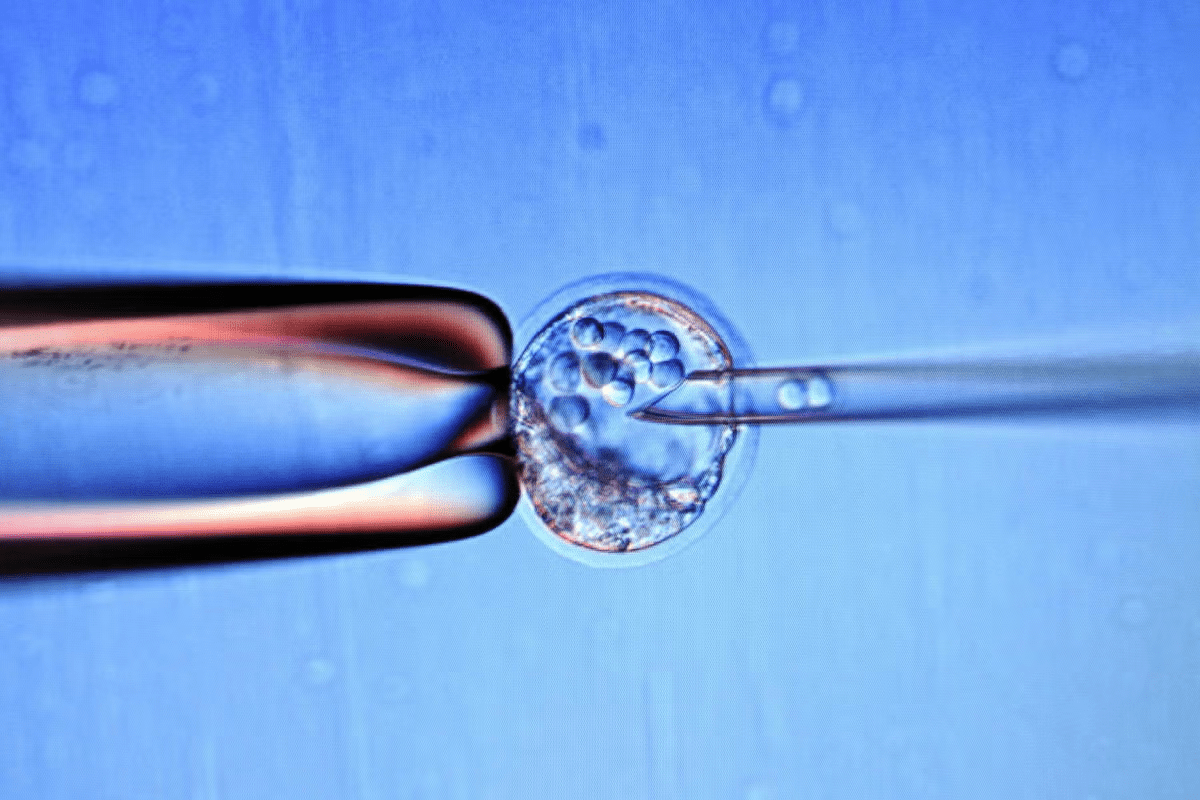
Choosing between fresh and frozen embryo transfer can be tough. At places like Liv Hospital, they focus on you and use the latest in healthcare. This leads to great results worldwide.A balanced look at the disadvantages of frozen embryo transfer compared to a fresh embryo transfer cycle.
New tech has changed how we think about IVF. The International Committee for Monitoring Assisted Reproductive Technologies says at least 12 million babies have been born thanks to IVF embryo transfers and other ARTs.
Studies show frozen embryo transfer (FET) works better for women over 38. Knowing the differences helps patients choose what’s best for them.
Key Takeaways
- The choice between fresh and frozen embryo transfer is key in IVF treatment.
- FET has better success rates for women over 38 years old.
- At least 12 million babies have been born through IVF and other ARTs.
- Patient-centered care helps decide between fresh and frozen transfer.
- New tech has made IVF outcomes better.
Understanding Embryo Transfer in IVF
In the IVF process, embryo transfer is a key moment. It needs precision and care. This step places a fertilized egg, now an embryo, into the woman’s uterus. The goal is to start a successful pregnancy.
What Happens During Embryo Transfer
Our fertility specialists use a pelvic ultrasound to guide the transfer catheter. This ensures the embryo is placed correctly in the uterus. The procedure is usually painless and doesn’t need anesthesia. It’s done with great care to increase the chances of a successful implantation.
