Last Updated on November 17, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
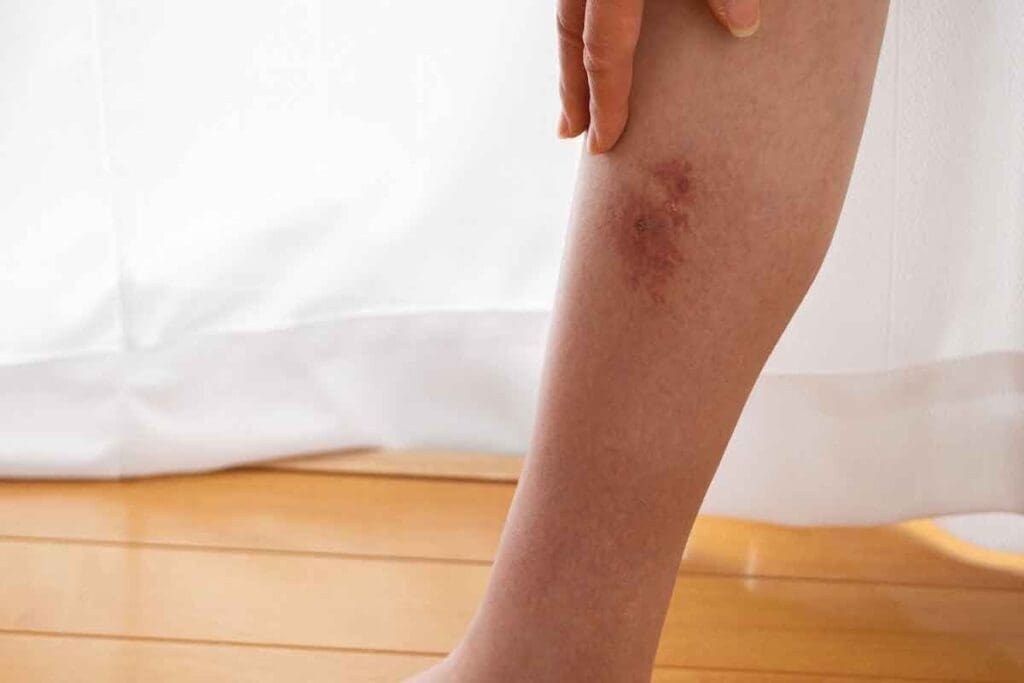
When you get injured, bruising is common — but sometimes it raises concerns about a contusion blood clot. A bruise, or contusion, happens when small blood vessels break under the skin, causing discoloration and tenderness. But in rare cases, a contusion blood clot can form when the body’s clotting process overreacts to the injury.
At Liv Hospital, we understand how a contusion blood clot might develop after trauma. While most bruises heal within days, deeper tissue damage can occasionally trigger clot formation. This is why monitoring pain, swelling, and warmth is important.
Bruising is a common result of injury. But have you ever thought about what happens under your skin? When we get hurt, like from a fall or a blow, the blood vessels under the skin can get damaged.
A bruise, or contusion, happens when blood leaks from damaged vessels into the tissue around them. This leakage is what makes bruises look discolored. The process involves several key parts:
Contusion Blood Clot: Can a Bruise Lead to a Blood Clot After Injury?
