Millions of aging men worldwide face the challenges of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) linked to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Many don’t know about the medical definition, symptoms, or treatment options.
It’s key to understand LUTS in BPH for early diagnosis and treatment. Good urology care means men get the right info and treatment. This improves their life quality.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia with LUTS is common in older men. It’s classified in the ICD-10 system. This helps with diagnosis, documentation, and getting paid for treatment.
Learn about BPH LUTS symptoms. What is LUTS (Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms) in the context of BPH, and the relevant ICD-10 codes explained.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding LUTS and BPH is key for better management and life quality.
- LUTS linked to BPH can really mess up daily life.
- The ICD-10 system helps with accurate diagnosis and getting paid.
- Comprehensive urology care offers tailored treatment plans.
- Patient-focused care is vital for handling BPH and LUTS symptoms.
Understanding Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS)

LUTS, or Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms, are a range of urinary issues. They can greatly affect your quality of life. These symptoms are not just a normal part of aging. They show there might be underlying conditions that need medical care.
Definition and Terminology
LUTS refer to urinary symptoms that affect the bladder and urethra. The term “LUTS” covers various symptoms. This includes daytime frequency, urgency, and nocturia for storage symptoms. Voiding symptoms include hesitancy, weak stream, straining, and incomplete bladder emptying.
Understanding LUTS is key for both patients and healthcare providers. It helps them talk about urinary health issues effectively.
A leading urology expert says, “LUTS is not just about symptoms. It’s about how those symptoms affect a man’s quality of life.”
“The presence of LUTS can significantly affect a man’s daily activities, sleep, and overall well-being.”
Prevalence and Epidemiology
LUTS become more common with age. Studies show LUTS affect about 3 percent of men ages 45-49 years. By the time men are over 85, this number jumps to 30 percent.
As the world’s population ages, LUTS will likely become more common. It’s vital for healthcare systems to be ready to handle this growing need. We need to understand LUTS better to prevent, diagnose, and treat it effectively.
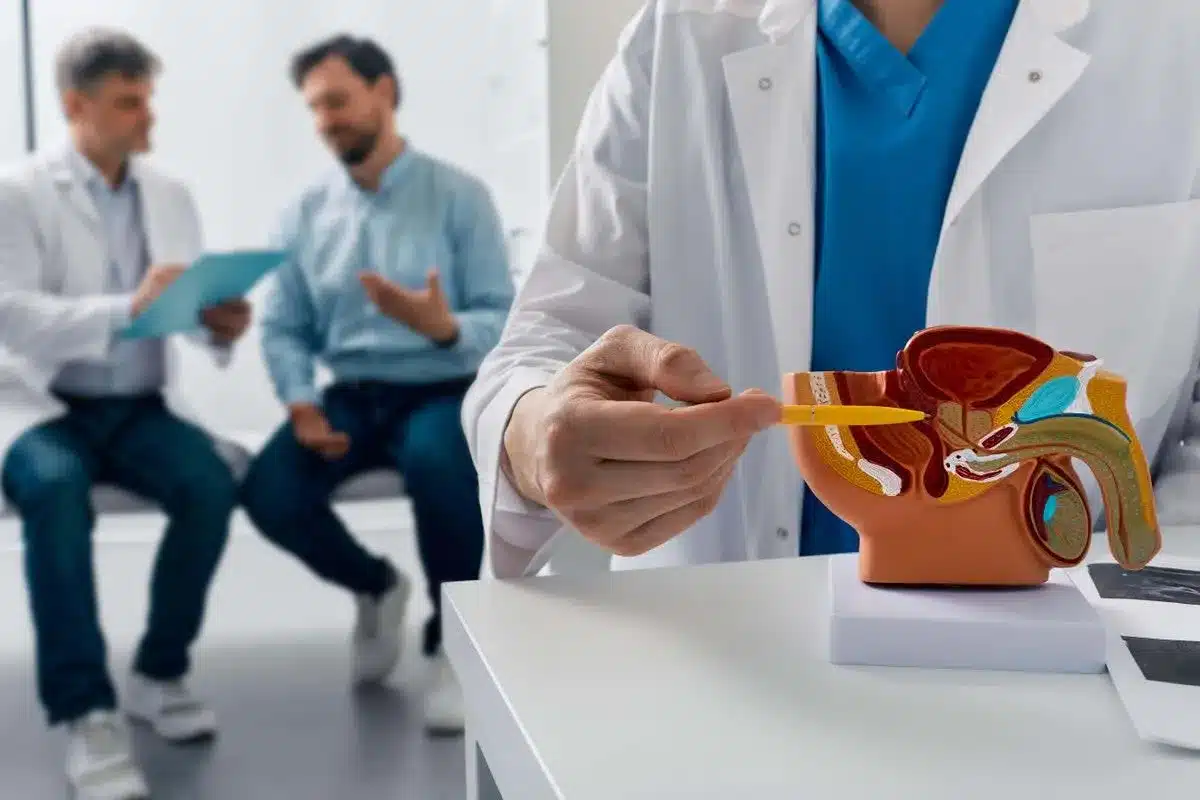
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): An Overview

BPH, or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, is when the prostate gland gets bigger. This can cause problems with urination. It’s a common issue for older men, affecting their daily life.
