of bone marrow biopsy. The procedure is usually safe, but some complications can happen. These can be common or rare.
Most people don’t have big problems after a bone marrow biopsy. But, some might feel pain or discomfort at the site. They might also see bruising or swelling, get an infection, or bleed.
These issues are usually not serious and get better quickly. They might need a little treatment or just time to heal.
There are also serious but rare risks. These include breaking a bone, damaging nerves, or having a bad reaction to the anesthetic.
These serious problems are rare but can really affect a person’s health.
Some things can make bone marrow biopsy risks higher. These include having too few blood platelets, trouble with blood clotting, or weak bones.
Knowing these risks before the biopsy helps doctors prepare better.
Doctors take steps to lower the risks of bone marrow biopsy. They look at the patient’s health history and current state. They use imaging to guide the procedure.
They also follow strict technique and keep everything clean. After the biopsy, they watch the patient closely. These actions help reduce the chance of problems.
It’s important for patients to know about the possible side effects of a bone marrow biopsy. This helps them prepare and take care of themselves better. The procedure is usually safe, but some people might face certain side effects. We’ll talk about the common ones, how long they last, and how to handle the discomfort.
Most people get through a bone marrow biopsy without major issues. But, some common side effects include:
These side effects are usually mild and short-lived. Managing discomfort well is key to a smooth recovery.
How long side effects last can vary. Generally:
It’s important to watch these side effects and get medical help if they don’t get better or get worse.
To handle discomfort after a bone marrow biopsy, patients can:
Following these guidelines can significantly improve the recovery experience.
While most side effects are manageable, there are times when medical help is needed. Patients should seek immediate care if they experience:
Knowing about these possible complications and when to seek help is key for a safe recovery.
Knowing the results of your bone marrow biopsy is key to planning your next steps. This test tells doctors about your bone marrow’s health. It helps them diagnose and treat blood-related issues.
Bone marrow biopsy results can show if your marrow is healthy or not. Normal findings mean your marrow is working right, with no disease signs. But, abnormal findings might point to cancer, infection, or other marrow problems.
Abnormal results could show odd cell shapes or counts. They might also find cells that shouldn’t be there. These signs help doctors spot diseases like leukemia or lymphoma.
How long it takes to get your bone marrow biopsy results varies. You might get some results in a few days. But, detailed tests could take a week or more.
Talking to your doctor about when you’ll get results helps manage your wait and worry.
Based on your first test, your doctor might suggest more tests. These could be more bone marrow biopsies, blood tests, or imaging studies.
Your bone marrow biopsy results are key in deciding your treatment. If it shows cancer, the type and stage guide your treatment. This might include chemotherapy, radiation, or a bone marrow transplant.
For non-cancer issues, treatment aims to manage symptoms and fix underlying problems. This could be infections or nutritional issues.
Your healthcare team will use your results, health history, and symptoms to create a treatment plan just for you.
We’ve looked into how bone marrow biopsies help diagnose and manage blood disorders. This procedure is key for doctors to check the health of our bone marrow. It helps find issues like anemia, leukemia, and myelodysplastic syndromes.
There are many reasons for getting a bone marrow biopsy. It’s used to check for anemia or to keep an eye on bone marrow diseases. Doctors use it to understand what’s causing a patient’s condition. This helps them make better treatment plans.
Even though bone marrow biopsies are mostly safe, there are risks. It’s important for patients to know about these risks and side effects. This knowledge helps patients make better choices about their health care.
In short, bone marrow biopsies are very important for diagnosing and treating blood disorders. Knowing about the procedure, its risks, and benefits helps patients feel more confident in their care.
A bone marrow biopsy is a medical test. It takes a sample of bone marrow for examination. This test helps diagnose and monitor blood disorders like anemia, leukemia, and lymphoma.
We suggest a bone marrow biopsy when other tests don’t give clear results. It helps us understand the bone marrow better. This is important for diagnosing anemia, blood cancers, and myelodysplastic syndromes.
A bone marrow biopsy is usually safe but can have risks. These include bleeding, infection, and nerve damage. We take steps to reduce these risks, and most people do well without major problems.
During the procedure, we numb the area with local anesthesia. You might also get sedation to relax. The whole process usually takes about 30 minutes to an hour.
To prepare, tell us about any medications you’re taking, like blood thinners. We might ask you to stop eating or drinking before the procedure.
Side effects can include pain, bruising, and swelling at the site. We can help manage these with pain medication and other treatments.
Results usually come within a few days to a week. We’ll discuss them with you and plan your next steps.
Yes, it can help diagnose certain anemia types when other tests are unclear. It shows how well the bone marrow makes blood cells.
Bone marrow aspiration takes a liquid sample, while biopsy removes a small tissue piece. We might do both to fully understand the bone marrow.
Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities for a few days. You can usually get back to normal activities within a few days.
Seek medical help if you have severe pain, increasing redness or swelling, or signs of infection like fever or chills after the procedure.
A bone marrow biopsy is a medical test. It takes a sample of bone marrow for examination. This test helps diagnose and monitor blood disorders like anemia, leukemia, and lymphoma.
We suggest a bone marrow biopsy when other tests don’t give clear results. It helps us understand the bone marrow better. This is important for diagnosing anemia, blood cancers, and myelodysplastic syndromes.
A bone marrow biopsy is usually safe but can have risks. These include bleeding, infection, and nerve damage. We take steps to reduce these risks, and most people do well without major problems.
During the procedure, we numb the area with local anesthesia. You might also get sedation to relax. The whole process usually takes about 30 minutes to an hour.
To prepare, tell us about any medications you’re taking, like blood thinners. We might ask you to stop eating or drinking before the procedure.
Side effects can include pain, bruising, and swelling at the site. We can help manage these with pain medication and other treatments.
Results usually come within a few days to a week. We’ll discuss them with you and plan your next steps.
Yes, it can help diagnose certain anemia types when other tests are unclear. It shows how well the bone marrow makes blood cells.
Bone marrow aspiration takes a liquid sample, while biopsy removes a small tissue piece. We might do both to fully understand the bone marrow.
Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities for a few days. You can usually get back to normal activities within a few days.
Seek medical help if you have severe pain, increasing redness or swelling, or signs of infection like fever or chills after the procedure.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!