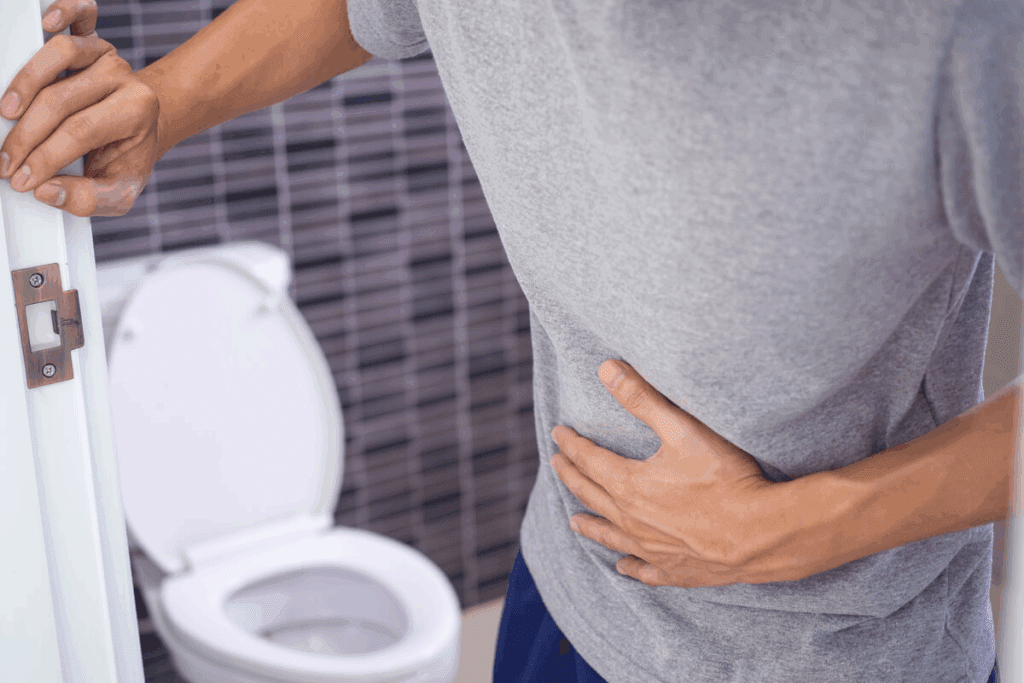
Having both kidney stones and digestive problems can be confusing.do kidney stones cause diarrheaWhat can you not do after stem cells? Many people wonder if one causes the other.
The truth is more complex. Kidney stones don’t directly cause diarrhea. But, they share links through dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and inflammation in the gut.
At Liv Hospital, we have decades of experience in treating complex conditions. It’s important to understand how kidney stones and diarrhea are connected. This helps us diagnose and treat them properly.
Key Takeaways
- The relationship between kidney stones and diarrhea is complex and not directly causal.
- Dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and gastrointestinal inflammation are key connections.
- Understanding these connections is key for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers complete care for patients with kidney stones and digestive issues.
- Expert diagnosis and treatment plans are vital for managing both conditions well.
Understanding Kidney Stones: Causes and Formation

It’s important to know about the causes and types of kidney stones. This knowledge helps in finding the right treatment and ways to prevent them. Kidney stones are not all the same. Each type has its own causes and risk factors.
Types of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can be classified into several types based on their composition. The most common types include:
- Calcium stones: These are the most common type, often linked to dietary factors and metabolic conditions.
- Uric acid stones: These stones are associated with diet, obesity, and certain medical conditions.
- Struvite stones: Typically resulting from urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Cystine stones: These are rare and usually occur in people with a genetic disorder that causes cystine to leak into the urine.
Knowing the type of kidney stone is essential for guiding treatment decisions and preventive measures.
| Type of Kidney Stone | Causes and Risk Factors |
| Calcium Stones | Dietary factors, metabolic conditions, family history |
| Uric Acid Stones | Diet, obesity, diabetes, certain medications |
| Struvite Stones | Urinary tract infections (UTIs), urinary tract abnormalities |
| Cystine Stones | Genetic disorder causing cystinuria |
Risk Factors for Kidney Stone Development
Several factors can increase the risk of developing kidney stones. These include:
- Diet: Consuming foods high in oxalate, sodium, and animal protein can increase the risk.
- Dehydration: Low fluid intake can concentrate minerals in the urine, promoting stone formation.