What is BPH?
BPH is when the prostate grows due to more cells. This makes the prostate bigger. It can block the urethra and make it hard to pee.
Medical Expert, a urology expert, says, “BPH is more than just a big prostate. It’s the symptoms that bother men every day.”
“The impact of BPH on a man’s quality of life should not be underestimated. It’s not just about urinary symptoms; it’s about the overall well-being of the patient.”
Pathophysiology of BPH
BPH happens because of hormonal changes and cell growth. As men get older, their hormones change. This affects how prostate cells grow.
A big part of BPH is when testosterone turns into DHT. DHT makes prostate cells grow more.
Factor | Role in BPH |
Hormonal Changes | Alters the balance between androgens and estrogens, influencing prostate cell growth. |
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) | Promotes prostate cell proliferation. |
Inflammatory Processes | Contributes to the development and progression of BPH. |
Age-Related Prevalence
BPH gets more common with age. Younger men might get treatment, but older men are more likely to need it. This shows why it’s key to watch prostate health as men get older.
Knowing how BPH changes with age helps doctors better manage symptoms. This improves how well patients do.
The Relationship Between BPH and LUTS
BPH and LUTS are closely linked. BPH often causes LUTS because of the prostate’s location. The prostate surrounds the urethra. When it grows, it can block urine flow, causing symptoms.
How BPH Causes LUTS
The prostate grows in BPH, pressing on the urethra. This blocks urine flow. Symptoms include a weak stream, straining, and long urination times.
The severity of LUTS varies. It depends on how much the prostate has grown and how much it blocks the urethra.
Medical Expert, a urologist, says, “The prostate’s location is key in LUTS with BPH.” This shows why knowing BPH’s effects is important for treating LUTS.
Other Causes of LUTS in Men
BPH is a main cause of LUTS, but not the only one. Other issues like infections, stones, and nerve problems can also cause symptoms. It’s important to find the real cause of LUTS in men.
“Accurate diagnosis is key to managing LUTS effectively, as it allows for targeted treatment strategies.” –
Medical Expert, Urology Specialist
Knowing all causes of LUTS helps in finding the right treatment. We’ll look at how to diagnose and treat LUTS next.
BPH LUTS Symptoms: Common Manifestations
BPH-related LUTS cause many urinary symptoms. These include both storage and voiding problems. Knowing these symptoms helps doctors give the right care to men with BPH.
Storage Symptoms
Storage symptoms include daytime frequency, urgency, and nocturia. Daytime frequency means needing to pee a lot during the day. Urgency is when you suddenly need to pee. Nocturia is waking up to pee at night, which can mess up your sleep.
These symptoms can really bother you. They can affect your daily life and how well you sleep. For example, waking up to pee can make you tired and less productive.
Voiding Symptoms
Voiding symptoms are about the act of peeing itself. Symptoms include hesitancy, weak stream, straining, and feeling like you didn’t empty your bladder. Hesitancy is hard to start peeing. A weak stream means your pee comes out slowly. Straining and feeling like you didn’t empty your bladder are common too.
To understand these symptoms better, let’s look at a table. It shows common LUTS in men with BPH:
Symptom Category | Specific Symptom | Prevalence |
Storage Symptoms | Daytime Frequency | 60-80% |
Storage Symptoms | Urgency | 40-60% |
Storage Symptoms | Nocturia | 50-70% |
Voiding Symptoms | Weak Stream | 70-90% |
Voiding Symptoms | Straining | 30-50% |
Voiding Symptoms | Incomplete Bladder Emptying | 40-60% |
It’s important to recognize these symptoms for diagnosing and treating BPH. Knowing about LUTS helps doctors create better treatment plans for their patients.
