Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
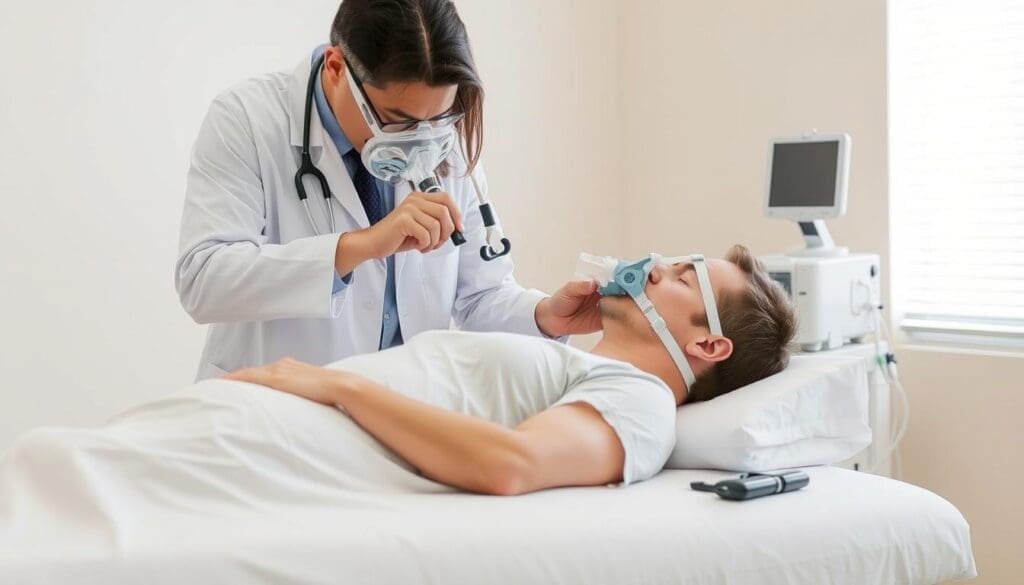
Central sleep apnea symptoms and a complete guide on how to treat this condition, often involving adaptive servo-ventilation (ASV).
Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a complex neurological disorder that affects millions globally. It can be tough to diagnose and treat. But, with the right help, people can manage their symptoms and live better lives.
The Medical organization says CSA happens when the brain can’t send the right signals to the breathing muscles at night. This causes pauses in breathing, messing up sleep patterns and health. In this guide, we’ll look at diagnosing, treating, and managing CSA.
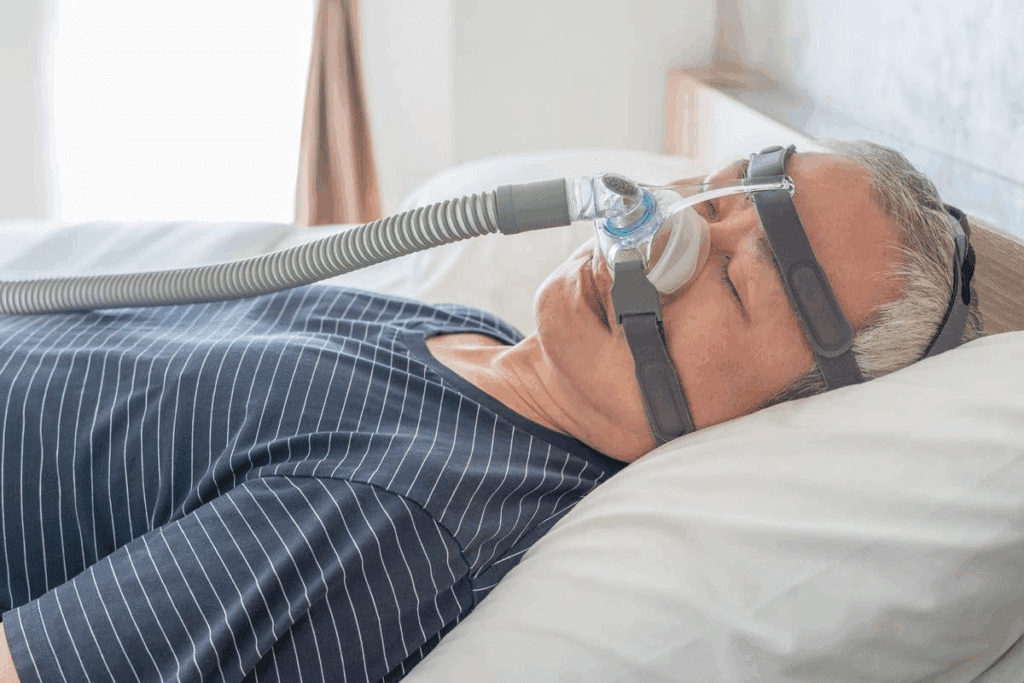
Central sleep apnea starts in the brain. It happens when the brain can’t send the right signals to breathe. This condition affects the brain’s control over breathing during sleep, causing pauses or shallow breaths.