- Family History: A family history of kidney stones increases an individual’s risk.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions like hyperparathyroidism, cystic kidney diseases, and UTIs can contribute to stone formation.
Studies have shown that approximately 9.14 percent of the population experience kidney stone prevalence. There is a positive correlation between chronic diarrhea and an increased risk of kidney stone formation. Understanding these risk factors can help in the prevention and management of kidney stones.
By recognizing the types of kidney stones and their associated risk factors, healthcare providers can develop targeted treatment plans. This approach not only helps in managing the condition but also in reducing the risk of recurrence.
Kidney Stone Prevalence and Statistics

It’s important to know how common kidney stones are. They affect a lot of people around the world and their numbers are growing. Studies have given us insights into who gets kidney stones and why.
Population Affected
Kidney stones are a common problem that affects millions. The chance of getting them is about 10-15% for men and 5-7% for women. More and more people are getting kidney stones, in many countries.
A 2024 study found that chronic diarrhea increases the risk of kidney stones by 68%. This shows how our gut health can affect our kidneys.
Demographics and Risk Groups
Kidney stones happen more in some groups than others. This is because of genetics, diet, and health conditions.
- Men are more likely to get kidney stones, but the gap is getting smaller.
- People with a family history of kidney stones are at higher risk.
- Those with chronic diarrhea or other gut problems are more likely to get kidney stones because of dehydration and imbalances in electrolytes.
A leading researcher said,
“The link between kidney stones and gut problems, like chronic diarrhea, shows we need to treat these conditions as a whole.”
Knowing who is at risk helps us find better ways to prevent and treat kidney stones.
Common Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can cause a lot of discomfort. Knowing the symptoms is key to getting the right treatment.
Pain Patterns and Locations
The pain from kidney stones is sharp and intense. It usually starts in the side or lower back. It can move to the groin and feel like waves, known as renal colic.
The pain can be so bad that it makes you feel sick to your stomach. You might throw up because of the pain.
Urinary Symptoms
Kidney stones also affect how you pee. You might pee a lot, feel pain while peeing, or see blood in your urine. The pee might look cloudy or smell bad.
In some cases, a stone can block the flow and cause infections.
Systemic Symptoms
Kidney stones can also make you feel sick all over. You might feel nauseous or throw up because of the pain. Sometimes, the blockage can even affect your bowels.
| Symptom Category | Common Symptoms |
| Pain Patterns | Sharp, intense pain in the side or lower back, radiating to the groin |
| Urinary Symptoms | Frequent urination, painful urination, blood in urine, cloudy or foul-smelling urine |
| Systemic Symptoms | Nausea, vomiting, potentially affecting bowel habits |
It’s important to know these symptoms to get help. Kidney stones can be very uncomfortable. But, knowing what to look for can help manage the problem better.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms Associated with Kidney Stones
Kidney stones mainly affect the urinary tract. But, they can also impact the gastrointestinal system. The pain from kidney stones can lead to various symptoms in the stomach and intestines. It’s important to know about these symptoms for better care.
Nausea and Vomiting
Many people with kidney stones feel nauseous and vomit. The pain can send signals to the brain, causing these symptoms. Sometimes, the pain is so bad it makes people throw up without even thinking about it.
Abdominal Discomfort
Abdominal discomfort is another symptom linked to kidney stones. This discomfort can be mild or very severe. It depends on where and how big the stone is. People might feel pain or tenderness in their belly, which can really upset them.
Changes in Bowel Habits
Some people with kidney stones might have changes in their bowel habits. This includes diarrhea. Not everyone will experience this, but it can happen. The connection between kidney stones and bowel habits is complex. It can be influenced by infections or how the body reacts to the stone.
To understand the link between kidney stones and stomach symptoms, let’s look at some data:
| Symptom | Prevalence | Possible Causes |
| Nausea and Vomiting | Common | Severe pain, nervous system response |
| Abdominal Discomfort | Frequent | Location and size of the stone, referred pain |
| Changes in Bowel Habits | Less Common | Kidney infection, indirect effects of kidney stones |
It’s key to know about these stomach symptoms when treating kidney stones. By understanding these symptoms, doctors can give better care and treatment plans.
Do Kidney Stones Cause Diarrhea? Examining the Evidence
Kidney stones are often linked to urinary issues, but research shows they might also affect the gut. We’ll look into studies to see how kidney stones and diarrhea are connected.
