Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
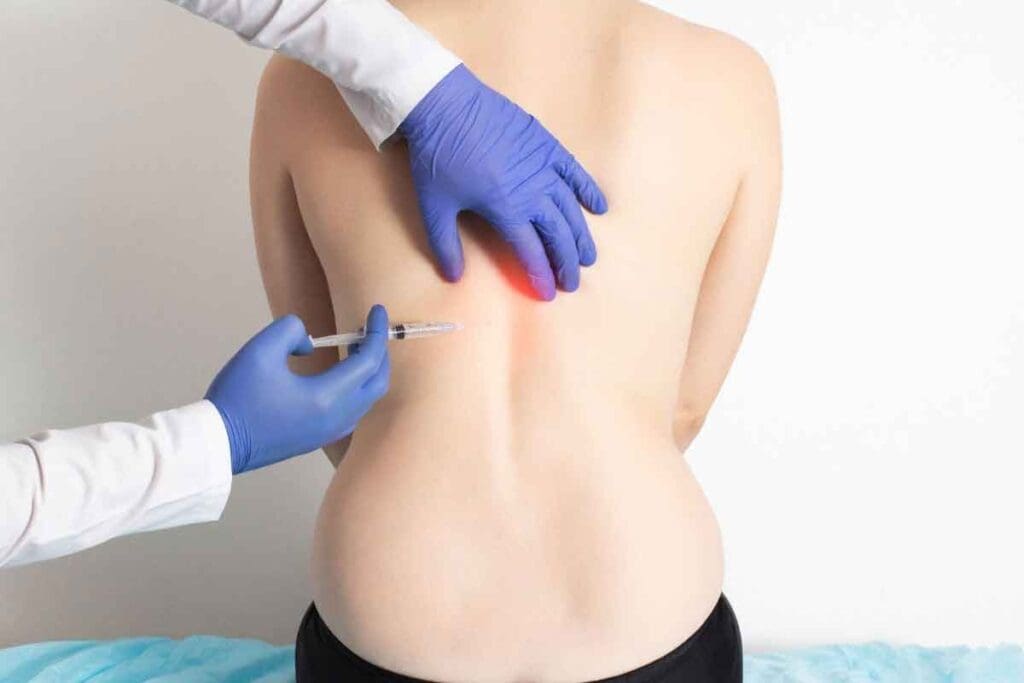
Step-by-step guide to the caudal epidural injection procedure, recovery tips, and safety details. At Liv Hospital, we know how tough lower back pain can be. That’s why we offer effective treatments like the caudal epidural injection. This method is a safe way to put medicine into the epidural space near the tailbone. It helps reduce pain and swelling.
This treatment involves putting medicine into the epidural space near the tailbone. It helps block pain signals. This makes it a great option for those with lower back and leg pain, including sciatica.
Knowing the steps and recovery tips can help patients make better choices. It’s a big step towards living without pain.
Key Takeaways
- Caudal epidural injections are used to treat lower back and leg pain.
- The procedure involves injecting medication into the epidural space near the tailbone.
- Understanding the steps and recovery tips is key tomaking informed decisions.
- This treatment option is effective for relieving pain and inflammation.
- Patients can greatly benefit from a detailed guide to the procedure and recovery.
What Is a Caudal Epidural Injection?
A caudal epidural injection is a method to treat chronic low back pain and radiculopathy. It involves putting medication into the epidural space around the spinal nerves. This helps many people who suffer from these conditions.
Definition and Medical Purpose
This procedure uses a mix of local anesthetic and corticosteroid in the caudal epidural space. The caudal epidural space is around the dural sac, which holds the spinal nerves. It’s reached through the sacral hiatus, at the sacrum’s lower end.
The goal is to cut down on inflammation and ease pain in the lower back and legs. By targeting the area directly, caudal epidural injections offer specific relief for spinal issues.
Caudal Spine Anatomy
Knowing the caudal spine’s anatomy is key to understanding caudal epidural injections. The sacrum, a fused bone set at the spine’s base, is the caudal end. The sacral hiatus is where the injection goes in.
The sacrum and its surroundings are vital for the success of these injections. Knowing the sacral anatomy well is needed for precise medication placement.
Therapeutic vs. Diagnostic Applications
Caudal epidural injections have both therapeutic and diagnostic uses. They help by easing pain through reducing nerve inflammation. They also help find pain sources by blocking certain nerves.
| Application | Description | Benefits |
| Therapeutic | Provides pain relief by reducing inflammation | Improves quality of life, reduces pain |
| Diagnostic | Helps identify the source of pain | Aids in precise diagnosis, guides further treatment |
Understanding caudal epidural injections’ dual role helps healthcare providers. They can use it to treat and diagnose spinal issues effectively.
