Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common but serious. They need quick attention and the right treatment. Most UTIs get better with antibiotics if treated fast. But, untreated or complicated infections can become very dangerous.Can you die from a bladder infection or UTI? Learn about the severe, though uncommon, risk of the infection leading to sepsis.
UTIs happen when bacteria get into the urinary tract through the urethra. They then spread in the bladder. Women are more likely to get UTIs because their urethra is shorter. We’ll look at how serious UTIs and bladder infections can be.
It’s important to know the risks and effects of UTIs to get them treated right away. In 2019, there were 404.61 million cases and 236,790 deaths from UTIs. This shows how big of a health issue UTIs are.
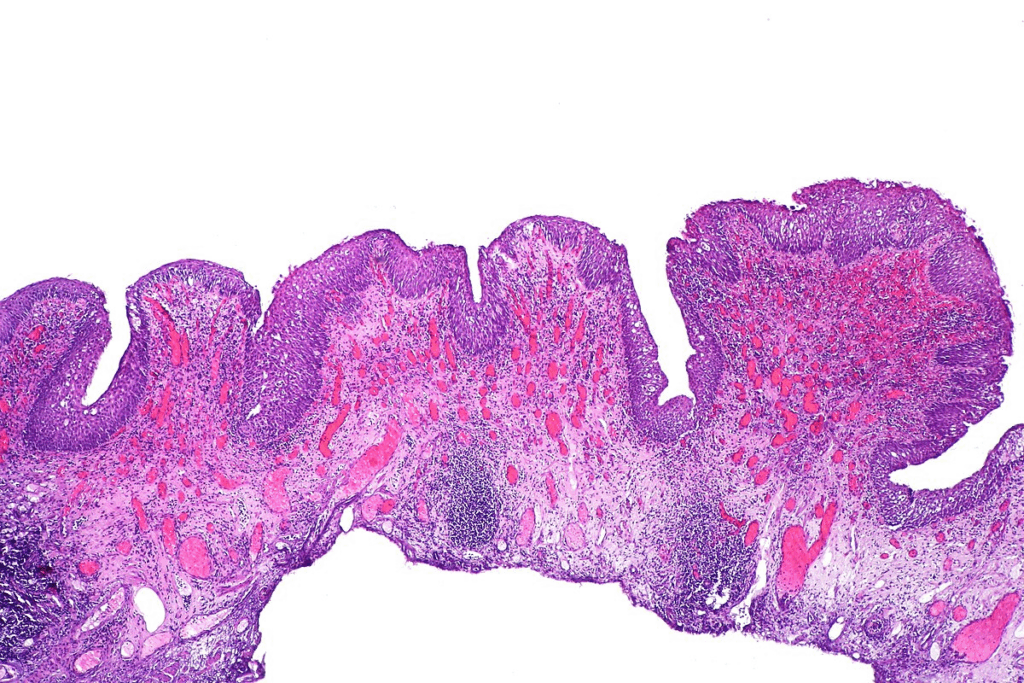
It’s important to know about UTIs to spot their signs early and get help fast. UTIs are infections caused by bacteria in the urinary system. This system includes the kidneys, bladder, and the tubes that connect them.
UTIs can be different based on where and how serious they are. Simple UTIs usually happen in healthy, non-pregnant women and can be treated with common antibiotics. Complicated UTIs are harder to treat because they involve other health issues or special conditions.
Knowing if a UTI is simple or complicated helps doctors decide how to treat it. Simple UTIs mainly affect the bladder. Complicated UTIs can reach the kidneys and cause more serious problems.
UTIs show a variety of symptoms, such as:
These symptoms can be more severe in complicated UTIs. UTIs are common, with millions of cases every year. Women are more likely to get UTIs because their urethra is shorter, making it easier for bacteria to get into the bladder.
Spotting UTI symptoms and knowing the types is key to managing them well and avoiding serious issues.
UTIs can range from mild to severe, affecting people differently. It’s key to know when a bladder infection is a serious threat. We’ll look at the different levels of UTIs and what makes them more serious.
UTIs are split into uncomplicated and complicated types. Uncomplicated UTIs happen in healthy people with normal urinary tracts. Complicated UTIs have higher risks due to factors like urinary tract blockages, weakened immune systems, and catheters.
Knowing the difference is vital for the right treatment. Uncomplicated UTIs usually get treated with common antibiotics. But complicated UTIs need stronger and longer treatments.
Bladder infections can turn dangerous if they spread to the kidneys or cause systemic infections. Pyelonephritis, a kidney infection, is a serious issue from untreated or poorly treated bladder infections.
Several factors can make UTIs worse, including:
Spotting these risk factors and knowing when a bladder infection is serious is key to avoiding severe problems.
