Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
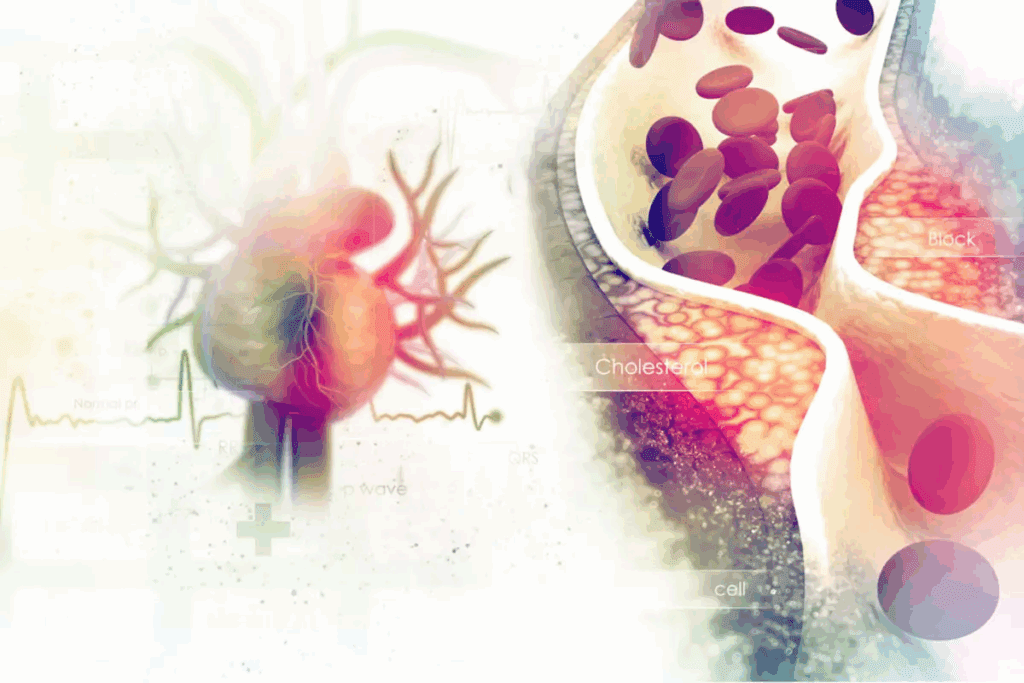
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a major killer worldwide. It caused over 371,000 deaths in the US in 2022. High cholesterol is a big risk factor for CAD. It’s key to know how it affects the disease.
High total cholesterol levels (240 mg/dL or more) raise CAD risk a lot. Between 2017 and 2020, 10% of adults aged 20 or older had levels above 240 mg/dL.
At LivHospital, we aim to give top-notch healthcare. We support international patients fully. Knowing how cholesterol and CAD are linked is key for stopping and treating the disease.
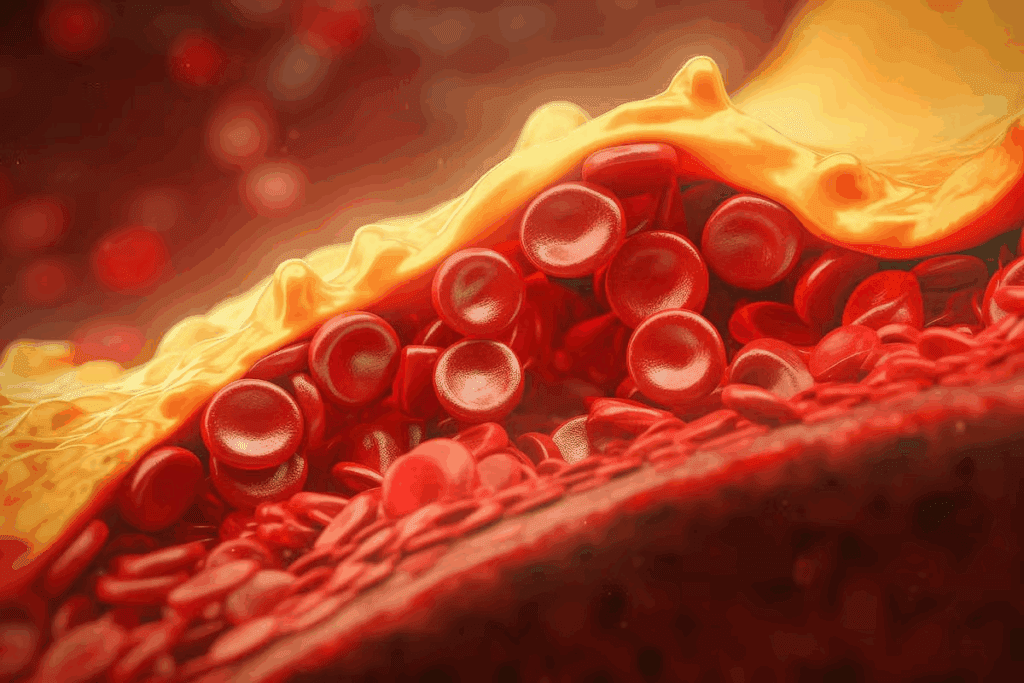
Cholesterol is key in the growth of coronary artery disease, a major killer globally. Knowing how cholesterol and CAD are linked is vital for fighting this disease.