Current Research Findings
Studies have looked into how kidney stones and diarrhea are related. They found that kidney stones don’t directly cause diarrhea, but there are links between them. For example, dehydration, common in kidney stone patients, can change bowel habits.
A study in a well-known medical journal found that kidney stone patients often get gastrointestinal symptoms. This is because their body reacts to the pain, which can mess with digestion and cause diarrhea.
Indirect Connections Between Kidney Stones and Diarrhea
There are several ways kidney stones and diarrhea are connected. Dehydration is a big factor. It happens when kidney stones block urine or when people don’t drink enough.
| Factor | Effect on Kidney Stones | Effect on Diarrhea |
| Dehydration | Increases concentration of minerals, potentially leading to stone formation | Can cause constipation, but severe dehydration can lead to diarrhea in some cases |
| Electrolyte Imbalance | Can contribute to the formation of certain types of kidney stones | May cause changes in bowel habits, including diarrhea |
| Severe Pain | N/A | Can lead to gastrointestinal symptoms, including nausea and changes in bowel habits |
Nervous System Response to Severe Pain
The pain from kidney stones can affect the gut. It can cause nausea, vomiting, and changes in bowel habits, like diarrhea.
In summary, kidney stones don’t directly cause diarrhea, but there are connections. Knowing these can help manage symptoms and avoid complications.
How Kidney Stones May Indirectly Lead to Digestive Issues
Kidney stones are mainly linked to urinary tract problems. Yet, they can also affect our digestive system indirectly. The connection between kidney stones and digestive issues is complex. It involves many factors that can harm our gut health.
Medication Side Effects
Some medicines for kidney stone pain can harm our digestive system. For example, opioids can cause constipation, nausea, and vomiting. Some drugs may also irritate the stomach or upset the gut.
It’s important to think about these side effects when treating kidney stones. They can greatly affect a patient’s life quality. Doctors should carefully consider the benefits of pain relief against the risks to the digestive system.
| Medication | Common Side Effects | Digestive Impact |
| Opioids | Constipation, nausea, vomiting | Significant risk of gastrointestinal upset |
| NSAIDs | Stomach pain, heartburn | Moderate risk of stomach irritation |
| Acetaminophen | Liver damage (rare) | Low risk of digestive issues |
Urinary Tract Infections and Inflammation
UTIs linked to kidney stones can cause inflammation. This inflammation may affect bowel habits. A kidney stone can block the urinary tract, creating a perfect environment for bacteria to grow.
UTIs can lead to symptoms like frequent urination, burning while urinating, and stomach pain. The inflammation from a UTI can irritate the intestines. This may change bowel habits or cause discomfort.
Referred Pain and Digestive Function
The pain from kidney stones can indirectly affect digestion. Referred pain can cause stomach discomfort or nausea. This pain can be so severe that it triggers a stress response in the body.
This stress response can affect digestion. It may cause nausea, vomiting, or changes in bowel habits. Understanding these complex interactions is key to treating patients with kidney stones effectively.
The Reverse Connection: How Diarrhea Contributes to Kidney Stone Formation
Gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea can play a big role in kidney stone formation. Kidney stones are known for causing severe pain and urinary symptoms. But their link to stomach problems is also important. We’ll look at how diarrhea leads to kidney stones, focusing on dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and chronic diarrhea’s role.
Dehydration and Mineral Concentration
Diarrhea can lead to dehydration, which is a major factor in kidney stone formation. When we have diarrhea, we lose a lot of fluids. If we don’t drink enough water, dehydration can happen. This dehydration makes our urine more concentrated, which is perfect for stone formation.
It’s key to drink plenty of water to dilute our urine and lower stone risk. But when we have diarrhea, staying hydrated can be tough. We suggest drinking lots of water to prevent dehydration and reduce mineral concentration in our urine.
Electrolyte Imbalances
Diarrhea not only causes dehydration but also leads to electrolyte imbalances. Electrolytes like potassium, sodium, and calcium are important for many bodily functions, including urine regulation. When these electrolytes are out of balance, it can help create kidney stones. For example, low levels of certain electrolytes can change urine pH, making it more likely for stones to form.
Understanding how electrolytes affect kidney stone formation is complex. But it’s clear that keeping them balanced is key. We’ll dive deeper into why electrolyte balance is important for preventing kidney stones.
Chronic Diarrhea as a Risk Factor
Chronic diarrhea is a big risk factor for kidney stones. The ongoing loss of fluids and electrolytes from chronic diarrhea makes it easier for stones to form. People with chronic diarrhea need to be extra careful about staying hydrated and looking after their urinary health.
