Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik
Understanding bursitis and its impact on foot health is essential for effective management and relief.
We often see patients struggling with foot bursitis due to repetitive motion, poorly fitting shoes, or underlying medical conditions. Early diagnosis and the right bursitis treatment can make a big difference in recovery. Effective bursitis treatment focuses on reducing inflammation, relieving pain, and preventing recurrence through lifestyle adjustments and proper footwear. Understanding bursitis and its impact on foot health is essential for long-term relief.

The foot’s anatomy is complex, with bursae playing a key role. These fluid-filled sacs reduce friction between moving tissues. Knowing how bursae function is essential to understanding bursitis.
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles. They reduce friction and allow for smooth movement. In the foot, they help with walking, running, and other activities.
“Bursae are essential for reducing friction and alleviating pressure between tissues,” medical professionals say. They prevent irritation and inflammation in sensitive areas.
Bursae are found in various locations in the foot. They are common in areas with high friction and pressure. Some common spots include:
Knowing where bursae are helps diagnose bursitis and other conditions. Healthcare professionals use this knowledge to find areas of inflammation and irritation.
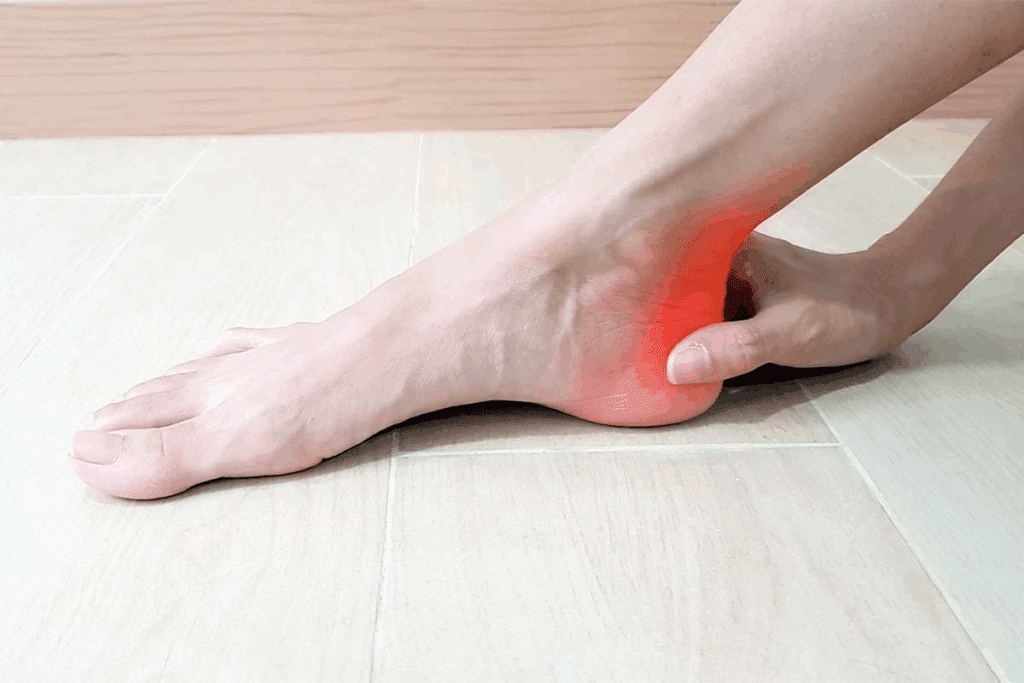
Understanding bursitis and its impact on foot health is essential for effective management and relief.
Overusing your foot or doing the same motion over and over can lead to bursitis. Running, dancing, or cycling are examples of activities that might cause it. Repetitive motion irritates and frays the bursae, causing inflammation.
Runners often get bursitis from the constant foot impact. Dancers might get it from the pressure on their toes. These activities put a lot of stress on the foot.
Getting hurt or having something press on your foot can also cause bursitis. A fall, a blow, or tight shoes can all put pressure on the bursae. Direct trauma can irritate it right away, while tight shoes can cause long-term problems.
Wearing the right shoes and protecting your feet is important. This can help prevent such injuries.
Some medical conditions can also lead to bursitis in the foot. Arthritis, gout, or unusual foot mechanics can increase your risk. For instance, people with arthritis might get bursitis because of the inflammation.
Those with gout might get it from urate crystals in the bursae. Knowing about these conditions can help you prevent and treat bursitis.
By understanding the causes, you can take steps to prevent and manage bursitis. This can help you avoid more serious problems.
