Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
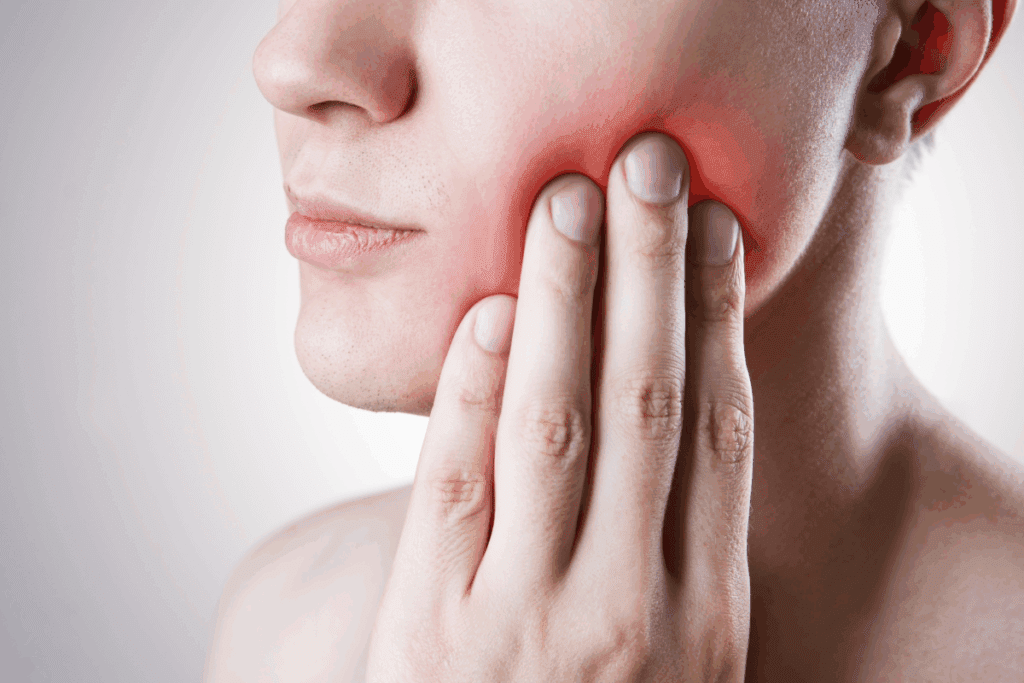
Jawbone cancer is a rare form of oral cavity cancer that can develop in the mandible (lower jaw) or maxilla (upper jaw). This condition can be scary, but knowing about it is the first step to dealing with it. What is cancer of the jawbone? Learn the key symptoms to watch for and the multidisciplinary treatment approach.
Most jawbone cancers start in squamous cells. These are flat cells that line the mouth, nose, and other areas. At Liv Hospital, our team of experts uses the latest diagnostic and treatment methods to help patients.
It’s important to know the signs of jawbone cancer, like jaw tumors and lumps on the jawline. This guide will explain the symptoms and treatment options for jawbone cancer.

Jawbone cancer, also known as mandibular or maxillary cancer, is a rare but serious condition. It affects the bones of the jaw. This type of cancer can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. It’s important to know its definition, classification, and how it affects the jaw.
Cancer of the jawbone refers to malignant tumors in the jaw bones. These can be in the mandible (lower jaw) or maxilla (upper jaw). The cancers are classified by their location and the type of cells affected.
Knowing how to classify jawbone cancer is key to choosing the right treatment. The most common types include squamous cell carcinoma, osteosarcoma, and others like chondrosarcoma and fibrosarcoma.
The jaw has two main bones: the mandible and the maxilla. The mandible is the lower jawbone, which moves and is vital for chewing and speaking. The maxilla is the upper jawbone, fixed and part of the upper mouth and palate.
Cancers in the mandible and maxilla affect treatment and prognosis differently. Mandible cancers often cause pain, swelling, and trouble chewing. Maxillary cancers can spread to nearby areas, like the sinuses and orbit, making treatment harder.
Healthcare providers need to understand these differences. They must tailor treatments to meet each patient’s unique needs.

It’s important to know about the different jawbone cancers for better treatment. Jawbone cancer can take many forms, each with its own traits and care needs.
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common jawbone cancer. It starts from squamous cells, which cover the skin and some organs. This type of cancer is aggressive and needs quick treatment.
A study in the Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery shows squamous cell carcinoma is a big part of jawbone cancers. It stresses the need for early detection and treatment to help patients.
Osteosarcoma is a rare bone cancer in the jaw. It grows fast and can spread. This serious condition needs strong treatment, like surgery, chemo, and radiation.
“Osteosarcoma of the jaw is a tough diagnosis needing a team effort for treatment. Quick action and strong therapy are key for better results.” – Medical Expert, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon
There are other jawbone cancers like:
These cancers are rare but can affect the jaw and overall health a lot.