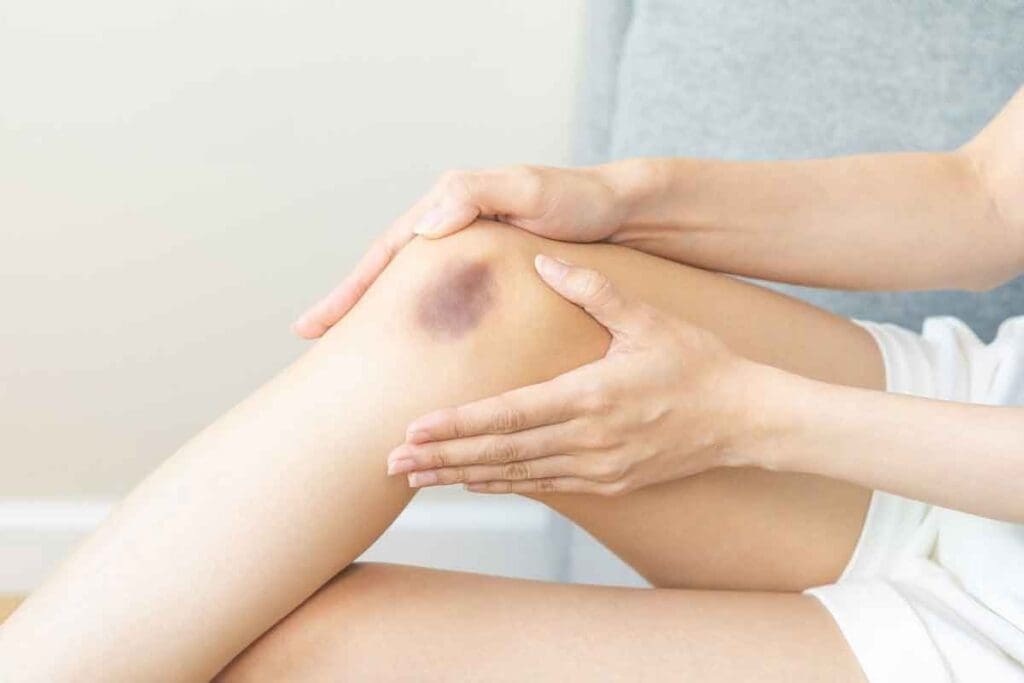
Bruises usually come from injuries, like hitting something hard, falling, or breaking a bone. These injuries can burst capillaries in the skin, causing bruises. Common situations include:
Knowing these causes can help prevent bruises. It also helps us understand when a bruise might be a sign of something more serious, like a blood clot.
When an injury happens, the body quickly starts the blood clotting process to stop too much bleeding. This process involves many parts of the blood working together to make a clot.
The blood clotting process is key to keeping the body stable after an injury. It goes through several steps to make a fibrin clot. This clot helps keep the initial platelet plug in place.
Platelets are small, colorless parts in the blood that are very important. They stick to the injury site and gather together to form a plug. This plug is the first step in stopping the bleeding.
The steps to form the platelet plug are:
The platelet plug is important but not strong enough to handle blood flow. Fibrin, made by the liver, is key in making the clot stronger. The coagulation cascade changes fibrinogen into fibrin.
Fibrin strands make a mesh that holds red blood cells, platelets, and other blood parts. This makes a stronger clot than the platelet plug. It provides a lasting fix for bleeding.
| Component | Function in Blood Clotting |
| Platelets | Form the initial plug at the site of injury |
| Fibrinogen | Converted into fibrin to strengthen the clot |
| Fibrin | Creates a mesh that traps blood cells, stabilizing the clot |
Knowing how the blood clotting process works after an injury is important. It helps us understand how bruises
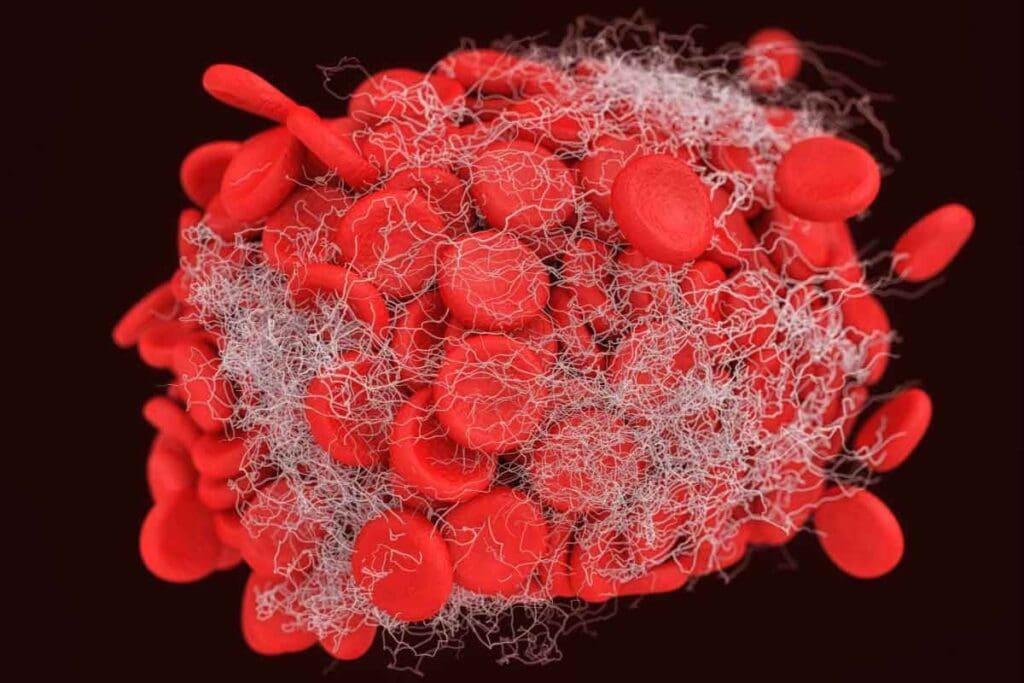
form and how they might lead to blood clots. The balance between platelet plug formation and fibrin clot stabilization is vital for stopping bleeding.