Impact of LUTS on Quality of Life
It’s important to know how LUTS affects a person’s life. Symptoms like those from Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia can really get in the way. They can mess with a person’s daily life, affecting their health, mind, and social life.
Physical Impact
LUTS can really affect a person’s body. Symptoms like needing to pee a lot, a weak stream, and straining can cause sleep problems, tiredness, and less activity. These issues can make it hard for people to do everyday things and stay independent.
Also, BPH with LUTS can lead to infections, bladder stones, or kidney damage. A study found that LUTS can really hurt a person’s quality of life, affecting both their body and mind.
“The presence of LUTS is associated with a significant burden on the quality of life, affecting both physical and mental health.”
Source: A study on LUTS and Quality of Life
Psychological and Social Impact
LUTS can also affect a person’s mind and social life. Symptoms can cause anxiety, depression, and feelings of shame. The need to pee a lot, fear of accidents, or discomfort from protective clothes can make people feel isolated and lower their self-esteem.
We need to look at how LUTS affects a person’s life, including their mental health and social life. Treating BPH with LUTS means dealing with both physical symptoms and the emotional and social effects.
Aspect | Impact of LUTS |
Physical | Sleep disturbances, fatigue, decreased physical activity |
Psychological | Anxiety, depression, decreased self-esteem |
Social | Social isolation, embarrassment |
Understanding the full impact of LUTS helps healthcare providers give better care. This can improve the quality of life for people with BPH.
Diagnosing BPH with LUTS
It’s important to accurately diagnose BPH with LUTS for effective treatment. We’ll look at how doctors do this. It includes medical history, physical exams, symptom checks, and tests.
Medical History and Physical Examination
First, doctors take a detailed medical history and do a physical exam. They check symptoms, health, and past treatments. This helps understand urinary issues.
A digital rectal exam (DRE) is key. It lets doctors check the prostate’s size and feel. This helps diagnose BPH.
Symptom Assessment Tools
To measure LUTS and treatment success, doctors use symptom tools. The International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) is common. It shows how symptoms affect daily life.
Laboratory and Imaging Tests
Doctors use tests to diagnose BPH with LUTS and rule out other issues. These include:
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) testing to check prostate health
- Urinalysis to find urinary tract infections or other problems
- Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS) to see the prostate’s size and shape
- Uroflowmetry to measure urine flow
Here’s a summary of the diagnostic tests and their purposes in a tabular format:
Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
PSA Testing | Assess prostate health and detect issues |
Urinalysis | Check for urinary tract infections or other problems |
TRUS | Evaluate the prostate gland’s size and structure |
Uroflowmetry | Measure the flow rate of urine |
ICD-10 Codes for BPH with LUTS
Using specific ICD-10 codes for BPH with LUTS makes healthcare better and more efficient. It’s key for doctors to follow billing rules and give the right care to patients.
Understanding Medical Coding for BPH
For BPH, doctors use ICD-10 codes that match the diagnosis and symptoms. The ICD-10 system helps everyone use the same codes, making healthcare more consistent.
Importance of Accurate Coding: Accurate ICD-10 codes are important. They help doctors get paid right, track patient health, and study BPH trends.
Primary ICD-10 Codes for BPH with LUTS
The main ICD-10 code for BPH with LUTS is N40.1. This code shows Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia with symptoms like trouble urinating.
ICD-10 Code | Description | Usage |
N40.1 | Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia with lower urinary tract symptoms | Used for BPH cases presenting with LUTS |
Secondary and Related Codes
There are also secondary codes for BPH with LUTS. These codes can show other symptoms, like trouble holding urine.
Example of Secondary Codes: For a patient with BPH and LUTS who also can’t hold urine, a code like R33.9 (Retention of urine, unspecified) might be used.
Always check the latest ICD-10 coding rules for the best info on BPH with LUTS coding.
Complications of Untreated BPH LUTS Symptoms
Ignoring BPH LUTS symptoms can lead to serious health issues. These symptoms, if not treated, can cause significant problems. They can affect your quality of life and overall health.
Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is a common problem from untreated BPH. It happens when the prostate gland blocks urine flow. Urinary retention can be acute or chronic, and might need catheterization to fix.
“Urinary retention is a serious condition that can lead to discomfort, pain, and further complications if not addressed promptly,” says a leading urologist. We must take BPH LUTS symptoms seriously to avoid such outcomes.
Urinary Tract Infections
Untreated BPH LUTS symptoms can also cause urinary tract infections (UTIs). When urine is not fully emptied, bacteria can grow, leading to infections. UTIs can cause significant discomfort and, if recurrent, may lead to more serious kidney damage.
