Patients often ask if frozen embryos have a heartbeat. This question is key when thinking about fertility treatments. Knowing the difference between early-stage embryos and growing fetuses is important. Clarifying the status: does a frozen embryo have a heartbeat before transfer and when it develops after implantation.
Frozen embryos are usually frozen when they are about five days old. They have around 128 to 256 cells at this time. They do not have a heartbeat yet. Freezing embryos, or cryopreservation, is a common part of fertility treatments.
We want to make sure you understand about embryo growth and what to expect. Knowing when embryos are frozen and when they start to have a heartbeat is vital. This knowledge helps patients make better choices in fertility treatments.
Key Takeaways
- Frozen embryos are typically frozen at the blastocyst stage.
- At the blastocyst stage, embryos do not have a heartbeat.
- Cryopreservation is a standard practice in fertility treatments.
- Understanding embryo development stages is key for making informed choices.
- Frozen embryos contain around 128 to 256 cells at the time of freezing.
Understanding Embryo Development and Freezing
It’s key to know how embryos grow to understand IVF and embryo freezing. Embryos go through many stages from fertilization to the blastocyst stage in about 5-6 days.
The Journey from Fertilization to Blastocyst Stage
The journey from zygote to blastocyst is vital in IVF. The zygote turns into a blastocyst, a cluster of cells, in 5-6 days. This is a time of fast cell growth and change.
IVF has several steps: ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, and embryo transfer. Freezing embryos at the blastocyst stage is best for implantation.
When Embryo Freezing Typically Occurs
Embryo freezing happens at the blastocyst stage. This is a key moment for implantation or freezing. Freezing at this stage gives people flexibility in IVF treatments.
| Day | Developmental Stage | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fertilization | The egg is fertilized by sperm. |
| 3 | Cleavage Stage | The embryo undergoes several cell divisions. |
| 5-6 | Blastocyst Stage | The embryo develops into a blastocyst, ready for implantation or freezing. |
Knowing about embryo development and freezing helps us see the value of IVF. It shows the importance of using frozen embryos.
Does a Frozen Embryo Have a Heartbeat?
[Add image here]
When embryos are frozen, they are usually at a stage where a heartbeat is not detectable. We will look into the developmental stage of frozen embryos. We will also find out when cardiac activity starts, answering this key question.
The Developmental Stage of Frozen Embryos
Frozen embryos are typically at the blastocyst stage when frozen. This stage is about 5-6 days after fertilization. At this time, the embryo has not yet developed a heartbeat.
The blastocyst stage is key for implantation. It’s the stage right before the embryo would normally implant in the uterus. Freezing happens carefully to keep the embryo’s viability for future transfer.
When Cardiac Activity Actually Begins
Cardiac activity in an embryo starts after thawing and transfer into the uterus. It begins after implantation. A heartbeat is usually detectable around 5-6 weeks into pregnancy.
This time is vital. It marks the start of the embryo’s growth into a fetus with a detectable heartbeat. Monitoring this growth is a key part of prenatal care.
It’s important to know that no heartbeat at the frozen embryo stage is normal. It doesn’t mean the embryo’s development is abnormal.
The Science of Embryo Cryopreservation
Understanding embryo cryopreservation is key for those looking into fertility options. This process, also known as embryo freezing, is used in fertility treatments. It helps preserve embryos for later use, giving hope to many.
Modern Freezing Techniques
Cryopreservation uses vitrification, a modern freezing method. It prevents ice crystals from forming, keeping the embryo intact. This method has greatly improved the success of embryo freezing.
Top labs have seen great success with vitrification. They can thaw up to 99% of frozen blastocyst embryos. This shows how far cryopreservation technology has come.
Success Rates of Embryo Thawing
The success of thawing embryos is vital for cryopreservation. Studies show that vitrification leads to high survival rates after thawing.
| Freezing Technique | Survival Rate | Clinical Pregnancy Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Vitrification | 99% | 50-60% |
| Slow Freezing | 80-90% | 30-40% |
The table shows vitrification beats slow freezing in survival and pregnancy rates. This highlights the need for advanced techniques in embryo cryopreservation.
Research is ongoing to improve embryo cryopreservation. Modern techniques have made it a key part of fertility preservation. They offer new chances for building families.
