Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
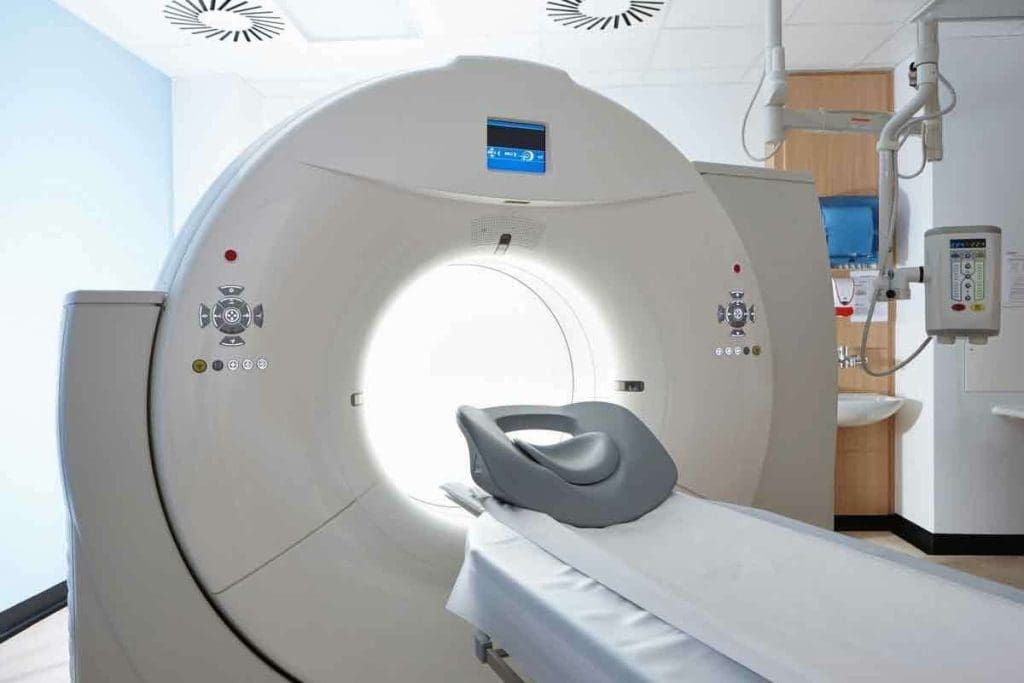
difference between cat scan and MRI
Understanding the difference between cat scan and MRI is key to your health. At Liv Hospital, we focus on top-notch, patient-focused care and excellence.
CT scans use X-rays, while MRIs use strong magnets and radio waves.
Key Takeaways
- CT scans use X-rays, while MRIs use strong magnets and radio waves.
- CT scans are faster, taking only a few minutes, whereas MRI scans can last between 20 and 40 minutes.
- CT scans involve a small dose of ionizing radiation, whereas MRI scans do not.
- CT scans are often used in emergency situations and for evaluating a wide range of conditions.
- MRIs are preferred for evaluating certain organs and soft tissues, detecting certain cancers, and detecting changes in the brain or bone.
Understanding Medical Imaging Technologies
Medical imaging technologies have changed how we diagnose diseases. CT scans and MRIs are key tools in this field. They help doctors give accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
What is a CAT/CT Scan?
A CAT/CT scan uses X-rays to make detailed images of the body. CT scans are very useful in emergencies. They help find injuries or bleeding inside the body.
During a CT scan, the patient lies on a table that moves into a big machine. The machine sends out X-rays that pass through the body. Detectors then measure these X-rays to create detailed images.
What is an MRI?
MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. It uses strong magnets and radio waves to make detailed images. MRIs are great for seeing soft tissues, like the brain and joints. They also help find tumors, inflammation, and infections.
In an MRI, the patient is in a strong magnetic field. Radio waves disturb the body’s hydrogen atoms. These signals help create detailed images.
Basic Principles of Each Technology
CT scans and MRIs work in different ways. CT scans use X-rays, while MRIs use magnetic fields and radio waves. This affects the images they produce and their safety and use.