Foot bursitis comes in different forms, each with its own set of symptoms and effects. Knowing these differences is key tothe right diagnosis and treatment. We’ll look at the main types of foot bursitis, where they occur, and what symptoms they cause.
Retrocalcaneal bursitis, or Achilles bursitis, happens at the back of the heel. It’s caused by repeated stress or direct injury to the area. Symptoms include pain and swelling at the back of the heel, which gets worse with activity.
Common causes: Overuse, poorly fitting shoes, and repetitive ankle motion.
Intermetatarsal bursitis affects the front of the foot, causing pain between the toes. It’s often linked to running or wearing tight shoes. The bursa in this area can get inflamed from friction or pressure, causing pain and discomfort when walking.
Risk factors: High heels, tight toe boxes, and repetitive stress on the forefoot.
Calcaneal bursitis is inflammation of the bursa at the heel. It can be caused by direct pressure or trauma to the heel, leading to pain and swelling. It’s important to tell calcaneal bursitis apart from other heel pain causes, like plantar fasciitis.
Metatarsophalangeal bursitis affects the joints at the base of the toes, causing pain and stiffness. It can be made worse by wearing the wrong shoes or having abnormal toe mechanics. Symptoms include pain when moving the toes and swelling around the affected joint.
Management: Proper footwear, toe exercises, and anti-inflammatory measures.
Understanding bursitis and its impact on foot health is essential for effective management and relief.
Pain and tenderness are key signs of foot bursitis. The pain can be mild or very bad. It gets worse when you move your foot or put pressure on it.
The pain can feel sharp or like a dull ache. This depends on how bad the inflammation is.
Swelling and redness are common signs of foot bursitis. The inflamed bursa makes the area swell and feel warm. It also turns red.
These signs show the body’s fight against inflammation. They mean bursitis might be present.
Foot bursitis makes it hard to walk or do daily tasks. The pain and discomfort limit how much you can move. This makes it hard to put weight on the affected foot or ankle.
Seeing these signs early helps manage and treat foot bursitis. Getting medical help early can ease symptoms and stop things from getting worse.
Understanding bursitis and its impact on foot health is essential for effective management and relief.
The first step is a detailed physical check-up. A doctor will look for swelling, redness, and tenderness in the affected area. They will also check how well you can move and do special tests to find the source.
This check is vital. It tells us right away about the foot’s condition and which bursae might be swollen. It helps us decide what tests to do next.
To be sure and check for other possible causes of pain, we suggest imaging tests. These might be:
These tests give us the info we need to figure out what’s causing the pain. Then, we can plan the best treatment.
When we diagnose foot bursitis, we also check for other possible causes of pain. These include plantar fasciitis, arthritis, tendonitis, and stress fractures. A full check-up makes sure we find and treat the real cause of pain.
| Condition | Common Symptoms | Diagnostic Tools |
| Foot Bursitis | Pain, swelling, limited mobility | Physical examination, MRI, Ultrasound |
| Plantar Fasciitis | Heel pain, pain with first steps | Physical examination, X-rays |
| Arthritis | Joint pain, swelling, stiffness | Physical examination, X-rays, and MRI |
By using the results from physical checks, imaging tests, and looking at the patient’s medical history, we can accurately diagnose foot bursitis. This way, we can tell it apart from other foot pain.
Effective bursitis treatment typically involves a combination of medical approaches to manage symptoms and address the root cause. We’ll look at different medical ways to treat bursitis. These aim to lessen inflammation, ease pain, and boost function.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often used to cut down pain and swelling from bursitis. We might suggest other meds to help with pain and discomfort. Sometimes, pain relief medications are given to better manage symptoms.
For serious bursitis cases, corticosteroid injections can be a good choice. These shots put anti-inflammatory medicine right where it’s needed. They help shrink swelling and ease pain, letting patients get back to their usual activities.
If other treatments don’t work, surgery might be needed. Surgical options for bursitis usually mean removing the swollen bursa or fixing any underlying issues. We only consider surgery when all else fails.
Effective bursitis treatment typically involves a combination of medical approaches to manage symptoms and address the root cause.
Several home remedies can help with foot bursitis symptoms. These self-care steps can ease pain and aid in recovery.
The RICE method is a top choice for foot bursitis. RICE means Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
Over-the-counter pain meds like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can ease pain and swelling. Always follow the dosage and talk to a doctor if needed.
Wearing supportive shoes and padding can ease pressure. Shoes with good arch support and cushioning help a lot.