Type of Cancer | Origin | Characteristics |
Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Squamous cells | Aggressive, common in oral cavity |
Osteosarcoma | Bone cells | Rapid growth, can spread |
Chondrosarcoma | Cartilage cells | Rare, can happen in jawbone |
Knowing about jawbone cancer types is key for good treatment plans. Each cancer is different, and a detailed diagnosis is vital for the right treatment.
The study of jawbone cancer epidemiology shows important trends. It’s a rare condition but affects public health a lot. Knowing its patterns helps in making better prevention and treatment plans.
Jawbone cancer is a small part of head and neck cancers. Its incidence changes by location. We’ll look into these trends to understand the disease better.
Key Statistics:
Survival rates for jawbone cancer patients have gotten better. This is thanks to new treatments. But, the outcome depends on many things.
Prognosis Factors:
Knowing these stats and factors helps doctors give better care. They can tailor treatment and support to each patient’s needs.
It’s key to know the signs of jawbone cancer early. This is because jawbone cancer, like other cancers, has clear symptoms. These symptoms can really affect a person’s life.
Spotting jawbone cancer early starts with noticing its first signs. You might see a painless lump or swelling in your jaw. You might also feel numbness or tingling.
It’s important to catch these signs early. They might seem small, but they can mean something big.
As jawbone cancer gets worse, symptoms get more serious. You might feel persistent pain in your jaw. Or, you might find it hard to open your mouth.
You might also feel ear and jaw pain on one side. These signs mean the cancer has grown and needs quick medical help.
If your jaw changes in a way that doesn’t go away, see a doctor. Finding cancer early is key to better treatment. So, if you notice any jaw symptoms, get medical help right away.
Knowing the signs of jawbone cancer and when to act can really help. We stress the need to be watchful and seek medical help if you notice anything odd.
Knowing the risk factors for jawbone cancer is key to preventing and catching it early. Several factors can increase your chance of getting this condition. Being aware of these can help you take steps to prevent it and seek medical help when needed.
Tobacco and alcohol use are major risks for oral cancers, including jawbone cancer. Using tobacco products, like cigarettes and smokeless tobacco, greatly raises your risk of oral cancers. Drinking alcohol, and even more so with tobacco, also increases this risk. It’s best to avoid or cut down on these substances to lower your jawbone cancer risk.
Jawbone cancer can happen at any age, but it’s more common after 40. Men are more likely to get jawbone cancer than women, but why isn’t fully understood. Knowing these demographic risks helps focus preventive efforts.
Poor oral health is linked to a higher risk of oral cancers. Also, some HPV strains, like HPV-16, raise the risk of oropharyngeal cancers, which can affect the jawbone. Good oral hygiene and HPV vaccination are key to reducing this risk.
Some people might be more likely to get jawbone cancer due to their genes. Certain genetic syndromes, like Li-Fraumeni syndrome, can increase cancer risk, including jawbone cancer. Knowing your family’s health history and genetic factors can help spot those at higher risk.
Risk Factor | Description |
Tobacco and Alcohol Use | Increases risk of oral cancers, including jawbone cancer |
Age | Risk increases after age 40 |
Gender | Men are more likely to be diagnosed than women |
Poor Oral Health | Linked to increased risk of oral cancers |
HPV Infection | Certain strains increase risk of oropharyngeal cancers |
Genetic Predisposition | Certain genetic syndromes increase cancer risk |
Finding jawbone cancer is a detailed task. It needs a mix of doctor checks and high-tech scans. We use a detailed method to find and measure jawbone cancer. This is key for making a good treatment plan.
The first step is a physical examination. We check the patient’s health and look for jawbone cancer signs. We look at the mouth, jaw, and neck for swelling, pain, or trouble swallowing.
Next, we use imaging studies to see the tumor and how big it is. These include:
A biopsy is key to confirm jawbone cancer. We take a tissue sample from the tumor. A pathologist then checks it to see if it’s cancer and what type.
After confirming the diagnosis, we start the staging process. We look at the tumor size, if lymph nodes are involved, and if cancer has spread. Knowing the cancer’s stage helps choose the best treatment and predict how well the patient will do.
Treatment for jawbone cancer often involves a mix of methods. The right treatment depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health. It also depends on what the patient prefers.
We will look at the different treatment options. We start with surgical interventions, which are key for jawbone cancer.
Surgery is a big part of treating jawbone cancer. It aims to remove the tumor and affected tissue. The goal is to get rid of the cancer while keeping jaw function and looks as good as possible.
Surgical techniques change based on the tumor’s size and location. For small tumors, a less invasive approach might be used. But for bigger tumors, more surgery might be needed, possibly including reconstruction.
Radiation therapy is another important treatment for jawbone cancer. It’s often used with surgery. It uses high-energy rays to kill or slow cancer cells.
