Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir

Difference in PET Scan and CT Scan: Understanding Cancer Imaging
A cancer diagnosis requires quick and accurate testing. Both PET scans and CT scans are essential tools in detecting and managing cancer, but they serve different purposes. Understanding the difference in PET scan and CT scan can help patients make informed decisions about their care.
A CT scan uses X-rays to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures, such as bones, organs, and tissues. It helps doctors locate tumors and assess their size and shape.
A PET scan, on the other hand, shows how the body’s cells are functioning by detecting metabolic activity using a safe radioactive tracer. It helps reveal whether cancer cells are active and if the disease has spread.
At Liv Hospital, we combine both PET and CT imaging for precise cancer diagnosis and treatment planning. Our expert team ensures that every patient receives accurate results, clear explanations, and compassionate care throughout their journey.
Key Takeaways
- PET scans are often used to diagnose and assess tumors affecting various parts of the body.
- CT scans provide more detailed images and are typically used to diagnose and assess cancers.
- A PET/CT scan combines the benefits of both imaging modalities for a more accurate diagnosis.
- PET scans can detect cellular changes, increasing the likelihood of finding cancer early.
- Both PET and CT scans are painless and take about 30 minutes to complete.
The Critical Role of Imaging in Cancer Diagnosis
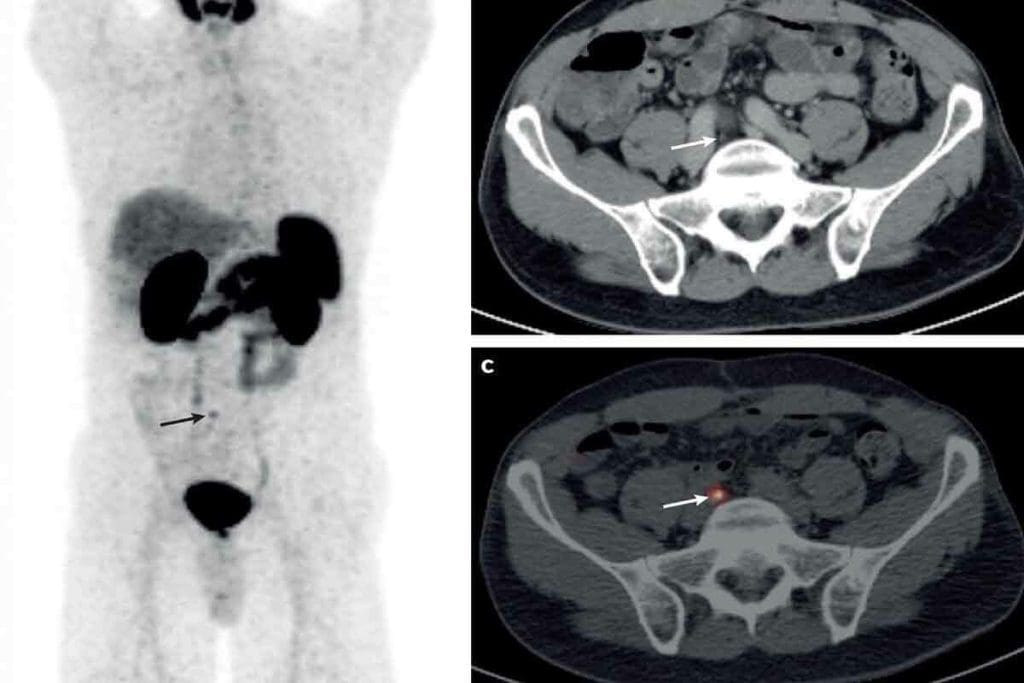
Imaging technologies are key in finding and treating cancer. Tools like PET and CT scans have changed how we fight cancer. They show where tumors are and how active they are.
How Medical Imaging Guides Treatment Decisions
Medical imaging does more than just find tumors. It helps doctors decide how to treat them. PET and CT scans show the tumor’s size, where it is, and how fast it’s growing. This helps doctors plan the best treatment.