The table below highlights the main differences between uncomplicated and complicated UTIs:
| Characteristics | Uncomplicated UTIs | Complicated UTIs |
| Population | Healthy individuals | Individuals with urinary tract abnormalities or other complicating factors |
| Treatment Approach | Standard antibiotic regimens | More intensive and prolonged treatment |
| Risk of Complications | Low | High |
Understanding UTI severity and recognizing complicated infections helps us act fast to avoid serious health issues.
It’s important to know that UTIs can be deadly. This is true if they are not treated or if treatment is delayed. Many of us have felt the pain of a urinary tract infection. But, we often don’t realize how serious these infections can be.
UTIs can cause serious problems like bacteremia and urosepsis. These conditions raise the risk of death. Research shows that the death rate from UTI-related bacteremia can be up to 10%.
When UTIs turn into urosepsis, death rates are between 2.8 to 4.6%. These numbers show how critical it is to treat UTIs quickly and effectively.
Some groups are more at risk for these severe problems. We will look into this further.
UTIs cause a lot of deaths worldwide. These infections are common, affecting millions every year. While death rates are low in healthy people, the number of cases is huge.
Recent studies show that UTIs have a big impact globally. Many deaths are linked to UTI complications each year. This shows we need to keep working on preventing, finding, and treating UTIs.
Understanding UTI risks is key for doctors and everyone. By knowing how serious these infections can be, we can lower the number of deaths from UTIs.
“The true burden of UTIs is likely underestimated due to underreporting and the complexity of attributing deaths to UTIs directly.” This statement highlights the need for better data and awareness about UTI severity.
UTIs can turn into serious conditions if not treated right away. We’ll look at how these infections can grow from a simple bladder infection to severe cases like pyelonephritis and urosepsis.
Cystitis is an infection of the bladder, the first stage of a UTI. If not treated quickly or if treatment is delayed, the infection can move up to the kidneys. This leads to pyelonephritis, a condition with severe flank pain, fever, and potentially life-threatening complications.
Pyelonephritis can harm the kidneys permanently if not treated on time.
The move from cystitis to pyelonephritis is a key step in UTI progression. Prompt medical intervention is key to stop this. We must spot symptoms early and know who’s at risk.
Urosepsis happens when a urinary tract infection spreads to the blood, causing a body-wide infection. This is a serious condition that needs immediate medical help. The bacteria break through the body’s defenses and get into the blood, leading to septic shock, organ failure, and death if not treated fast.
We must watch for signs of urosepsis, like high fever, rapid heart rate, and confusion. Spotting these symptoms early is key to survival. Knowing how a UTI can turn into urosepsis helps prevent severe outcomes.
When bacteria from a urinary tract infection (UTI) enter the bloodstream, they can cause bacteremia. This can lead to septic shock if not treated. This shows how serious UTIs can be and why quick treatment is key.
Bacteria can get into the bloodstream in different ways. For UTIs, the most common path is through the urinary tract. If a UTI isn’t treated well, bacteria can move up to the kidneys, causing pyelonephritis. Then, they can get into the bloodstream, leading to bacteremia.
Several factors can increase the chance of bacteria getting into the bloodstream. These include:
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Bacteremia Risk |
| Untreated or Recurrent UTIs | Failure to treat UTIs or frequent occurrences | Increases bacterial load and the chance of bacteremia |
| Urinary Tract Obstructions | Blockages in the urinary tract | Can trap bacteria, raising the risk of infection spread |
| Compromised Immune Systems | Weakened immune response | Reduces the body’s ability to fight off infections |
Sepsis is a dangerous condition where the body’s response to an infection harms its own tissues and organs. It’s important to know the signs of sepsis from a UTI to get help quickly. Symptoms include:
If you or someone you know has these symptoms, and they have a UTI, get medical help right away. Quick action can make a big difference in treatment success.
Understanding the risks of UTIs and their possible complications like bacteremia and septic shock is vital. It shows why UTIs should be taken seriously and why seeking medical care is important. Quick treatment can stop these serious problems, helping patients and reducing death risk.
It’s important to know who is most at risk for serious urinary tract infections (UTIs). Some people are more likely to face severe problems from UTIs. These can be deadly if not treated right.
Elderly people are at high risk for serious UTI problems. As we get older, our immune systems get weaker. This makes it easier for infections to take hold. Older adults often have health issues that make treating UTIs harder.
A study in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society shows UTIs are a big problem for older adults. This is true, even more so for those living in long-term care facilities.
Key Risk Factors for Elderly Patients:
People with weakened immune systems, like those with HIV/AIDS or on certain drugs, face a higher risk. Their bodies struggle to fight off infections. Quick and effective treatment is key.
