Explore the fundamentals of neurology and the nervous system. Learn what neurologists do, the conditions they treat, and the structure of neurological care through detailed insights.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Overview and Definition
Neurology: Advanced Brain, Nerve, and Spine Care
The human nervous system is the most complex network in the known universe, controlling everything from your heartbeat to your memories. Neurology is the medical branch dedicated to preserving this intricate system. At Liv Hospital, our Neurology Department serves as a regional center of excellence, combining the diagnostic precision of experienced clinicians with next-generation technology like 3 Tesla MRI and Video-EEG monitoring.
For international patients, navigating neurological issues can be frightening. Our mission is to provide clarity, rapid diagnosis, and integrated care plans that bridge the gap between medical neurology, neurosurgery, and rehabilitation.
What is Neurologyr?
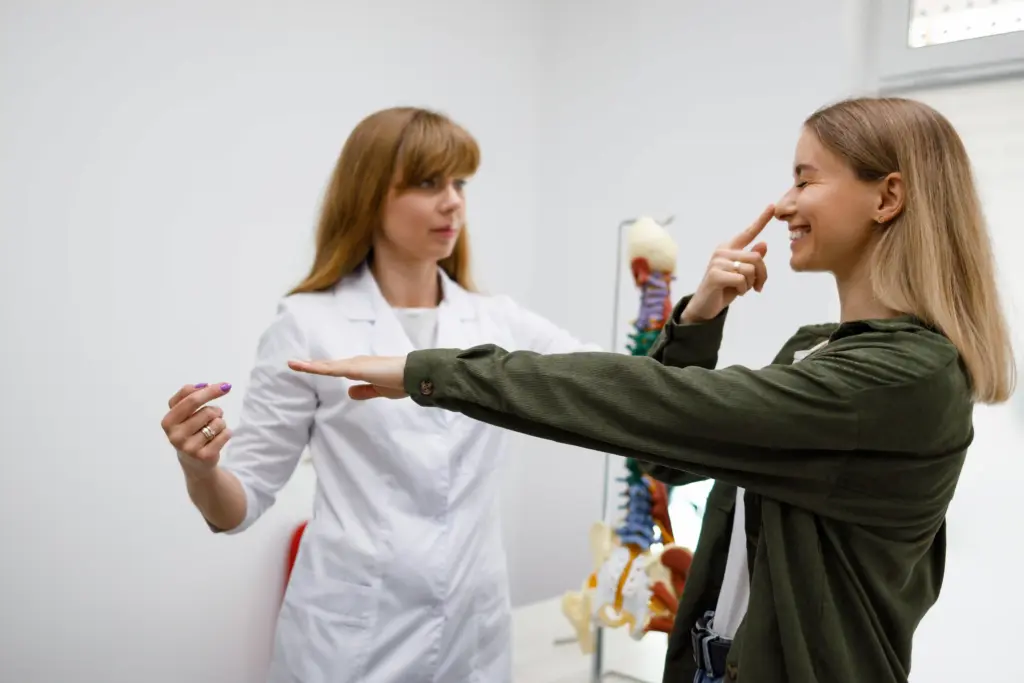

