Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir

Going through bowel surgery can be scary. But knowing about the different procedures can make you feel better. At Liv Hospital, we focus on trust, the latest techniques, and caring for our patients. This ensures the best results in bowel resection and reconstruction. Learn about bowel operation types and how they help treat colon and rectal cancers. Learn about bowel operations types and how they help treat colon and rectal cancers.
There are many important procedures in bowel operations. These include right hemicolectomy, left hemicolectomy, sigmoid colectomy, segmental ileal resection, and transverse colectomy. These surgeries aim to remove the sick parts of the intestine. It’s important for patients to know what each procedure means.
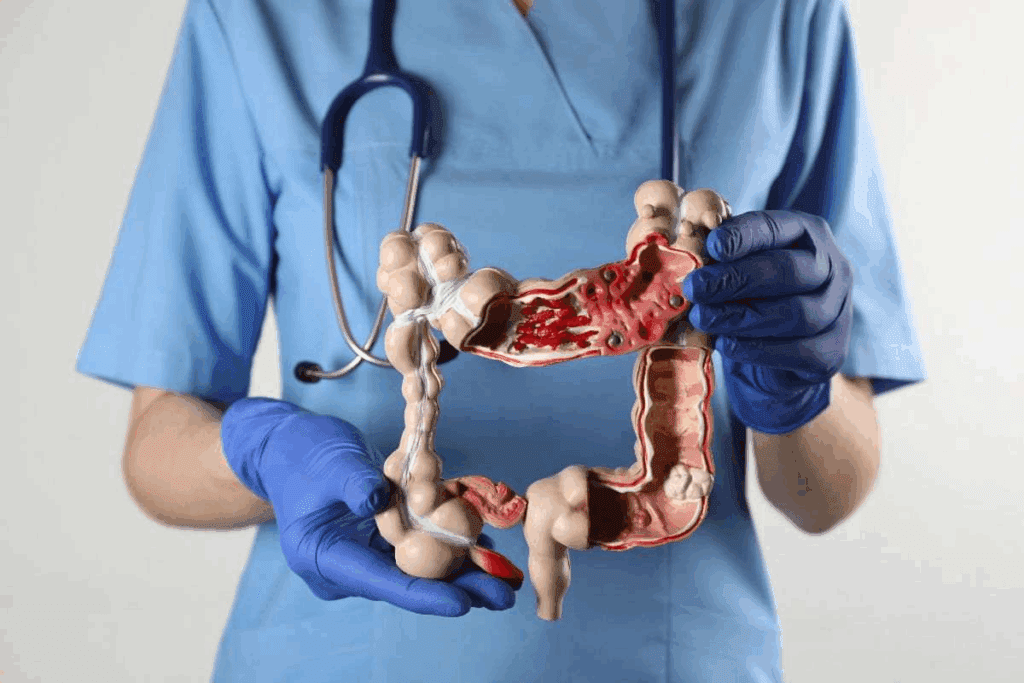
Bowel resection, also known as intestinal resection, is a surgery where a part of the intestine is removed. This is done because of disease or damage. The main goal is to remove the diseased part to ease symptoms and possibly cure the condition.
A bowel resection means taking out a part of the intestine that’s sick or hurt. This can happen because of colon cancer, Crohn’s disease, or ulcerative colitis. The surgery aims to cut out the bad part and join the healthy ends back together.
There are several reasons why someone might need bowel surgery. These include:
Before bowel resection surgery, a detailed check-up is done. This includes:
These steps are key to figuring out where and how far the disease is. They help decide the best way to do the surgery.

Knowing how our body breaks down food is key. The intestinal tract is a complex system. It digests food, absorbs nutrients, and gets rid of waste.
The small intestine is vital for absorbing nutrients. Its walls have finger-like projections called villi. These increase the surface area for nutrient absorption. The small intestine is split into three parts: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Each part has a special role in absorbing nutrients.
Nutrient Absorption Process: The small intestine’s walls absorb nutrients into the bloodstream. It breaks down nutrients into smaller pieces. These pieces are then used by the body.