Cholesterol is a lipid your body needs to work right. It’s part of cell walls, helps the liver make bile, and is used in hormone creation. The Medical organization says, “Cholesterol is a lipid your body needs to function. It’s part of cell membranes, helps your liver make bile, and serves as a building block for hormones.” There are two main types: LDL (bad) and HDL (good).
LDL cholesterol is called “bad” because too much can clog arteries. HDL is “good” because it helps clear other cholesterol from your blood.
CAD happens when the heart’s blood supply gets blocked by plaque. This plaque forms from lipids, macrophages, and other stuff, causing arteries to narrow.
High LDL cholesterol speeds up this process, raising CAD risk. CAD’s development involves many factors, like damaged endothelium, inflammation, and how the body handles lipids.
| Cholesterol Type | Function | Impact on CAD Risk |
| LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) | Transports cholesterol to cells | High levels increase CAD risk |
| HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) | Removes excess cholesterol from cells | High levels decrease CAD risk |
In conclusion, knowing how cholesterol and CAD are connected is key for heart health. By understanding cholesterol types and their effects on CAD, people can manage their cholesterol and lower CAD risk.

Preventing coronary artery disease (CAD) is closely tied to controlling cholesterol. The American Heart Association (AHA) says managing CAD means tackling various risk factors. Some can be changed through lifestyle and medicine, while others can’t.
Risk factors for CAD are split into two groups: modifiable and non-modifiable. Non-modifiable factors like age, gender, and family history can’t be changed. But, factors like cholesterol levels, blood pressure, smoking, and exercise can be improved.
Medical Expert, “We’ve moved away from strict cholesterol levels. We now consider cholesterol numbers with other heart disease and stroke risk factors.” This shows the need for a full risk assessment in managing CAD.
High cholesterol raises the risk of heart disease. High levels of LDL cholesterol can cause plaque buildup in arteries. This is a step towards CAD.
The table below shows how different cholesterol levels affect heart disease risk:
| Cholesterol Level | Category | Heart Disease Risk |
| <200 mg/dL | Desirable | Low |
| 200-239 mg/dL | Borderline High | Moderate |
| ≥240 mg/dL | High | High |
The table shows keeping cholesterol under 200 mg/dL lowers heart disease risk. The AHA stresses the importance of tackling cholesterol and other risk factors for CAD prevention.
CAD has a huge impact on public health worldwide. Looking at the numbers, it’s clear CAD is a big problem. It needs our urgent attention and action.
CAD is the top killer globally, causing millions of deaths yearly. The World Health Organization (WHO) says CAD leads to over 17.9 million deaths each year. This shows CAD’s big role in deaths worldwide.
CAD’s effects aren’t just in death numbers. It also badly affects the lives of millions. It can cause heart attacks, strokes, and other serious heart problems.