- CT scans are best for emergency situations and finding acute trauma.
- MRIs are better for soft tissues, joints, and the brain.
- Knowing how these technologies work helps doctors choose the right tool for each patient.
To show the difference, here’s an image:
Understanding CT scans and MRIs helps doctors make better choices. This ensures patients get the best diagnosis and treatment.
The Fundamental Difference Between CT Scan and MRI: Technology
CT scans and MRIs are two different ways to see inside the body. They use different technologies to make images of what’s inside us.
X-rays vs. Magnetic Fields and Radio Waves
CT scans and MRIs use different methods to create images. CT scans use X-rays, while MRIs use strong magnetic fields and radio waves. This difference affects the images they make and the information they give about our bodies.
CT scans make detailed pictures of bones and lungs using X-rays. MRIs, on the other hand, make detailed pictures of soft tissues using magnetic fields and radio waves.
How Each Technology Creates Images
CT scans and MRIs make images in different ways. CT scans rotate an X-ray source around the body to capture data. This data is then turned into detailed images using special algorithms.
MRIs, on the other hand, use a strong magnetic field to align hydrogen atoms in the body. Radio waves disturb these atoms, and the signals they send back are used to make the images.
Equipment Differences
The equipment for CT scans and MRIs is different. CT scanners are faster and more common, making them good for emergencies. MRI machines take longer to make images, but are better for soft tissues. They are also more expensive.
| Feature | CT Scan | MRI |
| Primary Technology | X-rays | Magnetic Fields and Radio Waves |
| Image Detail for Soft Tissues | Limited | High |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Typical Use Cases | Emergency, Bone Fractures, Lung Imaging | Soft Tissue Imaging, Detailed Structural Analysis |
Image Quality and Detail Comparison
Choosing between CT scans and MRIs often depends on the needed detail for a correct diagnosis. Each has its own strengths and is best for different medical needs.
We will look at when one might be better than the other based on image quality and detail.
When CT Scans Provide Better Images
CT scans are great for seeing bones, lungs, and finding acute trauma. They give quick, clear images that are key in emergencies. For example, they’re often first used to check for injuries from accidents or find internal bleeding.
- Clear bone imaging: CT scans show bones well, making them perfect for finding fractures or bone problems.
- Lung imaging: They’re good at showing lung images, helping spot issues like pneumonia or lung nodules.
- Acute trauma detection: CT scans are used in emergency rooms to quickly check for injuries and find internal injuries or bleeding.
When MRIs Offer Superior Detail
MRIs are top for soft tissues, joints, and the brain. They’re key for diagnosing issues in these areas, like neurological problems, musculoskeletal injuries, or some cancers.
- Soft tissue differentiation: MRIs can tell soft tissues apart, making them better for diagnosing issues with organs and soft tissues.
- Joint and musculoskeletal imaging: They show joints and muscles well, helping diagnose injuries or conditions like tendonitis or ligament sprains.
- Brain and neurological imaging: MRIs are great for brain images and diagnosing neurological issues, like stroke, tumors, or multiple sclerosis.
Research on Imaging Effectiveness
Many studies have compared CT scans and MRIs in different situations. The choice between them should depend on the clinical question and the patient’s condition.
For detailed soft tissue images, MRIs are usually better. But for emergencies or bone imaging, CT scans are often the best choice.
Time Requirements: Speed of Imaging
Medical imaging speed is as vital as image quality. In emergencies or acute conditions, quick imaging tests are key to better patient care.
CT Scan Duration and Process
CT scans are fast. Scanning itself takes under a minute. But getting ready and positioning can add a few minutes. On average, a CT scan takes about 15 minutes from start to finish.
Key factors influencing CT scan duration include:
- The specific body part being scanned
- The need for contrast agents
- The patient’s condition and ability to remain steady
MRI Duration and Process
MRI scans take longer than CT scans. They can last from 20 to 90 minutes. This depends on the scan’s complexity and the body parts involved.