Conditions Treated with Caudal Epidural Injections
Spinal conditions like lower back pain and sciatica can be managed with caudal epidural injections. These injections are a valuable treatment for many spinal disorders. They offer targeted relief to those with chronic pain.
Lower Back Pain Management
Lower back pain can greatly affect a person’s life. Caudal epidural injections help by delivering anti-inflammatory medication to the affected area. This reduces pain and inflammation.
A study in the Journal of Pain Research found these injections significantly relieved chronic lower back pain in patients.
Sciatica and Radicular Pain
Sciatica and radicular pain cause pain that spreads along the sciatic nerve. This pain is often due to nerve compression or irritation. Caudal epidural injections can help by reducing inflammation and pressure on the nerve.
“Caudal epidural steroid injections are a commonly used interventional technique for managing radicular pain and sciatica.”
Nerve Compression Syndromes
Nerve compression syndromes, like spinal stenosis, cause a lot of pain and discomfort. Caudal epidural injections are effective in managing these conditions. They deliver corticosteroids to the affected area, reducing swelling and relieving pressure on the compressed nerves.
Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammatory conditions, such as disc herniation and degenerative disc disease, can cause chronic pain and inflammation. Caudal epidural injections are used to treat these conditions. They reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
| Condition | Treatment Outcome | Success Rate |
| Lower Back Pain | Pain Relief | 70% |
| Sciatica | Reduced Radicular Pain | 80% |
| Nerve Compression Syndromes | Relief from Compression | 75% |
Understanding the conditions treated with caudal epidural injections helps patients see the benefits of this procedure.
Patient Selection and Contraindications
Choosing the right patients for caudal epidural injections is key to success. This treatment helps many, but isn’t for everyone. We must check each candidate to make sure the benefits are worth the risks.
Ideal Candidates
People with chronic low back pain and radiculopathy are often good candidates. They might have issues like herniated discs or spinal stenosis. These patients can see big improvements in pain relief and life quality.
Medical History Considerations
We look at a patient’s full medical history to decide if they’re right for the treatment. This includes past treatments, allergies, and any health issues that could affect the procedure. A detailed medical history helps spot risks and things we should avoid.
- Previous spinal surgeries or interventions
- Known allergies to corticosteroids or local anesthetics
- Existing infections or bleeding disorders
- History of adverse reactions to contrast agents if imaging guidance is used
Absolute Contraindications
Some conditions make caudal epidural injections a bad idea. Absolute no-goes include:
- Active infection at the injection site
- Severe bleeding disorders or anticoagulation therapy
- Known allergy to the medications used
- Pregnancy (relative but often considered absolute depending on the context)
Relative Contraindications
Some conditions might not completely rule out the treatmen,t but need extra thought. These include:
- Mild bleeding disorders
- Diabetes, as corticosteroids, can affect blood sugar levels
- Psychological conditions that may affect pain perception or reporting
By carefully looking at these factors, we can use caudal epidural injections wisely. This way, we help our patients as much as possible while keeping risks low.
Pre-Procedure Protocol
The steps before a caudal epidural injection are keytor safety and success. We focus on detailed preparation to reduce risks and improve results.
Patient Preparation Instructions
Getting ready for a caudal epidural injection is very important. We tell our patients to fast for a certain time before the procedure. They also need to share any medications they’re taking, like blood thinners and herbal supplements.
We remind them to have someone drive them home after. The injection might make it hard for them to drive safely.
Required Equipment and Medications
Having the right tools and medicines is essential for safe and effective injections. We need fluoroscopy or ultrasound guidance, sterile drapes, and the right size needles.
The medicines used are local anesthetics and corticosteroids. We choose them based on the patient’s condition and medical history.
Informed Consent Process
The informed consent process is very important. We make sure patients know the risks and benefits of caudal epidural injections. We also talk about other treatment options.
We encourage patients to ask questions and share their concerns. This way, we can meet their needs and give them personalized care.
Imaging Guidance for Caudal Injection Location
Imaging guidance is key for accurate caudal injections. Getting the location right is vital for the procedure’s success. It affects how well the treatment works and lowers the chance of problems.
Fluoroscopy Technique
Fluoroscopy is a common tool for guiding caudal epidural injections. It shows live X-ray images, helping doctors see where the needle is. Fluoroscopy makes the injection more accurate, cutting down on mistakes.
