Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik
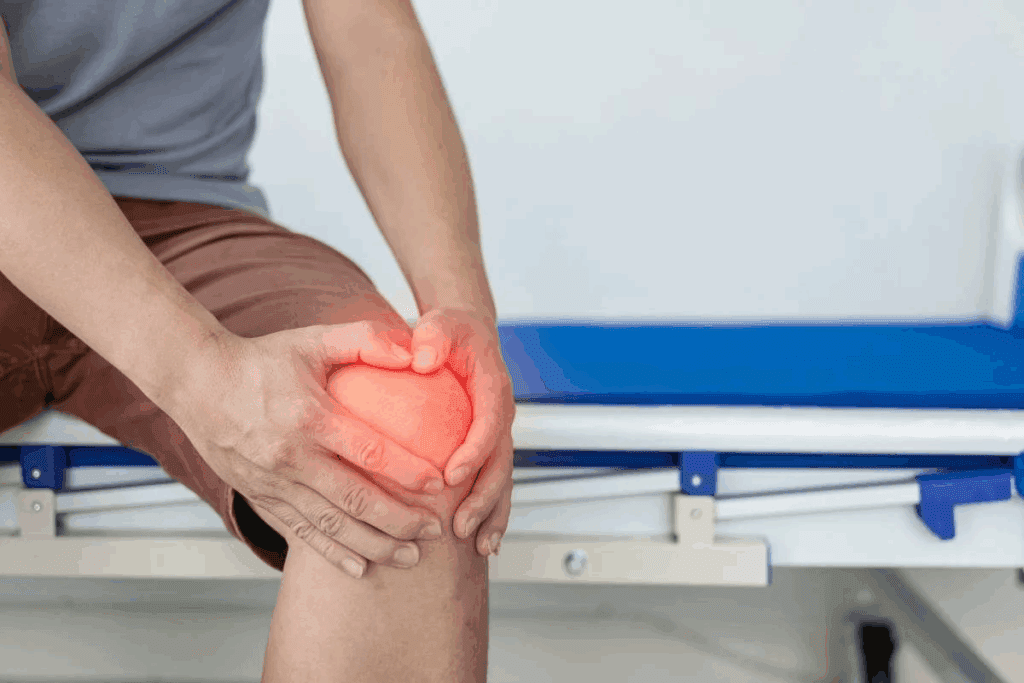
Bursitis affects millions worldwide, causing significant discomfort and impairment. Inflammation of the bursae, the fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints, can lead to chronic pain and limited mobility.
Understanding the risks associated with bursitis is key for effective management. If left untreated, bursitis can lead to increased risk of infection and long-term joint damage. We will explore the various complications and provide insights into prevention and treatment options.

The term bursitis means inflammation of bursae. These are important for smooth joint movement. Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and ligaments. They reduce friction and help with smooth motion.
A bursa is a closed sac filled with synovial fluid. It’s lined with synovial tissue. Its main job is to reduce friction between bones, tendons, and ligaments. This makes movement easier and reduces wear and tear.
Bursae are found in areas where friction is common. They are in the shoulders, hips, knees, and elbows. These spots are often stressed and need bursae for normal function.
Inflammation in bursitis can come from repetitive motion, trauma, or infection. When a bursa gets inflamed, it causes pain, swelling, and limited movement. Knowing why bursitis happens helps in treating it.
Telling bursitis apart from other joint issues is key for right treatment. Bursitis shows as localized pain and swelling. Other problems like arthritis might affect more joints. A correct diagnosis, often with tests, is needed to tell bursitis apart.

Bursitis is not just one condition; it has many forms, each with its own risks. It can affect different parts of the body, causing various symptoms. This makes diagnosis and treatment tricky.
Shoulder bursitis, often called subacromial bursitis, is common. It happens when the bursa between the acromion and rotator cuff tendons gets inflamed. This can cause shoulder pain and make it hard to move.
Hip bursitis, or trochanteric bursitis, affects the hip area. It leads to pain on the outside of the hip, getting worse with activities like walking. Knowing the causes and symptoms is key to managing it.
Knee bursitis comes in two types: prepatellar and pes anserine. Prepatellar bursitis causes swelling and pain in front of the kneecap. Pes anserine bursitis affects the lower inner knee, causing pain when walking.
Elbow bursitis, or olecranon bursitis, is inflammation of the bursa at the elbow’s back. It leads to swelling and pain, worse when leaning on the elbow. Treatment focuses on reducing swelling and preventing infection.