Factors affecting MRI duration include:
- The type of MRI (e.g., functional MRI, cardiac MRI)
- The need for multiple sequences or contrast agents
- The patient’s ability to stay calm during the scan
The American College of Radiology notes, “MRI offers great soft tissue detail but needs more time and patient cooperation than CT scans.”
Why Speed Matters in Medical Diagnosis
Speed is critical in medical diagnosis, like in stroke or trauma cases. Quick imaging helps doctors make fast decisions and act quickly. This can greatly improve patient care.
“Time is brain” is a mantra often used in stroke treatment, highlighting the importance of rapid imaging and intervention.
-Neurologist
A comparison of the time requirements for CT scans and MRIs is provided in the table below:
| Imaging Modality | Typical Duration | Factors Influencing Duration |
| CT Scan | Under 15 minutes | Body part scanned, need for contrast |
| MRI | 20 to 90 minutes | Type of MRI, multiple sequences, patient cooperation |
In conclusion, while both CT scans and MRIs are important in medical diagnosis, their different times can affect their use, mainly in urgent situations.
Cost Considerations: CT Scans vs. MRIs
When it comes to diagnostic imaging, knowing the cost difference between CT scans and MRIs is key. This knowledge helps both patients and healthcare providers manage expenses. It also affects patient choices.
Factors Influencing the Cost of MRIs
MRIs usually cost more than CT scans. This is because MRI technology is complex, using strong magnetic fields and radio waves. Also, MRI procedures take longer and need more technical skill, adding to the cost.
Key factors that drive up MRI costs include:
- The high cost of purchasing and maintaining MRI machines
- The need for specialized technicians to operate MRI equipment
- The longer duration of MRI procedures compared to CT scans
Insurance Coverage for CT Scans and MRIs
Insurance coverage is a big factor in what patients pay out-of-pocket for CT scans or MRIs. Most plans cover both, but how much can vary a lot.
| Imaging Type | Average Cost | Typical Insurance Coverage | Patient Out-of-Pocket |
| CT Scan | $500-$1,500 | 80%-90% | $50-$300 |
| MRI | $1,000-$3,000 | 70%-85% | $150-$600 |
Out-of-Pocket Expenses for Patients
What patients pay for CT scans and MRIs can differ a lot. It depends on their insurance and the healthcare provider. It’s important for patients to know their insurance details and any extra costs for their imaging.
Understanding the costs of CT scans and MRIs helps patients make better choices. It’s vital to talk about costs with healthcare providers and insurance companies. This way, patients can fully understand what they’ll have to pay.
Radiation Exposure and Safety Concerns
Medical imaging safety is a big deal for everyone. We need to know how safe CT scans and MRI are. This helps us decide which one is better for each patient.
Ionizing Radiation in CT Scans
CT scans use X-rays to see inside the body. This means they expose us to ionizing radiation. This kind of radiation can harm DNA and raise cancer risk.
Even though one CT scan is usually safe, many scans can be risky. This is true for kids and young adults more than others.
It’s important to think about these risks before getting a CT scan. New CT tech makes it safer, but we should always try to use less radiation. Following safety rules helps a lot.
Safety Profile of MRI Technology
MRI doesn’t use ionizing radiation. It uses strong magnets and radio waves instead. This makes MRI safer from radiation.
But MRI has its own risks. For example, it can affect some implants or devices. Some people can’t have an MRI because of this.
For many, MRI is safer than CT scans because it doesn’t use radiation. But it’s not always the best choice for everyone.
Risk Assessment for Different Patient Groups
When looking at risks, we must think about each patient’s needs. For example, pregnant women and children are more at risk from radiation. So, MRI might be safer for them.
But, some patients might prefer CT scans. This could be because MRI machines are closed in or they have metal implants. We need to choose the best imaging for each person.
By considering each patient’s situation, we can make sure they get the safest imaging. This way, we help them get the best care possible.