The embryo transfer process includes several important steps:
- Preparation of the transfer catheter with the selected embryo
- Guiding the catheter through the cervix into the uterus
- Placement of the embryo in the optimal location within the uterine cavity
- Verification of the embryo’s position using ultrasound
The Role of Embryo Transfer in IVF Success
The success of IVF treatment depends a lot on the embryo transfer process. A successful transfer needs a high-quality embryo and a receptive uterus. Our specialists aim to improve both to increase pregnancy chances.
Key factors influencing IVF success rates include:
| Factor | Description | Impact on Success |
|---|---|---|
| Embryo Quality | Grading based on embryo morphology and development | High-quality embryos have higher success rates |
| Uterine Receptivity | The uterus’s readiness for implantation | Optimal receptivity enhances implantation chances |
| Transfer Technique | The method used for embryo placement | Precise technique improves success rates |
Key Factors Affecting Transfer Outcomes
Several factors can affect the outcome of an embryo transfer. These include the embryo’s quality, the uterus’s receptivity, and the transfer technique. Knowing these factors helps patients make better choices for their IVF treatment.
By understanding these factors and tailoring the treatment, we can boost the chances of a successful pregnancy through IVF.
Fresh Embryo Transfer: The Traditional Approach
[Add image here]
Fresh embryo transfer is a key part of IVF, helping many achieve pregnancy. It involves putting an embryo into the uterus soon after it’s made, usually in 3-5 days. We’ll look into how it works, its timeline, and who it’s best for.
The Fresh Transfer Timeline
The timeline for fresh embryo transfer matches the patient’s natural cycle and egg retrieval. It usually takes 3-5 days after egg retrieval. Here’s what happens in those days:
- Egg retrieval and fertilization
- Embryo culture for 3-5 days
- Assessment of embryo quality
- Transfer of the selected embryo(s) into the uterus
How Fresh Transfers Are Performed
The fresh transfer process is precise and simple. It involves carefully placing the embryo in the uterus with a catheter and ultrasound. This method is gentle and accurate.
Ideal Candidates for Fresh Transfer
Not everyone is a good fit for fresh embryo transfer. Those at low risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) and with a healthy uterus do well. We assess each patient to choose the best transfer method.
| Candidate Characteristics | Ideal for Fresh Transfer | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Typically under 38 years | Age-related decline in egg quality |
| OHSS Risk | Low to moderate risk | High risk may require alternative strategies |
| Uterine Environment | Normal uterine lining | Any abnormalities may affect success rates |
Studies show fresh embryo transfer is good, but frozen embryo transfer (FET) is better for women over 38. This shows the need for tailored IVF plans.
Frozen Embryo Transfer: The Modern Alternative
Frozen embryo transfer has changed IVF treatment a lot. It’s a better choice than fresh embryo transfer. This method gives more flexibility and can lead to better results in IVF cycles.
More people are choosing frozen embryo transfer now. This is because of better freezing technologies and the benefits for IVF patients.
The Freezing Process Explained
Freezing embryos involves a few key steps. First, embryos grow to the blastocyst stage, 5-7 days after fertilization. Then, they are frozen using a quick cooling method called vitrification.
Vitrification stops ice crystals from forming in the embryo. This greatly improves survival rates when thawing. It’s now the main method used in most IVF clinics.
Vitrification Technology Advancements
New technology in vitrification has made frozen embryo transfers better. Modern methods use more cryoprotectants and cool faster.
These changes have made frozen embryo survival rates as good as, or even better than, fresh ones. The table below shows how survival rates have improved over time.
| Year | Survival Rate |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 80% |
| 2015 | 90% |
| 2020 | 95% |
The FET Procedure Step-by-Step
The frozen embryo transfer (FET) process is simple and less invasive than fresh transfers. Here’s how it works:
- Preparation of the uterine lining through hormonal treatment
- Monitoring of the uterine lining to determine the optimal transfer time
- Thawing of the frozen embryo
- Transfer of the thawed embryo into the uterus
- Post-transfer support with hormonal medications
The FET procedure has many benefits. It lets for genetic testing before transfer and lowers the risk of OHSS.
Knowing about the freezing process, vitrification advancements, and the FET steps helps patients make better choices for their IVF treatment.
Success Rates: Fresh vs Frozen Transfers
When thinking about IVF, knowing the success rates of fresh versus frozen embryo transfers is key. This choice can greatly affect the treatment’s outcome.
Overall Success Rate Comparisons
Research shows frozen embryo transfers (FET) are now as good as fresh ones in success rates. Recent studies suggest FET can be better for some patients. For example, a study in the Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics found FET had higher live birth rates than fresh transfers.
Success rates between fresh and frozen transfers vary. This depends on embryo quality, the woman’s age, and the IVF method used.
Age-Related Success Differences
Age is a big factor in both fresh and frozen transfer success. Research shows FET is better for women over 38. In this age group, FET live birth rates are 1.4 to 5.4 times higher than fresh transfers.