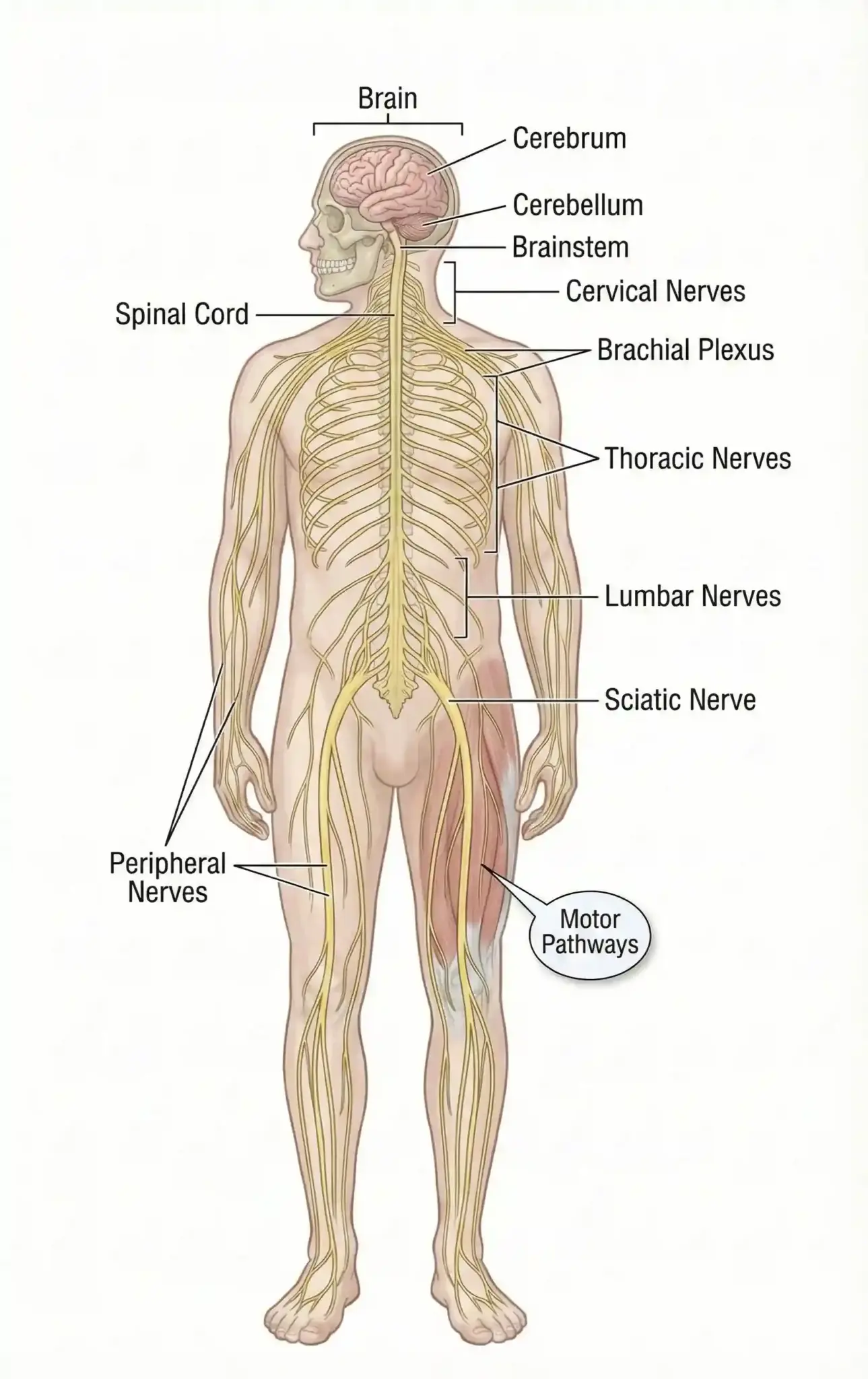
Neurology focuses on the diagnosis and non-surgical treatment of disorders affecting the nervous system. This system is divided into two primary parts, both of which are managed by our specialists:
Which Systems Does It Cover?
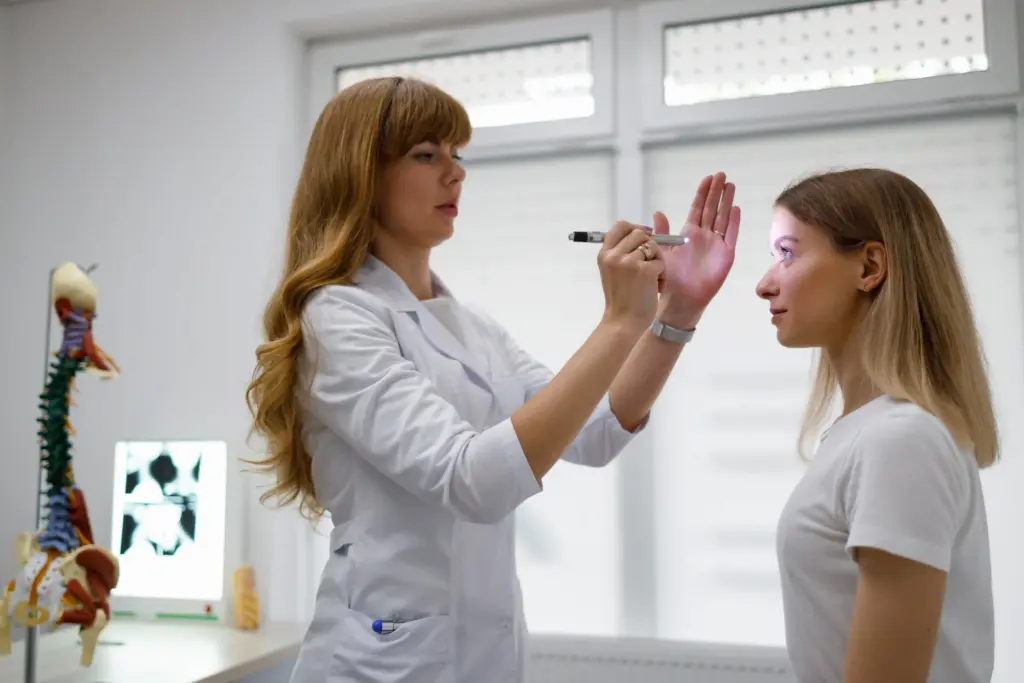
A neurological disorder can stem from electrical disruptions (like epilepsy), structural damage (like stroke), degeneration (like Alzheimer’s), or inflammation (like Multiple Sclerosis). Because these systems control movement, sensation, and cognition, a problem here can affect every aspect of daily life.
Neurologist vs. Neurosurgeon: Who Should You See?
One of the most common questions we receive is about the difference between these two specialists. Understanding the distinction is vital for seeking the right care.
At Liv Hospital, these two departments work in tandem. A neurologist often manages a patient for years but will immediately consult a neurosurgeon if a structural issue requires intervention.
Which Conditions Does the Neurology Department Treat?
The scope of neurology is vast. At Liv Hospital, our specialists are often sub-specialized in specific areas to ensure the highest level of expertise.
Common conditions managed in our clinic include:
Why is Early Neurological Intervention Critical?
In neurology, the phrase “Time is Brain” is often used, particularly regarding strokes, but it applies to almost all conditions. Neurons (nerve cells) have a limited ability to regenerate. Once they are lost, recovery becomes much more difficult.
Early diagnosis allows us to:
Manage Quality of Life: For chronic conditions like migraine or epilepsy, early management prevents the “kindling” effect, where untreated attacks make the brain more susceptible to future ones.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
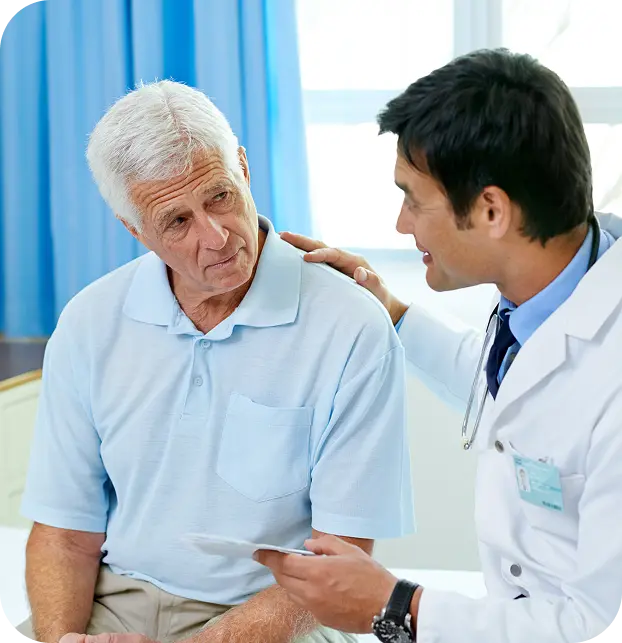