“Patients with immunocompromised conditions are more likely to experience recurrent UTIs and are at a higher risk for developing urosepsis, a life-threatening condition.” –
Medical Expert, Infectious Disease Specialist
Those with diabetes and other chronic conditions are also at risk. Diabetes can make it hard for the body to fight off infections. High blood sugar can damage blood vessels and nerves, including those controlling the bladder.
| Chronic Condition | Risk Level | Complications |
| Diabetes | High | Increased risk of urosepsis, kidney damage |
| Kidney Disease | High | Potential for kidney failure, sepsis |
| Heart Disease | Moderate | Increased risk of sepsis, organ failure |
Healthcare providers need to spot these high-risk groups early. They should give them special care to prevent serious UTI problems. Quick action and the right treatment can greatly lower the chance of death from UTIs.
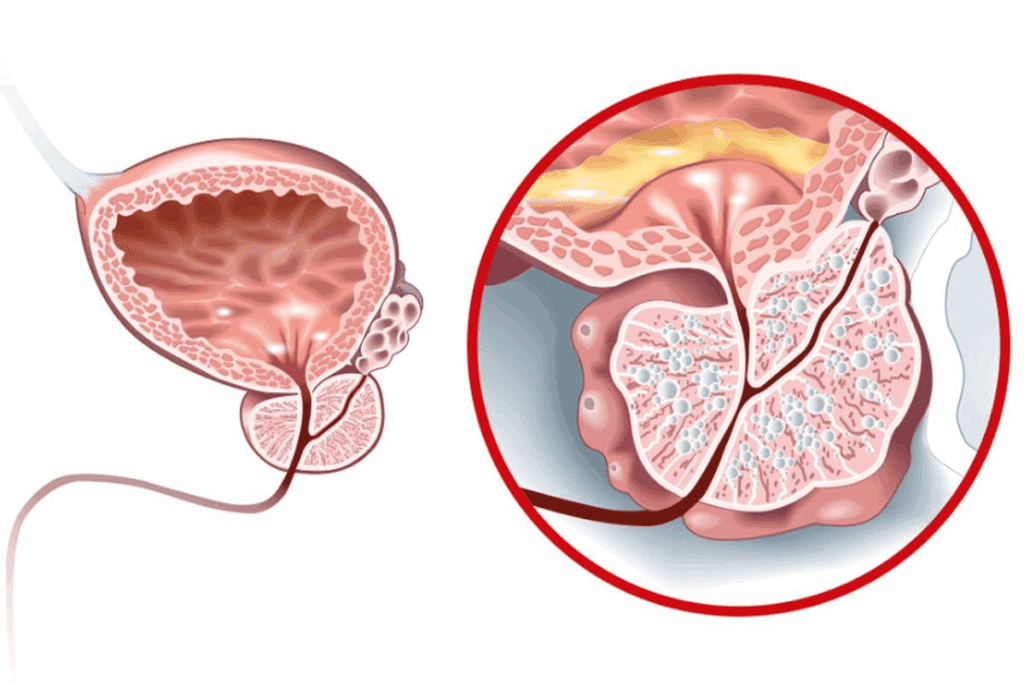
Urinary tract obstruction is a serious issue. It can greatly increase the risk of death in patients with urinary tract infections (UTIs). When the urinary tract is blocked, bacteria can build up. This can lead to infections spreading to the kidneys and even into the bloodstream.
Several types of obstructions can make UTIs worse. These include:
These obstructions can block the normal flow of urine. This creates a perfect environment for bacteria to grow. For example, kidney stones can physically block the flow. Tumors or BPH can compress or block the urinary tract.
Effective treatment for obstructive UTIs involves fixing the blockage and treating the infection. This may include:
It’s vital to quickly diagnose and treat obstructive UTIs to avoid serious complications. Understanding the causes and effects of urinary tract obstruction helps healthcare providers create effective treatment plans. This improves patient outcomes.
Antibiotic-resistant UTIs are becoming a big problem. They make treating UTIs harder. This health crisis needs our focus and action.
Antibiotic resistance in UTIs can lead to long suffering. It also raises the risk of serious and even deadly conditions.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are on the rise. Resistance to common antibiotics makes treating UTIs tough. We’re seeing more dangerous and resistant bacteria.
The main reason for this is the overuse and misuse of antibiotics. Using antibiotics when not needed pushes bacteria to become resistant. We also need new antibiotics, but they’re not being developed fast enough.
Dealing with antibiotic-resistant UTIs is tough. Treatment often needs stronger and pricier antibiotics. Sometimes, patients need to be in the hospital for IV antibiotics. This can cause more harm and even death.