Changing your lifestyle can also help with foot bursitis. Keep a healthy weight, avoid repetitive motions, and do exercises for your foot and ankle.
Using these home remedies daily can help manage foot bursitis symptoms and support your recovery.
Physical therapy is a key way to get better from foot bursitis. It helps you move better and get stronger. A good treatment plan tackles the symptoms and the root causes of the problem.
Stretching is a big part of treating bursitis. It makes your foot and ankle more flexible and less stiff. We suggest doing toe curls, heel raises, and ankle rotations to improve movement.
It’s important to do these exercises often. A physical therapist can help make a plan that fits your needs and how you’re doing.
Strengthening the muscles around your foot and ankle is also key. It helps support the area and keeps bursitis from coming back. You might do toe spreads, heel walks, and use resistance bands.
Stronger muscles mean you can handle daily activities better. This lowers the chance of getting hurt again.
Gait training is another important part of physical therapy. Bad walking habits can make bursitis worse. A physical therapist can help fix these issues.
They might look at how you walk and suggest ways to improve it. This could include using orthotics or changing your shoes.
Physical therapy is vital for easing bursitis symptoms. It also helps you recover fully and avoid getting it again.
Understanding bursitis and its impact on foot health is essential for effective management and relief.
Foot bursitis can last from a few weeks to months. Mild cases might heal in 2-4 weeks with rest and simple treatments. But,severe cases can take 6-12 weeks or even longer.
Everyone heals at their own pace. Your age, health, and any other health issues can affect how fast you heal. For example, people with diabetes or arthritis might heal more slowly.
Many things can change how long it takes to heal from foot bursitis. Knowing these can help make a better treatment plan.
| Factor | Impact on Healing Time |
| Effective bursitis treatment typically involves a combination of medical approaches to manage symptoms and address the root cause. | Mild: 2-4 weeks, Severe: 6-12 weeks or more |
| Treatment Effectiveness | Good treatment can make healing faster |
| Underlying Health Conditions | Can slow healing |
The recovery time for foot bursitis depends on many things. By understanding these and working with doctors, patients can get better faster.
“The key to recovering from foot bursitis is patience and adherence to treatment. With the right approach, most people can recover fully and return to their normal activities.”
In summary, while recovery times for foot bursitis vary, knowing what affects healing helps. This knowledge helps patients set realistic goals and work towards a successful recovery.
Alternative therapies can be a great addition to traditional treatments for bursitis. They help ease symptoms, speed up healing, and make life better overall.
Acupuncture uses fine needles to help the body heal and reduce pain. Acupressure is similar but uses pressure instead of needles. Both can help with bursitis by reducing swelling and improving blood flow.
Massage therapy can ease muscle tension, improve blood flow, and relax the body. It’s great for bursitis relief. Deep tissue massage and trigger point therapy are good for targeting bursitis areas.
Some herbal remedies and supplements have anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids are examples. But always talk to a healthcare professional before trying new supplements.
| Therapy | Benefits | Considerations |
| Acupuncture/Acupressure | Reduces pain and inflammation, improves circulation | Requires a licensed practitioner; may not be suitable for everyone |
| Massage Therapy | Reduces muscle tension, improves blood flow, promotes relaxation | Should be performed by a qualified therapist, may not be covered by insurance |
| Herbal Remedies/Supplements | Anti-inflammatory effects can be easily integrated into a daily routine | Quality can vary between brands, potentially interacting with medications |
Adding these alternative therapies to a treatment plan can help manage bursitis symptoms better. It can also improve overall well-being.
To prevent foot bursitis, it’s important to wear the right shoes, keep your feet clean, and change how you move. These steps can help lower your chance of getting bursitis in your foot.
Choosing the right shoes is key to avoiding foot bursitis. Shoes that fit well and support your feet can lessen pressure on bursae. Look for shoes with a comfy toe box, good arch support, and padding. Stay away from high heels and tight shoes to lower your risk.
Good foot hygiene is vital to prevent infections and lower bursitis risk. Washing and drying your feet and the spaces between your toes can stop bacteria and fungus.
Changing how you move to lessen foot stress can prevent bursitis. This means switching up your workouts, taking breaks, and avoiding things that make it worse.
By following these steps every day, you can lower your risk of foot bursitis. This helps keep your feet healthy and pain-free.
Knowing when to see a doctor for foot bursitis is key to good treatment and avoiding problems. Mild cases might get better with home care. But some situations need a doctor’s help right away.