If you have chronic diarrhea, talk to your doctor about managing it. They might suggest changes to your diet, medications for diarrhea, or more fluid intake to lower your risk of kidney stones.
Understanding Chronic Diarrhea and Its Impact on Kidney Health
Chronic diarrhea is more than just a stomach issue. It can harm our kidneys and lead to kidney stones. It’s important to see how it affects our health, including our kidneys.
Defining Chronic Diarrhea
Chronic diarrhea means having loose stools for over four weeks. It can cause a lot of fluid loss and change our body’s chemistry. This increases the risk of getting kidney stones.
Because it lasts so long, our body keeps losing important fluids and salts. These are key for our kidneys to work right.
Fluid Loss and Calcium Oxalate Crystal Formation
Fluid loss is a big problem with chronic diarrhea. It makes our urine more concentrated. This is perfect for calcium oxalate crystals to form, which are common in kidney stones.
Underlying Conditions That Cause Both Issues
Some conditions can cause both chronic diarrhea and kidney stones. For example, Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis can lead to chronic diarrhea. These diseases affect our digestive system and can also raise the risk of kidney stones.
| Condition | Effect on Kidney Health | Association with Chronic Diarrhea |
| Crohn’s Disease | Increased risk of kidney stones | Common cause of chronic diarrhea |
| Ulcerative Colitis | Potential for dehydration leading to kidney stone formation | Can cause chronic diarrhea |
| Gastrointestinal Infections | Risk of dehydration and electrolyte imbalance | May cause chronic diarrhea |
It’s important to understand how chronic diarrhea affects our kidneys. By fixing the root causes of chronic diarrhea, we can lower the risk of kidney stones. This helps keep our kidneys healthy.
Diagnosing Kidney Stones When Digestive Symptoms Are Present
When kidney stones and digestive symptoms show up together, finding the cause is harder. Doctors need to use many tests to figure out what’s going on. This is because many things can cause similar symptoms.
Differential Diagnosis
It’s important to tell apart kidney stones from other problems that cause similar symptoms. This includes things like appendicitis or inflammatory bowel disease. A good doctor will ask lots of questions and do a physical check to decide what tests to run.
To find out if you have kidney stones when you also have digestive issues, doctors look at a few things:
- The kind and how bad the pain is
- If you have blood in your urine or pain when you pee
- If you’re feeling sick to your stomach, throwing up, or if your bowel habits have changed
- If you’ve eaten something different or had an infection recently
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
To find kidney stones, doctors use imaging and lab tests. Non-contrast CT scans are the best for seeing stones clearly. Ultrasound is used too, like for pregnant women or when CT scans aren’t available.
Lab tests help too:
| Test | Purpose |
| Urinalysis | To check for blood, infection, or other issues in your urine |
| Blood tests | To see how your kidneys are working and if you have an infection or inflammation |
| 24-hour urine collection | To see how much of certain minerals you have, which can help with stone formation |
Working with Healthcare Providers
Getting a good diagnosis and treatment for kidney stones with digestive symptoms needs teamwork. Patients should tell their doctors everything about their symptoms, past health, and what makes them better or worse.
Together, doctors and patients can make a plan that treats both the kidney stones and any digestive problems.
Treatment Approaches for Kidney Stones
Treating kidney stones depends on the stone’s type and the patient’s health. Options range from simple treatments to surgery. Managing pain is key at every step.
Medical Management Options
For small stones, doctors often start with medical management. This method focuses on pain management and helping the stone move through the urinary tract. Alpha-blockers can make it easier for the stone to pass by relaxing the ureter muscles. Drinking lots of water is also important to help flush out the stone.
- Alpha-blockers to relax ureter muscles
- Hydration to help flush out the stone
- Monitoring to ensure the stone is passing
Surgical Interventions
For bigger stones or those causing blockage, surgery might be needed. There are several surgical options:
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): A non-invasive method that breaks the stone into smaller pieces with shock waves.
- Ureteroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure where a small scope is used to remove the stone or break it up with a laser.
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): A more invasive surgery for large stones, involving a small incision in the back to remove the stone directly from the kidney.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain management is vital for treating kidney stones. The pain can be very severe. Strategies include:
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe NSAIDs or opioids to manage pain.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out the stone and reduces pain.