The brain and breathing are closely linked. Normally, the brain tells the diaphragm to breathe. But in CSA, this link is broken. The brain can’t send the necessary signals, leading to breathing pauses or shallow breathing.
This problem can happen many times at night. It greatly affects how well you sleep.
It’s important to know the difference between CSA and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). OSA is caused by a blockage in the airway. But CSA is a brain issue where the brain can’t signal breathing.
CSA is often linked to heart failure or neurological disorders. This makes it harder to diagnose and treat. OSA, on the other hand, is often related to obesity, age, and physical factors.
Knowing the unique challenges of CSA helps doctors create better treatment plans. These plans focus on the brain issues, improving patient care.
Several factors can increase the risk of getting central sleep apnea (CSA). These include age and medical history. Knowing these risk factors helps in early diagnosis and treatment.
CSA affects different age groups and genders in different ways. Older adults, and those with heart conditions, are more likely to get CSA. Changes in the brain and body with age can affect breathing during sleep, raising the risk.
Studies show CSA is more common in men, and this is true for older adults. The reasons for this gender difference are not clear. It might be due to body composition, hormones, or other factors.
Some medical conditions raise the risk of CSA. These include:
Understanding these risk factors is key to early detection and management of CSA. By identifying high-risk individuals, healthcare providers can start the right treatments to improve outcomes.
It’s important to know the signs of Central Sleep Apnea early. This helps in getting the right treatment fast. CSA shows itself in different ways, both when you’re asleep and awake.
People with CSA might stop breathing for short times while asleep. This is because their brain doesn’t tell their breathing muscles to work. Other signs at night include:
These signs can really mess up your sleep. This can lead to other problems too.
CSA can also cause problems during the day. These include:
These symptoms can make it hard to do everyday things. They can also lower your quality of life.
If you notice these signs, see a doctor. Getting help early can make a big difference in managing CSA.
Knowing the signs of CSA helps you get help quickly. This can lead to better treatment results.
CSA includes several types, like idiopathic CSA, Cheyne-Stokes breathing, drug-induced CSA, and high-altitude periodic breathing. Knowing these types is key for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Idiopathic CSA means the cause of central sleep apnea is unknown. It’s diagnosed when other causes are ruled out. People with idiopathic CSA might have trouble controlling their breathing during sleep.
Cheyne-Stokes respiration is a CSA type with a unique breathing pattern. It alternates between deep, fast breathing and shallow breathing or pauses. This pattern often shows up in heart failure and can indicate how severe it is.
“Cheyne-Stokes respiration is not just a breathing pattern; it’s a window into the heart’s condition.” –
A sleep specialist
Some medications, like opioids, can cause central sleep apnea by slowing down breathing. Drug-induced CSA is a big worry because more people are taking opioids for pain.
Medication Type | Risk of CSA | Management Strategy |
Opioids | High | Reduce dosage or switch medication |
Benzodiazepines | Moderate | Monitor usage closely |
Other sedatives | Variable | Assess individual risk |
High-altitude periodic breathing is a CSA type that happens at high altitudes. The lower oxygen levels can cause unstable breathing, leading to periodic breathing.
Knowing the specific type of CSA is vital for the right treatment. Each type has its own causes and needs a specific approach to manage it.
Getting treated for central sleep apnea starts with a correct diagnosis. It’s important to understand your sleep patterns well. This is key for creating a good treatment plan.
A sleep study, or polysomnography (PSG), is a big part of diagnosing CSA. This test watches your body while you sleep. It looks at brain activity, eye movements, and breathing.
You’ll sleep in a special place, like a sleep lab or at home. The test data shows how often you stop breathing. This helps doctors figure out how to treat you.
Your doctor will check a few things from your sleep study. They look at:
They’ll also think about your health history, symptoms, and lifestyle. This helps them understand why you have CSA.
Your doctor might also do other tests. These help make sure CSA is the real problem. They might check:
Getting a correct diagnosis is the first step to treating CSA. Knowing the cause helps you and your doctor make a treatment plan just for you.
When treating Central Sleep Apnea, the first step is to tackle any underlying medical issues. “The cornerstone of CSA treatment lies in understanding and managing the underlying causes,” say sleep specialists.