To understand the differences and risks of these bursitis types, let’s look at a table:
| Type of Bursitis | Common Symptoms | Risk Factors |
| Shoulder (Subacromial) | Pain, limited mobility | Repetitive overhead activities |
| Hip (Trochanteric) | Pain on outer hip | Running, cycling, direct blows |
| Knee (Prepatellar) | Swelling, pain in front of kneecap | Kneeling, direct trauma |
| Knee (Pes Anserine) | Pain on lower inner knee | Overuse, poor biomechanics |
| Elbow (Olecranon) | Swelling, pain at back of elbow | Leaning on elbow, trauma |
Knowing about these bursitis types and their risks is vital for managing them. Recognizing symptoms and risk factors helps get the right medical care.
It’s important to know the difference between acute and chronic bursitis. This knowledge helps in managing the condition and avoiding long-term harm. We will look at the characteristics of each type and their risks.
Acute bursitis happens suddenly, often due to injury, infection, or repetitive actions. It causes pain, swelling, and limited movement in the joint. For example, a fall or sudden injury can cause it in the shoulder.
To manage acute bursitis, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) are recommended. Anti-inflammatory drugs can also help. But, if not treated, it can turn into chronic bursitis.
Chronic bursitis occurs when acute bursitis is not treated well or when the bursa is under constant stress. It leads to persistent pain and recurring inflammation, making it hard to manage.
People who do repetitive tasks or have poor work setup are at risk. For instance, athletes or workers doing the same thing over and over are more likely to get it.
Chronic bursitis can cause cumulative damage to the joint and tissues. This can lead to serious issues like:
The time it takes for complications to happen varies. It depends on the person and how severe the condition is. But, with quick treatment, many problems can be prevented.
| Timeframe | Potential Complications |
| Short-term (weeks to months) | Increased pain, swelling, and limited mobility |
| Long-term (months to years) | Joint degeneration, muscle atrophy, and chronic pain |
Knowing the difference between acute and chronic bursitis helps in managing it better. Early action and proper care are essential to avoid serious problems.
Bursitis can cause more than just pain and swelling. It can change our daily lives in many ways. If not treated, it can lead to serious problems that affect our quality of life.
Bursitis pain is a big concern. It can be so bad that it makes everyday tasks hard. Even simple things like getting dressed or doing chores can become a challenge.
For example, shoulder bursitis makes it hard to lift your arms. This can affect personal care and reaching high places. Knee bursitis can make walking or climbing stairs painful, limiting your movement and independence.
Bursitis can also limit how well you can move. As it gets worse, it can make it hard to do everyday things. This not only hurts your body but can also make you feel sad or trapped.
Chronic pain and limited movement can really lower your quality of life. People with untreated bursitis may not be able to do things they love. This can make them feel sad and frustrated.
The pain and discomfort can also mess with your sleep. This can make you tired and feel even worse. It can also hurt your relationships and mental health.
The mental effects of chronic pain from bursitis are real. The constant pain can make you anxious, depressed, and hopeless. It’s important to treat the physical and mental sides of bursitis.
Understanding bursitis and its effects can help us see why we need to treat it fully. We need plans that help with symptoms and improve our overall life.
Septic bursitis is a serious condition where a bursa gets infected. This can lead to severe problems if not treated quickly. We will look at the risks of septic bursitis, how bursae get infected, risk factors, symptoms, and the chance of systemic infection.
Bursae can get infected in several ways. Bacteria can enter through a cut or wound, a common cause. Bacteria can also spread through the blood from another infected area. Infections from nearby areas can also spread.
Some people are more likely to get septic bursitis. This includes those with injuries, rheumatoid arthritis, weakened immune systems, and diabetes. Knowing these risk factors helps in early treatment.
The symptoms of septic bursitis are clear. Look for more pain, swelling, redness, and warmth. Fever is also a sign. Spotting these symptoms early is key to treatment.
Ignoring septic bursitis can lead to a serious infection. Bacteria can spread to the blood, causing sepsis. This is a life-threatening condition that needs quick medical help.
| Risk Factor | Description | Implications |
| Trauma | Direct injury to the bursa | Increased risk of infection |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Pre-existing inflammatory condition | Higher susceptibility to septic bursitis |
| Immunosuppression | Weakened immune system | Reduced ability to fight off infection |
Knowing the risks and effects of septic bursitis is key. Early recognition and treatment can prevent serious issues.
Untreated bursitis can cause many problems in the musculoskeletal system. It affects not just the joint but also the tissues around it. This can lead to issues with joint function, mobility, and overall quality of life.
