Nuclear medicine is a field that uses tiny amounts of radioactive material to help doctors diagnose and treat diseases. Over 16 million nuclear medicine procedures are done every year in the United States. These help doctors check and manage health issues like heart disease and cancer. Some patients worry and ask, “Can nuclear medicine make you sick? since it involves exposure to radioactive material.
This method combines radioactive material with a carrier molecule to focus on specific body areas. It’s key in stress tests to check heart function and spot problems. Even though it involves radioactive material, the good it does in diagnosing and treating diseases usually outweighs the risks.
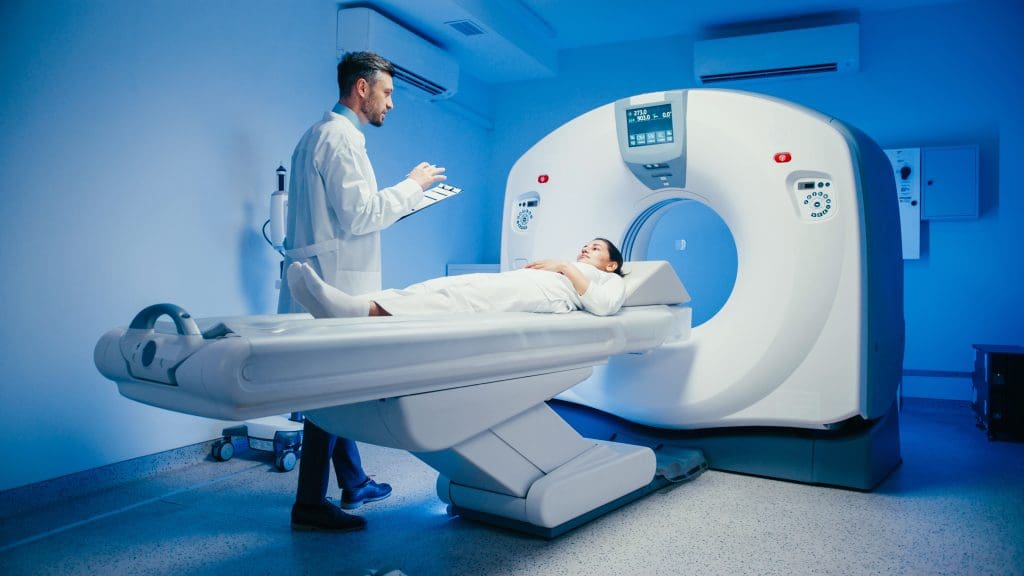
Nuclear medicine uses tiny amounts of radioactive tracers to see inside the body. It helps doctors diagnose and treat many diseases. This includes cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders.
Nuclear medicine uses small amounts of radioactive material. This material is given to the body through injection, ingestion, or inhalation. It goes to specific parts of the body, emitting signals that imaging equipment can detect.
The idea behind nuclear medicine is to target specific parts of the body. For example, some materials go to cancer cells. This lets doctors see tumors early, even before symptoms show up.
Here are some common nuclear medicine procedures:
These procedures are safe and give important information for treatment plans.
| Procedure | Description | Common Applications |
| PET scans | Uses small amounts of radioactive tracers to visualize metabolic processes in the body. | Cancer diagnosis, neurological disorders, cardiovascular disease. |
| Bone scans | Detects changes in bone metabolism, often used to identify cancer metastases or bone infections. | Diagnosis of bone cancer, infections, and skeletal disorders. |
| Cardiac stress tests | Assesses heart function under stress, typically using exercise or pharmacological stress. | Diagnosis of coronary artery disease, assessment of cardiac function. |
Cardiac stress tests are key for spotting and treating heart disease. They check how the heart works when it’s under stress. This is usually done through exercise or medicine to make the heart beat faster.
These tests aim to see if the heart can handle its toughest tasks. They look for problems with blood flow to the heart muscle. This can hint at coronary artery disease or other heart issues.
The test tracks the heart’s electrical activity, blood pressure, and other vital signs while the patient is stressed. This stress is usually through exercise on a treadmill or stationary bike. The workout gets harder until the heart rate hits a certain level or symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath appear.