We start by finding and treating health problems that cause CSA. This could mean managing heart failure, treating opioid dependency, or addressing other conditions that affect breathing at night.
Effective management of underlying conditions is key to better CSA symptoms. For example, improving heart failure treatment can help stabilize breathing during sleep.
Sometimes, certain medications can cause CSA. We might need to adjust or switch these medications to help symptoms. For instance, if opioid use is a factor, we might look for other pain relief options.
There are also specific medications for CSA. Acetazolamide is one used for CSA linked to high-altitude breathing.
For some, supplemental oxygen therapy is a first-line treatment for CSA. It provides extra oxygen at night to keep blood oxygen levels stable.
“Supplemental oxygen can be a game-changer for patients with CSA, helping to reduce the frequency of apneic events and improve overall sleep quality,” notes a leading sleep specialist.
By addressing underlying conditions, adjusting medications, and using supplemental oxygen when needed, we can manage CSA well. This improves the quality of life for those affected.
PAP therapy is key in treating Central Sleep Apnea. It’s important to pick the right PAP therapy to improve life quality for those with CSA.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) is a common PAP therapy. It’s often used for obstructive sleep apnea but can also help with CSA. CPAP delivers a constant flow of air through a mask to keep the airway open.
But CPAP might not work for everyone with CSA, like those with certain health issues. We need to check if CPAP is right for each person, looking at how severe their CSA is and their health.
Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) is another option. It has two pressure levels: one for inhaling and a lower one for exhaling. This makes breathing easier for some, like those who find CPAP hard to exhale against.
BiPAP is great for CSA patients who need higher pressures or can’t use CPAP. It’s more comfortable, which helps patients stick to their treatment plan better.
Adaptive Servo-Ventilation (ASV) is a more advanced PAP therapy for CSA. It monitors breathing patterns and adjusts pressure to keep breathing steady. This makes ASV very effective for CSA, like in Cheyne-Stokes respiration.
But ASV isn’t for everyone with CSA, like those with heart problems. We must check if ASV is right for each patient, based on their health and condition.
In conclusion, choosing the right PAP therapy for CSA is important. We work with patients to find the best option, whether it’s CPAP, BiPAP, or ASV. This helps manage CSA well and improves their life quality.
The world of Central Sleep Apnea treatment is changing fast. New technologies are giving patients new hope. As we learn more about this complex condition, we’re finding new ways to help those affected.
Phrenic nerve stimulation is a big step forward in treating Central Sleep Apnea. It uses a device to stimulate the phrenic nerve, which controls the diaphragm. This helps regulate breathing during sleep, cutting down on apneic events.
Studies have shown great promise with these implants. They offer a new option for those who haven’t found relief with other treatments. The implantation is a small surgery, and the device is controlled by a remote.
There are many new treatments being looked at for Central Sleep Apnea. These include new medicines, advanced PAP therapies, and device-based treatments. Clinical trials are key to figuring out if these treatments work.
These trials help us understand how these new treatments can help patients. As research keeps moving forward, we’ll see more options for treating Central Sleep Apnea.
Some of the new treatments being studied include:
These new treatments are a big leap forward in managing Central Sleep Apnea. They offer hope for better treatment results and a better life for patients.
Making lifestyle changes is key to treating Central Sleep Apnea (CSA). Simple adjustments can greatly improve your condition and life quality.
Our sleep position and environment greatly affect CSA symptoms. Sleeping on our side can lessen CSA episodes. Using a contoured pillow or body pillow helps keep this position all night.
Improving your sleep environment is also vital. Your bedroom should be dark, quiet, and comfortable. Blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine can help.
For many with CSA, excess weight makes symptoms worse. A healthy weight management program can help. This includes a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Weight Management Strategy | Description | Benefits |
Dietary Changes | Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains | Weight loss, improved overall health |
Regular Exercise | Engaging in moderate-intensity physical activity, such as brisk walking | Weight loss, improved cardiovascular health |
Professional Guidance | Consulting with a healthcare provider or a nutritionist | Personalized advice, sustainable weight loss |
Some substances can make CSA symptoms worse. It’s important to limit or avoid them. This includes alcohol and caffeine, which can disrupt sleep.
By making these lifestyle changes, people with CSA can see big improvements. It’s about making choices that help you sleep better and stay healthy.
Starting your journey with central sleep apnea treatment means learning to adapt to the plan. It’s complex, with many therapies and lifestyle changes. Getting good at this is key to managing your condition and living better.