We need to fight antibiotic resistance in many ways. This includes better use of antibiotics, better tests to guide treatment, and research for new antibiotics. Knowing the risks helps us find ways to fight antibiotic resistance in UTIs.
Catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) are a big worry in hospitals. They can lead to more sickness and even death. We look at the dangers and how to stop these infections.
Urinary catheters can let bacteria into the urinary tract, causing infections. Bacteria can grow on the catheter, leading to infection. The longer a catheter stays in, the bigger the risk of getting a UTI.
The catheter can also hurt the urethral lining, making it easier to get infected. Plus, catheters can get past the body’s natural defenses, like the urethral sphincter, letting in harmful germs.
To stop CAUTIs, we need to do many things. Proper catheter insertion and care are key. Healthcare workers should use clean techniques when putting in catheters and make sure they’re fitted right to avoid damage.
It’s important to check if a catheter is really needed and take it out quickly if not. Using catheter care bundles, like cleaning daily and only using them when needed, can help a lot. These steps can cut down CAUTI risks.
Teaching healthcare staff how to use and care for catheters is also key. Knowing the risks and using these steps can lower CAUTI cases and deaths.
UTIs are common, but some signs mean they’re serious and need quick action. Knowing these signs is key to avoiding big problems and getting help fast.
As a UTI gets worse, symptoms can get much worse too. You need to see a doctor right away if you notice:
If you’re feeling any of these, you need to see a doctor fast. Getting help early can stop UTIs from getting worse.
It’s important to know when to go to the emergency room. If you or someone you know has:
you should go to the emergency room right away. These signs mean the UTI could be turning into something very serious, like pyelonephritis or urosepsis. You need help fast.
In short, knowing the signs of a serious UTI can save lives. By spotting these symptoms and getting medical help quickly, you can avoid big problems and get better faster.
Severe UTIs need quick and effective treatment to avoid serious problems. We’ll look at the best ways to manage severe UTIs. This includes medical treatments and supportive care.
Intravenous antibiotics are often the first choice for severe UTIs. This method delivers medicine directly into the blood. It helps fight the infection faster and more effectively. Sometimes, patients need to stay in the hospital if they’re very dehydrated or have severe symptoms.
Doctors use different antibiotics like ceftriaxone or ciprofloxacin. The choice depends on the bacteria and local resistance patterns. It’s important to follow local guidelines for antibiotic use.
Supportive care is also key in treating severe UTIs. It includes giving fluids to stay hydrated, managing pain, and watching for signs of sepsis.
Supportive care might also include nutritional support. Patients with severe infections may need more nutrients. Keeping an eye on vital signs and organ function is important to catch any problems early.
Combining strong antibiotic treatment with supportive care helps patients with severe UTIs. It can improve their chances of recovery and lower the risk of death.
Urinary Tract Infections are a big health issue that needs quick action and proper care. We talked about the dangers of UTIs, like serious complications. These risks are higher for the elderly and those with weak immune systems.
It’s important to take UTIs seriously to avoid complications and get treatment fast. Knowing the symptoms and risks is key. Also, practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, and managing health conditions can help prevent UTIs.
By spreading awareness and teaching about UTI prevention, we can lower UTI rates and complications. We should be proactive about UTIs, knowing that early action can greatly improve results. Let’s focus on preventing and treating UTIs to reduce their risks.
Yes, if not treated, UTIs can cause serious problems. These include sepsis, which is very dangerous and can be fatal.
Symptoms include burning when you pee, needing to pee a lot, and urine that smells bad. Women may also feel pain in their pelvis.
Older people, those with weak immune systems, and those with diabetes are at higher risk. They can face serious complications from UTIs.
Yes, it can. Obstruction stops urine from flowing normally. This makes UTIs worse and can be deadly.
Urosepsis is a serious condition. It happens when UTI bacteria get into the blood. This can lead to a severe infection.
Catheters can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract. This increases the risk of UTIs, more so in healthcare settings.
Look out for severe pain, high fever, and nausea. Vomiting and signs of sepsis, like a fast heart rate and confusion, are also warning signs.
Yes, they can be. These UTIs are hard to treat. If not managed right, they can lead to severe complications, including death.
For severe infections, intravenous antibiotics are used. Sometimes, hospitalization is needed to manage the infection and prevent complications.
To prevent UTIs, practice good hygiene and stay hydrated. Pee when you need to, and avoid products that can irritate your urinary tract.
Most UTIs are not deadly. But, they can become life-threatening if not treated or if complications arise, mainly in high-risk groups.
Yes, a severe UTI, like urosepsis, can be fatal if not treated quickly and effectively.
UTIs can be deadly if they cause severe complications, like sepsis. This is more likely in vulnerable populations.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us