Choosing between PET and CT scans is important. CT scans show the body’s structure, while PET scans show how active the tumor is. This info helps doctors create a detailed treatment plan.
| Imaging Modality | Primary Use in Cancer Diagnosis | Key Benefits |
| CT Scan | Anatomical imaging, detecting structural abnormalities | High-resolution images of tumor size and location |
| PET Scan | Functional imaging, assessing metabolic activity | Provides information on tumor aggressiveness and spread |
The Evolution of Cancer Imaging Technologies
Cancer imaging has come a long way. From X-rays to today’s PET/CT and PET/MRI, we’ve made huge strides. These new tools help doctors diagnose and treat cancer better.
Using PET and CT together has improved cancer diagnosis. This combo gives doctors detailed info on tumors. It helps them make better choices for patient care.
What is a CT Scan?
A CT scan is a high-tech tool that uses X-rays from different angles to create detailed images inside the body. It helps doctors find and track many health issues, like cancer, very accurately.
How CT Technology Works
CT technology uses a moving X-ray tube and a detector to take pictures from all sides. A computer then makes detailed images of the body’s inside parts. This whole process is fast and doesn’t hurt, taking just a few minutes.
The Process of Undergoing a CT Scan
Getting a CT scan is easy. You lie on a table that slides into a big CT scanner. You hold your breath while the scan is done. From start to finish, it takes about 30 minutes.
Common Applications in Cancer Detection
CT scans are key in finding, checking, and monitoring cancer. They show how big and where tumors are, helping doctors plan the best treatment. Here’s a table showing how CT scans help with cancer:
| Cancer Type | Application of CT Scan | Benefits |
| Lung Cancer | Detection and staging | Helps identify tumor size and location |
| Colorectal Cancer | Monitoring treatment response | Assesses changes in tumor size |
| Lymphoma | Staging and assessing disease extent | Provides detailed images of lymph nodes |
CT scans are vital for spotting and managing cancer. Knowing what CT scans can do helps us make better choices for cancer imaging.
What is a PET Scan?
PET scans are key in finding cancer early. They look at how cells work, not just their shape. This helps doctors see what’s going on inside the body.
The Science Behind PET Imaging
PET scans work by spotting how cancer cells use energy. PET scans use small amounts of radioactive tracers, attached to sugar, to see this. Cancer cells use more sugar, so they show up more on the scan.
“The ability of PET scans to assess metabolic activity makes them invaluable in oncology,” notes a leading expert in nuclear medicine. “It’s not just about seeing the anatomy; it’s about understanding the biology of the disease.”
Radiotracer Use and Metabolic Activity Detection
The main tracer used is Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). It goes to areas that use a lot of sugar, like cancer. The PET scanner then shows where this sugar is, helping doctors see where the cancer is.
Patient Experience During a PET Scan
Getting a PET scan is easy. Patients usually fast before and avoid hard activities. They lie on a table that slides into the scanner for 30 to 60 minutes. It’s not painful, but some might feel trapped or uncomfortable.
Knowing about PET scans can make patients feel better. They help doctors see how cells are working. This helps make treatment plans and check if they’re working.
The Fundamental Difference Between PET Scans and CT Scanss
It’s important to know how PET scans and CT scans differ for cancer diagnosis. These tools have different uses and benefits. They are both key in fighting cancer.
Structural vs. Functional Imaging Approaches
CT scans show detailed structural information of the body’s inside. They help see tumor size and location. PET scans, on the other hand, look at functional imaging. They spot metabolic activity, like high glucose uptake in tumors.
CT scans give clear views of body parts. PET scans show how cells work. Together, they help fully understand cancer.
Resolution and Detail Comparison
CT scans have better spatial resolution for detailed anatomy. PET scans don’t have the same detail but show metabolic activity. This is ketoor cancer.