The large intestine, or colon, is also key. It absorbs water and packs waste into feces. The colon has sections like the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
Water Absorption and Waste Compaction: The colon absorbs water and electrolytes. This helps keep the body’s fluid balance. The packed waste is then passed out through the rectum and anus.
| Intestinal Segment | Primary Function |
| Small Intestine (Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum) | Nutrient Absorption |
| Large Intestine (Colon) | Water Absorption and Waste Compaction |
The intestinal tract’s parts work together for efficient digestion and nutrient absorption. The small intestine absorbs most nutrients. The large intestine absorbs water and packs waste. Knowing how they work together is important for understanding bowel resection and intestinal health.
Coordinated Function: The small and large intestines work together. They ensure the body gets the nutrients it needs and gets rid of waste properly.
Bowel surgery includes many procedures, each with its own purpose. These surgeries help with issues like cancer, blockages, and inflammation. It’s important for both patients and doctors to know about these operations.
There are two main ways to do bowel surgery: open and laparoscopic. Open surgery uses a big cut in the belly to reach the intestines. It’s often used for complex cases or when a direct approach is needed.
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive method. It uses small cuts and a camera to see inside. This method leads to less pain, faster recovery, and smaller scars. But it’s not for every case, and the choice depends on the patient and the surgeon.
Bowel surgery can be urgent or planned. Emergency surgery is for sudden, serious problems like blockages or infections. It’s done right away to save the patient’s life.
Planned surgery, on the other hand, is scheduled ahead of time. This allows for better preparation. Conditions like colon cancer might need planned surgery. The decision to have surgery is made after careful discussion with the healthcare team.
Getting ready for bowel surgery is key, whether it’s urgent or planned. For planned surgeries, patients follow a pre-operative regimen. This includes:
For emergency surgeries, preparation is quicker because of the urgent need. The surgical team works fast to get the patient ready for surgery safely.
A right hemicolectomy is a bowel resection surgery that focuses on the right colon. It treats cancer or severe disease. The surgery removes the sick part of the colon and joins the healthy parts back together.
We suggest a right hemicolectomy for those with colon cancer or other right colon diseases. The choice to have surgery comes after detailed tests and biopsies.
The main aim is to take out the sick colon part. This stops cancer from spreading or eases symptoms of other diseases.
In a right hemicolectomy, the right colon pa carefully removed. This includes the cecum and ascending colon. The surgery can be open or laparoscopic, based on the patient’s and surgeon’s choice.
After removing the sick part, we connect the healthy colon parts. This makes sure the digestive system works well after surgery.
After surgery, we watch for any problems, manage pain, and help you get back to normal. We guide you on what to eat and what activities to avoid early on.
Recovery times vary, but most people get back to their usual lives in a few weeks. We offer personalized care to help you recover well.
When diseases or cancers hit the left side of the colon, a left hemicolectomy might be needed. This surgery removes the affected colon segment. It’s ketor treating many left colon issues.
Left hemicolectomy is often needed for colon cancer, diverticulitis, and other left colon diseases. The surgery choice depends on the disease’s extent and location.
Common Indications:
The surgical method for left hemicolectomy can differ, with open or laparoscopic surgery options. The choice depends on the patient’s health, disease extent, and the surgeon’s skill.
Patients after left hemicolectomy will need time to recover. They’ll be watched for complications and helped with post-operative care.
| Recovery Aspect | Expected Outcome |
| Hospital Stay | Typically 5-7 days, depending on the surgical approach and patient’s health |
| Return to Normal Activities | Usually within 4-6 weeks |
| Dietary Adjustments | Gradual return to normal diet, with initial emphasis on liquid and soft foods |
When problems happen in the lower colon, like in the sigmoid colon, a sigmoid colectomy might be needed. This surgery removes the sigmoid colon, a big part of the large intestine. It helps fix issues in this area.
Sigmoid colectomy is often suggested for problems like cancer in the sigmoid colon, diverticulitis, and other diseases. Doctors decide on surgery after checking with tests and biopsies.
The table below shows when sigmoid colectomy is needed and why:
| Condition | Description | Treatment Approach |
| Sigmoid Colon Cancer | Cancer affecting the sigmoid colon | Surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation therapy |
| Diverticulitis | Inflammation of diverticula in the sigmoid colon | Antibiotics, dietary changes, and sometimes surgery |
| Other Diseases | Various conditions affecting the sigmoid colon | Depends on the specific condition; may include surgery |
The surgery for sigmoid colectomy removes the sick part of the sigmoid colon and joins the rest. Surgeons make sure the blood flow to the rest of the colon is good. They also make sure the connection works well.
