Answering can a bone density test show cancer (it can show bone lesions but is not a diagnostic tool for cancer). Many patients wonder if a DEXA scan can show cancer. A bone density test is mainly for checking bone strength and finding osteoporosis. It’s not for diagnosing cancer.
These quick, painless scans are key in preventive healthcare. But, it’s important to know their true uses and limits. This helps in making smart healthcare choices.
At top medical centers, doctors often face questions about DEXA scans and cancer. The answer depends on what a DEXA scan is meant to do.
A bone density test, also known as a DEXA scan, is a non-invasive way to measure bone mineral density. It’s key for spotting osteoporosis and predicting fracture risks.
DEXA stands for Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry. It uses low-dose X-rays to check bone density. The main goal is to find osteoporosis and predict fracture risks. It looks at bone mineral density in spots like the hips and spine.
Bone density tests use low-dose X-rays to measure bone mineral density. It works by sending two X-ray beams. One goes through soft tissue, and the other through bone. This way, it figures out bone density.
The test focuses on the lumbar spine and hips because they’re more likely to break due to osteoporosis. The results are compared to a healthy young adult’s to see if you have osteoporosis or low bone mass.
During a DEXA scan, you’ll lie on a table while a scanner moves over your body. It’s usually painless and takes 10-30 minutes. You must stay very quiet to get accurate results.
Getting ready for the test is easy. You might need to take off jewelry or clothes with metal. Wear something loose and comfy instead.
Bone density tests check bone health. They help find out if someone might break a bone easily. This is because of low bone mass or osteoporosis.
Bone density tests are mainly for osteoporosis screening. They spot low bone mass and osteoporosis. These conditions make bones weak and prone to breaking.
Early detection lets doctors act fast. This can stop fractures and make life better for patients.
These tests also check fracture risk in people at risk. This includes women after menopause and older adults. Doctors use them to find who’s most likely to break a bone.
Then, they suggest ways to prevent it. This could be through diet, exercise, or medicine.
Bone density tests also track how well treatments work. Doctors do these tests regularly. This lets them see if the treatment is helping.
If not, they can change the treatment plan. This helps patients get better faster.
In short, bone density tests are key in healthcare. They help screen for osteoporosis, check fracture risk, and see if treatments are working. Their main goal is to help doctors make better choices for their patients. This aims to lower the chance of fractures and keep bones healthy.
Bone density tests, also known as DEXA or DXA scans, use low-dose X-rays. They measure bone mineral density. This tool is non-invasive and helps check bone health, mainly for osteoporosis and fracture risk.
DEXA scans focus on the hip and spine. These areas are key because they are prone to fractures. They show how well the bones are doing overall.
By looking at these spots, doctors can understand a patient’s bone health and fracture risk.
DEXA scans have a low radiation dose. They use much less X-ray than CT scans.
Key points about radiation exposure:
The results of a DEXA scan are shown as T-scores and Z-scores. It’s important to understand these scores to interpret bone density test results.
A T-score compares a patient’s bone density to a healthy young adult of the same sex. It helps diagnose osteoporosis and assess fracture risk.
A Z-score compares a patient’s bone density to an age-matched and sex-matched control group. It’s useful for assessing bone density in children and premenopausal women.
Bone density tests are key for checking osteoporosis risk. But, many wonder if they can find cancer. These tests, or DEXA scans, mainly look at bone mineral density to spot osteoporosis or predict fracture risk.
DEXA scans use low-dose X-rays to determine bone density. They give useful info on bone health. Yet, they can’t spot cancerous tumors or lesions well.
DEXA scans can’t find cancer because they’re not detailed enough. They’re made to measure bone density, not see tumors. They show bone density in grams per square centimeter (g/cm²) and give scores to show bone health.
DEXA scans are for bone density, not for finding tumors. They’re made to see bone, not soft tissue like tumors. So, they can’t give the detailed images needed for cancer diagnosis.
Even though DEXA scans aren’t for cancer, they can sometimes find things that worry you. Like vertebral fractures or odd bone loss. If this happens, you might need more tests like X-rays or MRIs to figure out what’s going on.
In short, bone density tests are great for checking bone health. But, they’re not good for finding cancer. If you’re worried about cancer, talk to your doctor about your risk and what tests you should get.
Bone cancer can be divided into primary and metastatic types. Each affects bone density differently. Knowing these types helps in diagnosing and treating bone issues.
Primary bone cancers start in the bone tissue. The main types are:
Metastatic bone cancer happens when cancer from other parts spreads to the bones. It can weaken bones and raise the risk of fractures.