Bruising after an injury is normal. But, it’s key to know when it might be a sign of a serious issue, like a blood clot. Most bruises heal fine, but some can lead to serious problems.
It’s important to know the difference between various bruises. We’ll look at surface bruises and deep tissue contusions. We’ll also talk about what makes clotting a problem.
Bruises can be different depths and vary in severity. Surface bruises are closer to the skin and might look like discoloration without much swelling. Deep tissue contusions, on the other hand, affect deeper tissues and blood vessels, leading to more serious issues.
Deep tissue contusions are a big worry because they can harm deeper tissues and blood vessels. This type of bruising increases the risk of a blood clot because of the trauma it causes.
The body naturally clots to stop bleeding after an injury. But, sometimes this clotting can become a problem. The severity of the injury, where the bruise is, and your health can all play a part in this risk.
Clotting is good for healing, but too much or in the wrong place can cause trouble. It’s important to know the signs of bad clotting to get medical help quickly.
| Characteristics | Normal Clotting | Problematic Clotting |
| Location | Localized to the injury site | May occur in distant or unrelated areas |
| Symptoms | Mild swelling, pain, and bruising | Severe swelling, pain, warmth, and redness |
| Risk Factors | Minor injuries, normal healing process | Severe injuries, pre-existing clotting disorders, immobility |
“The key to managing bruising and preventing complications is understanding when a bruise might be more than just a simple injury.”
Medical Expert
Knowing the difference between normal and bad clotting helps. It lets people get medical help when needed, which can prevent serious problems.
It’s important to know the risk factors for blood clots after bruising. Some people are more likely to get blood clots because of health conditions or other factors. We’ll talk about these risk factors to help you understand when bruising might be serious.
People with clotting disorders are at higher risk for blood clots after bruising. These disorders can make it hard for the body to control clotting. Conditions like factor V Leiden thrombophilia or antiphospholipid syndrome can greatly increase clot risk.
The severity and where the bruise is can affect clot risk. Severe injuries, like deep tissue damage or large areas, are more likely to cause clots. Bruises on the legs are very concerning because of the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). This is a condition where blood clots form in deep veins, often in the legs.
| Location of Bruise | Risk Level for Blood Clot |
| Arms | Moderate |
| Legs | High |
| Internal Organs | Very High |
Being immobile after an injury is a big risk factor for blood clots. When you can’t move, blood flow slows down, making clots more likely. People who are bedridden or have limited mobility after an injury should be watched closely for blood clots.
Age and health are key in clot risk after bruising. Older adults and those with chronic conditions, like heart disease or diabetes, are more at risk. Lifestyle factors, like smoking, can also increase this risk. This can lead to conditions like “can bruises cause clots.”
It’s important to know the signs of a blood clot after an injury. Our body forms clots to stop bleeding after an injury. But sometimes, these clots can be a problem. Here are the main signs that might mean a blood clot has formed.
Swelling that goes beyond the bruise area could mean a blood clot. This swelling happens because the clot blocks blood flow. It causes fluid to build up in the limb.
