
Nearly 500,000 Americans get a coronary stent each year. This helps open blocked arteries and boosts heart health. But, having a stent doesn’t mean you’re done. You must stay careful about your heart health. Answering do you need blood thinners if you have a stent (yes, dual antiplatelet therapy) and the duration of blood thinners after stent.
People with a stent face risks of heart attack or stroke. That’s why medication, like blood thinners, is key. They stop clots from forming around the stent, keeping it open.
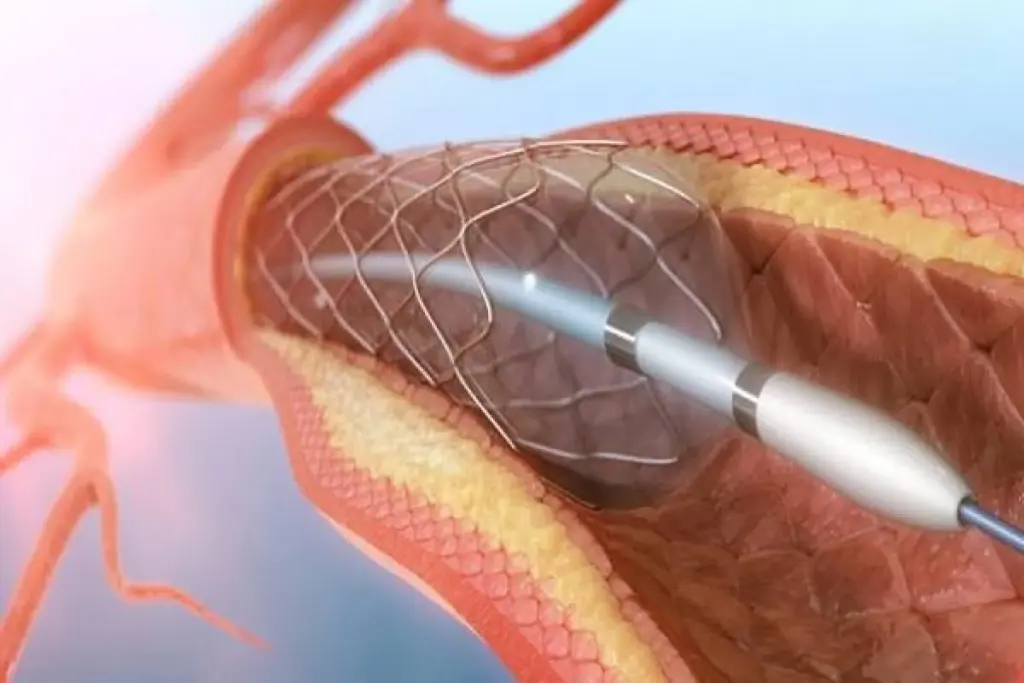
When a stent is put in an artery, it’s important to know how it works and the risks. A stent is a small, mesh-like device that keeps arteries open. This lets blood flow normally. Proper stent function is critical to prevent serious complications.
A stent is usually put in during an angioplasty. It expands to fit the artery, improving blood flow. “Stents have revolutionized the treatment of arterial blockages,” says a leading cardiologist, “but they require careful management to prevent clot formation.”
Blood clots can form in the stent, leading to serious problems like stent thrombosis. This can cause a heart attack or even death if not treated quickly. The risk of clotting is highest in the first few months after the stent is placed. This is why effective blood thinner therapy is needed.
By understanding stents and their risks, patients can manage their condition better. This helps reduce the chance of complications.
Blood thinners are key for patients after a stent is placed. They help prevent serious problems that can happen after the procedure.
Blood thinners stop blood clots that can cause stent thrombosis. This is a serious condition. Antiplatelet medications, a type of blood thinner, stop platelets from sticking together and forming clots. This greatly lowers the chance of stent failure.
Studies show that without the right meds, stent thrombosis risk goes up a lot. In fact, the rate of stent thrombosis can hit 1-2% in the first year after a stent is put in. If post-stent medication guidelines aren’t followed, the risk is higher. Following the stent care and blood thinners plan is key to lowering this risk.
Knowing how important blood thinners are and sticking to the plan can greatly improve stent success. The right blood thinner dosage after stent placement is vital. It helps avoid complications and makes sure the stent works right.
To ensure the success of stent placement, patients are usually prescribed medications that thin the blood. These medications are key in preventing blood clots. Blood clots can lead to serious complications.