PET/CT scans combine both. They offer detailed anatomy and metabolic info in one scan. This makes diagnosis more accurate and is now common in cancer care.
Radiation Exposure Considerations
PET and CT scans both use radiation. CT scans use X-rays, while PET scans use a radioactive tracer. Knowing the radiation dose is key to safe imaging.
In summary, PET scans and CT scans are different but work together in cancer care. Knowing their differences helps doctors choose the best imaging for patients.
Key Difference #1: Detection Capabilities of PET Scan Versus CT Scan
It’s important to know how PET scans and CT scans work for cancer diagnosis. Both are key in finding cancer, but they do it in different ways.
CT Scans’ Strength in Anatomical Visualization
CT scans are great at showing the body’s inside parts clearly. They help doctors see tumors’ size and where they are. This is key for planning surgery and knowing how far cancer has spread.
PET Scans’ Ability to Detect Metabolic Changes
PET scans look at how active cells are in the body. They use a special tracer to find cancer cells, which use more energy. This helps find cancer early, even before it’s big.
Sensitivity and Specificity Comparison
PET scans are better at finding cancer early because they see metabolic changes. For more on PET scans vs CT scans. CT scans are better at showing where tumors are exactly. Using both together gives a full picture of cancer.
In short, CT scans show body parts well, and PET scans show cell activity. Together, they help find and understand cancer better.
Key Difference #2: Timing in Cancer Diagnosis
Knowing the timing differences between PET scans and CT scans is key to cancer diagnosis. Finding cancer early can greatly improve treatment results.
Early Detection Capabilities
PET scans are great at finding cancer early. They spot metabolic changes in the body. This lets them find cancer before CT scans can.
Early detection is critical for better treatment results. PET scans can spot cancer cells early, even when there are few. This makes them very useful for early diagnosis.
When PET Outperforms CT in Cancer Timeline
PET scans are better than CT scans for early cancer detection, mainly for cancers with high metabolic rates. They can spot the increased glucose metabolism of cancer cells.
| Cancer Type | PET Scan Detection | CT Scan Detection |
| Lymphoma | Early metabolic changes | Later anatomical changes |
| Lung Cancer | Metabolic activity | Anatomical abnormalities |
Limitations of Each Modality in Early Detection
PET scans are good at finding metabolic changes, but CT scans show detailed anatomy. CT scans might not spot cancer until it’s big enough to be seen anatomically.
Each method has its own issues. For example, PET scans can sometimes show false positives due to inflammation or infection. CT scans rely on size and anatomical changes to find tumors.
Choosing between PET and CT scans depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health.
Key Difference #3: Accuracy in Staging Cancer
Accurate cancer staging is key. It helps doctors know how far cancer has spread. This is vital for choosing the right treatment. PET and CT scans are both important, but they work differently.
How CT Scans Map Cancer Spread
CT scans show detailed pictures of the inside of the body. They help find tumors and see if cancer has spread. But, they might miss cancer in normal-sized lymph nodes or when changes are small.
PET Scans’ Role in Determining Cancer Aggressiveness
PET scans show how active tumors are. They find areas with lots of activity, which means cancer cells are growing. This helps doctors understand how aggressive the cancer is.
The Difference Between PET CT Scan and CT Scan for Staging
PET/CT scans combine PET and CT scans. They give both functional and anatomical details. This combo is better at finding cancer spread and local disease than CT scans alone.
In summary, CT scans are great for body details, while PET scans show tumor activity. Together in PET/CT scans, they improve cancer staging. This makes PET/CT scans a top choice for many cancers.
Key Difference #4: Treatment Planning Applications
PET scans and CT scans are key in cancer treatment planning. They help with radiation therapy and checking how well treatments work. Imaging tech is vital in this process.
Using CT for Radiation Therapy Planning
CT scans are great for planning radiation therapy. They give detailed pictures of the body’s structures. This helps doctors target tumors well and avoid harming healthy tissues.
