Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a complex condition that affects many. While it’s diagnosed by looking at symptoms and behavior, new brain imaging tech has raised hopes for better understanding the condition, leading many to ask: does ADHD show up on a brain scan?
Brain scans, including SPECT imaging, give insights into brain health. But, their role in ADHD diagnosis is being studied. The FDA approval status of SPECT scans is key to their use in clinics.
The current SPECT scan regulatory approval is important for ADHD diagnosis. While brain scans aren’t used to diagnose ADHD, they offer valuable insights into brain function and structure.
Key Takeaways
- ADHD diagnosis involves a thorough evaluation, not just brain scans.
- SPECT imaging can offer insights into brain function and structure.
- The FDA approval status of SPECT scans is critical for their clinical use.
- Brain imaging is not typically used for ADHD diagnosis but can provide valuable information.
- Understanding SPECT scan regulatory approval is key to its use in ADHD.
The Neurobiology of ADHD
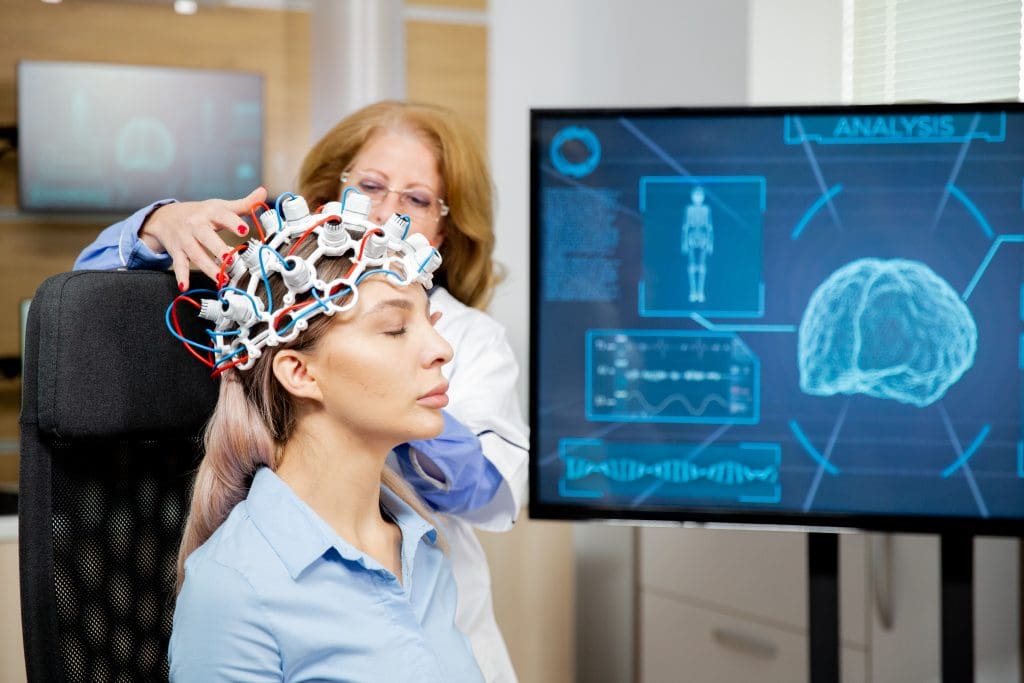
Understanding ADHD means looking into its neurobiology. Here, brain structure and neurotransmitter balance are key.
Brain Structures Affected in ADHD
Studies show ADHD brains differ from non-ADHD ones. ADHD brains mature slower, with some areas smaller.
Important brain areas include:
- The prefrontal cortex, key for decision-making and controlling impulses
- The cerebellum, involved in motor control and coordination
- The hippocampus, important for memory
- The amygdala, which handles emotions
| Brain Region | Function | Impact in ADHD |
| Prefrontal Cortex | Decision-making, impulse control | Impulsivity, attention deficits |
| Cerebellum | Motor control, coordination | Hyperactivity, motor restlessness |
| Hippocampus | Memory formation | Difficulty in learning and memory |
| Amygdala | Emotional processing | Emotional dysregulation |
Neurotransmitter Imbalances in ADHD
Neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine are vital in ADHD. Their imbalances can impact attention and impulse control.
Dopamine: It’s involved in reward and motivation. Imbalances can cause attention problems.
Norepinephrine: It affects attention and alertness. Imbalances can lead to inattention and hyperactivity.
Traditional Methods of ADHD Diagnosis
Diagnosing Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) traditionally involves several steps. Clinicians use clinical interviews, behavioral assessments, and rating scales to make a diagnosis. These methods help identify ADHD symptoms.