“Stress testing is a cornerstone in the diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease, providing valuable information on the heart’s function under stress.” – American Heart Association
There are many types of cardiac stress tests, each with its own use and benefits.
| Type of Stress Test | Description | Primary Use |
| Nuclear Stress Test | Uses radioactive material to visualize heart muscle and blood flow. | Diagnosing coronary artery disease. |
| Exercise Stress Test | Involves exercising to stress the heart. | Assessing heart function and diagnosing heart disease. |
| Pharmacological Stress Test | Uses medication to stress the heart for patients who cannot exercise. | Diagnosing heart disease in patients unable to perform physical exercise. |
Each stress test has its own use and is picked based on the patient’s health, history, and what doctors need to know.
To understand cardiac stress tests, knowing the Bruce protocol is key. It’s a test that checks how well the heart works when stressed. This is usually done on a treadmill or ergometer.
This test pushes the heart hard. It helps find out if there are heart problems.
The Bruce protocol has different stages, each one harder than the last. It starts easy and gets tougher. Each stage lasts 3 minutes, with the treadmill getting faster and steeper every 3 minutes.
The goal is to test the heart’s limits. This helps doctors see how well it works under stress.
The ECG stress test uses the Bruce protocol. It watches the heart’s electrical activity. This helps spot heart rhythm problems or signs of heart not getting enough blood.
The heart’s electrical activity is watched closely. Blood pressure is checked often too. The test stops if the patient feels pain or trouble breathing.
| Stage | Speed (mph) | Incline (%) | Duration (minutes) |
| 1 | 1.7 | 10 | 3 |
| 2 | 2.5 | 12 | 3 |
| 3 | 3.4 | 14 | 3 |
| 4 | 4.2 | 16 | 3 |
The Bruce protocol is a key tool for diagnosing heart issues. It offers a reliable way to check how the heart handles stress.
Knowing what to expect from a nuclear stress test is key. This test checks how well the heart works under stress. It’s mainly used to find coronary artery disease.
Getting ready for a nuclear stress test is important. Patients should avoid certain foods and medicines that might affect the test. They are told to:
It’s also recommended to avoid wearing jewelry or anything that could interfere with the test equipment. Arriving early is a good idea to fill out paperwork and get ready.
During the test, a small amount of radioactive material is given through an IV. The test has two parts: at rest and under stress. The stress part usually involves walking on a treadmill or biking.
Patients are watched closely with an ECG and a gamma camera. These tools capture heart images. Medical professionals are there to watch over the patient and adjust the test as needed.
After the test, most people can go back to their usual activities. Some might feel tired or sore, but these feelings usually go away soon.
It’s important to follow the doctor’s advice on what to do after the test. Patients should also tell their doctor if they notice anything unusual.
Understanding the nuclear stress test helps patients prepare and recover better. This makes the whole experience smoother.
Before getting a nuclear medicine test, it’s good to know the possible risks and side effects. This test is very useful for doctors to diagnose diseases. But, it’s important to know the safety issues it might have.
Nuclear medicine tests use tiny amounts of radioactive materials. Most people find them okay. But, some might feel:
These side effects are usually mild and go away quickly. You might not need to see a doctor for them.
The main worry with nuclear medicine is radiation exposure. The tracers used in these tests do give off radiation. This could slightly raise the chance of cancer or genetic problems. But, doctors use just the right amount of radiation to get good images and keep risks low.
“The benefits of nuclear medicine in diagnosing and treating diseases often outweigh the risks associated with radiation exposure.”
Some people should not get nuclear medicine tests because of health risks. These include:
| Group | Reason |
| Pregnant Women | Risk of radiation exposure to the fetus |
| Breastfeeding Women | Potential for radioactive tracer to be passed to the baby through breast milk |
| Individuals with Certain Medical Conditions | Conditions that may be exacerbated by the procedure or the radioactive tracer |
Talking to your doctor about your health and any worries is key before a nuclear medicine test.
Stress test results give us a peek into how well the heart works when it’s stressed. They’re key for spotting heart problems and figuring out the best treatment.
A normal stress test means the heart is doing well under stress. This is a positive sign, showing no big blockages in the heart’s arteries. But, abnormal findings might point to heart issues like coronary artery disease.
Abnormal results could show reduced blood flow or irregular heartbeats. These signs might lead to more tests to find the cause.