Pain that doesn’t go away or gets worse is a sign of a blood clot. This pain is often more intense than the injury itself. It also doesn’t get better with usual pain relief.
Warmth in the injured area could be a sign of a blood clot. The clot causes inflammation. This leads to higher temperatures in the tissue around it.
Redness that spreads beyond the bruise area might mean a blood clot. This redness comes from inflammation caused by the clot.
There are three more signs to watch for:
| Warning Sign | Description |
| Unusual Swelling | Swelling beyond the bruise area due to obstructed blood flow. |
| Persistent or Increasing Pain | Pain that is more severe than the initial injury pain. |
| Warmth in the Affected Area | Increased temperature due to inflammation caused by the clot. |
| Redness Extending Beyond the Bruise | Redness due to inflammation caused by the clot. |
| Tenderness to the Touch | Tenderness due to the underlying clot. |
| Discoloration | Change in skin color around the affected area. |
| Difficulty Walking or Moving | Pain or swelling causing difficulty in movement. |
Injuries can sometimes lead to blood clots. But, there are ways to lower this risk. It’s important to prevent blood clots after an injury for a safe recovery. We’ll look at methods to reduce blood clot risk, including immediate care, lifestyle changes, and special garments.
The RICE protocol is a good way to manage contusions and prevent blood clots. RICE means Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
Following the RICE protocol can greatly lower the chance of can a fall cause a blood clot. It helps by reducing the injury’s impact.
Rest is key right after an injury. But, moving gently and doing exercises can also prevent blood clots. Simple movements like flexing and extending the affected limb can improve blood flow.
A study showed how important moving is to prevent blood clots. It said, “Early ambulation is a critical component of venous thromboembolism prevention.”
Early ambulation is a critical component of venous thromboembolism prevention.
Source: Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery
Regular movement can also lower the risk of getting a blood clot from a bruise.
Drinking enough water and eating right are key to preventing blood clots. Water helps keep blood flowing and prevents dehydration, which can lead to clots.
| Nutritional Element | Benefit |
| Hydration | Maintains blood flow, prevents dehydration |
| Vitamin K | Essential for blood clotting regulation |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Helps reduce inflammation |
Drinking enough water and eating well can help avoid bruising blood clots.
Compression garments, like stockings, help improve blood flow and prevent blood clots. They work by applying more pressure at the ankle and less as they go up the leg.
Wearing compression garments is a good way to prevent blood clots. It’s helpful for people at higher risk or when they can’t move much.
Bruising is a common injury result that might lead to blood clots. Most bruises heal without issues, but knowing the risks is key. It’s important to prevent blood clots from forming.
Understanding how blood clots form and knowing risk factors helps. Being aware of signs like swelling or pain is vital. This way, you can get medical help quickly if needed.
To lower the risk of blood clots from injury, follow prevention and treatment plans. Use the RICE protocol, move properly, and stay hydrated. This balance helps avoid complications and aids in recovery.
Can a bruise cause blood clots? The risk is there, but being informed and proactive can lower it. By staying alert and taking the right steps, you can keep your health safe.
Yes, a bruise can sometimes lead to a blood clot. This is more likely if the bruise is severe or if there are health issues that affect blood clotting.
A bruise happens when blood leaks from damaged vessels into the tissue around them. A blood clot, on the other hand, is a mass of blood cells and proteins that can block blood flow.
Yes, a contusion, or bruise, can cause a blood clot. This is more likely if the injury is severe or if there’s a lot of damage to blood vessels.
Risk factors include having a clotting disorder, the severity and location of the injury, not moving much after injury, and being older or having health issues.
Warning signs include swelling that goes beyond the bruise, pain that doesn’t go away or gets worse, warmth in the area, and redness that spreads beyond the bruise.
To prevent blood clots, follow the RICE protocol, move around and stay active, drink plenty of water and eat well, and wear compression garments.
Yes, falling can lead to a blood clot, mainly if the fall causes significant injury or trauma.
Yes, bruises can cause blood clots in the legs, more so if the bruise is severe or if there are health issues that affect blood clotting.
Symptoms include swelling, pain, warmth, and redness in the leg, and may also include a feeling of heaviness or tightness.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!