Clinical Interviews and Behavioral Assessments
Clinical interviews are key in diagnosing ADHD. They involve detailed talks between the clinician and the patient or their caregivers. These talks focus on symptoms, medical history, and behavior patterns.
Behavioral assessments also play a role. They help understand a patient’s behavior through observations and reports from family, teachers, or others. Clinicians look for signs of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity during these assessments.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) guides clinicians. It sets criteria for diagnosing ADHD, ensuring consistent diagnosis.
Rating Scales and Questionnaires
Rating scales and questionnaires are also used. They help measure ADHD symptom severity and its impact on daily life. Tools like the Vanderbilt Assessment Scale and the Conners are common. They collect information from parents, teachers, and the individual themselves.
- The Vanderbilt Assessment Scale assesses ADHD symptoms and related conditions.
- The Conners offer a detailed look at behavior.
Limitations of Subjective Diagnostic Methods
While useful, these methods have their limits. They rely on the clinician’s judgment and the accuracy of the information given. Clinician experience and bias can impact accuracy.
These methods might not fully capture ADHD’s complexity. They can also confuse ADHD with other conditions. So, researchers look for more objective methods, like SPECT scans.
Types of Brain Imaging Technologies
Many brain imaging tools help diagnose and study ADHD. Each tool gives unique views into how the brain works and looks.
MRI and fMRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and functional MRI (fMRI) are key tools. MRI shows brain structures in detail. fMRI tracks brain activity by watching blood flow.
MRI helps spot brain structure issues. fMRI shows how brain areas work in real-time.
PET Scans
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans use a radioactive tracer. They measure brain function, like how it uses glucose or neurotransmitters.
PET scans are great for seeing brain metabolism. This helps understand ADHD’s brain biology.
SPECT Imaging
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) imaging shows brain function. It’s a nuclear medicine technique.
SPECT scans look at brain blood flow and activity. They offer insights into ADHD’s functional aspects.
EEG and qEEG
Electroencephalography (EEG) records brain electrical activity. Quantitative EEG (qEEG) analyzes EEG data more deeply.
EEG and qEEG check brain electrical patterns. They help diagnose and study ADHD, as specific patterns are linked to the disorder.
| Imaging Technology | Primary Use in ADHD | Key Features |
| MRI | Structural analysis | Detailed anatomical images |
| fMRI | Functional analysis | Measures changes in blood flow |
| PET Scans | Metabolic activity | Uses radioactive tracers |
| SPECT Imaging | Blood flow and activity | Functional information |
| EEG/qEEG | Electrical activity | Measures brain waves |
The use of neuroimaging techniques has significantly advanced our understanding of ADHD, providing insights into both the structural and functional aspects of the brain.
With many brain imaging tools, researchers and doctors can pick the best one. This helps improve ADHD diagnosis and study.
How SPECT Scans Work
SPECT imaging is a cutting-edge tool for diagnosing brain function. It uses a radioactive tracer to measure brain activity. This method is key in understanding neurological conditions, including ADHD.
The Science Behind SPECT Imaging
SPECT scans use a small amount of radioactive material, called a tracer, to see brain activity. The tracer is injected into the blood and goes to different brain parts. The scanner then captures gamma rays from the tracer, making a 3D image of brain activity.
The science behind SPECT imaging is based on brain activity and blood flow. Active brain areas get more blood and tracer. By tracking the tracer, SPECT scans show how active different brain parts are.
Radioactive Tracers and Blood Flow Measurement
The tracers in SPECT scans are safe and quickly leave the body. Technetium-99m is the most used, with a short half-life. This limits radiation exposure.
Measuring blood flow is key in SPECT imaging. It helps find abnormal brain activity. This info is vital for diagnosing neurological conditions.
SPECT Procedure and Patient Experience
The SPECT procedure is usually easy for patients. It starts with a tracer injection, followed by a wait for the tracer to spread. Then, the patient lies down while the scanner takes images of brain activity.
Patients must stay very quiet during the scan. It takes about 30 minutes to an hour. Some might feel uncomfortable from staying so long, but the scan itself is not painful.
After the scan, patients can go back to their usual activities. Experts then analyze the images to spot any brain activity issues.
Key aspects of the SPECT procedure include:
- Injection of a radioactive tracer
- Waiting period for tracer distribution
- SPECT scanning
- Image analysis by a specialist
Can ADHD Actually Be Seen on Brain Scans?
Brain scans are getting more attention in ADHD research. They can show brain differences between people with ADHD and those without. But, they are not used alone to diagnose ADHD.