One major problem is muscle weakness and atrophy. When a joint is inflamed, moving it can be very painful. This leads to less activity and muscle disuse.
Over time, muscles around the joint can weaken and shrink. For example, shoulder bursitis can weaken the deltoids and rotator cuff muscles. This makes it hard to do everyday tasks.
Untreated bursitis also changes how we move. People might move differently to avoid pain. This can put extra stress on other joints and muscles.
For instance, hip bursitis might make someone change their walking to avoid pain. This can strain the lower back or knee joints. Over time, this can cause chronic pain and dysfunction in other areas.
The inflammation from bursitis can also harm tendons and ligaments. Tendons connect muscles to bones, and ligaments connect bones to each other. They can become strained or inflamed due to the changed movement patterns and increased stress.
Knee bursitis, for example, can inflame the tendons and ligaments around the knee. This leads to more pain and instability.
Lastly, untreated bursitis can cause long-term problems with joint stability. Chronic inflammation and changed movement patterns can weaken the joint. This makes it more likely to become unstable and injured.
Chronic shoulder bursitis, for example, can weaken the shoulder muscles and change how it moves. This increases the risk of shoulder dislocation or other injuries.
| Musculoskeletal Complication | Description | Potential Consequences |
| Muscle Weakness and Atrophy | Reduced muscle mass and strength due to disuse | Impaired joint function, reduced mobility |
| Altered Biomechanics | Changes in movement patterns to avoid pain | Strain on other joints and muscles, chronic pain |
| Impact on Tendons and Ligaments | Strain or inflammation of surrounding tendons and ligaments | Additional pain, instability, and possible further injury |
| Long-term Joint Stability Issues | Compromised joint integrity due to chronic inflammation | Increased risk of joint dislocation, further injury, and chronic dysfunction |
It’s important to know about the risks of joint damage and degeneration from chronic bursitis. This condition can cause serious problems with joint health. It can lead to cartilage breakdown and osteoarthritis.
Chronic bursitis causes ongoing inflammation around the joints. This can wear down the joint structures. The inflammation can also damage cartilage, which is key for smooth movement.
Cartilage breakdown is a big worry with chronic bursitis. The inflammation can cause cartilage to break down. This leads to pain and makes it hard to move the joint. If not treated, it can get worse.
Chronic bursitis and osteoarthritis are closely linked. The inflammation from bursitis can speed up the damage seen in osteoarthritis. This can make joint health decline faster.
Chronic bursitis can also cause other changes in the joint. It can lead to bone spurs. These changes can make it harder for the joint to function and can worsen joint degeneration.
| Condition | Effect on Joint | Potential Complications |
| Chronic Bursitis | Inflammation around the joint | Cartilage degradation, osteoarthritis |
| Osteoarthritis | Degeneration of joint cartilage and bone | Joint pain, limited mobility |
| Bone Spurs | Abnormal bone growth | Additional joint damage, pain |
Nerve compression is a serious issue that can come from bursitis. It leads to neurological symptoms that can really affect your life. When bursitis happens, the swelling can press on nerves, causing many problems.
The swelling of the bursa can put pressure on nerves. This can cause pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness. The bursa’s close location to nerves makes it prone to compression, mainly in the shoulder, hip, and elbow.
People with bursitis and nerve compression may have symptoms like:
These symptoms can be different in everyone and can really affect your daily life.
If nerve compression from bursitis isn’t treated, it can cause permanent nerve damage. It’s important to treat the bursitis and nerve compression quickly. Chronic nerve compression can cause permanent damage, so early treatment is key.
Nerve compression can harm both sensory and motor functions. Sensory problems might include pain, numbness, or strange feelings. Motor function issues can cause weakness or less mobility. Fixing nerve function is important for better mobility and avoiding long-term problems.
It’s important to know about the neurological problems caused by bursitis. Treating both the bursitis and nerve compression can help avoid long-term issues. This approach can improve patient outcomes.
Bursitis can make it hard for people to do everyday tasks and work. It affects their quality of life a lot.
Bursitis causes pain and stiffness. This makes it tough for people to do their jobs well. It can lead to less work done, more time off, and more injuries.
Jobs that are hard on the body increase the risk of bursitis. It makes the job even harder, leading to more tiredness and less mobility. Employers should help by making work safer and supporting workers with bursitis.
