Last Updated on October 21, 2025 by mcelik
Childhood cancer is a big worry, with many types affecting kids. Leukemia used to be the deadliest, but now there’s a change.
Brain and CNS tumors are now the top cause of cancer-related deaths in kids, the CDC says. In 2014, almost one in three pediatric cancer deaths were from brain cancer. Early recognition of cancer childhood symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment initiation. Leukemia treatment has improved significantly, but brain cancer remains particularly challenging to treat because of the blood-brain barrier that limits the effectiveness of many therapeutic approaches.
It’s important to understand how childhood cancer mortality rates have changed. This helps us see if current treatments are working well. It also shows where we need to do better.
From 1975 to 2019, the rate of cancer deaths in kids dropped from 4.9 to 2.3 per 100,000. This is a big drop, showing a more than 50% decrease in cancer deaths in kids and teens under 20 from 1975 to 2022.

Childhood cancer in the U.S. is a complex issue. Some types of cancer have seen big improvements in survival rates. But others are harder to treat. This shows we need to keep researching and finding better treatments.
Childhood cancer death rates have dropped a lot over the years. This shows how far pediatric oncology has come. We’ve made big steps in chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery. We’ve also improved care for kids with cancer.
Key factors contributing to the decline include:
As we move forward in fighting childhood cancer, it’s key to understand these trends. This knowledge helps us find ways to lower death rates and help kids with cancer more.
Brain and central nervous system (CNS) tumors are now the top cause of cancer deaths in kids. This change shows how vital it is to know about these tumors. We need to understand their types, challenges, and survival rates.
Pediatric brain and CNS tumors include medulloblastoma, glioma, and ependymoma. Each type has its own traits and treatment challenges. The National Cancer Institute says knowing these differences is key to better treatments.
Brain tumors are hard to treat because of the blood-brain barrier. This barrier blocks drugs from reaching the tumor. Also, brain tissue is very delicate, making surgery risky. These reasons lead to higher death rates in kids with brain and CNS tumors.
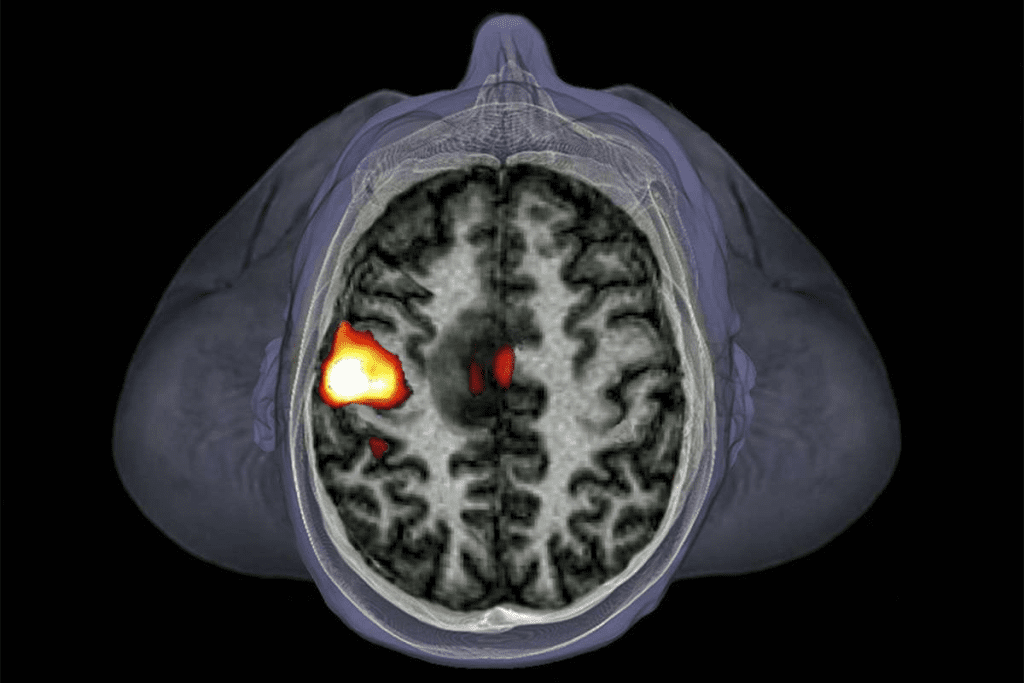
Thanks to new medical tech and treatments, kids with brain and CNS tumors now have a 60% 5-year survival rate. This shows the hard work in pediatric oncology is paying off. We need more research and innovation to keep improving survival rates and quality of life for these young patients.