Research Evidence on Brain Differences
Studies have found brain region changes in ADHD. For example, the prefrontal cortex, basal ganglia, and anterior cingulate cortex differ in ADHD. Functional MRI (fMRI) and SPECT scans have shown these differences.
A study in the Journal of Attention Disorders found ADHD adults had less activity in the prefrontal cortex. This was during tasks that needed attention.
“The findings suggest that ADHD is associated with distinct patterns of brain activity, which can be captured using functional neuroimaging techniques like SPECT scans.”
Limitations in Individual Diagnosis
Even with brain differences found, diagnosing ADHD with scans is hard. Brain structures and functions vary widely, making it tough to find a clear marker. Current research shows group differences, but not reliable individual diagnosis with scans alone.
Group Differences vs. Diagnostic Markers
It’s important to know the difference between group differences and diagnostic markers. Research can spot average differences between ADHD and non-ADHD groups. But, these don’t make a reliable test for each person.
Creating a diagnostic marker needs high specificity and sensitivity. Current brain imaging hasn’t reached this yet.
As research keeps improving, brain scans might help more in ADHD diagnosis. But for now, they are just a helpful tool, not a sure way to diagnose.
SPECT Scan FDA Approval Status: Current Standing
The FDA approval status of SPECT scans for ADHD is complex. SPECT scans are FDA-approved for some medical uses. But, their role in ADHD diagnosis is more nuanced.
FDA Classification of SPECT Technology
The FDA sees SPECT technology as a medical imaging device. This means SPECT scans are under FDA watch. They must meet safety and effectiveness standards.
But, the FDA approval process is tied to the device’s intended use. For ADHD diagnosis, SPECT scans don’t have FDA approval. Other tools, like the Neuropsychiatric EEG-Based Assessment Aid (NEBA) System, are approved for ADHD.
SPECT for ADHD: Off-Label Usage
Using SPECT scans for ADHD diagnosis is off-label. This means the FDA hasn’t given them the green light for ADHD. But, SPECT scans are FDA-approved for other uses.
Off-label use is common in medicine. It happens when a device or drug is used for a purpose not approved by the FDA. But, it must be backed by solid evidence and professional judgment.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
To follow FDA rules, healthcare providers must use SPECT scans for ADHD diagnosis carefully. They need to tell patients about the off-label use. And, they must use the scans as professionals do.
They also have to keep SPECT scan facilities up to par. This means regular checks on image quality and safety. And, following radiation safety rules.
FDA Guidelines for Neuroimaging Diagnostic Claims
To get FDA approval, neuroimaging claims need strong clinical evidence. The FDA checks if these technologies, like SPECT scans, work well for diagnosing ADHD.
Evidence Standards for Diagnostic Approval
The FDA has strict rules for approving neuroimaging technologies. They need well-designed clinical trials to prove their worth. These trials show if the technology can spot different conditions or find specific biomarkers.
Clinical validation is key in the FDA’s review. It compares the technology to known methods to check its accuracy and performance.
Clinical Trial Requirements
Clinical trials for neuroimaging must be fair and cover a wide range of patients. The FDA often asks for multi-center trials with diverse groups and skilled researchers.
These trials need to be big enough to show clear results. The FDA checks the trial plans to make sure they meet the needed standards.
Marketing Restrictions for Unapproved Uses
The FDA closely watches how diagnostic technologies are marketed. Manufacturers must clearly state the product’s intended use and any limits.
Marketing materials can’t make claims not backed by FDA-approved labels. This means no promoting uses not approved, like using a SPECT scan for ADHD without FDA okay.
Following these rules helps ensure neuroimaging technologies are safe and used right in medical settings.
SPECT Imaging for ADHD: Research Findings
SPECT imaging studies have given us important insights into ADHD. They show how the brain works differently in people with ADHD. This helps researchers understand the condition better.
Patterns of Brain Activity in ADHD Patients
People with ADHD have unique brain activity patterns. SPECT imaging helps us see these differences. It focuses on areas of the brain that control attention and impulses.
Studies have found that ADHD patients have different brain activity. For example, their prefrontal cortex, important for decision-making, shows less activity. This is a key area for controlling impulses.
Distinguishing ADHD from Other Conditions
Diagnosing ADHD can be tricky because it looks like other conditions. SPECT imaging is helping to tell ADHD apart from other disorders. It looks at brain activity patterns to find unique ADHD traits.
This helps doctors make more accurate diagnoses. It also leads to better treatments for ADHD.