We should be aware that UTIs are not just a minor inconvenience; they can be a sign of an underlying issue that needs medical attention. Ensuring proper treatment of BPH LUTS symptoms can help prevent such infections.
Bladder Stones and Damage
Another complication of untreated BPH is the formation of bladder stones. When urine is not fully emptied, minerals can crystallize and form stones. Bladder stones can cause pain, difficulty urinating, and recurrent infections.
Chronic obstruction can also lead to bladder damage over time. This can result in a loss of bladder function. We must address BPH LUTS symptoms to prevent long-term damage to the urinary system.
In conclusion, the complications of untreated BPH LUTS symptoms are significant and can have a lasting impact on health. We should seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time to avoid these complications.
Treatment Options for BPH with LUTS
Treatment for BPH with LUTS depends on how bad the symptoms are and how they affect a person’s life. We look at many options to manage BPH well.
Watchful Waiting and Lifestyle Modifications
For those with mild symptoms, watchful waiting is often suggested. This means keeping an eye on symptoms and not treating unless they get worse. Also, lifestyle changes can help. These might include:
- Drinking less water before bed
- Avoiding caffeine and alcohol
- Following a timed voiding schedule
- Staying active
These steps can help manage symptoms and improve life quality.
Pharmacological Treatments
When symptoms are more serious, medications are considered. The main drugs used are:
- Alpha-blockers: These relax muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, making it easier to pee.
- 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors: These shrink the prostate by blocking DHT, a hormone that makes the prostate grow.
- Combination therapy: Using both alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors can help men with moderate to severe symptoms.
Medications can greatly improve symptoms and life quality for many men.
Surgical Interventions
For severe symptoms or when other treatments don’t work, surgery might be needed. Surgical options include:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): A common procedure that removes part of the prostate.
- Laser surgery: Techniques like holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) are effective with fewer side effects.
- Open prostatectomy: A more invasive surgery, usually for larger prostates.
Surgery can offer significant relief for men with severe BPH symptoms.
In conclusion, treating BPH with LUTS is personalized. We consider the severity of symptoms and their impact on life quality. We work with patients to find the best treatment, whether it’s watchful waiting, medications, or surgery.
Conclusion
It’s important to know about LUTS and BPH for both patients and doctors. Symptoms of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) linked to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) can really affect a person’s life. It’s key to recognize these symptoms and understand what LUTS meaning is for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Getting a correct diagnosis means knowing how BPH and LUTS are connected. Using the right ICD-10 code for BPH with LUTS, like bph with luts icd 10, is also important. This helps in precise medical coding. Managing BPH LUTS symptoms well can greatly help patients.
We’ve looked at many parts of BPH and LUTS, like symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments. Getting the right diagnosis and treatment can really improve life quality. By grasping the details of BPH and LUTS, doctors can give better care. And patients can make better choices about their health.
FAQ
What does LUTS stand for in the context of BPH?
LUTS stands for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. These symptoms are often seen in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH).
What are the common symptoms of BPH LUTS?
Symptoms include needing to urinate often, waking up to use the bathroom, and a weak stream. You might also strain to urinate or find it hard to empty your bladder.
How is BPH with LUTS diagnosed?
Doctors use a medical history, physical exam, and symptom tools. They also do lab and imaging tests to check for other issues.
What is the ICD-10 code for BPH with LUTS?
The main ICD-10 code is N40.1. Secondary codes might be used to show LUTS is present.
What are the possible complications of untreated BPH LUTS symptoms?
Untreated symptoms can lead to urinary retention, infections, stones, and damage to the bladder.
What treatment options are available for BPH with LUTS?
Options include watching and waiting, lifestyle changes, medicines like alpha-blockers, and surgeries like TURP and UroLift.
How does BPH cause LUTS?
BPH blocks urine flow by making the prostate gland bigger. This causes symptoms when you store and release urine.
Can LUTS be caused by conditions other than BPH?
Yes, other conditions like infections, stones, and neurological issues can also cause LUTS.
How does LUTS impact quality of life?
LUTS can make life uncomfortable, cause emotional distress, and limit social activities.
What is the prevalence of LUTS among men?
LUTS affects more men as they get older. It’s common in men over 50.
What lifestyle modifications can help manage BPH LUTS symptoms?
Changes include eating right, managing fluids, doing pelvic floor exercises, and avoiding caffeine and alcohol.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). What is LUTS in BPH Symptoms and ICD10. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5717979/