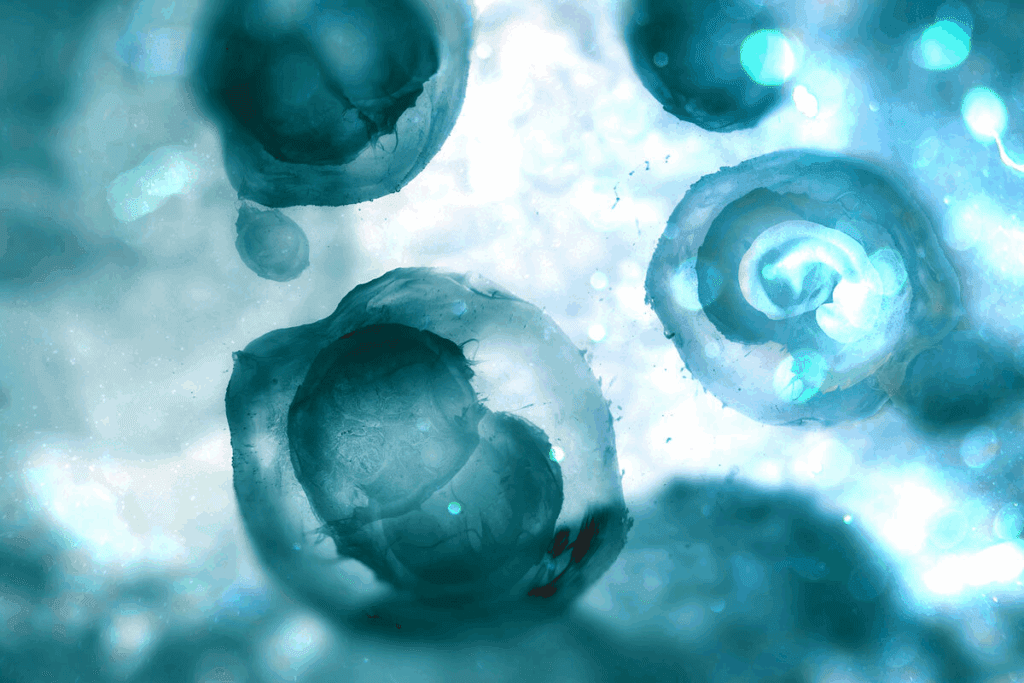
What Do Frozen Embryos Look Like?
Looking at frozen embryos under a microscope shows their unique features. These tiny clusters of cells are saved for future use in IVF treatments.
Microscopic Appearance of Blastocysts
Frozen embryos, usually at the blastocyst stage, look like small, rounded shapes. They might remind you of rice cakes or lumpy circles. This stage is key because the embryo is ready to implant in the uterus.
The look of these embryos can change a bit. This depends on the embryo’s quality and how it was frozen. But, they usually keep their shape well, which is important for them to work after thawing.
Visual Changes Before and After Freezing
Before freezing, embryos are at the blastocyst stage. They have a clear inner cell mass and a trophoblast layer. The freezing method, called vitrification, quickly cools them to stop ice crystals from forming.
After freezing, the embryos look mostly the same as before. Some minor changes might happen because of the cryoprotectants used. When thawed, the embryos are checked for damage and if they’re ready for transfer. High-quality embryos will have little damage and are good for transfer. Seeing these embryos under a microscope before and after freezing is key for checking their quality and success chance.
The Process of Embryo Transfer and Implantation
The journey of a frozen embryo to becoming a viable pregnancy involves a key step: embryo transfer. This is where the thawed embryo is placed into the uterus. It starts the implantation process.
Preparing Frozen Embryos for Transfer
Before the transfer, frozen embryos are thawed using advanced techniques. These methods help the embryos survive the thawing with little damage. The choice of embryo for transfer depends on its quality and the patient’s medical history.
The thawing happens a few hours before the transfer. After thawing, the embryo’s health is checked. The healthiest embryo is chosen for transfer. This careful choice is key for a successful pregnancy.
From Transfer to Heartbeat Development
After the embryo transfer, the next big step is implantation. Implantation happens when the embryo attaches to the uterine lining. This usually occurs 6-10 days after fertilization.
After successful implantation, the embryo starts to grow. A heartbeat can be seen around 5-6 weeks through ultrasound. This is a big milestone, showing the embryo is growing well.
It’s important to remember that while embryo transfer is critical, the heartbeat milestone comes later. Our medical team watches the pregnancy closely to ensure the best results.
Detecting and Monitoring Heartbeat After Transfer
Waiting for the first signs of a heartbeat after embryo transfer is exciting. Knowing when to expect these signs is key. The time after transfer is vital for watching how the embryo grows and stays healthy.
Timeline for Heartbeat Development Post-Transfer
By ultrasound, a heartbeat is usually seen around 5-6 weeks. This time is very important. Knowing what to expect can help manage hopes and worries.
Recent research has made spotting early heartbeats easier with better ultrasound tech. Also, scientists are looking into using artificial intelligence to guess how well a thawed embryo will do.
Methods for Detecting Early Cardiac Activity
Ultrasound is the main way to find a heartbeat. There are two types:
- Transvaginal ultrasound, which gives a close-up and clear view of the embryo.
- Transabdominal ultrasound, which is easy and shows more of the body.
Which one to use depends on how far along the pregnancy is and what the patient needs.
| Detection Method | Typical Use | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Transvaginal Ultrasound | Early pregnancy (5-6 weeks) | High-resolution images, early detection |
| Transabdominal Ultrasound | Later pregnancy stages | Non-invasive, broader view |
Knowing when and how to find a heartbeat helps doctors give better care early in pregnancy. This is after an embryo transfer.