Bursitis can cost a lot in healthcare, lost work time, and less money made. Here’s a look at the costs:
| Economic Factor | Impact of Bursitis | Estimated Cost |
| Healthcare Costs | Increased medical expenses | $1,000 – $3,000 per year |
| Lost Productivity | Reduced work hours and efficiency | $5,000 – $10,000 per year |
| Disability Benefits | Financial support for disabled individuals | $10,000 – $20,000 per year |
Bursitis doesn’t just hurt work life. It also makes everyday tasks hard. Like getting dressed or cooking. Managing bursitis well is key to staying independent and happy.
In severe cases of bursitis, the condition can spread beyond the initial area of inflammation. This can affect overall health. The body’s response to inflammation can overwhelm it, leading to secondary health issues.
Severe bursitis can cause an intense inflammatory response. This response can spread to multiple organ systems. It may lead to sepsis or systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS).
The release of pro-inflammatory cytokines into the bloodstream can cause widespread effects. These include fever, fatigue, and malaise.
In severe cases of bursitis, there’s a higher risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism. Inflammation can also lead to circulatory problems. This is because the body’s response to injury can affect blood vessel function and blood pressure.
Chronic inflammation from severe bursitis can deeply affect the immune system. Prolonged exposure to inflammatory mediators can lead to immune dysregulation. This makes the body more susceptible to infections or autoimmune conditions.
The immune system’s response to chronic inflammation can also lead to the production of autoantibodies. This can trigger or worsen autoimmune diseases. Also, the constant activation of immune cells can result in immune exhaustion. This impairs the body’s ability to fight off infections effectively.
Severe bursitis can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. It can lead to sleep disturbances and chronic fatigue. Pain and discomfort from bursitis can make it hard to sleep well. The systemic effects of chronic inflammation can also contribute to persistent fatigue.
These symptoms can create a vicious cycle. Poor sleep can worsen fatigue, and fatigue can make pain perception worse. This makes it challenging to manage the condition effectively.
When treating bursitis, it’s important to think about the patient’s health. This is true for groups like the elderly, athletes, people with autoimmune conditions, and diabetic patients. Each group faces special challenges with bursitis.
Elderly people are more likely to face serious problems from bursitis. This is because they often have less mobility and more health issues. Older adults are at a higher risk for developing chronic bursitis, which can really affect their life quality. We need to take these factors into account when treating them.
Athletes, who do sports that involve a lot of overhead movements or pressure on joints, are at a higher risk for bursitis. The repetitive stress can lead to chronic inflammation, making it hard to manage symptoms and prevent long-term damage. It’s important to have treatment and prevention plans tailored for athletes to help them recover faster and perform better.
People with autoimmune conditions, like rheumatoid arthritis, are more likely to get bursitis because their immune systems are weakened. The presence of autoimmune disorders can complicate the diagnosis and treatment of bursitis, needing a detailed approach that considers both conditions. We must be careful in managing these patients to avoid bad outcomes.
Diabetic patients are at a higher risk for infections and slower healing because of their glucose issues. Bursitis in diabetic patients can lead to more severe complications, like septic bursitis, which needs quick and effective treatment. It’s important to manage blood glucose levels well and watch for signs of infection in this group.
When treating bursitis, knowing the possible complications is key. Treatment can help reduce inflammation and ease symptoms. But, it comes with its own set of risks.
Medicines like NSAIDs and corticosteroids are often used to treat bursitis. But, they can have serious side effects. NSAIDs can cause stomach problems like ulcers and bleeding, mainly if used for a long time.
Corticosteroids help reduce inflammation but can cause weight gain, mood swings, and higher blood sugar levels.
Corticosteroid injections are a common treatment for bursitis. They provide relief from inflammation. But, they can cause problems like infection, nerve damage, and tendon rupture.
The risk of infection is high, as it can lead to septic bursitis. This is a serious condition that needs immediate medical care.
In some cases, removing the bursa (bursectomy) through surgery is needed. Surgery is generally safe but comes with risks like infection, bleeding, and nerve damage. The recovery can be long, requiring physical therapy to regain strength and mobility.
Recovering from bursitis treatment, whether medical or surgical, can be tough. Patients may face pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. This can affect daily life and work.
A good rehabilitation program is key to help patients fully recover and prevent future bursitis episodes.
We must think about these possible complications when planning bursitis treatment. We aim to minimize risks while effectively managing the condition.
Knowing when to get medical help for bursitis is important. Bursitis is when the bursae get inflamed. It can really affect your daily life if not treated right.
Some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. Look out for severe pain, swelling, or redness around the joint. Also, watch for fever.