Ultrasound Guidance Method
Ultrasound guidance is another good way for caudal epidural injections. It’s a safer choice than fluoroscopy, using sound waves to show the body’s layout. Ultrasound is great for those who can’t have X-rays, like pregnant women.
Anatomical Landmark Identification
Using landmarks is a traditional way to guide injections. It involves feeling for certain spots on the body to find the sacral hiatus. While it works, its success depends on the doctor’s skill and the patient’s body.
Accuracy Comparison Between Methods
It’s important to compare how accurate fluoroscopy, ultrasound, and landmarks are. Research shows fluoroscopy and ultrasound are usually more precise than landmarks. But the right choice depends on the patient and the situation.
Knowing the good and bad of each method helps doctors make better choices. This way, they can improve the results of caudal epidural injections.
Caudal Epidural Injection Procedure Step-by-Step
Administering a caudal epidural injection requires careful steps. Healthcare providers must follow these steps to ensure the procedure is safe and effective.
Room Setup and Sterile Field Preparation
First, we set up the room and prepare a sterile field. We arrange the equipment, like the fluoroscopy machine, and make sure all the needed supplies are ready.
Sterile technique is key to avoiding infection. We cover the area with sterile towels and clean the skin with antiseptic solutions.
Patient Positioning Techniques
Getting the patient in the right position is essential. We usually put them in a prone position. This helps us reach the sacral hiatus better.
We adjust the patient’s position for comfort and stability. This helps keep them steady during the procedure.
Sacral Hiatus Identification
Finding the sacral hiatus is a key step. We use landmarks and imaging, like fluoroscopy, to find it accurately.
The sacral hiatus is at the sacrum’s lower end. We feel the sacral cornua to locate it.
Local Anesthetic Administration
After finding the sacral hiatus, we give the local anesthetic. We insert a needle into the sacral hiatus and move it into the caudal epidural space.
We use fluoroscopic guidance to check the needle’s placement. This makes sure the medication goes where it should.
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
| 1 | Room Setup | Ensure all necessary equipment is available and within reach. |
| 2 | Patient Positioning | Place the patient in a prone position with a pillow under the abdomen. |
| 3 | Sacral Hiatus Identification | Use anatomical landmarks and fluoroscopic guidance. |
| 4 | Local Anesthetic Administration | Use fluoroscopic guidance to confirm needle placement. |
Caudal Nerve Block vs. Other Epidural Approaches
When looking at epidural injections for pain, knowing the differences is key. We’ll dive into these differences to help doctors pick the best method for their patients.
Anatomical Differences
The caudal nerve block injects medication near the tailbone. This is different from lumbar or cervical epidurals in terms of location and nerves affected.
Key anatomical differences include:
- The caudal approach uses the sacral hiatus for injection.
- It mainly targets the lower sacral and coccygeal nerves.
- This method is less invasive than some other epidurals.
Indications for Caudal Approach
The caudal nerve block is great for chronic pain in the lower back, legs, and pelvis. It’s often used for sciatica, radiculopathy, and chronic pelvic pain.
Specific indications include:
- Chronic lower back pain has not been helped by other treatments.
- Radicular pain or sciatica.
- Pain in the pelvic area.
Comparative Efficacy
Studies show mixed results on caudal nerve blocks versus other epidurals. But, caudal blocks are often chosen for their focused effect and lower risk of problems.
| Epidural Approach | Efficacy for Lower Back Pain | Risk of Complications |
| Caudal Nerve Block | High | Low to Moderate |
| Lumbar Epidural | High | Moderate |
| Cervical Epidural | Moderate to High | Moderate to High |
Risk Profile Differences
Each epidural method has its own risk level. Caudal nerve blocks are generally safer, with a lower risk of dural puncture compared to other. methods
Key differences in risk profile:
- Lower risk of dural puncture.
- Less risk of nerve root injury.
- Potential for infection or bleeding, as with any invasive procedure.
Understanding the differences between caudal nerve blocks and other epidurals helps doctors choose the best treatment for their patients.
Procedural Challenges and Solutions
Procedural challenges are common in caudal epidural injections. Skilled practitioners are needed to overcome these issues. We will discuss these challenges and offer solutions to improve procedure success.
Anatomical Variations
Anatomical variations can affect caudal epidural injection success. The sacral hiatus, key to the procedure, differs in size and shape among people.
Practitioners must be skilled in finding the sacral hiatus with imaging. Tools like fluoroscopy and ultrasound help make real-time adjustments during the procedure.
