Diagnostic radiology is a key medical field. It helps doctors find important answers inside the body. This leads to better care for patients through quick and accurate diagnoses.
This field uses many medical imaging methods. These include X-rays, CT scans, MRI, ultrasound, and nuclear medicine. They help create images of the body’s inside parts.
Diagnostic radiologists are key in finding and treating diseases. They look at imaging results and work with other doctors to help patients.

Diagnostic radiology uses many imaging methods to find and diagnose health issues. It’s a key part of healthcare today. It lets doctors see inside the body and find problems accurately.
Diagnostic radiology is a medical field that uses X-rays, CT scans, MRI, ultrasound, and nuclear medicine to find diseases. Its main goal is to give doctors clear images for accurate diagnoses. Diagnostic radiologic imaging is essential for patient care. It helps find and treat health issues early.
Different imaging methods are used for different health questions. For example, X-rays are good for bone problems, and MRI is better for soft tissue issues.
Diagnostic radiology has grown a lot, starting with Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen’s discovery of X-rays in 1895. New technologies have brought us CT scans and MRI. These have changed how we diagnose diseases.
Medical imaging has come a long way. It has made diagnostic radiology a complex and ever-changing field.
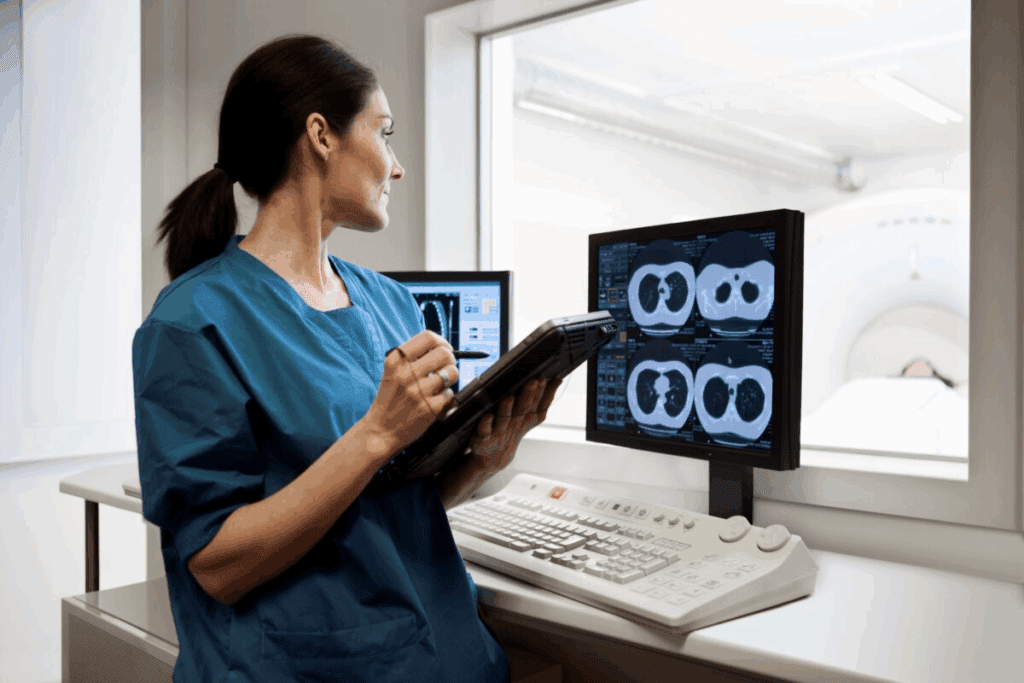

Diagnostic and interventional radiology use imaging tech, but in different ways. Diagnostic radiology looks at images to find diseases. Interventional radiology uses images to guide treatments.
Diagnostic radiology uses X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound to see inside the body. These non-invasive diagnostic approaches help doctors find many conditions without surgery. They look at these images to spot problems and help with patient care.
Interventional radiology does image-guided therapeutic interventions to treat diseases. They use imaging to guide procedures like biopsies and tumor treatments. These methods are less invasive than surgery, helping patients recover faster and with fewer risks.
This shows how wide-ranging radiology is in healthcare. It goes from finding diseases to treating them.
Diagnostic radiology uses key imaging modalities to see inside the body. These technologies have changed medical imaging a lot. They help doctors diagnose and treat many health issues well.
X-rays are a basic imaging tech in diagnostic radiology. They use ionizing radiation to show the body’s inside, mainly bones. Doctors use X-rays to find fractures, check for foreign bodies, and see lung issues.