First, you need to tackle the common hurdles. This might mean dealing with discomfort from therapies like PAP or making lifestyle changes. We know these can be tough, but with the right help and tweaks, you can get through them.
If PAP therapy is uncomfortable, there are ways to fix it. You could try different masks, adjust the pressure, or switch to BiPAP or ASV. It’s vital to work with your healthcare provider to find what works for you.
“The biggest challenge is not the disease itself, but how we adapt to the treatment and make it a part of our daily lives.” – A patient with central sleep apnea
Keeping an eye on how you’re doing is key. Regular visits to your healthcare provider can spot problems early and make needed changes. A sleep diary or sleep tracking device can also give you insights into your sleep and treatment.
Monitoring Method | Benefits |
Regular Check-ins with Healthcare Provider | Early identification of issues, personalized adjustments |
Sleep Diary | Detailed record of sleep patterns, symptoms, and treatment effects |
Sleep Tracking Devices | Objective data on sleep quality, duration, and disruptions |
It’s important to know when to change your treatment plan. If you’re uncomfortable, not seeing improvements, or having trouble sticking to it, it’s time to talk to your doctor. We suggest discussing any issues or changes in your condition with your healthcare provider.
Adjustments can be as simple as changing your therapy settings or adopting new habits. For example, tweaking your PAP therapy or trying a different mask can help a lot. Also, improving your sleep hygiene or changing your sleep environment can boost your treatment’s effectiveness.
Adapting to your central sleep apnea treatment plan takes time, effort, and sometimes, changes. By learning to overcome challenges, tracking your progress, and knowing when to adjust your treatment, you can make it work better for you. This will help improve your overall health and well-being.
It’s important to know when to get help right away if you have Central Sleep Apnea (CSA). Managing CSA takes time, but some moments are critical. You might need urgent care to avoid serious problems or even save a life.
Some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor fast. If you or someone you know has any of these, get emergency medical attention right away:
These signs can mean a serious problem that needs quick treatment. Knowing these warning signs and acting fast is key.
If you have CSA symptoms or have been diagnosed, seeing sleep specialists is vital. They can give you the care and advice you need. Here’s how to find a sleep specialist:
When you work with sleep specialists, share your symptoms, medical history, and any worries. This teamwork helps you get the best treatment plan for you.
Knowing when to get emergency medical attention and teaming up with sleep specialists can help you manage CSA. This way, you can live a better life.
Managing central sleep apnea (CSA) is key to a better life. We’ve seen how CSA is complex and needs a full treatment plan. This includes medical care, lifestyle changes, and constant monitoring.
Knowing about CSA’s causes, symptoms, and treatments is the first step. It’s important to work with doctors to create a plan that fits you. This plan should meet your specific needs.
CSA is treatable. The right mix of medical care and lifestyle changes can greatly improve sleep and health. We urge those with CSA to get professional help and actively manage their condition.
Dealing with CSA is a journey that needs patience, dedication, and support. With these, you can look forward to a better life, improved health, and restful sleep.
Central sleep apnea is a sleep disorder. It causes pauses in breathing during sleep. This happens because of a problem with the brain’s breathing control center, not a blockage in the airways.
Many things can cause central sleep apnea. These include medical conditions, certain medicines, and high altitude. Sometimes, the cause is unknown.
Doctors use a sleep study to check breathing patterns. They also do other tests to find out if there are other sleep disorders or health problems.
Symptoms include pauses in breathing at night. People might also feel very tired during the day, have trouble focusing, and get headaches in the morning.
Treatment depends on the cause. It might include fixing health problems, changing medicines, using oxygen, or positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy. This includes CPAP, BiPAP, and ASV.
CPAP gives a constant air pressure. BiPAP changes air pressure for breathing in and out. BiPAP might be more comfortable and is often used for central sleep apnea.
ASV is a PAP therapy. It adjusts air pressure for each breath. It helps keep breathing steady during sleep, often for central sleep apnea and Cheyne-Stokes respiration.
Yes, making lifestyle changes can help. This includes sleeping better, managing weight, and avoiding things that make symptoms worse. These changes can improve sleep quality.
Get medical help right away if symptoms are severe. This includes trouble breathing, chest pain, or feeling very tired during the day.
Adapting means overcoming challenges and keeping an eye on progress. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare professional.
Phrenic nerve stimulation implants are a new treatment. They help restore normal breathing by stimulating the diaphragm during sleep.
Yes, there are new treatments being tested. These include new technologies and therapies that aim to improve treatment results.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). How to Treat Central Sleep Apnea Complete Guide. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40820608/).
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!