Look out for signs of infection like more redness, swelling, warmth, or pus around the bursa. Infection can cause serious problems if not treated. Also, if you have a fever or feel really sick, see a doctor.
If your foot bursitis symptoms don’t get better with home care in a few weeks, see a doctor. Persistent symptoms might mean you need more help than just home remedies.
Severe pain or trouble walking because of foot bursitis means you need to see a doctor. Severe cases might need stronger treatments like injections or physical therapy to help with pain and mobility.
In short, if you see signs of infection, symptoms don’t get better, or pain is really bad, see a doctor. This way, you can avoid bigger problems and get the right care.
It’s important to know the differences between bursitis and other foot problems. Foot pain can come from many sources. Knowing what causes it helps in treating it correctly.
Plantar fasciitis hurts the heel and the bottom of the foot. It’s different from bursitis, which affects the bursae. The pain from plantar fasciitis is worse in the morning and gets better with activity.
Understanding bursitis and its impact on foot health is essential for effective management and relief.
Arthritis is a wide term for joint pain and swelling. In the foot, it can hurt many joints. This leads to pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Bursitis also causes swelling and pain, but affects the bursae. Tests like X-rays and MRI can show if it’s arthritis or bursitis by looking at the joints.
Tendonitis is when tendons, which connect muscles to bones, get inflamed. It can cause pain and swelling in the foot, like bursitis. But tendonitis is about the tendons, while bursitis is about the bursae.
The pain and swelling’s location can tell you which it is. For example, Achilles tendonitis hurts the back of the heel, while bursitis hurts above it.
Stress fractures are tiny cracks in bones, often from too much stress or overuse. They can hurt and swell, like bursitis. But stress fractures usually happen after a specific event or when activity increases.
The pain is often more focused on the fracture area. Tests like X-rays or MRI can spot stress fractures and tell them apart from bursitis.
| Condition | Location of Pain | Nature of Pain | Associated Symptoms |
| Bursitis | Variable, depending on the bursa affected | Constant pain, often with swelling and redness | Swelling, redness, limited mobility |
| Plantar Fasciitis | Heel and the bottom of the foot | Pain is worse in the morning, improves with activity | Stiffness, pain with first steps |
| Arthritis | Joints of the foot | Pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints | Joint deformity, limited mobility |
| Tendonitis | Near the affected tendon | Pain and swelling along the tendon | Swelling, pain with movement |
| Stress Fractures | Localized to the area of the fracture | Pain that worsens with activity | Swelling, pain with weight-bearing |
Getting the right diagnosis is key to good treatment. Knowing the differences between bursitis and other foot issues helps doctors treat patients better.
Understanding bursitis and its impact on foot health is essential for effective management and relief.
A good treatment plan includes medical care, home remedies, physical therapy, and other therapies. We’ve covered the main points to show how important a complete treatment plan is. It’s also vital to wear the right shoes, take care of your feet, and adjust your activities to avoid bursitis.
We want to help people understand how to deal with bursitis. If your symptoms don’t get better or get worse, see a doctor. This ensures you get the right help and have the best results.
Bursitis in the foot occurs when the bursae, fluid-filled sacs, become inflamed. These sacs cushion joints and reduce friction between bones, tendons, and skin.
Overuse and repetitive motion injuries can cause bursitis. So can trauma and direct pressure. Also, certain medical conditions can lead to it.
Symptoms include pain and tenderness. You might also see swelling and redness. Walking can become hard, and mobility is limited.
Doctors diagnose it through a physical exam. They might use X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound. They also rule out other conditions that could cause similar symptoms.
Treatment includes pain and inflammation medications. Corticosteroid injections are also used. For severe cases, surgery might be needed. Home remedies like the RICE method and over-the-counter pain relievers are also options.
Understanding bursitis and its impact on foot health is essential for effective management and relief.
Yes, it can be prevented. Wear proper footwear and keep your feet clean. Also, modify activities to avoid bursitis.
See a doctor if you notice signs of infection. If symptoms don’t get better with treatment, or if you have severe pain or can’t walk, seek medical help.
Physical therapy improves flexibility with stretching. It strengthens the foot and ankle. It also helps with walking mechanics through gait training.
Alternative therapies include acupuncture and acupressure. Massage therapy and herbal remedies, and supplements are also options.
Bursitis is different from conditions like plantar fasciitis and arthritis. It has its own symptoms and needs an accurate diagnosis for treatment.
Proper footwear reduces pressure and friction. It provides support and cushioning. It also helps with walking mechanics.
References
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!