Technique Modifications
Technique adjustments are often needed for patient-specific anatomical features. For example, changing the needle angle or using different needles can improve injection accuracy.
Practitioners should know various techniques and be ready to adapt their approach. This flexibility is essential for overcoming procedural challenges.
| Technique Modification | Indication | Benefit |
| Adjusting needle angle | Difficulty accessing the sacral hiatus | Improved access and reduced risk of complications |
| Using different needle types | Variations in sacral hiatus size | Enhanced precision and safety |
Intraoperative Complications Management
Intraoperative complications can happen, even with careful planning. These may include vascular penetration, nerve irritation, or unintended space injection.
Managing these complications effectively requires quick recognition and proper action. It’s vital to have emergency protocols and ensure practitioners are trained in them.
By addressing procedural challenges, healthcare providers can reduce risks and improve outcomes for patients undergoing caudal epidural injections.
Immediate Post-Procedure Management
Good care after a caudal epidural injection is key for patient safety and well-being. We explain the main steps of immediate care to help healthcare teams provide the best care.
Vital Signs Monitoring
Watching vital signs closely is a big part of post-procedure care. We look for any quick changes in blood pressure, heart rate, or oxygen levels. This helps us spot and handle any problems fast.
Neurological Assessment
We do a detailed check of the nervous system to see how the patient is doing. We look for numbness, weakness, or other signs that might mean there’s a problem. This helps us decide what to do next and when it’s okay to go home.
Discharge Criteria
Before sending a patient home, we make sure they meet certain criteria. They need to have stable vital signs, be in less pain, and be able to walk safely. We also give them clear instructions on what to do next and when to come back for a check-up.
Same-Day Activity Guidelines
On the day of the procedure, we tell patients what activities are safe. We advise against hard work, heavy lifting, and bending. We suggest they start with light activities and gradually do more as they feel able, to avoid problems and help them heal.
By sticking to these guidelines, we can make sure our patients have a safe and easy recovery after a caudal epidural injection.
Caudal Epidural Injection Recovery
Recovering well from a caudal epidural injection means resting, managing pain, and getting follow-up care. We help patients through this to get the best results.
Expected Timeline
Recovery times can differ, but most people can get back to normal in a few days. Some pain might happen during recovery, but relief can start right away.
Here’s what you might experience during recovery:
| Timeframe | Expected Recovery Progress |
| First 24 hours | Rest and soreness at the injection site |
| 2-3 days | Start getting back to normal activities |
| 1 week | Pain should start to feel much better |
Activity Restrictions
Some activities should be avoided or done carefully to recover well. Following these tips helps avoid problems.
- Don’t lift heavy or bend
- Stay away from hard activities for 48 hours
- Start doing normal things again when you feel okay
Pain Management Strategies
Managing pain well is key to recovery. Rest, ice, and medicine can help with this.
“Pain management is not just about alleviating the immediate discomfort but also about creating a conducive environment for healing.”
Expert Opinion
Here are some ways to manage pain:
- Use ice packs on the area when needed
- Take pain medicine as told
- Keep track of your pain levels
Follow-up Appointment Scheduling
Getting follow-up care is important to check how the injection is working. We usually schedule a check-up a few weeks after.
At this visit, we’ll see how you’re doing, talk about more treatment if needed, and answer any questions.
Caudal Epidural Injection Side Effects
Caudal epidural injections can have side effects and complications. Patients need to know these risks. This helps them make informed decisions about their treatment.
Common Minor Side Effects
Most people have minor side effects after these injections. These effects are usually temporary and can be managed. Some common side effects include:
- Temporary soreness or discomfort at the injection site
- Mild headache
- Facial flushing
- Nausea
These side effects usually go away in a few days. It’s key to monitor and manage these symptoms for a smooth recovery.
Rare but Serious Complications
While rare, serious complications can happen. It’s important to know about these risks:
- Infection at the injection site
- Nerve damage
- Allergic reactions to the medications used
- Bleeding complications
Spotting these complications early can greatly affect their management and outcome.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Know the symptoms that need immediate medical attention. These include:
- Severe pain or swelling at the injection site
- Fever or chills
- Numbness or weakness in the legs
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
If you have any of these symptoms, seek medical help right away.