Nuclear stress test results are read by looking at the images taken. These images show how the heart muscle gets blood at rest and when stressed. Differences in perfusion can mean ischemia or dead heart tissue.
Doctors also check the heart’s pumping and size. This helps them understand the heart’s condition fully.
Doctors look at several things when they check stress test results. They check the heart’s electrical activity for any odd rhythms or ischemia. They also see how well the heart pumps and if it’s failing.
They compare these results with other tests like echocardiograms or cardiac catheterization. This gives a full view of the heart’s health.
Stress test results change a lot with age. This makes age very important when we look at these tests. People’s performance is checked in several ways, like how long they can stay on the treadmill, their heart rate, and how hard they work.
Younger people can usually stay on the treadmill longer than older ones. This is because they can handle more physical activity. Here’s a table showing how long different age groups can stay on the treadmill.
| Age Group | Average Treadmill Time (minutes) |
| 20-29 | 12-15 |
| 30-39 | 10-13 |
| 40-49 | 8-11 |
| 50-59 | 6-9 |
| 60+ | 5-7 |
A normal heart rate during a stress test is between 70% to 85% of the maximum heart rate. This maximum rate is found by subtracting your age from 220.
How well someone does on a stress test can really vary. This is because of things like fitness level, health conditions, and medicines. For example, a very fit 60-year-old might do as well as a less fit 40-year-old.
It’s very important for doctors to understand these differences. This helps them make the best choices for their patients.
Certain symptoms and risk factors can show you need a stress test. Spotting these signs early is key to keeping your heart healthy and avoiding problems.
Cardiac symptoms are a big clue you might need a stress test. These symptoms include:
Several risk factors can make you more likely to need a stress test. These include:
Whether or not to get a stress test is usually decided with your doctor. They’ll look at your health, medical history, and risk factors to decide if a stress test is right for you.
If you’re feeling any cardiac symptoms or have several risk factors, talk to your doctor. They can give you advice tailored to your situation and suggest the right tests.
A stress test is more than just a procedure. You need to know about the test’s duration, costs, and insurance coverage.
The time needed for a stress test varies. It can last from 30 minutes to several hours. This depends on the test type and your health.
Here’s what you can expect in terms of time:
Plan to spend at least half a day at the testing facility.
The cost of a stress test changes based on several factors. These include location, facility type, and doctor-ordered tests.
| Test Type | Average Cost | Range |
| Standard Stress Test | $300 | $200 – $500 |
| Nuclear Stress Test | $1,000 | $800 – $1,500 |
| Stress Echocardiogram | $500 | $300 – $800 |
These prices are estimates and can change based on your location and insurance.
Most insurance plans cover stress tests when they’re medically necessary. But, coverage can differ based on your insurance and plan details.
It’s key to talk to your insurance before a stress test. This way, you’ll know what’s covered and any costs you might face.
Knowing these practical aspects helps you prepare for a stress test. It’s important for both your health and finances.
Nuclear medicine is key in finding and treating many health issues, like heart disease. It helps us understand how these tools work. This knowledge is important for everyone.
Stress tests give us important info about the heart. They help doctors find and treat heart problems. This info helps doctors make the best plans for patients.
Nuclear medicine keeps getting better, helping us check heart health more accurately. With these advances, doctors can create treatment plans that really work for each patient.
A nuclear stress test is a procedure that checks how well your heart works when it’s stressed. It uses exercise or medicine to make your heart rate go up.
A stress test shows how well your heart works when it’s under stress. It can help find heart problems, like coronary artery disease.
The time on a treadmill for a stress test varies by age. It usually lasts from 7 to 12 minutes.
The normal heart rate during a stress test depends on your age. It should reach 80-90% of your maximum heart rate for your age.
The time it takes for a stress test can vary. It can be from 30 minutes to several hours. This depends on the test type and your condition.
Signs you might need a stress test include heart symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath. Risk factors like family history, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol also matter.
The Bruce protocol is a standard test for heart stress tests. It has stages that get more intense. You usually use a treadmill or ergometer.
A nuclear stress test uses a radioactive material. Your heart rate is watched with a gamma camera during the test.
Nuclear medicine can have side effects like allergic reactions or minor issues. There’s also a risk of radiation exposure.
Some people should not have nuclear medicine tests. This includes those who are pregnant or breastfeeding because of radiation risks.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)