Antiplatelet medications are a cornerstone in managing patients with stents. They prevent platelets in the blood from clumping together to form clots.
Aspirin is commonly prescribed to patients after stent placement. It has antiplatelet properties. It prevents clot formation by inhibiting the production of thromboxane A2 in platelets.
“Aspirin has been a mainstay in the prevention of cardiovascular events in patients with stents.”
The dosage of aspirin can vary. It is usually continued indefinitely unless there are side effects or other medical reasons.
P2Y12 inhibitors, such as Plavix (clopidogrel), Brilinta (ticagrelor), and Effient (prasugrel), are another class of antiplatelet medications. They block the P2Y12 receptor on platelets. This prevents platelet activation and aggregation.
While antiplatelet medications are the primary therapy for preventing clot formation in stent patients, anticoagulants may be used in certain cases. Anticoagulants work by inhibiting the coagulation cascade. This reduces the formation of blood clots.
In some patients, anticoagulants may be prescribed alongside antiplatelet therapy. This is for those with additional risk factors for clot formation. But, this combination increases the risk of bleeding complications.
For those with a stent, DAPT is now the main treatment to stop clots. It uses two medicines to cut down the chance of stent thrombosis.
DAPT mixes two antiplatelet drugs: aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor (like clopidogrel, prasugrel, or ticagrelor). These medicines work together to stop platelets from sticking and clumping. This helps prevent clots from forming on the stent.
Doctors prescribe DAPT to give strong protection against clots, mainly right after the stent is put in. This is when the risk of clotting is the highest.
Research proves DAPT is better than one medicine for stopping stent thrombosis and big heart problems. Here’s a look at how different treatments stack up:
|
Treatment Strategy |
Stent Thrombosis Risk Reduction |
Major Adverse Cardiac Events |
|---|---|---|
|
Aspirin alone |
30% |
20% |
|
P2Y12 inhibitor alone |
40% |
25% |
|
DAPT (Aspirin + P2Y12 inhibitor) |
70% |
40% |
The numbers show DAPT greatly lowers the risk of stent thrombosis and heart problems compared to one medicine.
The time you need to take blood thinners after a stent depends on the stent type and your health. The goal is to stop the stent from getting blocked and avoid bleeding.
The type of stent you get affects how long you’ll take blood thinners. Bare metal stents usually need 1-3 months of treatment. But, drug-eluting stents might need 6-12 months or more because they have a higher risk of blockage.
Choosing between short-term and long-term blood thinner therapy depends on your risk and disease complexity. Short-term therapy might be right for those at low risk. But, long-term therapy is often better for those at higher risk.
“The optimal duration of DAPT after stent placement remains a topic of debate, with guidelines evolving based on new evidence.”
Several things can change how long you need to take blood thinners, including:
Doctors look at these factors to decide the best treatment length for you.
Blood thinners help prevent clots but can also cause problems. They are key to avoiding stent issues. But, it’s important to watch out for side effects.
People on blood thinners might see bruising, bleeding gums, or nosebleeds. These signs are usually mild. But, they show the medicine is working. It’s key to keep an eye on these signs to avoid bigger issues.
Severe problems can happen, like heavy bleeding or blood in urine or stool. Spotting these symptoms early is vital. Rarely, blood thinners can cause allergic reactions or mix badly with other drugs.
If you see unusual or severe symptoms, call your doctor right away. This includes bleeding that won’t stop, severe pain, or trouble breathing. Regular visits with your doctor can also help manage risks and adjust your treatment.
Using blood thinners after a stent is placed requires careful thought. Patients need to know the risks and how to manage their meds well.
Before surgery, those on blood thinners must talk to their doctor. The doctor might suggest stopping or changing the blood thinner dose to lower bleeding risk. It’s key to follow these directions to ensure a safe surgery.
Dental work can be risky for those on blood thinners. Telling the dentist about the meds is important, as some dental procedures might need the blood thinner dose changed or stopped. Keeping up with dental care and good oral hygiene can help avoid needing complex dental work.
Blood thinners can interact with other meds and supplements, raising bleeding risk or making them less effective. It’s vital to tell your doctor about all meds, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, to avoid bad interactions.
|
Medication/Supplement |
Potential Interaction |
Action |
|---|---|---|
|
Aspirin |
Increased risk of bleeding |
Consult doctor before taking |
|
Ibuprofen |
Increased risk of bleeding |
Use alternative pain relievers |
|
Vitamin K supplements |
Counteracts blood thinner effects |
Avoid unless prescribed |
Deciding when to stop blood thinners after a stent is complex. It depends on many medical factors and the patient’s health.