Brain tumors cause the most childhood cancer deaths, followed by leukemia. Knowing about these tumors and their survival rates is key to better treatments. The 60% 5-year survival rate for kids with brain and CNS tumors shows we must keep researching and improving treatments.
Leukemia is the most common cancer in kids, but it’s no longer the deadliest. This change comes from better ways to diagnose and treat it. We now understand the disease better.
Leukemia is a big part of childhood cancers, with most being Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). About 3 out of 4 cases are ALL. The exact cause is often unknown, but genetics and environment play a role.
Knowing how common and what types of leukemia are important for treatment. Research shows some kids might be born with genetic risks. This raises questions about if you can be born with cancer.
The 5-year survival rate for leukemia in kids has jumped over 85%. This shows how far medical science has come. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to better survival rates.
Survival rates depend on the type of leukemia and other factors. Age at diagnosis and treatment response also matter. More research and treatment improvements are expected to help more kids.
Leukemia treatment has gotten better, with therapies being more precise and less harsh. Chemotherapy, radiation, and sometimes bone marrow transplants are used. These changes have led to better survival rates and fewer side effects.
Today’s treatments are customized for each child. New drugs and strategies are being developed. This makes leukemia a serious but not always fatal disease.
Childhood cancer includes many types, each with its own survival rates. It’s important to compare these rates to find where we need to focus more research.
Neuroblastoma starts in the adrenal glands, neck, chest, or spinal cord. It mainly affects young kids, often under five. The 5-year survival rate for neuroblastoma has risen to about 80% for kids diagnosed between 2011 and 2017. But, high-risk neuroblastoma is harder to treat, with a lower survival rate.
Bone cancers, like osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma, are rare in kids but have unique traits. Osteosarcoma is the most common bone cancer in kids, found in long bones. Ewing sarcoma can happen in any bone or soft tissue. Treatment has boosted the 5-year survival rate for osteosarcoma to about 70%. Ewing sarcoma’s 5-year survival rate is around 75%.
Soft tissue sarcomas come from connective tissues like muscle, fat, and blood vessels. Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most common soft tissue sarcoma in kids. Thanks to multi-modal therapy, the 5-year survival rate for rhabdomyosarcoma is now about 70%.
Lymphomas are cancers of the lymphatic system, divided into Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Both can affect kids, but Hodgkin lymphoma is more common in teens. Better chemotherapy and radiation have greatly improved survival rates. Hodgkin lymphoma’s 5-year survival rate is over 90%.
Looking at mortality rates across childhood cancers shows we’ve made progress in treatment. But, there’s more work to do. We need to keep researching and improving medical care to help more kids survive cancer.
Spotting the signs of childhood cancer is key to getting help fast. Early treatment is vital for better chances of survival. Different cancers show different symptoms, so it’s important for parents and caregivers to know the common and specific signs.
Some common signs that might mean cancer include fever that won’t go away, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. Other signs are bruising or bleeding easily, and bone pain or swelling. While these can mean many things, seeing them often or together means it’s time to see a doctor.
Brain and CNS tumors can cause symptoms like headaches, vomiting in the morning, and vision changes. Kids might also have seizures, weakness, or changes in behavior or cognitive function.