X-rays are everywhere and give quick results. This makes them key in both emergency and regular checks.
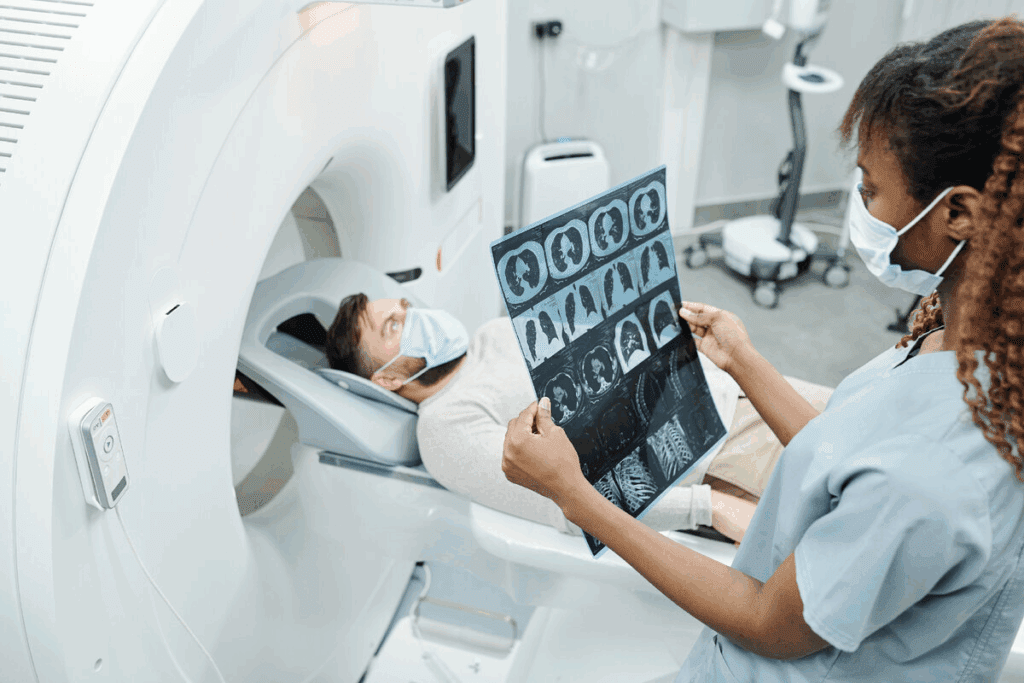
Computed Tomography (CT) scanning is advanced imaging tech. It uses computer-processed X-rays to show detailed body cross-sections. CT scans give more info than X-rays, helping find many health issues like vascular diseases and cancers.
CT scans are fast and accurate. They’re very useful in emergency situations.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is non-invasive imaging. It uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to show body details. MRI is great for soft tissues like organs and tendons.
It’s key for checking the brain, spine, and muscles. MRI gives clear images without ionizing radiation.
Ultrasound imaging, or sonography, uses sound waves to show body details. It’s safe, non-invasive, and not too expensive. Ultrasound is often used for pregnancy and abdominal checks.
It’s good for finding issues with the gallbladder, liver, kidneys, and reproductive organs. Its live imaging helps with procedures.
In summary, X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound are vital in diagnostic radiology. Each has its own uses and benefits. These technologies have greatly improved medical diagnostics, leading to better patient care.
Advanced imaging methods are changing how doctors diagnose and treat diseases. These new technologies have made diagnostic radiology better. Now, healthcare providers can give more accurate and effective care to patients.
Nuclear medicine and molecular imaging are key in diagnostic radiology. They use small amounts of radioactive materials to diagnose and treat diseases. Molecular imaging lets us see biological processes at the molecular level. This gives us insights into how diseases work and grow.
Techniques like scintigraphy and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) give detailed info about organs and tissues. This info is vital for diagnosing and managing diseases, including cancer and neurological disorders.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a complex imaging method. It shows the metabolic activity of tissues and organs. PET scans are great for oncology, neurology, and cardiology. They help doctors diagnose and monitor diseases better.
PET imaging uses a radioactive tracer, like fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). This tracer goes to areas with high metabolic activity. It helps find abnormalities, like tumors, and check how well treatments are working.
The field of diagnostic radiology is always changing. New technologies and techniques are coming to make diagnosis more accurate and patient care better. Emerging technologies, like hybrid imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) applications, will be key in the future.