Severe pain that makes it hard to move or sleep is a big warning sign.
Infection or septic bursitis is very serious and needs quick medical care. Look for signs like more redness, warmth, swelling, or pus around the bursa. Also, fever or chills are signs to watch for.
If you see these, get medical help right away.
| Symptom | Description |
| Increased Redness | The area around the bursa becomes more red or inflamed. |
| Warmth or Swelling | The affected area feels warm to the touch or becomes swollen. |
| Fever or Chills | Presence of fever or chills, indicating a possible infection. |
Nerve problems can show up as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the limb. This means the bursitis might be pressing on or irritating nerves. You should see a doctor about this.
If your symptoms don’t get better or get worse, it might mean treatment isn’t working. This could be because of many reasons, like not treating it right, other health issues, or complications. Keep an eye on your symptoms and tell your doctor about any changes.
Knowing when to get medical help for bursitis is important to avoid lasting damage. By spotting red flags, signs of infection, nerve problems, and treatment failure, you can start getting better sooner.
To avoid serious complications from bursitis, we need a multi-step plan. Understanding and using these strategies can greatly lower the risk of problems. This helps those with bursitis get better faster.
Acting fast when bursitis symptoms start is key. Getting medical help right away can stop the condition from getting worse. Early treatment can cut down inflammation, ease pain, and get the area working right again. We suggest seeing a doctor as soon as symptoms show up to find the best treatment.
Studies show early action makes a big difference in managing bursitis. Tackling the issue early means less pain and less chance of lasting harm.
Keeping a good posture and body mechanics is vital, mainly for those who do repetitive tasks or manual labor. Setting up workspaces to support good posture and ease joint stress can help avoid bursitis.
Also, being careful with body mechanics in everyday life can prevent bursitis. This means avoiding repetitive actions, taking breaks, and lifting correctly.
For those in high-risk activities or sports, wearing protective equipment is a must. This includes knee pads, elbow pads, and other gear to protect joints from impacts and frictions.
Wearing the right protective gear can greatly lower the risk of bursitis and other injuries. It’s also important to make sure the gear fits well and is used correctly for the best protection.
Doing strengthening and flexibility programs can help prevent bursitis. These exercises improve joint stability and lessen bursae strain. Strengthening the muscles around the joint adds extra support and protection.
Flexibility exercises, like stretching, also help keep joints moving freely and lower bursitis risk. A customized exercise plan, based on the individual’s needs and activities, is a great way to prevent bursitis.
Bursitis is a complex condition that can have serious effects if not treated well. We’ve looked at what bursitis is, its types, risks, and possible complications in this article.
Knowing the dangers of bursitis is key to making good treatment plans. We’ve talked about different bursitis types, like shoulder and knee, and their risks.
Early action, good ergonomics, and protective gear are vital to avoid serious issues. By managing bursitis well, people can avoid long-term damage and other serious problems.
We hope this article has given a clear view of bursitis and how to manage it. This should help people take charge of their condition and get the right medical care.
Bursitis causes pain, swelling, and limited movement in the joint. The pain can be sharp or ongoing. Swelling may also bring redness and warmth.
Doctors use a physical exam, medical history, and imaging tests like X-rays or MRI to diagnose bursitis. Sometimes, they rule out other conditions to make a diagnosis.
Untreated bursitis can cause chronic pain and limited mobility. It also raises the risk of infection. Without treatment, it can damage joints and lead to disability.
Yes, bursitis can cause serious infections like septic bursitis. It can also weaken muscles, change how joints move, and harm tendons and ligaments.
To prevent bursitis, take breaks to rest and stretch. Use proper ergonomics and wear protective gear. Also, do exercises to strengthen and stretch.
Treatments include medicine, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery. Medicines like NSAIDs and corticosteroids help. Physical therapy improves strength and range of motion.
Bursitis can be managed well, but it’s not always curable. Proper treatment and prevention can reduce risks and improve life quality.
Bursitis can limit mobility and reduce productivity. It also affects mental health, causing anxiety and depression.
Yes, elderly, athletes, people with autoimmune diseases, and diabetics are at higher risk. They need extra care to avoid complications.
Signs include more pain, swelling, redness, and warmth. Fever and chills are also signs. Seek medical help right away if you notice these.
Yes, chronic bursitis can damage joints over time. This includes cartilage loss and osteoarthritis. Early treatment and prevention can help avoid this.
Managing chronic bursitis needs a mix of medicine, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and prevention. A healthcare professional can help create a good plan.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!