“The use of frozen embryo transfer has been shown to be very beneficial for older women, giving them significantly higher live birth rates than fresh transfers.”
Embryo Quality Impact on Outcomes
Embryo quality is also key in success rates. High-quality embryos lead to successful pregnancies, whether fresh or frozen. Better technology for freezing embryos has made FET a better option.
- Assessing embryo quality involves looking at its shape and genetic health.
- Techniques like preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) help choose better embryos.
- Vitrification has greatly improved frozen embryo transfer outcomes.
Recent Research Findings
New studies have given more insight into fresh and frozen transfer success rates. A meta-analysis in Fertility and Sterility found FET had higher live birth rates and lower OHSS risk than fresh transfers.
It’s clear that both fresh and frozen transfers have their roles in IVF. The right choice depends on the patient’s situation, medical history, and specific needs.
Advantages of Fresh Embryo Transfer
Fresh embryo transfer is a traditional method in IVF. It has many benefits for patients. This method makes the process faster, cutting down the time from egg retrieval to embryo transfer.
Shorter Treatment Timeline
One big plus of fresh embryo transfer is the shorter time it takes. Patients can have their embryo transferred just days after egg retrieval. This quicker process is great for those who want to start a family quickly or are on a tight schedule.
Lower Overall Treatment Costs
Fresh embryo transfer also means lower overall treatment costs. It avoids the need for freezing and thawing embryos. This saves money on freezing and storing embryos. It makes IVF more affordable for those worried about costs.
Avoiding Freeze-Thaw Risks
Another advantage is avoiding risks from freezing and thawing. Even with modern techniques, there’s a small risk of damage. By using fresh embryos, patients can minimize this risk and possibly have better success rates.
Psychological Benefits of Quicker Process
The quicker process also has big psychological benefits. IVF can be very stressful, and finishing faster is a big plus. By using fresh embryos, patients can reduce the emotional burden of long treatment cycles.
In summary, fresh embryo transfer has many benefits. It’s faster, cheaper, avoids risks, and is less stressful. These reasons make it a popular choice for many IVF patients.
Disadvantages of Frozen Embryo Transfer
Choosing frozen embryo transfer (FET) means looking at its good points and bad. FET is a key part of IVF, giving patients flexibility and sometimes better success rates. But, it also has its own set of challenges.
Extended Treatment Timeline
FET takes longer than fresh embryo transfer. It needs extra time for freezing and getting the uterus ready. This can be tough for those who want to start a family quickly.
Additional Cryopreservation Costs
FET costs more because of the freezing process. Special equipment and places are needed for freezing and storing embryos. These costs can be a big problem for many, affecting their IVF budget.
Potential Embryo Damage During Freeze-Thaw
There’s a risk of damage to embryos during freezing and thawing. Even with new technology, this is something to think about. The health of the embryo is key for a successful transfer.
Emotional Impact of Waiting
The wait for FET can be hard on patients emotionally. The time between the first IVF and the FET can be stressful. It’s important for patients to prepare for this wait emotionally.
| Disadvantage | Description | Impact on Patients |
|---|---|---|
| Extended Treatment Timeline | Additional time required for cryopreservation and uterine lining preparation | Increased stress and longer wait for pregnancy |
| Additional Cryopreservation Costs | Costs associated with freezing and storing embryos | Financial burden on patients |
| Potential Embryo Damage | Risk of damage to embryos during freeze-thaw process | Potential reduction in success rates |
| Emotional Impact of Waiting | Stress and anxiety caused by delay between IVF cycle and FET | Increased emotional strain on patients |
Recent studies show FET works better for women over 38. This shows how important it is to think about each person’s situation when looking at FET’s downsides.
Medical Considerations for Each Transfer Type
Choosing between fresh and frozen embryo transfer depends on many medical factors. Our specialists look at these carefully for each patient. This helps make a choice that increases the chances of a successful IVF outcome.
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome Risk
OHSS risk is a big medical consideration. Patients at risk might do better with frozen embryo transfer. This avoids the risk of OHSS during a stimulated cycle. Our team watches patients closely during stimulation to spot risks and plan how to lower them.
Endometrial Receptivity Factors
How well the endometrium receives the embryo is key. The endometrium’s thickness, texture, and hormones play a big role. Sometimes, frozen embryo transfer is better because it lets the endometrium develop more naturally, which can help with implantation.
Hormonal Environment Differences
The hormonal environment changes a lot between fresh and frozen transfers. Fresh transfers are influenced by stimulation, which can affect how well the endometrium receives the embryo. Frozen transfers, on the other hand, happen in a more natural cycle, which might be better for implantation.