Liv Hospital integrates medical neurology with advanced technology and rehabilitation services, creating a “360-degree” care circle for international patients.
Doctors use advanced imaging tools such as 3 Tesla MRI, CT, and PET scans to visualize the brain’s structure. They also use tests like EEG to assess brain activity and EMG to assess nerve and muscle function. These help find the exact problem.
The neurologist is the main doctor who determines what is causing your symptoms by reviewing your test results. They manage your treatment and work with neurosurgeons if you need surgery.
Treatment plans can include medications for conditions like epilepsy or migraines, or urgent procedures for strokes. Each plan is designed to slow the disease and help manage symptoms as much as possible.
Your care may begin with urgent hospital treatment, followed by a period of stabilization. After that, you will move to a long-term plan that includes adjusting medications and having regular check-ups.
Multidisciplinary approach: Highlight the collaboration between neurologists, neurosurgeons, neuroradiologists, and rehabilitation specialists. This team approach ensures that whether a patient needs surgery, medication, or physical therapy, all aspects of their neural health are considered.
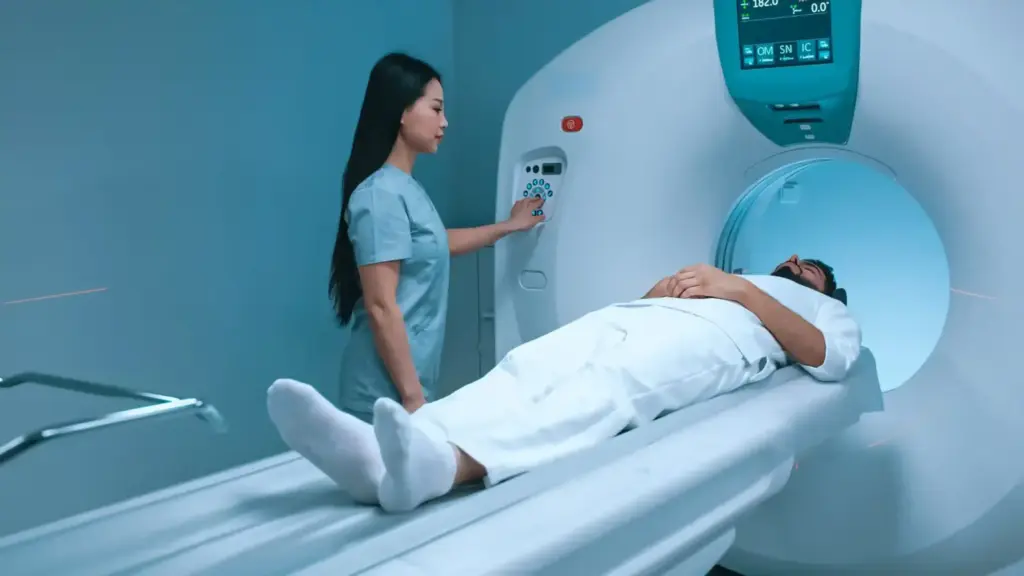
Many neurological conditions last a long time and require ongoing care rather than a quick fix. It’s important to take your medications as prescribed and be open to making changes in your daily habits to stay safe and independent.