In the US, CAD causes over 371,000 deaths each year. This number shows we need strong ways to fight this disease.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says 86 million US adults have high cholesterol. Almost 25 million have very high cholesterol. These numbers show how common high cholesterol is, a big risk for CAD.
| Category | Total Cholesterol Level (mg/dL) | Number of Adults (US) |
| High Cholesterol | >200 | 86 million |
| Very High Cholesterol | >240 | 25 million |
Knowing these numbers helps us find ways to fight CAD. By controlling risk factors like high cholesterol, we can lower CAD cases and deaths.
Elevated cholesterol levels are key in atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in arteries. This complex process narrows and hardens arteries, leading to coronary artery disease (CAD).
Plaque starts with LDL cholesterol sticking to artery walls. Here’s how it happens:
As plaque grows, it narrows arteries. The steps include:
This shows why controlling cholesterol is vital to stop atherosclerosis and lower CAD risk.
The American Heart Association (AHA) has set clear guidelines for preventing CAD. These focus on managing cholesterol levels. They aim to help doctors and patients lower CAD risk together.
To follow these guidelines, a mix of lifestyle changes and medical treatments is needed.
Medical Expert. This depends on a person’s health, medical history, and heart disease risk.
The AHA guidelines highlight the need to:
Visual aids can show the difference between good and bad cholesterol levels.
By sticking to the AHA’s CAD prevention guidelines, people can lower their risk of heart disease. This improves their heart health overall.
By controlling cholesterol levels, we can greatly lower the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD). Managing cholesterol well is key to preventing heart attacks and strokes.
Studies show that controlling cholesterol can stop tens of thousands of heart attacks each year. Medical Expert, “For those at high risk, starting a statin is the best way to lower cholesterol and prevent heart attacks and strokes.” This highlights how vital cholesterol management is in stopping CAD.
Many studies prove that lowering cholesterol can cut heart attack risks. The American Heart Association (AHA) stresses the role of cholesterol control in preventing CAD.
| Study | Findings | Impact on CAD |
| Statin Therapy Study | Significant reduction in LDL cholesterol | Reduced risk of heart attacks by 30% |
| AHA Guidelines Review | Emphasis on cholesterol management | Recommendations for statin therapy in high-risk patients |
| Population-Level Study | Cholesterol reduction benefits | Prevention of tens of thousands of heart attacks annually |
Cholesterol reduction benefits not just individuals but the whole population. Effective cholesterol management can lessen the impact of CAD on public health.
Key benefits include:
As we focus more on cholesterol management, it’s clear that controlling it well can greatly reduce CAD. By following AHA guidelines and using statins when needed, we can aim for fewer heart attacks and strokes in the future.
Managing cholesterol and CAD requires different medical treatments. These include statins and new treatments. They help lower the risk of heart problems and improve health outcomes.
Statins are a common treatment for high cholesterol. Medical Expert, “Statins are one of the most well-studied, most well-tolerated medications that exist.” They block the liver’s cholesterol-making enzyme.
Statins lower bad cholesterol, fight inflammation, and improve blood vessel function. But, they can cause side effects like muscle pain and liver issues.
For those who can’t take statins or need more help, non-statin drugs are good options. These include bile acid sequestrants, ezetimibe, and PCSK9 inhibitors.
PCSK9 inhibitors, for instance, greatly lower bad cholesterol when used with statins. They target the PCSK9 protein, helping the liver clear bad cholesterol.
| Medication Class | Mechanism of Action | Primary Effect |
| Bile Acid Sequestrants | Bind bile acids in the intestine | Lower LDL Cholesterol |
| Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors | Inhibit cholesterol absorption | Lower LDL Cholesterol |
| PCSK9 Inhibitors | Inhibit PCSK9 protein | Significantly Lower LDL Cholesterol |
New treatments offer hope for managing cholesterol and CAD. Inclisiran, a small interfering RNA, targets PCSK9 for LDL cholesterol reduction.
Liv Hospital leads in these advancements. It aims to provide top-notch care with the latest treatments. This ensures patients get the best care for their cholesterol and CAD.
Changing your lifestyle can greatly improve your cholesterol levels and lower CAD risk. It’s key to manage cholesterol and prevent coronary artery disease (CAD). We’ll look at proven ways to better your cholesterol and lower CAD risk.