Common sources of metastatic bone cancer include:
Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer that affects plasma cells in the bone marrow. It can cause bone pain, fractures, and osteoporosis.
It also leads to hypercalcemia, or high calcium levels in the blood. Multiple myeloma weakens bones by creating lytic lesions, areas of bone destruction. This increases the risk of fractures.
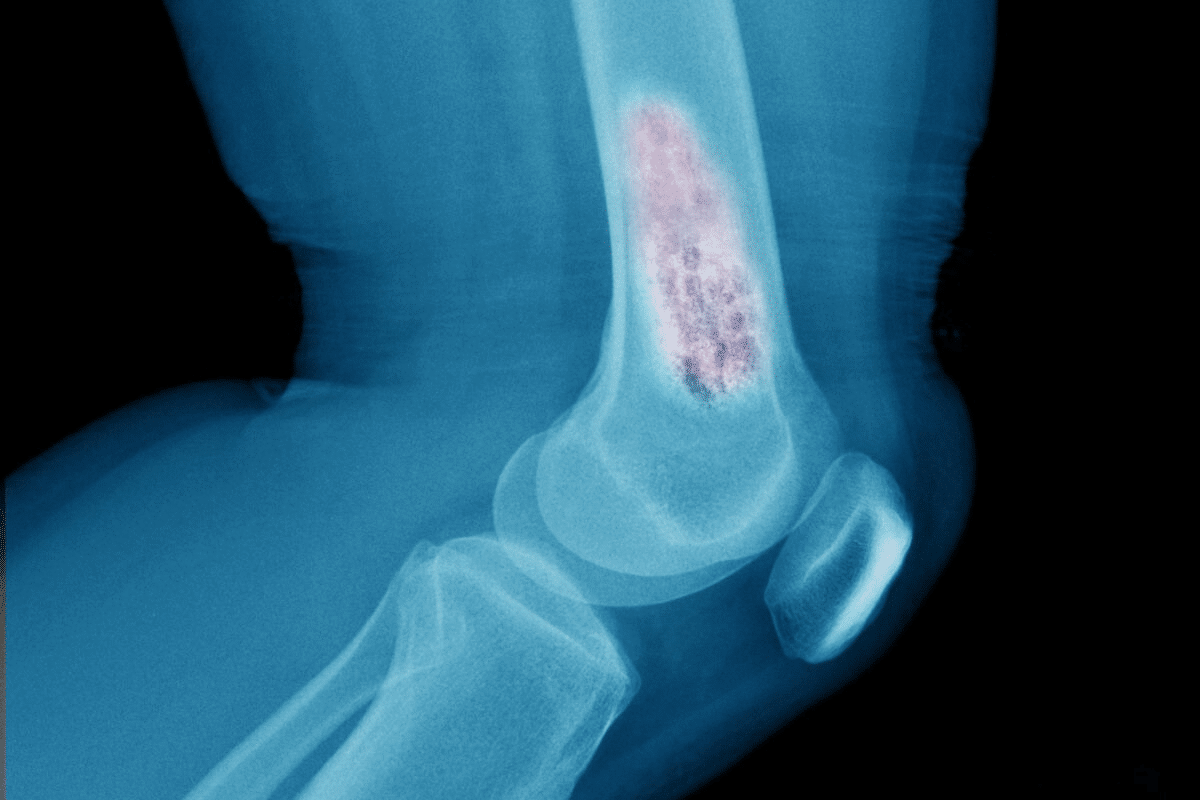
Several specialized imaging tests are recommended for detecting bone cancer. These tests help diagnose and stage bone cancer. They provide important information for treatment planning.
X-rays are the first test used when bone cancer is suspected. They show bone structure abnormalities, like lesions or fractures. But, X-rays can’t see soft tissue involvement or early bone density changes well.
CT scans and MRIs give detailed images of bones and tissues around them. CT scans are great for looking at bone structure and finding tumor calcification. MRI is better for seeing soft tissues and how far tumors have spread.
CT scans are good for bone images. MRIs are better for soft tissue.
PET scans use a radioactive tracer injected into the body. This tracer goes to areas with high activity, like cancer cells. They’re great for finding cancer spread and checking treatment results.
Bone scans use radioactive material to show bone metabolism. They’re good at finding bone metastases and showing how far the disease has spread.
In conclusion, a mix of imaging tests is used to diagnose and stage bone cancer. Each test gives unique info. Together, they help doctors plan the best treatment.
Abnormal bone density results can point to health issues that need more checking. Bone density tests are mainly for osteoporosis. But, they can show unusual patterns or anomalies that need more tests.