Artificial Intelligence in Predicting Embryo Outcomes
The use of artificial intelligence in IVF is changing how we predict embryo success. AI looks at many factors to help doctors choose the best embryos for transfer.
Thanks to AI, how we check embryo health is getting better. AI algorithms can quickly look through lots of data. They find patterns that humans might miss.
How AI Algorithms Assess Embryo Viability
AI looks at things like how the embryo looks, how it grows, and its genes. This helps doctors pick the best embryos for transfer.
AI uses smart machine learning to learn from lots of data. It’s trained on embryo images and videos. This way, it can spot signs of successful implantation and pregnancy.
Predicting Fetal Heartbeat Success Rates
AI is also great at predicting if a fetal heartbeat will happen. It looks at past embryo transfers to guess the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Research shows AI can make IVF treatments more successful. It helps doctors pick the best embryos for transfer. This leads to better chances of a successful pregnancy.
As AI gets better, we’ll see even more accurate predictions and better IVF results. This technology is shaping the future of fertility care. It brings hope to those trying to start a family.
Health Outcomes of Babies Born from Frozen Embryos
As frozen embryos become more common in fertility treatments, it’s important to know how they affect children’s health. We look at the health of babies born from frozen embryos. We compare them to babies born from fresh embryo transfers and discuss long-term studies.
Comparing Health Metrics with Fresh Embryo Transfers
Studies have looked at the health of children born from frozen embryos and fresh embryo transfers. They found that frozen embryo babies generally have good health. But, some studies found small differences in health metrics.
A study in Fertility and Sterility found frozen embryo singleton births had lower risks of low birth weight and preterm birth. Another study in Human Reproduction found frozen embryo babies had similar health to fresh transfer babies. But, there were some differences in birth weight and gestational age.
Comparing frozen and fresh embryo transfers is complex. It depends on the mother’s age, embryo quality, and freezing techniques. We must look at these factors when judging frozen embryo babies’ health.
Long-term Studies on Children Born from Frozen Embryos
Long-term studies on frozen embryo babies are key to understanding their health. Research shows these children grow and develop normally. Some studies even found advantages in certain health areas.
- A study in The Lancet found frozen embryo babies had similar cognitive and motor skills to fresh transfer babies.
- Another study followed frozen embryo babies until age 5. It found no big differences in their health compared to naturally conceived kids.
These findings are good news for those thinking about frozen embryos. But, more research is needed to fully understand their long-term health effects.
In summary, babies born from frozen embryos generally have good health. But, there are some differences in health metrics compared to fresh embryo transfers. Ongoing research will give us more insights for parents and healthcare providers.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into how frozen embryos grow and the importance of finding a heartbeat in IVF. Frozen embryos, usually at the blastocyst stage, don’t have a heartbeat when frozen. But, a heartbeat starts after the embryo is transferred and implants, around six weeks into pregnancy.
New ways to freeze embryos have made IVF more successful. These methods keep embryos healthy, leading to good IVF results. Artificial intelligence also helps pick the best embryos, showing great promise.
Research shows babies from frozen embryos are as healthy as those from fresh ones. Long-term studies are watching these children’s health and growth. This gives us important info on the safety and success of IVF with frozen embryos.
As we keep improving in reproductive medicine, it’s key to understand frozen embryos well. The path from a frozen embryo to a beating heart is complex. It depends on the embryo’s quality, the freezing method, and the womb environment.
FAQ
Do frozen embryos have a heartbeat?
No, frozen embryos do not have a heartbeat. They are frozen at the blastocyst stage. Heart activity starts after thawing and implantation in the uterus.
What do frozen embryos look like?
Frozen embryos at the blastocyst stage look like small clusters of cells. They resemble rice cakes or lumpy circles under a microscope.
When does cardiac activity become detectable after embryo transfer?
Cardiac activity is detectable a few weeks after transfer. It usually happens around 5-6 weeks into pregnancy, seen through ultrasound.
How are embryos frozen, and what is the success rate of thawing?
Embryos are frozen using vitrification, a quick freezing method. It prevents ice crystals and keeps the embryo intact. This method has greatly improved thawing success rates.
What is the role of artificial intelligence in predicting embryo outcomes?
Artificial intelligence is used in IVF to pick the best embryos for transfer. It checks viability and predicts fetal heartbeat success rates.
Are there any differences in health outcomes for babies born from frozen embryos compared to fresh embryo transfers?
Babies from frozen embryos generally have good health outcomes. Some studies show slight differences in health metrics compared to fresh transfers.
What does “unsolicited in a way” mean in the context of IVF or embryo freezing?
The phrase “unsolicited in a way” is not related to IVF or embryo freezing. It’s a crossword clue answer. Its meaning depends on the crossword context.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Frozen Embryos: Heartbeat Presence and Fertility Treatment Considerations. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6344149/