Clinical Applications: When to Use Each Imaging Method
CT scans and MRIs have different uses in healthcare. Knowing when to use each is key for doctors to care for patients well.
Ideal Scenarios for CT Scans
CT scans are great in emergencies because they’re fast. They’re best for finding injuries like brain bleeding, fractures, and internal damage. They’re the top choice for trauma cases because they show bones, lungs, and solid organs clearly.
Here are some times when CT scans are best:
- Trauma and emergency situations
- Finding internal injuries or bleeding
- Helping with biopsies and other procedures
Optimal Uses for MRI Technology
MRI is better for non-emergency cases needing soft tissue detail. It’s great for brain, spine, and joint issues, and some cancers.
MRI’s detailed soft tissue images are key for complex conditions like multiple sclerosis, some neurological problems, and muscle injuries.
| Imaging Modality | Ideal for | Not Ideal for |
| CT Scan | Emergency situations, trauma, internal injuries | Soft tissue detailed imaging |
| MRI | Soft tissue imaging, non-emergency diagnoses | Acute trauma, emergency situations |
Emergency vs. Non-Emergency Imaging
Choosing between CT scans and MRI depends on the urgency. CT scans are quicker and better for emergencies. MRI is better for detailed soft tissue images in non-emergency cases.
Knowing each imaging method’s strengths helps doctors make better choices. This leads to better care for patients.
Patient Experience During Imaging Procedures
It’s important to know how patients feel during medical imaging tests. This knowledge helps both doctors and patients. When we talk about CT scans and MRIs, we must think about how each test makes patients feel.
What to Expect During a CT Scan
CT scans are usually quick and easy. Patients are in and out in about 30 minutes. They lie on a table that moves into a big, ring-shaped machine. The machine takes X-ray pictures from all sides.
Preparation is simple, like removing metal items and maybe getting a contrast agent. The scan is painless, but some might feel uncomfortable from staying very quiet or from the contrast agent.
What to Expect During an MRI
MRI tests can take longer and might be more uncomfortable for some. The scan can last from 15 to 90 minutes. Patients must stay very quiet in a big, tube-like machine.
The machine’s loud noises are a big issue during an MRI. Patients often get earplugs or headphones to help. Like CT scans, MRIs might use a contrast agent too.
Claustrophobia and Other Comfort Considerations
One big worry for MRI patients is claustrophobia. The tight space of the MRI machine can scare or upset some people. For these patients, open MRI machines or sedation might be suggested.
To understand the differences in how patients feel during CT scans and MRIs, let’s look at a comparison:
| Procedure | CT Scan | MRI |
| Duration | Typically under 30 minutes | 15 to 90 minutes |
| Claustrophobia Concerns | Less likely to cause claustrophobia | More likely due to the enclosed space |
| Noise Level | Minimal noise | Loud knocking or banging sounds |
Knowing these differences helps doctors prepare patients better. This makes the experience better for everyone.
Preparation Requirements for Patients
Patients getting ready for CT scans and MRIs have to follow certain steps. These steps help make sure the tests go well. We’re here to help you understand what you need to do.
Preparing for a CT Scan
Before a CT scan, you’ll need to:
- Take off any metal items, like jewelry or glasses, that might get in the way.
- Wear clothes that are easy to move in.
- Follow special diet rules, which might mean not eating for a while.
Some CT scans use a special dye to make things clearer. We’ll talk more about this dye later.
Preparing for an MRI
MRI prep is similar to CT scan prep, but there are some differences:
- Remove all metal things, like piercings, glasses, and clothes with metal.
- Tell your doctor about any metal implants, like pacemakers.
- Some MRIs use a dye.
If you’re scared of tight spaces, we have open MRI machines or sedation to help.
Contrast Agents and Their Use
Contrast agents help make things clearer in medical images. Both CT scans and MRIs might use them, but they’re different.
| Imaging Type | Contrast Agent Type | Administration Method |
| CT Scan | Iodine-based or Barium | Oral or Intravenous |
| MRI | Gadololinium-based | Intravenous |
Knowing how to prepare for your CT scan or MRI is key. It helps get the best images and accurate results. If you have questions, talk to your doctor.