Eating a heart-healthy diet is vital for managing cholesterol. The American Heart Association (AHA) suggests a diet rich in:
It’s also important to cut down on saturated and trans fats. Eating less than 300 milligrams of dietary cholesterol daily can boost your LDL (bad) cholesterol.
| Dietary Component | Recommended Intake |
| Saturated Fats | Less than 5-6% of total daily calories |
| Trans Fats | Avoid as much as possible |
| Dietary Cholesterol | Less than 300 mg/day |
Regular exercise is key for better cholesterol levels and heart health. The AHA advises at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise weekly.
Exercise can increase HDL (good) cholesterol and lower triglycerides. Even simple activities like brisk walking can improve your cholesterol.
Quitting smoking is vital for lowering CAD risk. Smoking harms blood vessel linings, making them more prone to blockage. Stopping smoking can greatly improve heart health.
Managing stress is also important. Chronic stress can raise cortisol levels, harming cholesterol. Meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress.
By making these lifestyle changes, you can significantly improve your cholesterol levels and lower CAD risk. It’s important to work with healthcare professionals to create a plan tailored to your needs and goals.
Liv Hospital is dedicated to top-notch cardiac care. We use the latest research and tech to help our patients. This ensures the best results for them.
We’re proud of our cardiac care at Liv Hospital. Our team works hard to give our patients the best care. It’s on par with the world’s top hospitals.
Our commitment to excellence shows in our facilities and following the latest guidelines. This includes the American Heart Association’s (AHA) CAD management rules.
We’re always up-to-date with medical breakthroughs. We use the latest tools and treatments for better patient results. This includes managing cholesterol and CAD.
Our care is more than just treatment. We teach patients about lifestyle changes. These can greatly improve their heart health and cholesterol levels.
| Clinical Protocol | Description | Benefit |
| AHA Guidelines for CAD | Evidence-based recommendations for CAD management | Improved patient outcomes through standardized care |
| Statin Therapy | Medication to lower cholesterol levels | Reduced risk of heart attacks and strokes |
| Lifestyle Modification Programs | Education on diet, exercise, and stress management | Empowers patients to manage their condition effectively |
At Liv Hospital, we aim to lead in cardiac care. We’re known for our ethics and new ideas. Our care is effective, caring, and respects our patients.
“Liv Hospital supports these advances through its mission to deliver internationally competitive outcomes and implement the most current clinical protocols.”
We’re always looking to improve with new tech and research. Our goal is to create a culture of excellence. This helps our patients and advances cardiac care worldwide.
Managing cholesterol is vital for heart health. We’ve seen how cholesterol affects coronary artery disease (CAD). The American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines help prevent CAD by focusing on cholesterol control.
Medical Expert. This helps understand their risk. Managing cholesterol can greatly lower CAD risk. We’ve looked at medical treatments and lifestyle changes to help.
Combining healthy diets, exercise, and stress management can keep cholesterol levels in check. Liv Hospital shows how important a full care plan is for better health.
Controlling cholesterol can lower CAD risk and heart problems. We urge readers to talk to doctors for a plan to keep cholesterol healthy and prevent CAD.
Cholesterol is key in the development of coronary artery disease (CAD). High levels of certain cholesterol types can cause plaque in arteries. This increases CAD risk.
Cholesterol builds up in artery walls, forming fatty streaks and plaque. This narrows and hardens arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart.
Risk factors for CAD include high cholesterol, blood pressure, smoking, and lack of exercise. These can be managed with a healthy diet, exercise, quitting smoking, and stress relief. Medical treatments like statins also help.
The AHA suggests managing cholesterol through lifestyle changes and medical treatments. They stress controlling cholesterol to prevent CAD and heart attacks.
Managing cholesterol well can greatly lower heart attack risk. Studies show lowering cholesterol improves heart health.
Eating well, exercising, quitting smoking, and managing stress can improve cholesterol and lower CAD risk.
Treatments like statins, non-statin drugs, and new therapies help manage cholesterol and CAD. They can lower heart attack risk.
Liv Hospital focuses on top-notch cardiac care and follows the latest treatment protocols for cholesterol and CAD. They aim for complete care and new solutions for CAD patients.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!