The high-resolution images from CT scans help doctors see tumors and important areas clearly.
PET’s Value in Determining Treatment Response
PET scans show how active tumors are, helping doctors see if treatments are working. They check metabolic changes to see if treatments are effective.
PET scans are great because they can show early if a treatment is working. This is before any changes are seen on CT scans.
Monitoring Cancer Recurrence: CT vs PET Scan for Cancer
Both CT and PET scans help watch for cancer coming back. But they look for different things. CT scans find changes in the body’s shape that might mean cancer is back.
PET scans find metabolic changes that could mean cancer is returning. They are good at spotting these changes early.
| Imaging Modality | Primary Use in Cancer Treatment Planning | Key Benefits |
| CT Scan | Radiation Therapy Planning | High-resolution anatomical images, precise tumor targeting |
| PET Scan | Assessing Treatment Response | Early detection of metabolic changes guides treatment adjustments |
In conclusion, the choice between PET scans and CT scans depends on what’s needed in treatment planning. Knowing what each can do is key to good care and treatment.
Key Difference #5: Cost and Accessibility Factors
It’s important to know the cost and availability differences between PET and CT scans. These factors can greatly affect how cancer is diagnosed and treated.
Comparing Procedure Costs
The cost of PET and CT scans varies a lot. It depends on the hospital, location, and whether the tests are used too. PET scans are usually pricier because of the special dye used. In the U.S., a PET scan can cost between $1,000 and $3,000 or more. CT scans, on the other hand, can range from $300 to $1,500.
Other things, like contrast agents for CT scans or special preparation for PET scans, can also raise costs. These details can make a big difference in the total cost.
Insurance Coverage for PET vs CT Scan Cancer Diagnostics
Insurance coverage is getincludesng PET and CT scans for cancer. Most plans cover both, but how much can vary. Medicare and Medicaid usually cover them if they’re needed, but there might be rules.
It’s vital for patients to check their insurance. They should know what they’ll have to pay out of pocket. The differences in coverage can affect which scan is chosen.
Availability of Technology Across Healthcare Settings
Where you can get PET and CT scans differs. CT scanners are more common in hospitals and clinics. PET scanners are less common and often found in big hospitals or special centers.
PET/CT scanners, which do both, are becoming more common. But, they’re not everywhere, and can be hard to find in rural or less served areas.
Key Difference #6: Patient Considerations for CT Scan or PET Scan for Cancer
Choosing between a CT scan and a PET scan for cancer depends on many factors. These include how ready you are for the test, how long it takes, how comfortable you feel, and your health conditions.
Preparation Requirements
For a CT scan, you might need to take off metal items and drink a contrast agent. This helps doctors see certain parts of your body better. But getting ready for a PET scan is more complex. You’ll need to fast for hours beforehand and might have to skip some medications or activities.
Key preparation differences include:
- CT scans: Removing metal objects, possibly consuming a contrast agent.
- PET scans: Fasting for several hours, avoiding certain medications or activities.
Procedure Duration and Comfort
CT scans are usually faster, lasting 10-30 minutes. PET scans, though, can take longer because of the time it takes for the radiotracer to spread through your body.
Comfort levels during the procedures can differ:
- CT scans are straightforward. You lie on a table that slides into the scanner.
- PET scans also require lying down, but they can be longer. Some people might find it uncomfortable because they have to stay very quiet for a long time.
Contraindications and Special Populations
Some conditions or situations might make one scan better than the other. For instance, people with kidney disease might face risks with CT scan contrast agents. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid PET scans because of radiation.
Special considerations include:
| Condition | CT Scan Consideration | PET Scan Consideration |
| Kidney Disease | Risk with contrast agents | Generally safe |
| Pregnancy/Breastfeeding | Radiation exposure concern | Radiation exposure concern |
Key Difference #7: The Power of Combined PET/CT Imaging
The fusion of PET and CT scans into one system has changed how we diagnose cancer. This new method combines CT’s detailed images with PET’s metabolic insights. It gives a deeper look into the disease.