As a surgical expert said,
“The key to a successful sigmoid colectomy lies in meticulous surgical technique and post-operative care, ensuring the patient’s recovery and return to normal bowel function.”
After the surgery, bowel function might change, but most people get back to normal. The recovery includes care after surgery and check-ups to see how healing is going.
Having surgery is a big deal, but thanks to better surgery and care, recovery can be easier. It’s key to follow the doctor’s advice for the best results.
When the ileum gets sick or hurt, doctors might need to do surgery. The ileum is the last part of the small intestine. It helps our body absorb important nutrients like vitamin B12 and bile salts.
The ileum helps our body absorb key nutrients. It has a big surface area because of villi and microvilli. This helps keep our nutrition balanced.
The ileum’s role in vitamin B12 absorption is very important. Vitamin B12 is needed for our nerves, brain, and to make blood cells. If the ileum gets sick, we can get a vitamin B12 deficiency.
Several conditions might need segmental ileal resection. These include Crohn’s disease, tumors, and injuries to the ileum. Crohn’s disease can damage the ileum, causing problems like a narrow intestine and fistulas.
Tumors, whether they are benign or cancerous, might need to be removed. If someone gets hurt in the abdomen, surgery might be needed to fix or remove the damaged ileum.
The surgery to remove part of the ileum involves taking out the sick part and joining the healthy parts back together. This can be done with open surgery or laparoscopic surgery, depending on the situation.
After surgery, it’s important to watch for any problems, manage pain, and slowly start eating and moving again. Doctors will tell patients how to handle their bowel movements and watch for any signs of infection or other issues.
Surgery to remove the transverse colon is called a transverse colectomy. It’s a complex operation that needs precise techniques. This surgery is done to treat diseases or conditions in the transverse colon, like colon cancer or benign tumors.
Transverse colectomy is needed for several conditions, mainly affecting the middle colon. The main reasons include:
The surgery involves carefully cutting the transverse colon from its attachments. It’s done to keep the blood supply to the remaining colon. The method used can be open or laparoscopic, based on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s choice.
One big challenge is the transverse colon’s location and its closeness to other vital structures. Surgeons must be very careful to avoid damage to nearby organs. They also need to make sure the anastomosis (reconnection) is secure after the resection.
Recovery from transverse colectomy takes time, with a hospital stay followed by weeks at home. Patients are watched for complications like infection or leakage from the anastomosis. Most can get back to normal activities in a few weeks, but may need to adjust their diet to manage bowel function.
The outcomes after transverse colectomy are usually good, with most patients having minimal long-term changes in bowel habits. But the extent of the resection and the patient’s overall health can affect the outcome.
The resection process is a detailed part of bowel surgery. It involves removing the diseased part of the intestine and joining the healthy parts back together. This is key to getting the bowel to work right again and keeping the patient healthy.
Surgeons use different methods to take out the diseased part. They aim to remove all bad tissue and keep as much good intestine as they can. Minimally invasive techniques, like laparoscopic surgery, are used to make recovery faster and leave fewer scars.
The surgical team looks closely at the intestine to figure out how much needs to be removed. They find the diseased part and check the health of the nearby tissue. Advanced imaging techniques help plan the exact removal of the bad area.
After removing the diseased part, the surgeon joins the healthy ends together through anastomosis. There are hand-sewn and stapled methods for this, depending on the surgery and the surgeon’s choice.
Anastomosis is a critical step in the resection process. It must be done in a way that makes a strong and leak-free connection. This is important to avoid problems like infection or bowel blockage. The team makes sure the anastomosis is secure before finishing the surgery.
It’s important to make sure the anastomosis site has enough blood for healing and to avoid problems. Surgeons check the blood flow to the intestinal segments. They look at the color and how well the tissue is getting blood.
They also work hard to prevent leakage at the anastomosis site. They use careful suturing or stapling and check the anastomosis during the surgery. Post-operative care is also key in watching for any signs of leakage or other issues.