Neuro-rehabilitation includes physical, occupational, and speech therapy to help you regain lost abilities. The main goal is to help you become as independent as possible and improve your quality of life, even with neurological challenges.

Yes severe stress can cause physical symptoms like headaches dizziness and memory problems mimicking neurological disorders.
No numbness can be caused by many things including pinched nerves or sleeping in an awkward position but sudden numbness is a stroke warning sign.
Many have a genetic component but not all are directly inherited lifestyle and environment also play huge roles.
Dementia is a general term for a decline in mental ability while Alzheimer’s is a specific disease and the most common cause of dementia.
This is usually a physiological tremor caused by adrenaline and is normal however persistent shaking when calm should be checked.

Can Stress Cause Epilepsy? Understanding the Connection Between Stress and Seizures <image1> Did you know that stress can trigger seizures in some individuals? Research shows
A recent study in the Radiation Oncology journal found that 13% of patients died within 30 days after getting palliative radiotherapy for bone metastases. Another

Choosing to have a carotid endarterectomy is a big decision. It’s important to know what to expect during recovery. Did you know that almost 100,000

Finding a lump inside your cheek can be scary. But knowing what it might be and when to see a doctor can help. At Liv
When serious bone damage happens, like from fractures or disease, our body might not heal on its own. That’s when a bone graft operation is
Cadaver bone grafts have changed orthopedic surgery a lot. They help patients who need bone replacement because of injuries, diseases, or surgery problems. Johns Hopkins

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)