Reproducibility of SPECT Findings
It’s important for any diagnostic tool to be reliable. SPECT imaging has given us insights into ADHD. But, we need to make sure these findings are consistent across studies.
To ensure this, it’s key to follow strict SPECT scan quality standards. This means using the right protocols and making sure equipment is accurate.
Controversies Surrounding SPECT for ADHD Diagnosis
There’s a big debate in the scientific world about using SPECT scans for ADHD diagnosis. Some people think it could help understand and diagnose ADHD. But others have big worries about its accuracy and usefulness.
Scientific Community Perspectives
Opinions on SPECT scans for ADHD diagnosis are split. Some believe they can show important details about brain function and help diagnose ADHD. But others say there’s not enough proof to use them for diagnosis.
Criticisms point to the lack of standard SPECT imaging methods and the varied ways results are interpreted. There’s also doubt about whether SPECT scans can tell ADHD apart from other conditions with similar symptoms.
Claims and Methodologies
SPECT scans can spot specific brain patterns in ADHD. This helps in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. They use radioactive tracers to measure blood flow in the brain, linking it to brain activity.
Key aspects of their approach include:
- Using SPECT scans to assess brain function
- Identifying patterns of brain activity associated with ADHD
- Tailoring treatment plans based on SPECT scan results
Scientific Validation Concerns
Many experts say there’s not enough proof for SPECT scans as a sole diagnostic tool for ADHD.
“The use of SPECT imaging for psychiatric diagnosis, including ADHD, remains controversial and is not widely accepted by the mainstream medical community.”
Patient Testimonials vs. Clinical Evidence
While some patients report positive results, others question the lack of strong clinical trials backing SPECT scans for ADHD diagnosis.
As the discussion goes on, it’s important to weigh the benefits of new methods against the need for solid scientific proof.
Alternative Brain Imaging Approaches for ADHD
There are many new ways to look at the brain for ADHD diagnosis and treatment. Researchers are looking into different methods to find better and more personal ways to diagnose ADHD.
Functional MRI Studies
Functional MRI (fMRI) is a key tool in ADHD research. It lets us see how the brain works in real-time. Studies have found special brain activity patterns in ADHD, mainly in areas for attention and control.
DTI and Structural Imaging
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and structural imaging show us the brain’s structure and white matter tracts. They’ve found changes in ADHD that might link to its symptoms. Structural imaging also shows brain size and thickness differences in ADHD patients.
Emerging Technologies with FDA Consideration
New brain imaging technologies are coming, with some already in FDA review. These include advanced MRI methods like resting-state fMRI and arterial spin labeling. They don’t use radioactive tracers. These advancements could give us more ways to diagnose ADHD.
- Advanced MRI techniques
- Resting-state fMRI
- Arterial spin labeling
These new brain imaging methods could help us understand ADHD better. They might also make diagnosing ADHD more accurate. As research keeps moving forward, these technologies could become part of everyday treatment plans.
Clinical Guidelines on Neuroimaging for ADHD
As we learn more about ADHD, big medical groups have set guidelines for using neuroimaging in diagnosis. These guidelines help doctors use the best tools to diagnose ADHD.
American Academy of Pediatrics Recommendations
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) says a full check-up is key for ADHD diagnosis. This includes talking to the doctor, behavioral tests, and rating scales. They don’t say neuroimaging is needed for most ADHD cases. But, they suggest it might help in cases where there are signs of other brain issues.
American Psychiatric Association Position
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) also has advice on ADHD diagnosis. They say neuroimaging shouldn’t be the main way to diagnose ADHD. But, they see its value in research and when there’s a strong hint of a brain problem.
International Consensus Statements
Experts from around the world have agreed on ADHD diagnosis. They agree that while neuroimaging is promising, it’s not for everyday diagnosis. This is because it’s not always clear or accurate enough.
The table below shows what big medical groups say about using neuroimaging for ADHD:
| Organization | Recommendation on Neuroimaging for ADHD |
| American Academy of Pediatrics | Not routinely recommended; may be considered in cases with neurological indications |
| American Psychiatric Association | Not recommended as a primary diagnostic tool; may be useful in research and specific cases |
| International Consensus | Not recommended for everyday diagnosis; has promise for research and understanding ADHD |
In short, major medical groups agree that neuroimaging shouldn’t be the first choice for ADHD diagnosis. But, they see its value in certain situations and for research to better understand ADHD.
The Future of Brain Imaging in ADHD Diagnosis
New research is making ADHD diagnosis more accurate with brain imaging. The future of diagnosing ADHD will likely see better tools. These tools could make diagnoses more reliable and objective.