These new advancements will help healthcare providers give more personalized and effective care. This will improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Diagnostic radiologists use imaging technologies to help doctors make decisions. They are medical doctors who use X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound to diagnose and treat diseases.
They are key in looking at images to find problems. They check for abnormalities, diagnose conditions, and see how severe diseases are. This involves:
They need to know a lot about human anatomy, disease, and how imaging works.
They work closely with other doctors. They give detailed reports of what they find in images. This is key for patient care. They:
Good communication is important for the best care for patients.
They also make sure imaging is done right and safely. They:
By improving imaging, they help patients and save money.
Diagnostic radiological services are key for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. They have changed medicine by giving doctors detailed views of the body.
Diagnostic radiology has many uses in patient care. It impacts several areas importantly.
Diagnostic imaging helps find diseases early. This is vital for quick treatment and better results. Tools like mammography and low-dose CT scans are used for screening. They help spot conditions like cancer early.
Diagnostic radiology is key for planning and tracking treatment. MRI and CT scans give detailed info on disease extent. This helps doctors create focused treatment plans.
In emergencies, diagnostic radiology quickly checks injury extent. X-rays and CT scans are used for trauma patients. They help doctors make quick decisions.
Key Benefits:
Diagnostic radiological services boost patient care and outcomes. They support early disease detection, treatment planning, and emergency assessment.
General diagnostic radiology has many subspecialties for different medical needs. These focus on specific body areas or imaging types. They help improve diagnosis and care for patients.
Neuroradiology deals with brain, spine, and nervous system disorders. It uses MRI and CT scans for detailed images of complex conditions.
Musculoskeletal imaging looks at muscle, bone, and joint issues. It’s key for checking injuries, infections, and chronic problems like arthritis.
Cardiovascular radiology images the heart and blood vessels. It uses angiography and cardiac MRI to spot and track heart diseases, aiding in treatment plans.
Pediatric diagnostic imaging meets the unique needs of children. It needs special skills and methods for safe and effective tests on young patients.
Subspecialties in diagnostic radiology work together for full care. For complex cases, images from several areas are needed for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
These subspecialties show the wide range and complexity of diagnostic radiology. They highlight the need for specialized knowledge and training.
Patient experience and safety are key in diagnostic radiology. It’s important to give patients top-notch care and keep risks low.
Radiation safety is a big deal in diagnostic radiology. Optimizing radiation doses is key to keep exposure low and image quality high. This is done through:
These steps help reduce the risks of radiation exposure.
Getting patients ready for radiological exams is important. It ensures their safety and comfort. This includes:
By educating patients and addressing their concerns, healthcare providers can improve the patient experience in diagnostic radiology.
Diagnostic radiology is key in today’s healthcare. It helps doctors find and treat many health issues. The field keeps growing with new imaging tech and expert radiologists.
Radiology in medicine includes many imaging tools like X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound. These tools have changed how doctors diagnose and care for patients.
Diagnostic radiology has many uses, from finding diseases early to planning treatments. It also helps track how well treatments are working. Special areas like neuroradiology and musculoskeletal imaging show how complex and vital it is.
In conclusion, diagnostic radiology is a changing field that’s vital for healthcare’s future. Its role in improving patient care and outcomes is huge. It’s a critical part of today’s medical practice related to the radiology definition medical.
Diagnostic radiology is a medical field. It uses X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound to find and track health issues.
They look at imaging results and talk to doctors. They also make sure imaging is done well.
Diagnostic radiology uses non-invasive methods. Interventional radiology uses procedures guided by images.
Key technologies include X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound.
Nuclear medicine uses tiny amounts of radioactive materials. It helps diagnose and treat diseases, often with other imaging.
PET scans show how active body cells are. They help find and track diseases like cancer.
They help by giving accurate diagnoses. They guide treatment and track disease changes.
Subspecialties include neuroradiology, musculoskeletal imaging, and more. They focus on specific areas like the brain or bones.
Safety comes from using the right amount of radiation. Equipment is kept in good shape, and protocols are followed.
Patients should follow their doctor’s instructions. This might mean fasting or avoiding certain medicines.
It’s vital for early disease detection. It helps make treatment plans and improves patient care.
It’s the use of imaging to see inside the body. This includes X-rays, CT scans, and more.
Radiology is a field that uses images to diagnose and treat diseases. Diagnostic radiology is a big part of it.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!