Pre-existing Medical Conditions
Medical conditions like PCOS, endometriosis, or thyroid issues can affect the choice of transfer type. Our team looks at how these conditions might impact treatment. For example, PCOS patients might face a higher risk of OHSS, making frozen transfer a better option.
We aim to create a treatment plan that’s right for each patient. By considering these medical factors, we can improve the chances of success. Our goal is to offer the safest and most effective treatment, tailored to each person’s needs.
Making Your Decision: Key Factors to Consider
Choosing between fresh and frozen embryo transfer in IVF is a big decision. It depends on many personal factors.
Your Age and Fertility Status
Your age and fertility status are key. Women under 35 often see good results with both fresh and frozen transfers. But, women over 38 might do better with frozen transfers because of the controlled hormones.
Financial Considerations
Money matters too. Fresh transfers might seem cheaper at first because they don’t have extra freezing costs. But, frozen transfers can save money in the long run because you can try again with the same embryos.
| Factor | Fresh Embryo Transfer | Frozen Embryo Transfer |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower upfront costs | Additional costs for freezing/thawing |
| Success Rate | Variable based on ovarian response | Potentially higher due to controlled hormonal environment |
| Timeline | Faster, as it’s part of the same cycle | Longer, as it requires a separate cycle |
Timeline Preferences
Your timeline preferences also matter. If you want to start a family quickly, fresh transfers might be better. But, if you need more time, frozen transfers offer flexibility.
Doctor Recommendations
Your fertility specialist’s advice is very important. They will look at your medical history and current health to help you decide. It’s important to talk openly with your doctor about your options.
Choosing between fresh and frozen embryo transfer is a personal decision. It should be based on your age, fertility, financial situation, timeline, and your doctor’s advice. By thinking about these factors, you can make a choice that fits your unique situation and goals.
Conclusion: Personalizing Your IVF Journey
Choosing between fresh and frozen embryo transfer is a personal decision. It depends on your medical history, age, and what you prefer. Studies show frozen embryo transfer (FET) works better for women over 38. This shows how important it is to think about your own situation when picking an IVF option.
Both fresh and frozen embryo transfers have their benefits. Knowing what each offers helps you make a choice that fits your needs. At our place, we offer top-notch healthcare and support for patients from around the world. We help you through every step of your fertility treatment to get the best results.
By looking at your own situation and talking to a healthcare provider, you can pick the best IVF path for you. It might be fresh or frozen embryo transfer. Our aim is to give you the care and support you need to succeed in your IVF journey.
FAQ
What is the difference between fresh and frozen embryo transfer?
Fresh embryo transfer happens soon after fertilization, usually in 3-5 days. Frozen embryo transfer freezes embryos at the blastocyst stage. Then, they are transferred later.
What are the advantages of fresh embryo transfer?
Fresh embryo transfer is quicker. It might cost less and avoids risks from freezing. It also feels faster, which is a big plus.
What are the disadvantages of frozen embryo transfer?
Frozen embryo transfer takes longer. It costs more for freezing. There’s a risk of damage during thawing. Waiting can be tough emotionally.
How do success rates compare between fresh and frozen embryo transfers?
Frozen embryo transfers are getting better. Some studies show they work better for certain ages. Success depends on age, embryo quality, and health.
What medical considerations should be taken into account when deciding between fresh and frozen embryo transfer?
Think about OHSS risk, how well the uterus accepts the embryo, and hormone differences. Also, any health issues you have. These can affect your choice.
How does the risk of OHSS impact the decision between fresh and frozen embryo transfer?
If you’re at risk for OHSS, frozen transfer might be safer. It avoids risks from fresh transfer during stimulation.
What is vitrification, and how has it improved frozen embryo transfer?
Vitrification is a fast freeze method. It has greatly improved embryo survival. This makes frozen transfer a strong option against fresh.
How do I decide between fresh and frozen embryo transfer?
Consider your age, fertility, budget, and how fast you want to move. Talk to your fertility doctor for advice.
Is frozen embryo transfer more expensive than fresh embryo transfer?
Frozen transfer might cost more for freezing. But, the total cost difference depends on your situation.
Can I choose between fresh and frozen embryo transfer based on my personal preferences?
Yes, your personal preferences matter. Think about your timeline and emotional readiness. Talk to your doctor to decide.
What is the impact of age on the success of fresh versus frozen embryo transfer?
Age is key for both methods. Frozen might work better for some ages. But, it varies by person.
How does embryo quality affect the outcome of fresh and frozen embryo transfer?
Good embryo quality is essential. It boosts success chances, whether fresh or frozen. High-quality embryos lead to better outcomes.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Fresh Versus Frozen Embryo Transfer: IVF Technology Impact. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6852395/