Doctors look at several things to decide when to stop blood thinners. They consider the stent type, other heart conditions, and the patient’s health. They check these to see if stopping blood thinners is safe.
Stopping blood thinners too soon can cause big problems. It might lead to stent thrombosis, which can be deadly. It’s important to listen to your doctor about when to stop taking them.
Doctors often suggest tapering off blood thinners slowly. This helps avoid bad reactions and lets them watch for any complications. Regular check-ups are key during this time.
For those who can’t use common blood thinners after a stent, new hope exists. Research into various alternatives is underway. This is to find effective ways to prevent clots.
Patients at high risk of bleeding or who can’t handle standard treatments have options. Single antiplatelet therapy is one choice for those at high risk of bleeding. Another is novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs), which prevent clots without constant monitoring.
The American Heart Association says treatment should match the patient’s risks. This means personalized plans for stent patients are key.
New treatments are being looked into to overcome blood thinner limits. Polymer-free drug-eluting stents aim to cut clot risk without long-term therapy. Also, trials are checking target-specific oral anticoagulants in stent patients.
A study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology shows promise. It suggests novel anticoagulants could be a better choice than traditional therapy for heart disease patients.
As research grows, better and safer blood thinner alternatives will likely emerge. This will help stent patients get better results.
Living with a stent means you need to manage your health well, even with blood thinners. It’s key to avoid problems and keep the stent working right.
Eating right is important for those on blood thinners. You should watch your vitamin K intake. Foods like spinach and kale are high in vitamin K.
It’s better to eat these foods regularly than to avoid them completely. Always talk to your doctor about what to eat.
Staying active is good for your heart. But, if you’re on blood thinners, you need to be careful. Try low-impact activities like walking or swimming.
Talking to your doctor about how much exercise is safe is very important.
To avoid bleeding, follow some simple steps. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and electric razors to avoid cuts. Also, be careful when doing things that might hurt you.
By choosing smart lifestyle habits, you can manage your stent well. This helps lower the risks of blood thinner side effects.
Success with a stent needs a full plan. This includes taking blood thinners and making lifestyle changes. Blood thinners are key to keep the stent open and prevent blockages.
Stent care and blood thinners are linked. Patients must team up with their doctors to manage their treatment. It’s important to know about different blood thinners and their side effects.
Using blood thinners for a long time may be needed to avoid problems. Making healthy choices, like eating right and being careful with exercise, helps a lot. This way, you can lower risks and get the most from your stent.
In the end, a good treatment plan and lifestyle changes are key for long-term success with a stent. By focusing on stent care and blood thinners, you can lower your risk of complications. This leads to better health overall.
Blood thinners stop blood clots from forming. After a stent is placed, they are key to prevent a serious condition called stent thrombosis.
Antiplatelet meds, like aspirin and Plavix, stop platelets from sticking together. Anticoagulants, on the other hand, affect how the liver makes clotting factors. Both prevent clots but in different ways.
DAPT combines aspirin with a P2Y12 inhibitor like Plavix. It’s used after stent placement to protect against stent thrombosis, mainly in the first year.
The time needed for blood thinners varies. It depends on the stent type, patient health, and other conditions. Drug-eluting stents usually need 12 months or more of DAPT. Bare-metal stents might need only a month.
Side effects include bruising, bleeding gums, and nosebleeds. Serious issues like stomach or brain bleeding can also happen. Always tell your doctor if you notice any unusual bleeding.
Always talk to your doctor before stopping blood thinners for any reason. They might need to adjust your medication to reduce bleeding risks. Your doctor will give you personalized advice.
Yes, there are other options for those who can’t take standard blood thinners. These include different meds or new treatments. Talk to your doctor about what’s best for you.
Manage your lifestyle by watching your diet and staying active. Avoid high-risk activities and use strategies to prevent bleeding. Follow your doctor’s specific advice.
Stopping blood thinners too soon raises the risk of stent thrombosis. This can lead to heart attacks or serious problems. Never stop your medication without your doctor’s okay.
Your doctor will check your blood thinner therapy regularly. They might do blood tests to see how your body is responding. They’ll adjust your treatment as needed to keep you safe.
National Institutes of Health. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/stents/living-with
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!