Long-term Safety Considerations
Studies on the long-term safety of these injections are ongoing. Current evidence shows they are generally safe for long-term use. But repeated injections may have cumulative effects. It’s important to discuss your individual risk factors with your healthcare provider.
| Potential Side Effects | Frequency | Management |
| Temporary soreness | Common | Over-the-counter pain relievers |
| Infection | Rare | Antibiotics, medical attention |
| Nerve damage | Rare | Medical evaluation, possible intervention |
Understanding the side effects and complications of caudal epidural injections helps patients. They can better navigate their treatment options. Working closely with healthcare providers is key to managing risks.
International Best Practices for Caudal Procedures
Following international best practices in caudal epidural injections makes procedures safer and more effective. Medical professionals aim to improve patient care by sticking to the latest guidelines.
Evidence-Based Protocols
Evidence-based protocols are key to caudal epidural injection best practices. They are made from thorough reviews of clinical data and research. This ensures that healthcare providers use the most up-to-date methods.
Key elements of evidence-based protocols include:
- Pre-procedure patient assessment
- Standardized injection techniques
- Use of imaging guidance
- Post-procedure care guidelines
Quality Assurance Measures
Quality assurance is vital for maintaining high standards in caudal epidural injections. It includes regular audits, peer review, and patient feedback.
| Quality Assurance Measure | Description | Frequency |
| Regular Audits | Comprehensive review of procedural data | Quarterly |
| Peer Review | Evaluation of practitioner competence | Bi-annually |
| Patient Feedback | Collection and analysis of patient satisfaction data | After each procedure |
Specialized Training Requirements
Healthcare professionals need specialized training for caudal epidural injections. This training should cover both theory and practical skills.
Training programs should include:
- Anatomical knowledge
- Procedural techniques
- Complication management
- Imaging interpretation
Facility Standards
Facility standards are important for safe and effective caudal epidural injection services. These standards cover equipment, staffing, and environment.
Our facilities must have the right technology, like imaging equipment. Our staff should be well-trained and enough in number to provide top-notch care.
Conclusion
Caudal epidural injections are a great way to treat lower back and leg pain. We’ve covered the main points of this procedure. This includes who can get it and how to care for yourself after.
Knowing the basics of caudal epidural injections helps doctors give better care. They need to pick the right patients and do the procedure carefully. This ensures the treatment works well.
In wrapping up, caudal epidural injections are a powerful tool against chronic pain. Doctors following the best practices can greatly help their patients. This improves patients’ lives and how well they can function.
FAQ
What is a caudal epidural injection?
A caudal epidural injection is a small procedure. It injects medicine into the epidural space through the sacral hiatus. This helps relieve pain in the lower back and legs.
What is the purpose of a caudal epidural injection?
The main goal is to put corticosteroids and local anesthetics in the right spot. This reduces inflammation and pain.
What conditions can be treated with caudal epidural injections?
This treatment helps with lower back pain, sciatica, and nerve compression. It’s also good for radicular pain.
Who is an ideal candidate for a caudal epidural injection?
People with chronic lower back pain or radicular symptoms are good candidates. They should have tried other treatments first.
What are the contraindications for caudal epidural injections?
You shouldn’t get this treatment if you have bleeding disorders, active infections, or severe spinal deformities.
How is the caudal epidural injection procedure performed?
First, the sacral hiatus is found. Then, local anesthesia is given. Corticosteroids and local anesthetics are injected into the epidural space under imaging.
What are the differences between fluoroscopy and ultrasound guidance for caudal epidural injections?
Fluoroscopy shows real-time X-rays, while ultrasound uses sound waves. Both are chosen based on the patient’s anatomy and the doctor’s preference.
What are the expected side effects of caudal epidural injections?
Minor side effects include temporary pain at the injection site. Serious but rare complications include infection, nerve damage, or allergic reactions.
What is the expected recovery timeline after a caudal epidural injection?
Most people can go back to normal activities in a few days. Pain relief can take from immediate to several weeks.
How can I manage pain after a caudal epidural injection?
Use ice packs, take pain meds as prescribed, and slowly increase activity levels.
What are the international best practices for caudal epidural injections?
Follow evidence-based protocols and ensure quality assurance. Also, adhere to specialized training and facility standards.
What are the long-term safety considerations for caudal epidural injections?
Repeated injections may affect bone density. Always watch for signs of nerve damage.
Can I undergo a caudal epidural injection if I have a medical condition?
It depends on your condition. Some may be contraindications, while others need special precautions or procedure modifications.
How often can I receive caudal epidural injections?
Injection frequency varies based on response and condition. Usually, it’s limited to a few times a year.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2017). Evidence-based guidelines for opioid prescribing for chronic pain in outpatient settings. CDC Guideline. https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/prescribing/guideline.html