External beam radiation therapy is the most common type for jawbone cancer. It sends radiation from outside the body. Sometimes, brachytherapy is used, where radioactive material is placed near the tumor.
Chemotherapy is used for jawbone cancer, mainly when it’s spread or advanced. It uses drugs to kill or stop cancer cells from growing.
The choice of chemotherapy drugs and how they are given can change based on the cancer type and patient’s health. Chemotherapy can be used alone or with other treatments like surgery and radiation.
New treatments for jawbone cancer are being researched. These include targeted therapy and immunotherapy. Targeted therapy uses drugs to target specific cancer cells. Immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Clinical trials are key for testing these new treatments. They help see if these treatments work and are safe. Patients should talk to their healthcare provider about joining clinical trials.
The process of reconstruction and rehabilitation is key for patients recovering from jawbone cancer. It helps them physically and emotionally. This phase is vital for restoring function and improving quality of life.
Jaw reconstruction is complex and may involve surgery. Reconstructive surgery can rebuild the jawbone and restore facial symmetry. We use advanced techniques like microvascular reconstruction for the best results.
The choice of reconstruction method depends on several factors. These include the tumor’s size, the patient’s health, and their preferences. Prosthetic rehabilitation may also be used to improve oral function and appearance.
Patients often face challenges with speech and swallowing after jawbone cancer treatment. Speech and swallowing therapy is essential for recovery. We work with speech-language pathologists to create personalized plans.
Therapy includes exercises for tongue mobility and swallowing strength. It aims to improve speech clarity. The goal is to enhance communication and eating safety, boosting quality of life.
Jawbone cancer diagnosis and treatment can affect patients’ mental health. Psychological support is vital for emotional and mental well-being. We provide counseling, support groups, and resources to help manage stress and anxiety.
Long-term follow-up care is critical for monitoring recovery and early detection of recurrence. Regular appointments and surveillance are emphasized. This care ensures ongoing health and well-being.
Our follow-up care includes check-ups, imaging, and rehabilitation services. It addresses ongoing or emerging issues. This ongoing support is essential for maintaining health over time.
Understanding jawbone cancer is key for early detection and treatment. We’ve looked at its definition, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. This knowledge is vital.
A jawbone cancer summary shows the need to spot early signs like pain and swelling. If ignored, symptoms can worsen, affecting teeth and jaw movement. Quick medical help is necessary to stop the disease’s spread.
A detailed treatment guide for jawbone cancer includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. New treatments bring hope. Reconstruction and rehabilitation help restore function and improve life quality.
Cancer support is essential, providing emotional and psychological help. It’s important to have a supportive network and complete care for jawbone cancer patients.
By grasping jawbone cancer’s complexities, we aim to enhance patient outcomes and life quality. Our mission is to offer top-notch healthcare and support to patients worldwide.
Jawbone cancer is a type of tumor that grows in the jawbone. This can happen in the lower jaw (mandible) or upper jaw (maxilla). The most common type is squamous cell carcinoma.
Early signs include a painless lump or swelling in the jaw. It may grow over time. Other signs are numbness or tingling in the jaw, loose teeth, or dentures that don’t fit right.
Risk factors include smoking and drinking alcohol, being over 40, and being male. Poor oral health, HPV infection, and genetics also play a role.
Doctors use a physical exam, imaging studies like X-rays and CT scans, and a biopsy to diagnose. The biopsy confirms cancer cells. Staging shows how far the cancer has spread.
Treatments include surgery to remove the tumor, radiation, chemotherapy, or a mix of these. New treatments like targeted therapy are also being explored.
Jaw reconstruction is surgery to fix or rebuild the jaw after removing a tumor. It helps restore appearance, chewing, and quality of life.
Cancer and treatment can change the jaw’s structure and function. This affects speech and swallowing. Speech and swallowing therapy help patients regain these skills.
The prognosis depends on the cancer’s stage, overall health, and treatment response. Early detection and care can improve outcomes.
While not all cases can be prevented, reducing risk factors helps. This includes quitting smoking, drinking less alcohol, keeping good oral health, and getting HPV vaccines.
Long-term care is key for monitoring the patient’s condition. It helps catch any recurrence or metastasis and manages treatment effects.
A cancerous jaw tumor is a malignant growth in the jawbone. It can be aggressive and invade surrounding tissues. It needs immediate medical attention and treatment.
Mandibular cancer is cancer in the lower jawbone. It can affect the bone, tissues, and nerves around it.
Ear and jaw pain on one side can be a symptom of jawbone cancer. This is true if the tumor is in the mandible or affects jaw nerves.
National Health Service (NHS). (2025). What Is Jawbone Cancer Symptoms and Treatment Guide. Retrieved from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/mouth-cancer/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!