Certain bone loss patterns can hint at other health issues. For example, an unusual rate of bone loss or changes in specific areas might not be just osteoporosis. It’s key to spot these patterns to see if more tests are needed.
Some unusual patterns include:
Bone density changes can be either in specific areas or all over. Localized changes happen in certain spots, like around a joint. Generalized changes affect the whole skeleton.
|
Characteristics |
Localized Changes |
Generalized Changes |
|---|---|---|
|
Affected Areas |
Specific bones or joints |
Overall skeleton |
|
Possible Causes |
Injury, infection, or localized disease |
Systemic conditions, hormonal imbalances |
|
Diagnostic Approach |
Targeted imaging and biopsy |
Comprehensive medical evaluation |
If your bone density test shows odd results, your doctor might want more tests. These tests help find the cause of the abnormal bone density.
Some common tests include:
Understanding when to investigate abnormal bone density results helps patients. It shows the importance of a detailed medical check-up.
When a bone density test shows something odd, a detailed plan is set in motion. This plan is key to figuring out what’s going on. It helps spot health problems like cancer early on.
Healthcare providers often suggest more tests after getting odd bone density results. These tests aim to learn more about what’s happening.
These tests help doctors understand the odd findings. They decide the best next steps.
At times, a bone biopsy is needed for a clear diagnosis. It involves taking a small bone sample. This sample is then checked for any signs of disease.
“Bone biopsies are key in diagnosing cancer. They help find out the type and stage of the disease.” Medical Expert, Orthopedic Oncologist
Bone biopsies are top-notch for diagnosing some bone issues. They give vital info for treatment plans.
If cancer is suspected, a full cancer check is done. This includes:
This detailed check helps doctors create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Bone density tests are mainly for checking osteoporosis. But, many patients wonder if they can find cancer too. It’s important to know what these tests can and can’t do when it comes to cancer.
Patients worry if bone density tests can miss cancer. It’s key to know that these tests, or DEXA scans, aren’t for finding cancer. They look at bone density to see if you might get osteoporosis or break bones.
Key points to consider:
Each imaging test has its own job. For example, DEXA scans are great for checking bone density. But, tests like CT scans, MRIs, or PET scans are better for finding cancer.
Here’s a brief overview of when different tests are used:
|
Test Type |
Primary Use |
|---|---|
|
DEXA Scan |
Bone density measurement |
|
CT Scan |
Detailed imaging of internal structures, can be used for cancer detection |
|
MRI |
Soft tissue imaging, useful in detecting tumors and metastases |
|
PET Scan |
Tracking cancer metabolism, assessing spread of cancer |
Patients should talk to their doctor about their risk factors. If they’re worried about cancer, the doctor might suggest more tests. This depends on their medical history, risk factors, and symptoms.
Patients should ask their doctors about:
Bone density tests are key in checking bone health. They help spot osteoporosis and predict fracture risks. But, it’s important to know their limits.
DEXA scans, the main type of bone density test, don’t find cancer. They might show other things that need more looking into. But their main job is to measure bone density.
These tests are great for managing osteoporosis and seeing how treatments work. Yet, for finding bone cancer or other issues, you need special scans. X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, or PET scans are better for that.
In short, knowing what bone density tests can and can’t do is key. This helps both doctors and patients. It lets people make smart choices about their bone health and get the right care.
A bone density test, or DEXA scan, is not for finding bone cancer. It helps check bone health but can’t diagnose cancer.
A DEXA scan is not for finding cancer. It’s used to see how strong your bones are and if you might get osteoporosis or fractures.
Usually, a bone density scan doesn’t show cancer. But sometimes, it might find something that needs more looking into.
No, a bone density test can’t find bone cancer. For that, you need special tests like X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and PET scans.
Many cancers can change bone density. This includes primary bone cancers and cancers that spread to bones from other places.
A DEXA scan isn’t for finding bone cancer. It checks bone mineral density, not for cancer.
No, a DEXA scan isn’t for finding cancer. It’s for checking bone health, not for spotting tumors or cancer cells.
No, a DEXA scan doesn’t find cancer. It’s for looking at bone health, not for diagnosing cancer.
Usually, a bone density scan wouldn’t show cancer. It’s not a tool for cancer detection.
No, a bone density test can’t show bone cancer. It’s for checking bone health, not for finding cancer.
If you worry about bone cancer, talk to your doctor. They can suggest the right tests and procedures for you.
You might need more tests if your bone density results look unusual or show red flags. Your doctor will tell you what to do next.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. DEXA Scan: Not for Cancer Diagnosis, Osteoporosis Screening. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23151967/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!