Advancements in Imaging Techniques
Studies show advanced brain imaging can help diagnose ADHD better. Techniques like functional MRI (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) can spot unique brain patterns in ADHD.Brain imaging is changing how we see ADHD and other mental health issues. The use of SPECT scans has shown that individuals with ADHD have distinct patterns of brain activity compared to those without the condition.”
Potential Biomarkers for ADHD
Finding biomarkers for ADHD is a big research goal. Brain imaging might find special markers for ADHD. This could make diagnoses more accurate.
| Imaging Technique | Potential Application in ADHD Diagnosis |
| fMRI | Identifying functional neural networks associated with ADHD |
| DTI | Analyzing white matter tracts and structural connectivity |
| SPECT | Assessing regional brain activity and perfusion patterns |
Regulatory Pathway to Approval
For brain imaging to be used in ADHD diagnosis, it must pass strict tests and get FDA approval. The FDA ensures these tools are safe and work well.
The regulatory pathway involves several key steps:
- Preclinical studies to establish the safety and possible effectiveness of the tool
- Clinical trials to check how well the tool works in real settings
- Submission of a premarket approval (PMA) application to the FDA
- FDA review and approval of the PMA application
As research advances, using brain imaging for ADHD diagnosis looks promising. There are challenges, but the hope for better diagnosis and treatment plans is real.
Ethical Considerations in Brain Scanning for ADHD
Brain scanning for ADHD raises many ethical questions. As this technology gets better, we must think about its ethical sides. This ensures it’s used the right way.
Patient Rights and Informed Consent
One big issue is making sure patients know what’s happening. Patients must be fully aware of the process, its limits, and risks. Informed consent is not just a rule; it’s a moral must.
“Informed consent is about making sure patients understand what they’re getting into.” Marketing Claims vs. Scientific Evidence
It’s tricky to promote new diagnostic tools without making false promises. Marketing efforts need to be based on real science. This stops patients and doctors from being misled.
“The promise of brain scanning for ADHD diagnosis must be tempered by the reality of its limitations and the need for further research,” says a renowned ADHD expert.
Financial Conflicts of Interest
Money can sometimes cloud judgment in healthcare. Transparency is essential to handle these issues. It helps keep things fair.
A study in a top medical journal showed we need better rules to deal with money problems in research and practice.
Conclusion: The Current State of Brain Imaging for ADHD
The field of brain imaging for ADHD is complex and always changing. Technologies like SPECT scans are being looked at to help diagnose ADHD. But, the FDA’s approval status of SPECT scans is very important.
Right now, using SPECT scans for ADHD is not officially approved. This means we need more research and clear rules about using SPECT scans. It’s important for doctors, researchers, and patients to understand where we are in this field.
Brain imaging could make diagnosing ADHD more accurate. But, it’s important to think about the evidence, rules, and ethics before using it in clinics. More research could lead to better ways to diagnose and treat ADHD.
FAQ
Is SPECT scan FDA approved for ADHD diagnosis?
SPECT scans are FDA cleared for some medical conditions. But, they are not FDA approved for ADHD diagnosis. Their use for ADHD is considered off-label.
What is the FDA approval status of SPECT imaging for neurological disorders?
SPECT imaging is FDA cleared for certain neurological uses. It helps assess brain blood flow and diagnose some conditions. But, it’s not approved for ADHD diagnosis.
Can brain scans diagnose ADHD?
Brain scans, like SPECT, might show differences in ADHD patients. But, they are not used alone to diagnose ADHD.
What are the limitations of using SPECT scans for ADHD diagnosis?
Using SPECT scans for ADHD has limitations. There’s no FDA approval, scan results can vary, and more research is needed.
Are there alternative brain imaging approaches for ADHD diagnosis?
Yes, there are alternatives. Functional MRI, DTI, and structural imaging are options. New technologies are also being considered.
What is the future of brain imaging in ADHD diagnosis?
The future may bring biomarkers and new imaging technologies. More research could lead to better diagnostic tools for ADHD.
How does SPECT imaging work for assessing brain activity?
SPECT imaging uses radioactive tracers to measure blood flow and activity. It provides insights into brain function and possible abnormalities.
Can SPECT scans distinguish ADHD from other conditions?
Research has looked into SPECT scans’ ability to differentiate ADHD from other conditions. More studies are needed to confirm its effectiveness.
What are the patterns of brain activity in ADHD patients as shown by SPECT imaging?
SPECT imaging has found different brain activity patterns in ADHD patients. These include differences in blood flow and activity compared to healthy controls.