Understanding the resection and reconnection process helps patients see the care and complexity of bowel surgery. This knowledge can ease worries and prepare patients for what’s to come.
After bowel resection, patients may need to adapt to life with an ostomy. This requires careful management and care. An ostomy is a surgically created opening in the abdomen that allows waste to pass out of the body. The need for an ostomy depends on the extent and location of the bowel surgery.
Not all patients need a colostomy bag after small bowel resection. The necessity for a colostomy bag depends on the specific surgery and the patient’s condition. If the surgery involves removing a significant portion of the small bowel or if there’s a need to divert the bowel’s function temporarily, an ostomy might be necessary.
We understand that the prospect of having an ostomy can be daunting. But it’s a common procedure that can significantly improve the patient’s quality of life in certain situations. Our medical team will guide on whether an ostomy is required and what type of ostomy is most suitable.
There are two main types of ostomies: temporary and permanent. A temporary ostomy is often used to allow the bowel to heal after surgery. Once the healing is complete, the ostomy can be reversed, and the bowel function restored. On the other hand, a permanent ostomy is typically required when a significant portion of the bowel is removed or is non-functional.
Temporary ostomies are usually created to divert the fecal stream temporarily, allowing the bowel to heal. The reversal surgery is typically planned after a few months, once the bowel has healed sufficiently.
Permanent ostomies, on the other hand, require long-term management and adaptation. Patients with permanent ostomies need to learn how to care for their ostomy and manage their lifestyle.
Caring for an ostomy involves keeping the ostomy site clean, managing the ostomy bag, and adapting to lifestyle changes. We advise patients on how to properly clean and maintain their ostomy site to prevent complications. Managing the ostomy bag includes learning how to change it, ensuring a proper fit, and dealing with issues like leakage or skin irritation.
Lifestyle adaptations may include dietary changes, adjusting clothing to accommodate the ostomy bag, and being mindful of physical activities. While having an ostomy requires some adjustments, many patients find that with time and practice, they can lead active and fulfilling lives.
We are committed to supporting our patients through every step of their ostomy care journey. We provide them with the necessary guidance and resources to manage their condition effectively.
Recovering from bowel resection surgery is a big step. It marks the start of a new chapter in your life. We’ve looked at different types of bowel operations and what they mean for recovery and rebuilding.
Many people do well after bowel resection surgery and get back to their usual lives. Knowing about the various bowel operations helps a lot. This knowledge can make your recovery smoother.
Life after bowel resection surgery needs patience, care, and support. With the right care and management, you can face recovery’s challenges and look forward to a good outcome. We’re here to help you with the guidance and support you need. We want to make sure you have a smooth transition back to your normal life, helping you fully recover and enjoy a better quality of life after surgery.
A bowel resection, also known as intestinal resection, is a surgical procedure. It removes a part of the intestine because of disease or damage.
People get a bowel resection for several reasons. These include colon cancer, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and bowel obstruction.
Whether you need a colostomy bag after small bowel resection varies. It depends on the surgery and your health. Some might have a temporary ostomy, while others might have a permanent one.
A right hemicolectomy removes the right part of the colon. It’s often for colon cancer or diseases on the right side. A left hemicolectomy removes the left part of the colon. It’s usually for colon cancer or diseases on the left side.
Sigmoid colectomy is a surgery to remove the sigmoid colon. This is the lower part of the colon. It’s often for sigmoid colon cancer or diverticulitis.
Segmental ileal resection is a surgery to remove a diseased or damaged part of the ileum. The ileum is the last part of the small intestine.
Transverse colectomy removes the transverse colon. This is the part of the colon that crosses the upper abdomen. It’s usually for colon cancer or diseases in this area.
The resection process removes the diseased intestinal part. Then, the healthy ends are connected. Surgeons use techniques to minimize damage and ensure a secure join.
Ostomy care includes keeping the ostomy site clean and managing the bag. It’s also about adapting to lifestyle changes. This is key for patients after certain bowel surgeries.
There are five main types of bowel operations. These are right hemicolectomy, left hemicolectomy, sigmoid colectomy, segmental ileal resection, and transverse colectomy.
Before bowel resection surgery, tests like imaging and endoscopy are done. A biopsy might also be needed. These help find the disease’s extent and location.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!