- Medical expulsion therapy: Using medications like alpha-blockers to help the stone pass more quickly and with less pain.
Good pain management helps patients feel more comfortable while waiting for the stone to pass or during further treatment.
Managing Digestive Symptoms During Kidney Stone Episodes
Managing digestive symptoms is key when you have kidney stones. These symptoms can really affect your life. We’ll look at ways to ease these symptoms, making you feel better.
Dietary Modifications
Changing what you eat is important for managing symptoms. Some foods can make things worse, while others can help.
- Avoid foods high in sugar and fat, which can worsen digestive discomfort.
- Incorporate foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, to help regulate bowel movements.
- Stay away from spicy or acidic foods that can irritate the stomach.
Keeping a food diary can help you figure out which foods are troublemakers. This way, you can tailor your diet to your needs.
| Food Type | Recommended | Avoid |
| Fruits | Bananas, Melons | Citrus Fruits |
| Vegetables | Cucumbers, Carrots | Broccoli, Cauliflower |
| Grains | White Rice, Oatmeal | Whole Wheat Bread |
Hydration Strategies
Drinking enough water is critical for kidney stone patients. It helps move stones out and keeps mineral levels balanced.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day, aiming for at least 8-10 glasses.
- Consider increasing fluid intake during periods of high temperature or physical activity.
- Limit beverages that can act as diuretics, such as coffee and alcohol.
Over-the-Counter Remedies
OTC remedies can help with digestive symptoms from kidney stones. But, always check with a doctor before taking any medicine.
- Antacids can help neutralize stomach acid and relieve heartburn.
- Anti-diarrheal medications may be used to manage diarrhea, but should be used cautiously to avoid constipation.
- Gas relief medications can help alleviate bloating and discomfort.
It’s vital to talk to a healthcare provider about the best treatment for your symptoms during kidney stone episodes.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into how kidney stones and diarrhea are connected. Even though kidney stones don’t directly cause diarrhea, there are links between them.
It’s key to understand these connections to help patients. Chronic diarrhea can lead to dehydration and imbalances in electrolytes. This can raise the risk of getting kidney stones.
Healthcare providers can offer better care by knowing these risks. They can improve patient outcomes and quality of life. We should treat both kidney stones and digestive issues together.
In summary, the link between kidney stones and diarrhea shows the need for integrated care. By understanding this complex relationship, we can better support our patients.
FAQ
Do kidney stones directly cause diarrhea?
No, kidney stones don’t directly cause diarrhea. But, they can indirectly affect the gut. Severe pain from kidney stones might mess with the nervous system. This can lead to stomach issues.
Can chronic diarrhea increase the risk of developing kidney stones?
Yes, chronic diarrhea can up the risk of kidney stones. It happens because of dehydration and imbalances in electrolytes. These can make mineral salts in urine concentrate, forming stones.
How do kidney stones affect bowel habits?
Kidney stones can mess with your bowels. The pain they cause might make you feel sick and vomit. This can change your bowel habits, sometimes leading to diarrhea or constipation.
What are the gastrointestinal symptoms associated with kidney stones?
Symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain are common with kidney stones. They can also change your bowel habits, causing diarrhea or constipation.
Can certain medications used to treat kidney stones cause digestive issues?
Yes, some meds for kidney stones can upset your stomach. This might lead to diarrhea as a side effect.
How can patients manage digestive symptoms during kidney stone episodes?
To handle digestive issues with kidney stones, try changing your diet. Stay hydrated and use over-the-counter remedies.
Are individuals with chronic diarrhea at a higher risk of developing kidney stones?
Yes, people with chronic diarrhea are more likely to get kidney stones. This is due to dehydration and imbalances in electrolytes.
Can kidney stones cause constipation?
Yes, kidney stones can cause constipation. The pain and discomfort they bring can change your bowel habits.
How do healthcare providers diagnose kidney stones in patients with digestive symptoms?
Doctors need to do a thorough check-up to diagnose kidney stones in patients with digestive issues. This includes a detailed medical history and the right tests.
What are the treatment options for kidney stones?
Treatment for kidney stones varies. It can include medical management, surgery, or pain relief. The choice depends on the stone’s size, location, and the patient’s symptoms and health.
References
- Amico, J., King, M., & Sahni, S. (2022). Shockwave therapy for erectile dysfunction: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. American Family Physician, 106(7), 410-412. https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2022/1000/fpin-hda-shockwave-therapy-erectile-dysfunction.html