Common Misconceptions About CT and MRI Scans
There’s a lot of wrong information about CT scans and MRI technology. This can confuse patients and affect their choices about medical tests. We want to clear up some common myths.
Are CT Scans Magnetic?
Many people think CT scans are magnetic because they’re used with MRI machines. But, CT scans are not magnetic. They use X-rays to show what’s inside the body. The mix-up comes from some CT scan parts having magnets, but the main tech is X-ray, not magnetism.
Radiation Myths and Facts
There’s a big misunderstanding about radiation. It’s true that CT scans use ionizing radiation, which can raise cancer risk, mainly in kids. But the radiation from one CT scan is usually small.
Some worry about long-term radiation effects from CT scans. True, long-term exposure is a worry. But CT scans are often needed fast, and their benefits can be big, even for emergencies.
Understanding Image Limitations
People think CT scans and MRIs show the same details. But, each has its own good points and bad points. MRIs are better for soft tissues, while CT scans are better for bones and finding bleeding fast. Knowing these differences helps pick the right test for a problem.
We hope to help patients make better health choices by clearing up these myths. It’s important to talk to a doctor about any worries or questions. This way, you get the right info for your health.
Conclusion
Knowing the differences between CT scans and MRIs is key to making smart choices about medical imaging. We’ve looked at how they differ in technology, image quality, time needed, cost, radiation, and how they’re used in medicine.
Choosing between CT scans and MRIs depends on the medical need. This includes the type of tissue being looked at and the situation. By knowing these differences, patients and doctors can pick the best imaging method.
CT scans are quicker and better for urgent cases. MRIs, on the other hand, show more detail for soft tissues. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks. The choice should match the patient’s condition and medical history.
In wrapping up our look at CT scans vs MRI, it’s clear they’re both essential in healthcare. Picking the right imaging method helps get accurate diagnoses and effective treatments. This leads to better health outcomes for patients.
FAQ
What is the main difference between a CT scan and an MRI?
CT scans use X-rays to create images. MRIs, on the other hand, use magnetic fields and radio waves.
Which is better for emergency situations, a CT scan or an MRI?
CT scans are better for emergencies. They can quickly show internal injuries.
Are CT scans and MRIs used for the same purposes?
No, they are not used for the same things. CT scans are good for bones and lungs. MRIs are better for soft tissues and the brain.
How do CT scans and MRIs compare in terms of image quality?
MRIs show soft tissues better. CT scans are better for bones and chest imaging.
Is there a significant difference in the time required for CT scans and MRIs?
Yes, CT scans are much faster. They take just a few minutes. MRIs can take 15 to 90 minutes.
Are CT scans and MRIs equally safe?
Both have safety concerns. CT scans use radiation. MRIs are safer but not for everyone, like those with metal implants.
How do the costs of CT scans and MRIs compare?
MRIs are usually more expensive. Costs can vary based on insurance and the need for contrast agents.
Can CT scans and MRIs be used interchangeably?
No, the choice depends on the medical condition. Each imaging type is needed for accurate diagnosis.
Are there any specific preparations required for CT scans and MRIs?
Yes, patients need to follow certain instructions. This includes fasting and removing metal objects. Contrast agents may also be needed.
Is it true that CT scans are magnetic?
No, CT scans are not magnetic. They use X-rays. MRIs, on the other hand, use strong magnetic fields.
How do CT scans and MRIs handle claustrophobia?
MRIs can be hard for those with claustrophobia. Some MRI facilities offer open machines or sedation to help.
What are the advantages of choosing Liv Hospital for CT scans and MRIs?
Liv Hospital aims for world-class care. We ensure accurate diagnoses and support for all imaging procedures.
References:
- Journal of International Crisis and Risk Communication Research. (2024). Comparison of CT and MRI for Brain Imaging: Review Article, 337“351. https://jicrcr.com/index.php/jicrcr/article/view/364