How Integration Enhances Diagnostic Accuracy
Combined PET/CT imaging significantly enhances diagnostic accuracy. It offers both the structure from CT scans and the function from PET scans. This mix helps in:
- Precise localization of tumors
- Accurate assessment of tumor metabolism
- Improved detection of cancer spread
Clinical Scenarios Where PET/CT is Preferred
PET/CT shines in many clinical situations, including:
- Cancer staging: It shows how far cancer has spread.
- Treatment monitoring: It checks if the cancer is responding to treatment.
- Recurrence detection: It spots cancer coming back early.
Future Developments in Hybrid Imaging
The world of hybrid imaging is always growing. Researchers are working on new tracers and better tech. These advancements will likely make PET/CT even better for cancer care.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Cancer Imaging
Knowing the difference between PET scans and CT scans is key to smart cancer imaging choices. We’ve looked at how PET scans and CT scans help find and understand cancer. Each has its own strengths and uses.
When we compare PET scans and CT scans, we see they’re good at different things. CT scans show detailed body structures. But PET scans reveal how cells are working. This mix is vital for picking the best way to diagnose cancer.
Using both PET and CT scans together gives a full picture of cancer. This combo lets doctors make more precise diagnoses and plans. It’s a step towards better cancer care.
In the end, picking between PET scans and CT scans depends on the patient’s needs and cancer type. Knowing the differences helps both patients and doctors make better choices. This leads to better cancer care and outcomes.
FAQ
What is the main difference between a PET scan and a CT scan for cancer diagnosis?
PET scans look at how cells work, while CT scans show the body’s structure. This helps doctors find cancer cells more easily.
How do PET scans and CT scans differ in terms of radiation exposure?
Both scans use radiation, but in different ways. CT scans use X-rays, and PET scans use a small radioactive tracer. The dose from a PET scan can be similar to or a bit more than a CT sscan
Which is more accurate for cancer staging: PET scan or CT scan?
PET scans are better at showing how aggressive cancer is. They look at metabolic changes. CT scans are better at showing where cancer has spread.
Can PET/CT scans be used together for cancer diagnosis?
Yes, PET/CT scans are often used together. They combine detailed body images from CT scans with metabolic info from PET scans. This makes diagnosis more accurate.
How do PET scans and CT scans compare in terms of cost and accessibility?
CT scans are cheaper and easier to find than PET scans. PET scans need special equipment and a radiotracer, making them pricier and less common.
What are the preparation requirements for a PET scan versus a CT scan?
For a PET scan, you usually need to fast and avoid certain medications. CT scans might need contrast dye and fasting, but the prep is simpler.
Are there any contraindications for PET scans or CT scans?
Yes, some conditions make one or both scans not safe. For example, severe kidney disease might stop CT scans with contrast. Pregnancy or breastfeeding is a concern for both scans due to radiation.
How do PET scans and CT scans differ in their ability to detect cancer early?
PET scans might spot cancer sooner than CT scans because they look at metabolic changes. But early detection depends on the cancer type and imaging methods used.
What is the role of PET/CT scans in treatment planning for cancer?
PET/CT scans help plan cancer treatment by showing tumor details. This info is key for radiation therapy and checking treatment success.
Can PET scans or CT scans be used to monitor cancer recurrence?
Both scans can track cancer recurrence, but PET scans are often preferred. They spot metabolic changes that show cancer is back. The choice depends on the cancer type and clinical situation.
References
- National Health Service (NHS). (2023). Computed tomography (CT) scan. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/computed-tomography-ct-scan/
- Mettler, F. A., Huda, W., Yoshizumi, T. T., & Mahesh, M. (2008). Effective doses in radiology and diagnostic nuclear medicine: A catalog. Radiology, 248(1), 254-263. https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/radiol.2481071451