Leukemia, the most common childhood cancer, shows symptoms like fatigue, pale skin from anemia, infections that keep coming back, and easy bruising or bleeding. Kids might also have bone pain or swollen lymph nodes.
Knowing these symptoms can help catch cancer early. If a child keeps showing these signs, it’s important to see a doctor right away.
The exact causes of childhood cancer are not yet fully understood. But research has found several risk factors. Knowing these factors helps us find ways to prevent and detect cancer early.
Genetics play a big role in some childhood cancers. Certain genetic conditions, like Down syndrome, raise the risk of specific cancers, like leukemia. Genetic mutations or changes can be passed down or happen on their own, leading to cancer.
Families with a history of certain cancers might be at higher risk. For example, mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, linked to adult breast and ovarian cancers, can also affect childhood cancer risk.
Environmental exposures are also key in childhood cancer risk. Being exposed to ionizing radiation, certain chemicals, and infections during pregnancy or early childhood may lead to cancer.
Childhood cancer rates have been rising, but the reasons are complex. Changes in environmental exposures, better diagnostic techniques, and shifts in population demographics might all play a part.
To understand why childhood cancer rates are going up, we need more research on genetic and environmental risk factors. This knowledge is key to creating effective prevention and early detection strategies.
Modern ways to find and treat childhood cancer have made big strides. New medical tech and treatment plans have greatly helped kids with cancer.
Diagnosing childhood cancer is now more precise and quick thanks to new tech. MRI and CT scans give clear images of tumors. This helps doctors spot cancer better.
Genetic testing is also key in finding out what kind of cancer a child has. It lets doctors create treatment plans that fit each child’s needs.
How we treat childhood cancer has changed a lot. Now, we use chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery together. This mix helps fight different kinds of pediatric cancer.
New treatments like targeted therapy and immunotherapy are also helping. They aim at specific cancer cells or boost the body’s immune system to fight cancer. This gives kids with cancer new hope.
Getting to specialized pediatric cancer centers is very important. These places have the latest tech and teams of experts in treating childhood cancer.
Children treated there get all-around care. This includes top-notch treatments and support services made just for them.
Childhood cancer care has made big strides. New treatments and diagnostic tools have boosted survival rates. Yet, some cancers, like blood cancers and solid tumors, are tough to beat. This is true, even with advanced treatments, if the cancer has bad genes or is found late.
Recent studies show that more kids with cancer are living longer. Over 85 percent now beat cancer and live more than five years after diagnosis. But, cancers like acute myeloid leukemia and neuroblastoma have much lower survival rates.
We need to keep researching and working together to tackle childhood cancer’s challenges. We must find better treatments and reduce the lasting effects of cancer care. By pushing forward in pediatric cancer care, we aim to better the lives of kids with cancer.
Brain and CNS tumors are now the leading cause of cancer deaths in kids. This is because treatments for leukemia have improved a lot.
Leukemia is the most common cancer in kids. Then come brain and CNS tumors, neuroblastoma, bone cancers, soft tissue sarcomas, and lymphomas.
Brain tumors are hard to treat because of the blood-brain barrier. This barrier stops treatments from reaching the tumor.
Symptoms include persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and pain. Specific symptoms depend on the cancer type. For example, headaches and seizures are common in brain tumors. Leukemia might cause bruising and infections.
Thanks to better treatments, the survival rate for childhood leukemia has jumped over 85%.
Researchers are looking into genetic and environmental factors as possible risks. But, most childhood cancers’ causes are not yet known.
New diagnostic tools help diagnose childhood cancers more accurately and quickly. This leads to better treatment plans.
The 5-year survival rate for brain and CNS tumors in kids is about 60%.
Yes, some kids are born with cancer. Genetic factors can increase the risk of certain childhood cancers.
Treatment plans have gotten better. Kids now get care from specialized pediatric cancer centers, ensuring top-notch treatment.
There’s a worry that childhood cancer rates might be going up. But, the exact reasons are not yet clear.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!